Governments face multiple challenges which are further getting highlighted by the ongoing global crisis. They have to manage the countries’ financial performances, reducing fiscal deficits. Every economy – whether emerging or mature – face challenges in bridging economic and social divides and ensuring equal access to infrastructure across the population. Most governments have challenges associated with the changes in demographics – whether because of rapid urbanisation, a fast ageing population or those associated with immigration policies.
Government agencies have the task of ensuring reliable public service, keeping their citizens safe, and striving for cost optimisation. In this constantly evolving world, agencies need to rely on technology to manage ever-growing citizen expectations and rising costs. Several government agencies have started their digital transformation (DX) journey replacing their legacy systems to transform the way they deliver services to their citizens.
Drivers of Transformation in Public Sector
Creating cross-agency synergies
Government agencies have access to enormous quantities of citizen data. But much of that data resides with individual agencies, often with no real synergies between them. For improved cost management and better utilisation of the data, it is imperative for governments to think of cross-agency collaboration systems and tools which give the larger entity a better visibility of their resources, contracts and citizen information. This involves, developing procedures, frameworks and working beyond their limited boundaries, leveraging technology to share information, applications, platform and processes. While this has been in discussion for nearly a decade now, most government agencies still work in departmental siloes and find it hard to work as a networked entity. The Ecosystm AI study finds that nearly three-quarters of public sector organisations find data access a challenge for their AI projects.
Improving citizen engagement
Increasingly, citizens are becoming tech-savvy and are expecting digital services from their government agencies. Not only that, but they are also ready to have conversations with agencies and provide feedback on matters of convenience and public safety. With the popularity of social media, citizens now have the capability to take their feedback to a wider open forum, if the agency fails to engage with them. Public sector organisations have to streamline and automate the services they provide, including payments, and provide real-time services that require collaborative feedback and increased participation from citizens. Smart governments are successfully able to leverage their citizen engagement to use open data platforms – Data.gov and data.gov.uk, are allowing communities to target and solve problems for which governments do not have the bandwidth. With citizen centricity and open government policies, there is also an ever-increasing need for greater accountability and transparency.
Managing project performance and costs
Most government projects involve several stakeholders and are complex in terms of the data, infrastructure and investments required. To take better decisions in terms of project complexity, risks and investments, public sector agencies need to have a structured project management framework, using an optimum mix of physical. technical, financial and human resources. In an environment where citizens expect more accountability and transparency, and where projects are often funded by citizens’ taxes, running these projects become even more complicated. Government agencies struggle to get funding, optimise costs (especially in projects that run over multiple years and political environments), and demonstrate some form of ROI. There is also an overwhelming requirement to detect and prevent frauds.
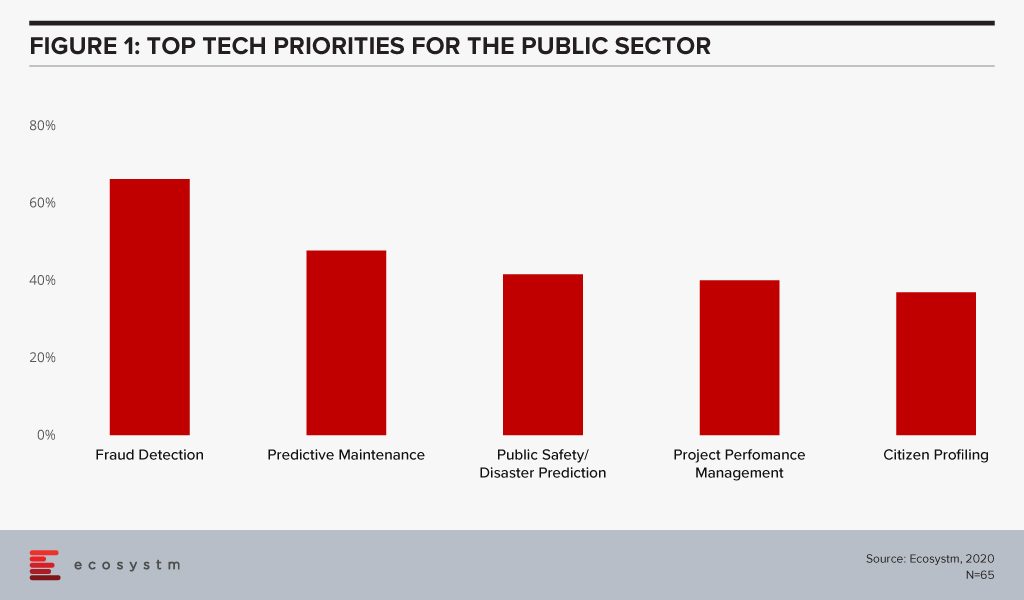
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for public sector, that are focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). It is very clear that the key areas of focus are cost optimisation (including fraud detection and project performance management) and having access to better data to provide improved citizen services (such as public safety and predicting citizen behaviour).
Technology as an Enabler of Public Sector transformation
Several emerging technologies are being used by government agencies as they look towards DX in the public sector.
The Push to Adopt Cloud
To prepare for the data surge that governments are facing and will continue to face, there is a push towards replacing legacy systems and obsolete infrastructure. The adoption of cloud services for data processing and storage is helping governments to provide efficient services, improve productivity, and reduce maintenance costs. Moreover, cloud infrastructure and services help governments provide open citizen services. The Government of India has built MeghRaj, India’s national cloud initiative to host government services and applications including local government services to promote eGovernance and better citizen services. The New Zealand Government has sent a clear directive to public sector organisations that public cloud services are preferred over traditional IT systems, in order to enhance customer experiences, streamline operations and create new delivery models. The objective is to use public cloud services for Blockchain, IoT, AI and data analytics.
Transparency through Communication & Collaboration technologies
Since the 1990s, the concept of eGovernment has required agencies to not only digitise citizen services but also work on how they communicate better with their citizens. While earlier modes of communication with citizens were restricted to print, radio or television, digital government initiatives have introduced more active communication using mobile applications, discussion forums, online feedback forms, eLearning, social media, and so on. Australia’s Just Ask Once allows citizens to access information on various government services at one place for better accessibility. More and more government agencies are implementing an omnichannel communication platform, which allows them to disseminate information across channels such as web, mobile apps, social media and so on. In the blog The Use of Technology in Singapore’s COVID-19 Response, Ecosystm analysts spoke about the daily updates shared by the Government through mobile phones. Demonstrating cross-agency collaboration, the information disseminated comes from multiple government agencies – the same channel is also used to drip-feed hygiene guidelines and the evolving government policies on travel, trade and so on.
AI & Automation for Process Efficiency and Actionable Intelligence
Governments are focusing on leveraging centralised resources and making processes smarter through the adoption of AI platforms. Initiatives such as the Singapore Government’s concept of Single Sources of Truth (SSOT), where all decision-making agencies have access to the same data, is the first step in efficient AI adoption. Singapore’s government agencies also have three data aggregators – Trusted Centers (TCs). This enables initiatives such as Vault-Gov.SG which allows government officials to browse a metadata catalogue and download sample data to run exploratory analytics. To push the adoption of AI, several governments are focusing on roadmaps and strategies such as Singapore’s National AI Strategies to transform the country by 2030, and the Government of Australia’s AI Roadmap and framework to help in the field of industry, science, energy, and education.
The first step of AI adoption is often through automation tools, such as virtual assistants and chatbots. The US Citizen and Immigration Service (USCIS) introduced an AI powered chatbot Emma to better support citizens through self-service options and reduce the workload of their customer service agents. The department of Human Services in Australia rolled out various chatbots named Roxy, Sam, Oliver, Charles and the most latest in progress PIPA (Platform Independent Personal Assistant) to provide information on various services and assist on queries.
Real-time data access with IoT
Governments have the responsibility of enforcing law and order, infrastructure management and disaster management. Real-time information data access is key to these initiatives. IoT sensors are being used in various government applications in object detection, and risk assessment in cities as well as remote areas. For example, IoT-enabled traffic monitoring and surveillance systems are embedded to provide real-time updates and continuous monitoring that can be used to solve issues, as well as provide real-time information to citizens. In a futuristic step, the US Department of Transportation (USDOT) is working with auto manufacturers on embedding vehicle to vehicle communication capabilities in all vehicles to avoid collision with emergency braking and vehicle speed monitoring. In an effort to promoting smart city initiatives and for infrastructure maintenance, New Zealand has installed smart cameras with automated processing capabilities, and IoT based street lighting system. IoT has tremendously benefited the supply chain and logistics sector. The US Army’s Logistics Support Activity (LOGSA) is using IoT for one of the Government’s biggest logistics systems. and military hardware with on-board sensors to analyse data directly from the vehicles for better asset maintenance. Again like in AI, there is a need for a clear roadmap for government adoption of emerging technologies, especially considering the safety and ethics angle. The Government of UK has introduced IoTUK, a program to help the public sector and private enterprises to come together and develop IoT technologies considering aspects such as privacy, security, and reliability.
Blockchain enabled Traceability & Transparency
Moving paper-based systems to digitised systems makes processes efficient to a degree. However, more is required for full traceability and transparency. Managing the data flow and safeguarding the information is vital for government organisations, especially as there is an increase in cross-agency collaboration. Government agencies and departments across the globe are increasingly collaborating using Blockchain technology, while at the same time maintaining the security of the data. For instance, in Georgia, the government department of Land, Property and Housing Management is using Blockchain to maintain land and property records. The blockchain-based land registry allows speedier approvals with no involvement of paperwork or multi-party signatures on physical documents. This is enhancing service quality while offering better security measures as the data is digitally stored in the National Agency of Public Registry’s land title database. Estonia is using Blockchain to protect their digital services such as electronic health records, legal records, police records, banking information, covering data and devices from attacks, misuse, and corruption.
Technology-led digital transformation has become the norm for public sector organisations across both emerging and mature economies. However, agencies need to create clear roadmaps and frameworks, including RoI considerations (which may not only be financial but should include citizen experience) and avoid ad-hoc implementations. The key consideration that government agencies should keep in mind is citizen security and ethics when adopting emerging technologies.

In 2018, DBS Bank came together with AI start-up impress.ai to implement Jim – Job Intelligence Maestro – a chatbot that helps the bank shortlist candidates for positions in their wealth planning team. This is primarily for screening for entry-level positions. Apart from process efficiency, the introduction of AI in the recruitment process is also aimed at eliminating bias and objectively finding the right candidate for the right job. The DBS chatbot uses cognitive and personality tests to assess candidates, as well as providing them with answers to the candidates’ frequently asked questions. The scores are then passed on to actual recruiters who continue with the rest of the recruitment process. DBS claims that they have curtailed the initial assessment time of each applicant by an average of 22 minutes.
While some organisations have started evaluating the use of AI in their HR function, it has not reached a mass-market yet. In the global Ecosystm AI study, we find that nearly 88% of global organisations do not involve HR in their AI projects. However, the use cases of AI in HR are many and the function should be an active stakeholder in AI investments in customer-focused industries.
Telstra employs AI to vet Applicants
Last month, Australia’s biggest telecommunications provider Telstra announced its plans to hire 1,000 temporary contact centre staff in Australia to meet the surge in demand amidst the global pandemic. In response to the openings, Telstra received overwhelming 19,000 applications to go through and filter, with limited workforce. To make the recruitment process more efficient, the company has been using AI to filter the applications – and has been able to make initial offers two weeks from the screening. The AI software takes the candidates’ inputs and processes them to find the right match for the required skills. The candidates are also presented with cognitive games to measure their assessment scores.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Audrey William speaks about the pressure on companies such as Telstra to hire faster for their contact centres. “Several organisations are needing to replace agents in their offshore locations and hire agents onshore. Since this is crucial to the customer experience they deliver, speed is of essence.” However, William warns that the job does not stop with recruiting the right number of agents. “HR teams will need to follow through with a number of processes including setting up home-based employees, training them adequately for the high volume of voice and non-voice interactions and compliance and so on.”
The Future of AI in HR
William sees more companies adopting AI in their HR practices in the Workplace of the Future – and the role of AI will not be restricted to recruitment alone. “A satisfied employee will go the extra mile to deliver better customer experience and it is important to keep evaluating how satisfied your employees are. AI-driven sentiment analysis will replace employee surveys which can be subjective in nature. This will include assessing the spoken words and the emotions of an individual which cannot be captured in a survey.”
In the future, William sees an intelligent conversational AI platform as an HR feedback and engagement platform for staff to engage on what they would like to see, what they are unhappy about, their workplace issues, what they consider their successes and so on. This will be actionable intelligence for HR teams. “But for a conversational AI platform to work well and to encourage users within the organisation to use it, it must be designed well. While it has to be engaging to ensure employee uptake, the design does not stop at user experience. It must include a careful evaluation of the various data sets that should be assessed and how the AI can get easy access to that data.”
AI and Ethics
With the increased use of AI, the elephant in the room is always ethical considerations. While the future may see HR practices using conversational AI platforms, how ethical is it to evaluate your employees constantly and what will be the impact on them? How will the organisation use that data? Will it end up giving employers the right reasons to reduce manpower at will? These and allied issues are areas where stricter government mandates are required.
Going back to AI-assisted recruitment, William warns, “Bias must be assessed from all angles – race, education, gender, voice, accents. Whilst many platforms claim that their solution removes bias, the most important part of getting this right is to make sure that the input data is right from the start. The outcomes desired from the process must be tested – and tested in many different ways – before the organisation can start using AI to eliminate bias. There is also the added angle of the ethical use of the data.”
Identifying and selecting a vendor for your tech project can be a daunting task – especially when it comes to emerging technologies or when implementing a tech solution for the first time. Organisations look for a certain degree of alignment with their tech vendors – in terms of products and pricing, sure, but also in terms of demonstrable areas of expertise and culture. Several factors are involved in the selection process – vendors’ ability to deliver, to match expected quality standards, to offer the best pricing, to follow the terms of the contract and so on. They are also evaluated based on favourable reviews from the tech buyer community.
Often businesses in a particular industry tend to have their unique challenges; for example, the Financial Services industries have their specific set of compliance laws which might need to be built into their CRM systems. Over the years, vendors have built on their industry expertise and have industry teams that can advise organisations on how their business requirements can be met through technology adoption. These experts speak in the language of the industry and understand their business and technology pain points. They are able to customise their product and service offerings to the needs of the industry for a single client – which can then be repeated for other businesses in that industry. Vendors arm themselves with a portfolio of industry use cases, especially when they are entering a new market – and this often gives them an upper hand at the evaluation stage. In the end, organisations want less customisations to keep the complexity and costs down.
Do organisations evaluate vendors on industry experience?
Ecosystm research finds that industry experience can be a significant vendor selection criterion for some tech areas (Figure 1), especially in emerging technologies such as AI. AI and automation applications and algorithms are considered to be distinctive to each industry. While a vendor may have the right certifications and a team of skilled professionals, there is no substitute for experience. With that in mind, a vendor with experience in building machine learning models for the Telecommunications industry might not be perceived as the right fit for a Utilities industry implementation.
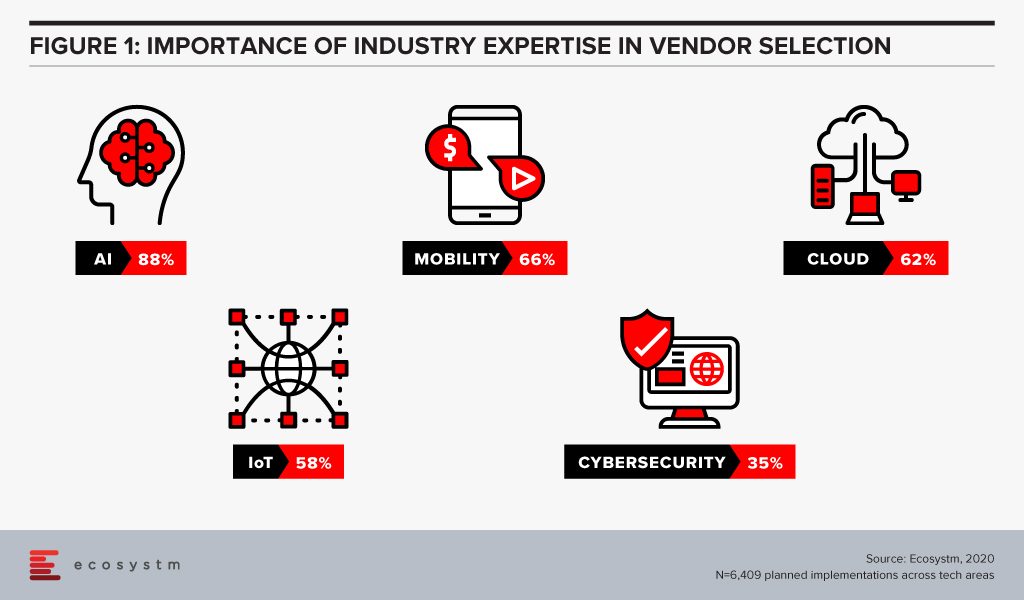
Whereas, we find that cybersecurity is at the other end of the spectrum, and organisations perceive that industry expertise is not required as network, applications and data protection requirements are not considered unique to any industry.
Is that necessarily the right approach?
Yes and no. If we look at the history of the ERP solution, as an example, we find that it was initially meant for and deeply entrenched in Manufacturing organisations. In fact, the precursor to modern-day ERP is the Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) software of the 1980s. Now, we primarily look at ERP as a cross-industry solution. Every business has taken lessons on inventory and supply chain management from the Manufacturing industry and has an enterprise-wide system. However, there are industries such as Hospitality and Healthcare that have their niche vendors who bundle in ERP features with their industry-specific solutions. This will be the general pattern that all tech solutions will follow: a) an industry use case will become popular; b) other industries will try to incorporate that solution, and in the process; c) create their own industry-specific customisations. It is important, therefore, for those who are evaluating emerging technologies to cast their net wide to identify use cases from other industries.
AI and automation is one such tech area where organisations should look to leverage cross-industry expertise. They should ask their vendors about their implementations in other allied industries and, in some cases, in industries that are not allied.
For cybersecurity, their approach should be entirely different. As companies move on from network security to more specific areas such as data security and emerging areas such as GRC communication, it will be important to evaluate industry experience. Data protection and compliance laws are often specific to industries – for example, while customer-focused industries are mandated on how to handle customer data, the Banking, Insurance, Healthcare and Public Sector industries have the need to store more sensitive data than other industries. They should look at solutions that have in-built checks and balances in place, incorporating their GRC requirements.
So, the answer to whether organisations should look for industry expertise in their vendors is that they should for more mature tech areas. An eCommerce company should look for industry experience when choosing a web hosting partner, but should look for experience in other industries such as Banking, when they are looking to invest in virtual assistants.
Are some industries more focused on industry experience than others?
Ecosystm research also sought to find out which industries look for industry expertise more than others (Figure 2). Surprisingly, there are no clear differences across industries. The Services, Healthcare and Public Sector industries emphasise marginally more on industry expertise – but the differences are almost negligible.
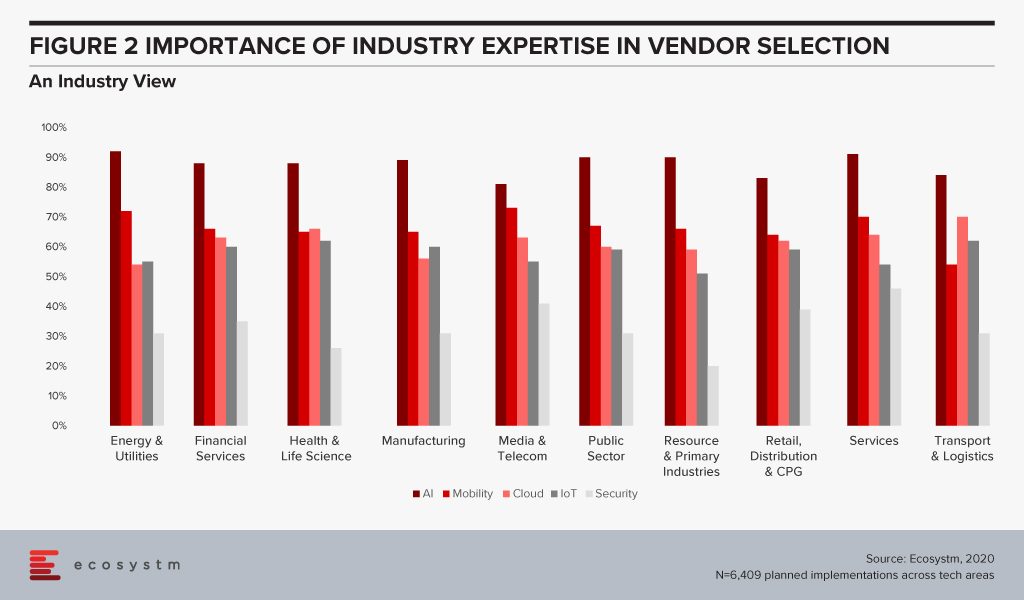
There are some differences when we look at specific tech areas, however. For example, industries that may be considered early adopters of IoT – Transportation, Manufacturing and Healthcare – tend to give more credit to industry experience because there are previous use cases that they can leverage. There are industries that are still formulating standards when it comes to IoT and they will be more open to evaluating vendors that have a successful solution for their requirement – irrespective of the industry.
The Healthcare Industry Example
Ecosystm Principal Analyst, Sash Mukherjee says, “In today’s fast-evolving technology market, it is important to go beyond use cases in only your industries and look for vendors that have a demonstrated history of innovation and experience in delivering measurable results, irrespective of the industry.” Mukherjee takes the example of the Healthcare industry. “No one vendor can provide the entire gamut of functionalities required for patient lifecycle management. In spite of recent trends of multi-capability vendors, hospitals need multiple vendors for the hospital information systems (HIS), ERP, HR systems, document management systems, auxiliary department systems and so on. For some areas such as electronic health records (EHR) systems, obviously industry expertise is paramount. However, if healthcare organisations continue to look for industry expertise and partner with the same vendors, they miss out on important learnings from other industries.”
Talking about industries that have influenced and will influence the Healthcare industry in the very near future, Mukherjee says, “Healthcare providers have learnt a lot from the Manufacturing industry – and several organisations have evaluated and implemented Lean Healthcare and Six Sigma to improve clinical outcomes. The industry has also learnt from the Retail and Hospitality industries on how to be customer focused. In the Top 5 Healthtech trends for 2020, I had pointed out the similarities between the Financial and Healthcare industries (stringent regulations, process-based legacy systems and so on). As the Healthcare industry focuses on value-based outcomes, governments introduce more regulations around accountability and transparency, and people expect the experience that they get out of their retail interactions, Healthtech start-ups will become as mainstream as Fintech start-ups.”
It is time for tech buyers to re-evaluate whether they are restricting themselves by looking at industry use cases, especially for emerging technologies. While less industry customisations mean easier deployments, it may also hamper innovation.
In The Top 5 Cloud trends for 2020, Ecosystm Principal Analyst, Claus Mortensen had predicted that in 2020, cloud and IoT will drive edge computing.
“Edge computing has been widely touted as a necessary component of a viable 5G setup, as it offers a more cost-effective and lower latency option than a traditional infrastructure. Also, with IoT being a major part of the business case behind 5G, the number of connected devices and endpoints is set to explode in the coming years, potentially overloading an infrastructure based fully on centralised data centres for processing the data,” says Mortensen.
Although some are positioning the Edge as the ultimate replacement of cloud, Mortensen believes it will be a complementary rather than a competing technology. “The more embedded major cloud providers like AWS and Microsoft can become with 5G providers, the better they can service customers, who want to access cloud resources via the mobile networks. This is especially compelling for customers who need very low latency access.”
Affirmed Networks Brings Microsoft to the 5G Infrastructure Table
Microsoft recently announced that they were in discussions to acquire Affirmed Networks, a provider of network functions virtualisation (NFV) software for telecom operators. The company’s existing enterprise customer base is impressive with over 100 major telecom customers including big names such as AT&T, Orange and Vodafone. Affirmed Networks’ recently appointed CEO, Anand Krishnamurthy says that their virtualised cloud-native network, Evolved Packet Core, allows for scale on demand with a range of automation capabilities, at 70% of the cost of traditional networks. The telecom industry has been steadily moving away from proprietary hardware-based infrastructure, opting for open, software-defined networking (SDN). This acquisition will potentially allow Microsoft to leverage their Azure platform for 5G infrastructure and for cloud-based edge computing applications.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Shamir Amanullah says, “The telecommunications industry is suffering from a decline in traditional services leading to a concerted effort in reducing costs and introducing new digital services. To do this in preparation for 5G, carriers are working towards transforming their operations and business support systems to a more virtualised and software-defined infrastructure. 5G will be dynamic, more than ever before, for a number of reasons. 5G will operate across a range of frequencies and bands, with significantly more devices and connections, highly software-defined with computing power at the Edge.”
Microsoft is by no means the only tech giant that is exploring this space. Google recently announced a new solution, Anthos for Telecom and a new service called the Global Mobile Edge Cloud (GMEC), aimed at giving telecom providers compute power on the Edge. At about the same time, HPE announced a new portfolio of as-a-service offering to help telecom companies build and deploy open 5G networks. Late last year, AWS had launched AWS Wavelength that promises to bring compute and storage services at the edge of telecom providers’ 5G networks. Microsoft’s acquisition of Affirmed Networks brings them to the 5G infrastructure table.
Microsoft Continues to Focus on 5G Offerings
The acquisition of Affirmed Networks is not the only Microsoft initiative to improve their 5G offerings. Last week also saw Microsoft announce Azure Edge Zones aimed at reducing latency for both public and private networks. AT&T is a good example of how public carriers will use the Azure Edge Zones. As part of the ongoing partnership with Microsoft, AT&T has already launched a Dallas Edge Zone, with another one planned for Los Angeles, later in the year. Microsoft also intends to offer the Azure Edge Zones, independent of carriers in denser areas. They also launched Azure Private Edge Zones for private enterprise networks suitable for delivering ultra low latency performance for IoT devices.
5G will remain a key area of focus for cloud and software giants. Amanullah sees this trend as a challenge to infrastructure providers such as Huawei, Ericsson and Nokia. “History has shown how these larger software providers can be fast, nimble, innovative, and extremely customer-centric. Current infrastructure providers should not take this challenge lightly.”
As far back as in 2018, Tencent had set its eyes on the business customer, starting a Cloud and Smart Industries business group (CSIG). Since then it has not lost focus on what businesses need and has continued to evolve its offerings. Late last year, Tencent Meeting , a video-conferencing app for its enterprise business was launched. This was a savvy move, as it came right after Zoom was blocked from the China market forcing local users to search for in-country alternatives.
Tencent’s Go-to-Market Strategy
Talking about Tencent’s go-to-market strategy, Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Niloy Mukherjee says, “The current leader in the video-conferencing space, Zoom is not available in China so that market alone can sustain an offering like Tencent Meeting. With the popularity of WeChat, Tencent has a huge opportunity to combine conferencing on the desktop and the mobile and I see that as an advantage for Tencent when compared to other players in the market.”
In another savvy move, as enterprises grapple with remote employees and video-conferencing solution grow in importance, Tencent rolled out its video-conferencing solution for the global market. VooV Meeting, the global version of the domestic app Tencent Meeting, was launched in over 100 countries including the larger Asia Pacific markets such as Malaysia, Hong Kong, Singapore and Japan.
Mukherjee says, “At this particular moment in time, the COVID-19 crisis has suddenly brought video-conferencing front and centre. While people are now resorting to it out of compulsion, they are likely to discover that this is a great way to work. As bandwidths and connectivity improve across countries, video-conferencing emerges as a really viable solution. Organisations will soon realise that this technology can help save tremendous amounts of travel and facility rental costs. So, usage is likely to grow exponentially – and it is not a bad time at all for Tencent to enter this market.”
The Video-Conferencing Market is Heating up
The video-conferencing market continues to grow and providers such as Zoom, Microsoft, Google, and Slack have made many of their offerings free. In the current milieu industries such as healthcare, education and professional services are using unprecedented video collaboration tools, both internally and for customer interactions.
Zoom is gaining global popularity with stock prices rising 28% in the last month in an otherwise under-performing global market. Zoom continues to evolve user-friendly features such as the virtual background, forcing other conferencing providers such as Microsoft to emulate them. Microsoft Teams has also seen a steep rise in popularity, with the company reporting over 50% rise in chat volume in the last month.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Audrey William says, “Expanding the capabilities beyond video will be critical for a larger market share. Zoom is now expanding its offering to include calling capabilities with Zoom phone. Beyond video, collaboration platforms are growing in importance and Microsoft Teams, as an example, has made the platform feature-rich across voice, video and collaboration capabilities. Users will want features that will make chat, video, voice and collaboration sessions rich and intuitive. If the experience is not good, they will find another platform to use. It will all come down to user experience!”
Tencent is by no means the only tech organisation from China that is eyeing the global market. Recently, Alibaba launched a free international collaboration platform based on their productivity app Dingtalk for medical professionals to share information and advice on prevention and treatment of COVID-19. In a boost to Tencent however, the United Nations (UN) announced that they will be using VooV Meeting to host their online conversations, especially for their initiatives to mark their 75th anniversary – UN75. Not only will the UN use Tencent’s video-conferencing capabilities, they will also leverage other Tencent offerings such as WeChat Work, and Tencent AI SI.
William thinks that the market might be crowded and Tencent will face some challenges. “Tencent’s challenge is that it is entering an established market. To make a mark, it will have to continue to innovate on features, focus on platform security and ensure that the experience is seamless. Tencent announced in January that the solution can support 300 attendees simultaneously. To sustain this and make a bigger push internationally, it will need to work with local partners to help take this product to market.”
“With all the options around, people will not use VooV Meeting just because it is free – they will if they find the features to be unique and the experience brilliant.”
Mukherjee adds, “Tencent is one of the most admired companies in China – it is a top pick for most graduates as their preferred employer and is seen as a better company to work for than other big players in China. This is a reflection of its strong corporate culture and continuing success. Tencent has, so far, had a good track record of competing with the likes of Alibaba and I believe that they will move quickly to muscle in and take a leadership space in the global video-conferencing market.”
Enterprise mobility was a key area of focus for organisations for many years in the late 2000s and early 2010s. Many businesses invested significant amounts of money and time in helping their employees access the information they needed while on the go – until the consumer smartphone era drove our attention away from our employees. Now we are focused on providing the best mobile apps, websites and experiences possible.
The constant evolution of the capabilities of smartphones, along with the drive to offer an ever-improving customer experience (CX) has kept our attention firmly on our customers. However, smart businesses now understand that in order to offer a great CX, they need to keep their employees happy. And giving them access to the technology that delivers the right information at the right time is a key factor in achieving better employee experience.
“Investment in enterprise mobility tools and platforms is forecast to increase significantly over the next few years. And the COVID-19 pandemic may even see some of that spend accelerated as businesses look to better support their remote and work-from-home employees,” says Tim Sheedy, Ecosystm Principal Advisor.
What to Expect from this New Wave of Enterprise Mobility
#1 Growth of UEM Adoption
Sheedy adds,“Today, many businesses are empowering their employees by providing the best end-user computing experience that will drive the best outcome. This often sees them looking beyond a single device (phone, PC etc) towards the entire experience – including the application, interface, management and security of the experience.”
A robust unified endpoint management (UEM) solution provides IT teams with a transparent and traceable overview of all endpoints within the network as well as the power to manage all connected devices from a single platform. It maps out the network setup and structure by carrying out a complete inventory of all network devices, configurations, installed software, and the drivers for endpoint subsystems. Ecosystm research finds that more than 60% of global organisations have either adopted UEM or are evaluating it (Figure 1).
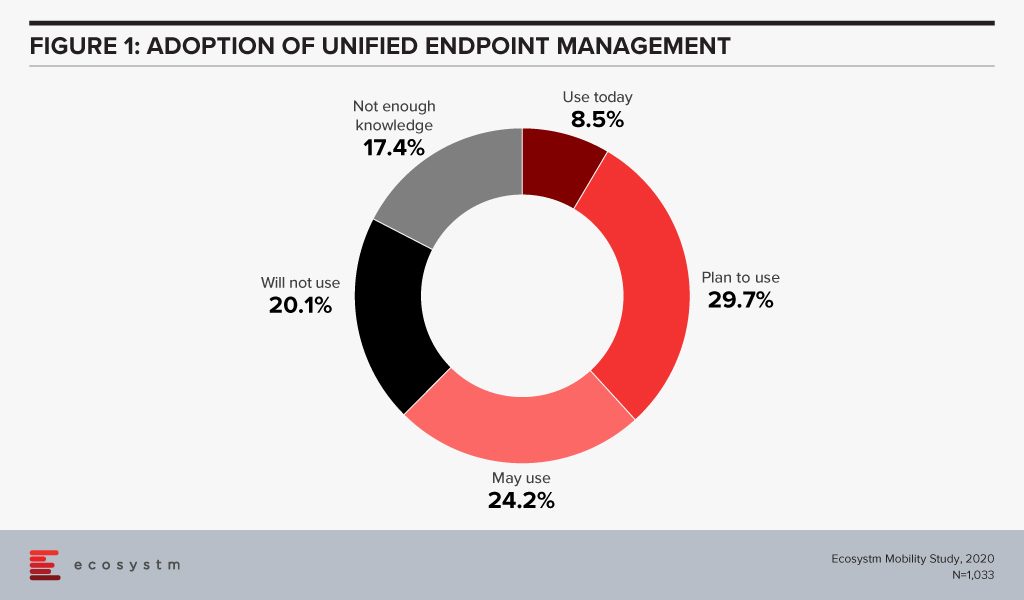
This trend will only go up with the rise in the number of devices organisations have to manage remotely. The workplace of the future will become exponentially digital and tech vendors will further strengthen their portfolio to offer UEM solutions.
#2 Greater C-Level Visibility in Mobility
In his report, The Enterprise Mobile Landscape in 2020, Sheedy notes that enterprise mobility decision, including the choice of devices supported often have C-level involvement (Figure 2). “A large government agency in Australia has had the Director General intervene in their mobility decisions to stamp his personal preference on decisions, and a CIO at a large bank makes sure that Apple devices are always preferred – even when it makes little business sense to do so!”
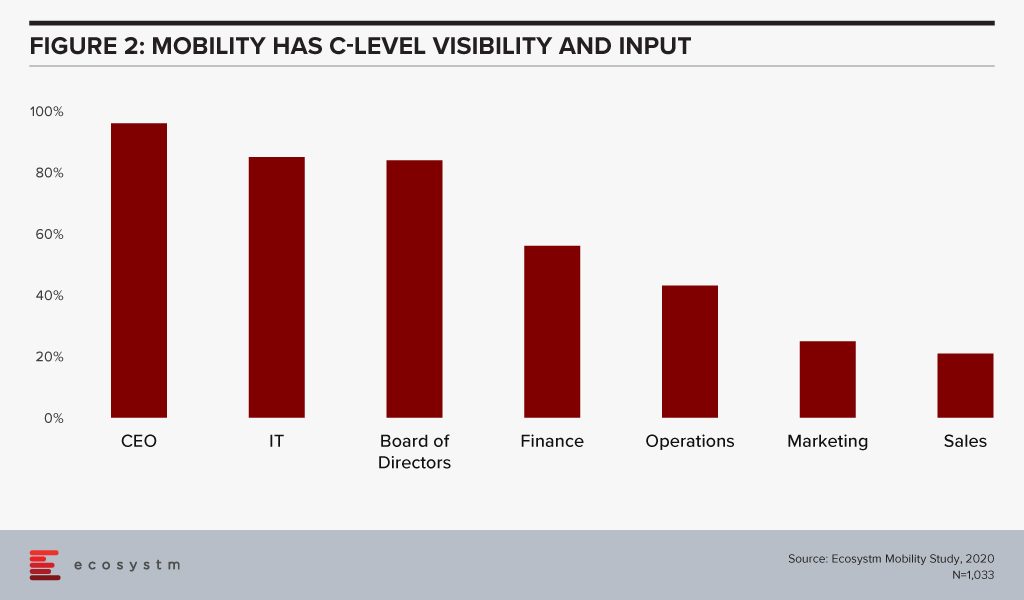
Choice of mobile devices is personal and most organisations have realised that. Less than a third of global organisations issue corporate devices and only 6% continue to believe that they can manage by only supporting corporate devices. However, nearly no organisation has gone fully BYOD either.
Apart from mobile device choice, mobility solutions also have to take into consideration the huge amounts of traffic it has to support. When organisations adopt a Mobile First Strategy it is an acknowledgement that it will involve multiple stakeholders, right from the inception of the vision. This is clearly a technology area where user experience and uptake is of importance. So, the mobility strategy should have senior level overview and input so that it can be a company-wide policy.
#3 There will be renewed interest in Mobile Security
Ecosystm research finds that the global adoption rate of mobile device management (MDM) solutions is about 44%, while only about 17% of organisations indicate the adoption of a Mobile Security solution focused on identity management, multilayered security and threat analysis.
Organisations are aware that mobility initiatives increase their risk profile (Figure 3). An enterprise mobility solution that allows people to work on their device and OS of choice and from where they choose to, will become increasingly important in the current milieu. But the threats to organisation are equally real.
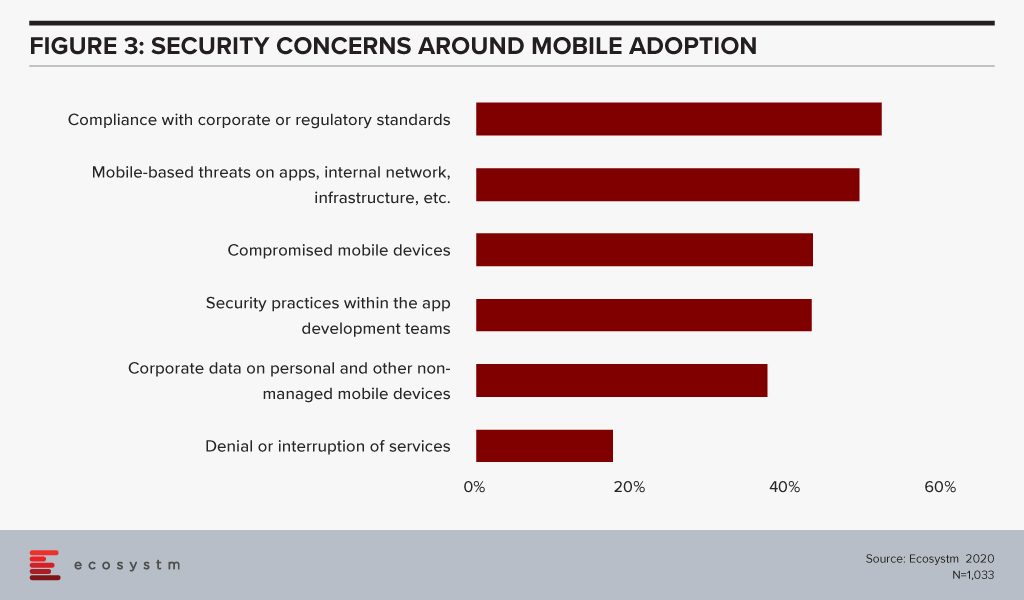
More than half of the organisations are concerned about compliance with corporate or regulatory standards in implementing mobility solutions. This is a good indication that the Mobile First strategy implementations have a strong compliance angle to them, both internally and for external agencies.
However, as Sheedy notes, it is still a challenge for the IT team. “Organisations provide one or two more operating systems that the IT team needs to manage, patch and secure. The mobile applications provide more entry points for would-be hackers and others to use and threaten the business. The devices and applications provide another set of user interface that need to be managed and governed to ensure regulatory compliance. They can also gather highly personal data (such as the location of customers when they are using – or not using – the application) so this data needs to be secured and governed.” As adoption matures, organisations will need to invest in niche Mobile Security solutions to combat their security concerns.
#4 Mobility will Drive SaaS Adoption
What organisations want most from their mobility solutions is cloud capabilities. One of the main reasons why organisations look for cloud capabilities is because mobile workloads tend to be unpredictable and cloud solutions are best equipped to handle the unexpected spikes. Most organisations also consider cloud solutions for a seamless integration with back-end systems and because a mobile workforce needs to make real-time decisions based on real-time data. Given the disparity of the data sources in a typical organisation, hosting on a neutral platform becomes more attractive. Also as organisations become more conscious about mobile security, cloud options also give them better traceability on remote device and data access.
However, conversely mobility will also drive the adoption of SaaS enterprise solutions and tools. Many businesses have mobilised their email, eCommerce platforms and unified communications and collaboration tools. But beyond that, organisations are not really empowering their employees to work on their mobile devices (Figure 4). This will have to – and will change – fast.

In his report, Make Remote Working Successful, Sheedy notes, “It goes without saying that your employees’ productivity levels will improve if they have access to the applications they need. And while many organisations already have enabled universal (or near-universal) application access from PCs and laptop computers, many of these applications should also be available from smartphones and tablets. This will allow your employees to work when they are on the move – not just when they are at home.”
It is time for organisations to re-evaluate their enterprise mobility if they have to remain productive in these difficult times, and beyond. Sheedy says, “Ultimately, our employee’s reliance on great mobile and targeted end-user computing experiences is increasing – and 5G services will only accelerate the transition away from traditional telephony, communications services and desktop applications. Businesses will need to continue to mobilise their enterprise systems to make them easier to use. Employees have now experienced great mobile apps and systems – and most enterprise mobility systems don’t stand up in that comparison.”

The Law Society’s Lawtech Adoption Research, February 2019 finds that there are significant drivers to tech adoption by legal firms. The drivers range from increasing workloads and job complexity, the needs of the younger tech-savvy legal workforce and the eternal client needs of lower costs and faster delivery. The research also finds that the B2B market is the more mature in their tech adoption – particularly the larger law firms – and solutions such as legal analytics, project management, governance and compliance, and contract management are being evaluated. Technologically mature law firms appear to have already adopted collaboration tools, document management, IP management and eBilling solutions. While the B2C market is yet to show the same level of tech adoption, law firms are beginning to evaluate customer services such as chatbots, DIY law, robot lawyers and triage tools.
The research shows that there is a growing appetite for legaltech and indicates that countries across the world would do well to start their investments to support their legal community now.
Singapore Continues to Invest in Legaltech Research
The Singapore Government recently announced a grant of SGD 10.8 million to the Singapore Management University (SMU) School of Law to manage a legal technology research program. The grant comes from the National Research Foundation Singapore, under the Prime Minister’s Office. Ecosystm Vice President and General Counsel, Nandini Navale calls this step commendable and timely. “This is indeed proof that streamlining and digitalisation of the laws and the legal ecosystem in Singapore – although expensive – is an imperative investment.”
SMU intends to establish a Centre for Computational Law (CCL) and a five-year research program, focusing on Smart Contracts and Smart Statutes. Navale says, “The CCL has the potential of evolving into a robust platform for lawyers, legaltech professionals and law firms who are gearing up to adopt legal technology, artificial learning (AI) and machine learning to remain relevant in the new age. Legaltech such as AI-based due diligence tools, auto-generated contract solutions, practise management software, and deal room software have certainly changed the traditional law firm model in the recent past.” Navale sees the CCL as being able to deliver self-executing Smart Contracts and alternate coding solutions based on blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT), which will potentially transform the way the world works promising more transparency, and time and cost-efficiency.
The CCL follows the example of the Centre for Technology, Robotics, Artificial Intelligence & the Law (TRAIL), a research unit under the National University of Singapore Faculty of Law (NUS Law), launched in December 2019. TRAIL was set up with the intentions of being an international think-tank that enables inter-disciplinary communities to research into legal, ethical, policy, philosophical and regulatory issues associated with the use and development of IT, AI, data analytics and robotics in the practice of law.
“Digitalisation has undoubtedly transformed the world, established a new normal and redefined the ‘Future of Work, Play and Living Life’. While one of the most glaring advantages of digitalisation is significant simplification and ease, the flip side is that the legal systems and regulators are constantly faced with both policy and practical challenges, such as implementation and enforcement,” says Navale. “Fintech solutions such as Digital Banking, RegTech, SupTech and SaaS-based compliance and anti-money laundering (AML) tools – are all solid examples of the rapid impact of technology. This creates an immediate and imperative need for regulators to constantly reflect on, review and revise existing laws, policies, and regulations. And initiatives such as the CCL may just be the solution.”
Authored by Mervyn Cheah, Aga Manhao and Sash Mukherjee
In January we wrote a blog on How Technology is Helping to Combat the Coronavirus – since then the COVID-19 outbreak has fast become a global threat, disrupting healthcare systems and economies. As the world struggles to contain the spread, Singapore’s response to the crisis shows how governments can use policies and technology to combat emergencies. While it is true that Singapore’s size is its advantage, and most of what it was able to do cannot be replicated in larger, more spread-out countries, there are still lessons there – in the simplicity and responsiveness of the measures. The threat is by no means behind us and the Government will need to implement many more policy changes in the near future. But it is worthwhile to look at what Singapore has done so far to contain the spread.
#1 Identifying and acknowledging the threat early
Like other Asian countries, Singapore suffered during the SARS outbreak in 2003. While the number of people infected during SARS was less at 238, at the end of the outbreak the country had recorded 33 deaths. Having learnt from that experience, Singapore knew that early response is key. Acknowledging the threat early allowed Singapore to have test kits made available to all major hospitals through the Agency of Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR). A*STAR is a statutory board under the Ministry of Trade and Industry, Singapore. The agency supports R&D that is aligned to areas of competitive advantage and national needs. By the time the first case was reported on 23rd January, health professionals were equipped with testing capabilities. Health authorities and biotech companies have continued to modify and launch newer testing technology – like the fast-track swab test kits launched in early March – as global research continues.
#2 Focusing on contact tracing
Right from the start, Singapore has been focused on contact tracing. Following the chain of the virus allows government agencies to identify and isolate people at risk, including their close contacts. This became more important as the virus spread into the local community with the first reported case on the 4th February. The contact tracing process has been a concerted effort using technology, manpower and dedication. As Singapore faces a second wave of spread from returning travellers, the Government launched Trace Together, an app that records distancing between users and the duration of their encounters. Individual consent is required to share the data which is encrypted and deleted by the Ministry of Health (MOH) after 21 days. This allows the MOH to contact citizens in the case of possible contact with an infected individual.
#3 Keeping the citizens in the loop
The speed in imposing border controls, meticulous tracing of known carriers and aggressive testing are all positive steps in combating a crisis like this. But arguably the most productive strategy was to get citizen buy-in. The need was felt most when the country’s Disease Outbreak Response System Condition (DORSCON) level was raised from yellow to orange on 7th February. With the raised DORSCON level, buildings and public facilities with a high volume of people were required to do fever screening and collect personal details for further communication and alerts, if required. Simultaneously, the Government started sharing clear, transparent, daily public communication through mobile phones. The messages contain anonymised details of the patients (to make people aware of their own possible exposure), as well as an update of the number of patients being treated and released. The 2 deaths were also reported promptly – but enough details were shared to avoid panic. Demonstrating cross-agency collaboration, the information disseminated comes from multiple government agencies – the same channel is also used to drip-feed hygiene guidelines and the evolving government policies on travel, trade and so on.
The message from the leadership has also been clear and timely, and an economic stimulus package was announced fairly early. The Government is currently working on a second stimulus package, as the threat to the economy continues.
#4 Dispelling misinformation
Taking this daily communication to the next level, the Government has been prompt in stopping the spread of rumours. Not only does the MOH website share all the latest details, any spread of misinformation (usually through social media) is being quelled by official statements. It is extremely important to be able to address issues such as these, because it impacts trust in the government and the healthcare system. The daily updates are now a ‘single source of truth’ on all COVID-19 related information. The Cyber Crime Portal has also been activated with the intention to track unverified messages especially regarding the treatment and cure of COVID-19.
#5 Empowering healthcare professionals and citizens with digital tools
Unfortunately, the community spread appears to be happening in waves, especially as Singapore has a high volume of returning travellers. Healthcare facilities continue to be stretched. Although Singapore has adequate healthcare facilities to cope with the number of current cases, the Government is also prepared with additional quarantine facilities. Meanwhile, hospitals have set up makeshift triage centres in their car parks to deal with the growing number of patients needing to get tested. To counter the need for more infrastructure and the cost to get additional facilities ready, the use of digital health, remote patient monitoring and online care planning is being explored to limit patients presenting themselves to providers. KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital has launched UPAL – Urgent Paediatric Advice Line – as a pilot online consultation channel. It is expected that more healthcare facilities will offer services such as these. Being cloud based, these solutions can be deployed within days and high-risk patients can be immediately onboarded, easing the burden on the healthcare system and providing relief to patients and families. Telemedicine and remote monitoring are not new, having been proven and tested by several healthcare systems. In these extraordinary times, technology will help the healthcare system keep all in Singapore safe.
#6 Having a strong Data and Digital infrastructure
Singapore’s data and digital services infrastructure is the overarching factor that has allowed the Government to act quickly and efficiently to fight this community threat. While this is not linked directly to the current response measures against COVID-19, it is the true enabler. Firstly, the electronic health record system has access to records of all patients who have availed of the public healthcare system (private, primary care organisations have also started contributing to the system – enabling the vision of complete longitudinal health records). This is the backbone of the Government’s healthcare measures in these difficult times. Secondly, the network infrastructure allows the introduction of online consultation services. Moreover, people are able to work from remote locations seamlessly using collaboration tools such as Zoom, Skype and WebEx. This allows the Government to encourage people to work from home, to stay away from healthcare facilities and other measures to reduce overcrowding of public spaces to prevent the spread. And finally, Singapore has a strong access to eCommerce and online platforms, allowing people to access almost anything they choose to, online.
While the battle against the pandemic is far from over, Singapore has so far managed to avoid complete disruption by using technology to be responsive to the community’s needs.

The FMCG industry has always been competitive given the need to drive high sales volume because of the low profit margins of the products. As the industry faces changes – such as the demographics of the consumer base and the need to introduce newer sales channels – technology is playing an important role in ensuring that the organisations can remain competitive.
eCommerce Disrupting the FMCG Industry
The concept of online retail is said to have originated in some form in the 1960s. But with the growth of the access to the Internet in the 1990s and Amazon’s competitive business model, it has disrupted the retail and FMCG industries. As we see a steady growth in smartphone usage, digital payments, online banking and app-based platforms, online retail is becoming mainstream. While initially thought to be ideal for the purchase of durables and entertainment products and services (where price comparison is key), it has become common for FMCG companies to use eCommerce platforms. Even perishables are being purchased online with the rise in the number of online grocery stores. This is impacting the FMCG industry in a number of ways:
Change in Marketing Strategy
FMCG companies need to continue their traditional marketing strategy for in-store consumers. But at the same time, they need to reach out to a wider base of consumers who shop online. The profile of these consumers is different – younger and technologically savvier. They do not necessarily believe in brand loyalty. While the browse-to-buy ratio for FMCG products is high, they are having to invest in digital marketing strategies including personalised campaigns and presence in social media and online forums. Even packaging for in-store and online products need to be different for some products.
Increased Competition
An online presence means that your brand can reach a wider audience – this also means that the competition becomes tougher. Now global brands compete with brands from other countries as well as local brands on the same online platform. This raises the bar, with companies competing not only on price and product but also on delivery services and better customer feedback.
Increased Complexity of the Supply Chain
No longer can an FMCG company depend solely on trucks delivering their products to stores at a fixed time of day. As they play increasingly in the B2C space, they have to constantly be aware of seasonality and spikes. This means that their supply chain operations become that much more complicated, and they are having to spend more on logistics and transportation. There is also the need to handle a larger volume of data.
Changing Consumer Profile
As mentioned earlier, the consumer profile of the FMCG industry has changed to include younger consumers who want to shop online. It also includes consumers in newer markets made possible by eCommerce platforms. FMCG companies also have to cater to consumers who are conscious about product quality, the environment and ethics. This means they want to know where the products were grown or manufactured, their carbon footprints and generally want more traceability of the products they are purchasing. This has led governments to come up with guidelines to protect consumer rights. Recently, the UK government issued guidelines on the quality, labelling, standards and food safety including the right logos, health and identification marks.
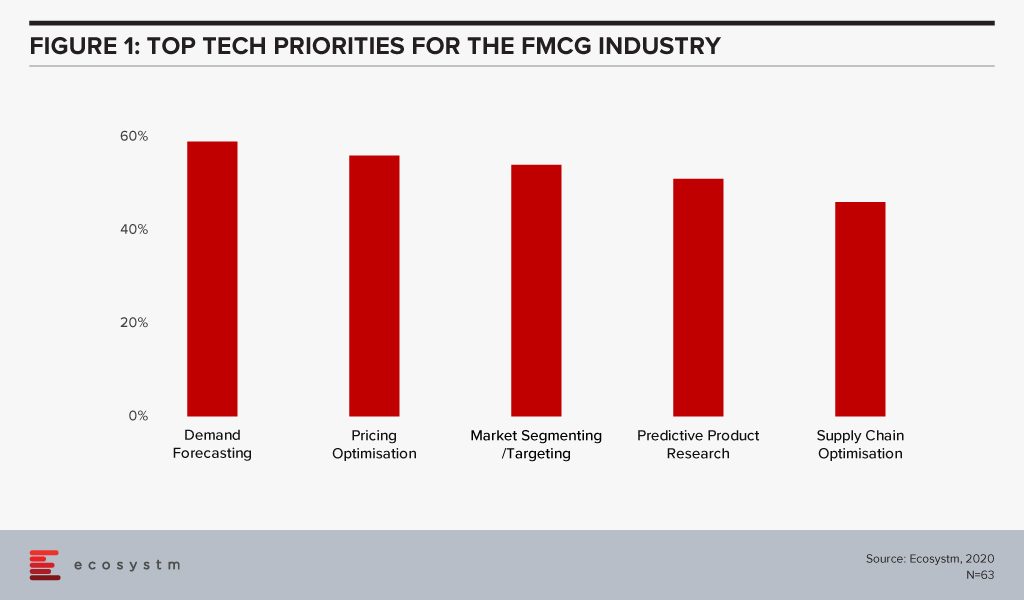
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for FMCG companies, focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). It is clear that their key priority is to handle the competitive market by focusing both on the consumer and the supply chain. Supply chain optimisation through demand forecasting ensures that they are not managing extra stock, and simultaneously not losing out on customers because of lack of stock. This just-in-time inventory management includes initiatives such as pricing optimisation in response to market demand, competition and – especially in the case of perishables – ensuring that stock closer to the use by date is cleared.
Technology as an Enabler of FMCG Transformation
The one advantage that FMCG companies have today is they have access to enormous customer and inventory data. As a result, they are able to leverage several emerging technologies to transform.
Digital Marketing
One area that is transforming the industry is digital marketing which includes multiple aspects such as search engine marketing, video marketing, social media activity and email marketing. While several technologies come together for a digital marketing solution and AI is a key component of the solutions, there are platforms that provide an end-to-end solution.
Digital marketing is most effective with a targeted group of customers and when organisations can identify digital or social champions. Johnson & Johnson’s Babycenter.com is a good example of how creating a digital community can help market products. The core idea behind the website is to give expecting and new mothers advice on early childhood. While on the surface it appears disassociated from Johnson & Johnson, the site almost exclusively carries their advertisements. This gives them a targeted base to push their products to. Dollar Shave Club is another example of how brands can leverage digital marketing. Their social media engagement has been so successful that they got bought over by Unilever. The digital campaign includes incentivising members with their products for posting about them on Instagram or Facebook.
Blockchain
FMCG companies are investing in Blockchain and digital ledger technologies for track and trace functionalities and operational efficiency. The technology not only helps manage the supply chain better by effective shipping timelines maintenance, delivery management and inventory management; it also helps build trust in a brand. It helps in compliance management, reduces the number or need for middlemen, easier handling of cross-border transactions and brings about an end-to-end accountability.
Danone initiated a Track & Connect service for their baby formula using Blockchain for transparency and traceability to show the authenticity of their products to parents and for a better customer experience. FMCG companies will benefit immensely from the farm-to-fork accountability concept initiated by Agriculture.
AI
From predictive analysis to machine learning to deep learning, AI is bringing a lot of benefits to FMCG companies. AI is enabling companies to discover gaps (both in their consumer interactions and in the supply chain) and make their processes intelligent – including demand forecasting, supply chain optimisation, personalised product offerings, social media analytics, consumer sentiment analytics and recommendation engines.
FMCG organisations are analysing internal and external data sources for both sales and improved customer experience. As FMCGs are forced to sell online to remain competitive, they have access to a high volume of the consumer as well as supply chain and inventory management data. Coca-Cola remains one of the leaders in the FMCG market by leveraging this data, including product research and social data mining. Even their vending machines are looking to leverage AI for personalised offerings and for loyalty programs.
The need to enhance the customer experience has also seen innovations like the Maggi Chatbot – “Kim”- that helps customers learn about Maggi recipes, ingredients, and dietary requirements, through Facebook Messenger.
FMCG companies that cannot afford to invest in technologies such as AI also have the option of leveraging the technology offerings of their online retail platform. eBay offers analytics as a service to the sellers – offering them data, metrics, and analytics to help them succeed. They also introduced computer vision technology to help sellers create clearer and more attractive images for the platform.
In this competitive market, we will see FMCG companies – and not just the big global brands but also the local producers – embrace more technology.











