
Digital and IT organisations are going through some dramatic changes as they adopt cloud and as-a-service capabilities. In this post, I want to write about two of these – one that is very much a consequence of the other.
Contract Numbers are Exploding
We’re seeing an explosion in the number of IT suppliers to a typical organisation.
Pre-cloud, the typical organisation probably had five to ten contracts that covered most of the external services that were in use. With suppliers increasingly providing niche functionality and the increased use of credit cards to buy external services, it is often difficult to determine exactly how many contracts are in place. Or, indeed, have a clear understanding of the terms and conditions of each of these contracts.
Where once an organisation might have had contracts for an on-premises ERP and CRM system, a typical organisation will still have those contracts as well as a supply chain forecasting service, a marketing email management tool, not to mention online spreadsheets and task management capabilities.
So with many more contracts in place, the complexity of managing these contracts and understanding the technical, legal and business risks encapsulated in these contracts has become dramatically more difficult.
I’ll return to this point in a later post, as most organisations struggle with this increasing complexity.
What Is Happening to Your People?
The existence of these contracts means that you are increasingly becoming dependent on the people employed by these external organisations. But when you sign up for these contracts, do you investigate how these suppliers develop their talent?
The New Zealand Herald recently carried an interesting article on one organisation that has developed a paid intern program. Something very rare in the industry.
The article prompted me to think through some of the implications of using cloud services. Tech buyer organisations will have less need for technical capabilities as increasingly these are delivered by the cloud suppliers.
But the growth in demand for digital and IT skills just continues to increase as more and more industries digitalise. In the past, tech buyer organisations would have invested (at least the good employers did!) in the development of their people. The cloud suppliers are increasingly doing this talent development.
Most contract negotiations are based on cost, quality and customer service. A significant proportion of cloud contracts are now boilerplate – you pay with a credit card for a monthly service and have little or no ability to negotiate terms and conditions.
The trade-off is required to get a short commitment term and a variable cost profile. No tech vendor can afford to negotiate bespoke contracts for this type of commercial arrangement.
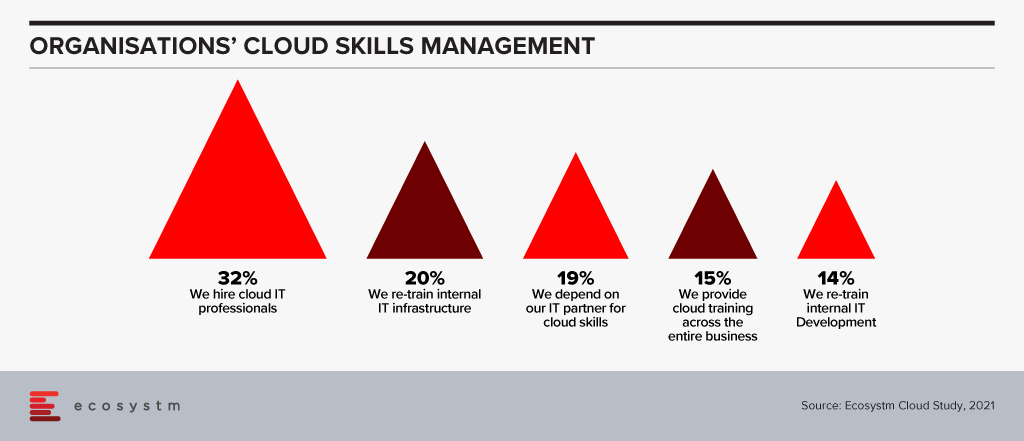
This situation leaves the question of how tech buyers can influence tech vendors to develop their people’s talent appropriately. Some would say that the tech vendors will do this as a matter of course, but the statistics, as highlighted in the Ecosystm research data in Figure 1, show that we are not bringing people in at the rate the industry requires.
Advice for Tech Buyers
I recommend you look closely at using two tactics with the tech vendors that you are working with:
- First, look to consolidate as much workload as practical under a single contract with the supplier. This is not a new recommendation for contracts – but with the increasing use of boilerplate contracts, it is one of the few ways an organisation can increase its value and importance to a tech vendor.
- Second, start finding those tech vendors that are developing new and existing talent in practical ways and favour these organisations in any purchase decision.
Most organisations, individually, do not have the commercial power to dictate terms to the cloud providers. Still, if enough tech buyers adopt this critical criterion, the cloud providers may see the value in investing in the industry’s talent development in meaningful ways.
The downside? Talent development does not come free. Tech buyers may need to pay a higher fee to encourage the suppliers but paying a low-cost provider who does not develop their talent sounds like a recipe for poor quality service.
If you would like to discuss any of these thoughts or issues further, please feel free to reach out and contact me. This is an industry issue and one for our broader society, so I would be interested in hearing how your organisations are addressing this challenge.








Thanks Alan for this great insight and analysis! I would also suggest that skills acquisition should be the focus of buyers of technology services. The fact that 32% of businesses hire external cloud experts says it all to me. We know that hiring the right person can take 3-12 months – and our need is often immediate – so if we are relying on the market for our skill acquisition, then we’ll have to put projects on hold as we don’t have the skills to move them forward…
But I am enthused by the fact that 15% of businesses provide cloud skills across an entire business – these are the businesses that realise that cloud technologies will impact their entire organisation and that these skills are required to keep up with customer requirements. These are the businesses that will transform themselves, industries and markets – because they saw the importance of having the right skills in their business.