Innovation is often fuelled by the evolution of technology, which unlocks greater potential for businesses. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is often considered the trendiest of today’s emerging technologies, viewed as the real enabler of innovation. Many businesses are adopting AI and investing in AI-based solutions. However, every emerging technology faces the same stumbling block – trust. AI has been no different and despite the growing adoption, not everyone is ready to jump on the AI bandwagon yet.
The other major stumbling block for AI has been the inability of the common man to grasp the implications of the technology and differentiate it from what has been depicted in Science Fiction and dystopian novels. There is also confusion in the mind of technologists on the definition of AI. Some experts will say that only Deep Learning with non-linear algorithms is AI, while most vendors promote their automation tools like AI. A few misconceptions have hence arisen regarding AI, its uses and its impact on the workforce and society.
#1 AI is a new technology
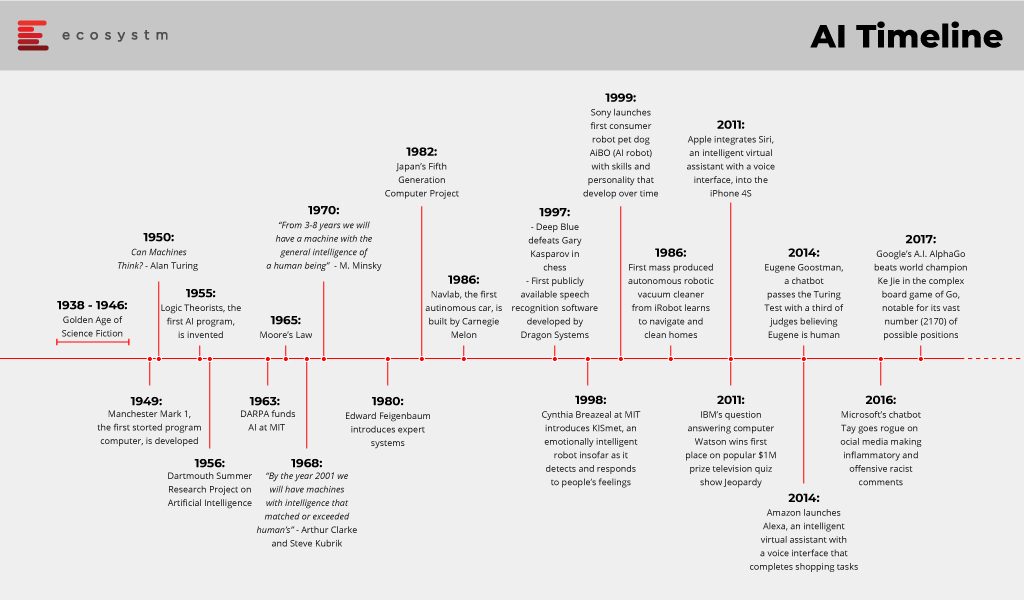
Despite recent hype around the technology, AI is not a new technology and not a product of this century’s innovations. The beginnings of AI can be traced to the middle of the 20th century and then it gained pace. During the second world war, an English mathematician and computer scientist, Alan Turing documented his ideas on creating an intelligent machine. Turing’s test theory proposed that if a machine could engage in full conversation with no detectable variances from a human, the machine could be deemed as a thinking machine. Turing worked to crack the German military’s encryption, the ‘Enigma’ code.
Later in 1956, American computer scientist John McCarthy organised the Dartmouth Conference, where the term ‘Artificial Intelligence’ was first used.
Today, AI is a much broader term and refers to a range of technologies from Automation to Deep Learning.
#2 AI can replace the human brain – completely
Humans have evolved over millions of years from being hunter-gatherers to agricultural societies to a modern-day man who can succeed in secondary and tertiary industries. We have adapted, evolved and became good at surviving in the real world. Despite this many people hold an opinion that AI will replace the driving force of one of the most complex machines on this planet – the human brain.
AI has clearly come a long way. Its ability to learn vast amounts of data, recognise patterns, and produce results is improving us in countless ways. However, the problem with achieving true AI is also its greatest strength – that it does not learn like a human. The technology behind AI is scientific and complex and building a competitive AI from scratch requires expensive specialised talent. For instance, a successful image recognition solution is more accurate than most humans, but the same coding cannot address another type of problem.
AI cannot replace a complex structure of neurons and humans will continue to use their intelligence for more innovation. Humans do and will continue to, play a major role in most AI applications, especially critical ones in research and medicine. Each of our innovations has made the race more productive, and that is what AI will further add to the human race.
#3 AI poses a threat to security & privacy
While the benefits of AI and Big Data technologies are being felt, people also consider them as a threat to their anonymity and privacy.
With online social accounts, digital identities and other digital data gathering entities – both private and government – privacy has become a pertinent question. With the emergence of sophisticated AI systems, these privacy concerns have been aggravated. AI brings the ability to fetch, combine, and analyse a huge quantity of data from varied sources. The impression is that AI can perform these designated operations with no supervision and there is fear that humans will lose control of a system entirely. Instances of data and privacy breaches heighten this fear.
This fear may be unfounded. Today, AI systems can simplify user privacy policies on websites, which most of the users do not bother to read and simply click on the ‘Accept’ box. Polisis is an AI-powered automated analysis tool for privacy policies. Polisis pulls a website’s privacy policy and takes around 30 seconds to interpret it, display a summary, and present a flowchart of the policy with highlights on how the online service will handle user data. An AI-powered chatbot called PriBot, answers questions about the privacy policy of any company.
In reality, AI technologies are being utilised to create a safer and more secure society. AI brings speed, scale, and automation to computing and is changing the way we work, live, and interact. We are guiding AI capabilities for better healthcare provision, citizen safety, research accuracy, and even enhanced cybersecurity. Very often, the data used by these algorithms are aggregated and anonymised.
#4 AI will replace jobs
There is an abundance of fear, uncertainty, and doubts about the risk and opportunity of AI. Will it create jobs or destroy them?
There is no doubt that AI is poised to transform jobs and will change the face of employment. It is easier to see existing jobs disrupted by new technology than to envision what new jobs the technology will enable. AI is poised to replace tasks, not jobs. Some functions – and sometimes all the functions – of an individual or team might be automated. Employees with no plans or desire to re-skill should be concerned, but those who are continuously improving and changing their skill sets need not be too concerned that automation will put them in an unemployment queue.
“While businesses will face pain, as they adjust to new lower cost and higher productivity expectations – and employees will need to continually update their skills – the overall assessment is for jobs growth. It is just that the jobs created will be different to the jobs that exist today”, as Tim Sheedy (Principal Analyst, AI & Automation, Ecosystm) puts it in his report Automation Will Transform Jobs – Plan for Change Now
Read Report – https://www.ecosystm360.com/#/link?type=report&id=155b38c6-3764-4715-a9ad-1ec6447260ac
A few businesses today are creating Automation Teams or Centres of Excellence – banks, telecommunications providers and utilities are leading this push. With continued effort, AI will eventually become intelligent enough to understand the tasks and make them easier for the workforce. Employees need to trust, use and maximise the full potential of the technology, and see its benefits for scaled implementation.
The NAB Cloud Guild is a good example of how organisations should provide training to not just technology staff but to any interested employee, on emerging technologies to equip their business for future demands.
#5 AI is implemented only by large vendors
AI is driving many Digital Transformation (DX) projects and large vendors, especially with platform and enterprise capabilities, have had the first movers’ advantage in AI deployments. Businesses are striving to make their systems more intelligent for better process automation and customer retention. After 40 years of automating manual tasks using enterprise applications (such as ERP, SCM, and CRM), intelligent systems will make many of these systems redundant – or at the least reduce business reliance on them.
One of the big challenges for large businesses – and their IT teams – today is to customise their AI to their organisations’ DX requirements. Many companies have made their first foray into the world of AI – often starting with technologies such as RPA, IoT sensor analytics, and chatbots. They are now looking to go beyond evolving their RPA solutions into Smart Process Automation (SPA) solutions. They are also going beyond basic chatbots/ virtual assistants to implement NLG and semantic computing, as their customer focus deepens. For these large enterprises, integration of AI solutions with internal systems and other AI solutions is the key challenge, and they often prefer to partner with their existent enterprise vendor or systems integrator for their AI implementations.
However, smaller organisations and start-ups are equally leveraging AI. Several tech start-ups also exclusively focus on AI and are developing a niche, industry-specific solutions. These smaller solution providers will probably be integrated into larger vendors’ partner ecosystems, as their capabilities deepen, and their customer base grows. Organisations need not look to only larger, established vendors for their AI implementations.
AI is still an emerging technology and it might take some time for AI to be trusted. The truth, however, is that AI opens up immense possibilities for individuals, enterprises, and governments.
Do the supposed threats outweigh the benefits of AI? We would very much love to hear your suggestions, ideas, and thoughts on this subject.