Technological innovation is dramatically changing how organisations interact with modern consumers in the rapidly evolving banking, financial services, and insurance (BFSI) industry. The growing dependence on digital communication tools and platforms lies at the core of this transformation. These tools have become vital for BFSI organisations to meet the dynamic needs of today’s customers, enabling agile, responsive Sales & Support teams that can use real-time data to sustain customer engagement, ensure data security, comply with regulations, and streamline operations.
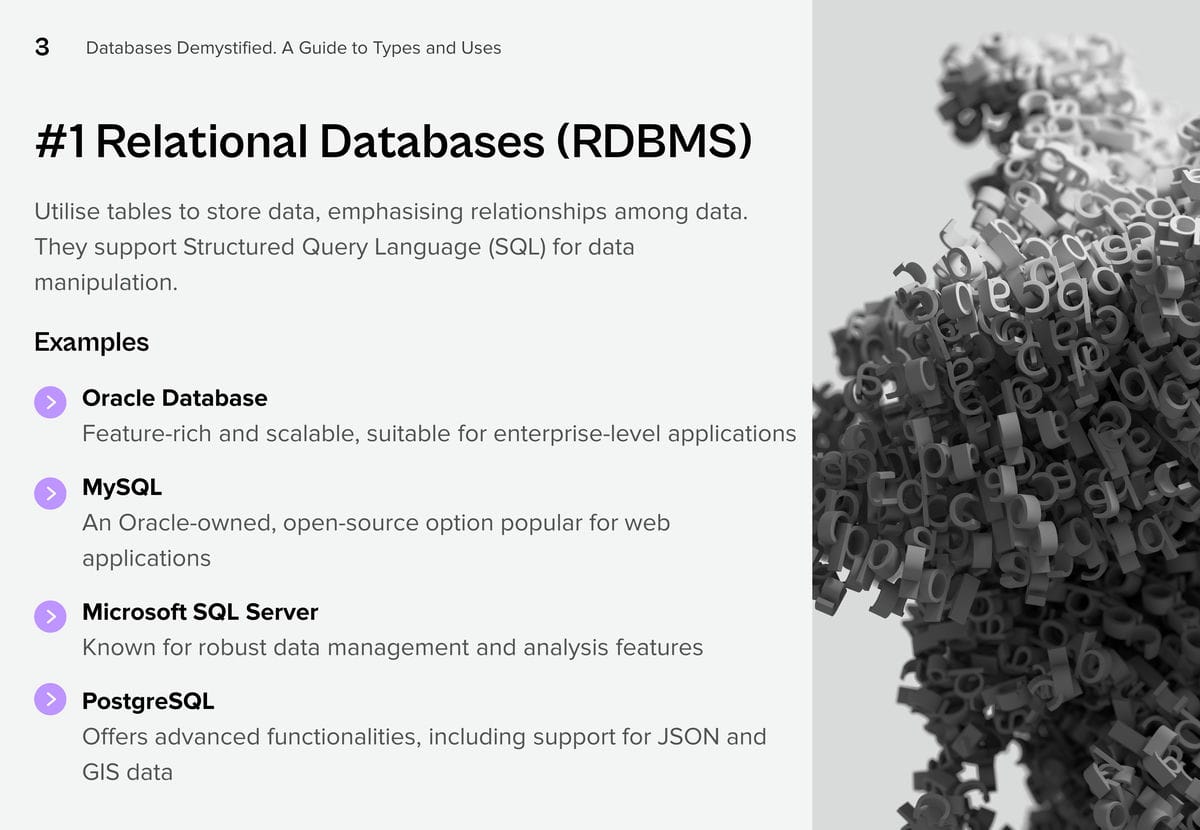
Customer Engagement Challenges in BFSI Organisations
Security Concerns. Customers in the BFSI industry are increasingly concerned about the security of their financial transactions and Personal Identifiable Information (PII). With the rise of cyber threats, customers expect robust security measures to protect their accounts and sensitive information. BFSI organisations need to continually invest in cybersecurity infrastructure and technologies to reassure customers and maintain their trust.
Customer Expectations. In the competitive landscape of the BFSI industry, customer retention and attraction are critical to sustaining profitability. Organisations must prioritise an agile approach that adapts swiftly to market changes. Central to this strategy is the delivery of personalised experiences aligned with individual preferences and needs, driven by advancements in digitalisation. To achieve this, BFSI organisations have to increase investments in AI-driven solutions to gain deep insights into customer behaviour, enabling them to accurately anticipate and meet evolving needs.
Regulatory Compliance. The industry operates in a highly regulated environment with strict compliance requirements imposed by various regulatory bodies. Ensuring compliance with constantly evolving regulations such as GDPR, PSD2, Dodd-Frank, etc., poses a significant challenge for organisations. To complicate the landscape further, institutions with cross-border operations need to consider the laws in different countries. Compliance efforts often result in additional operational complexities and costs, which can impact the overall customer experience if not managed effectively.
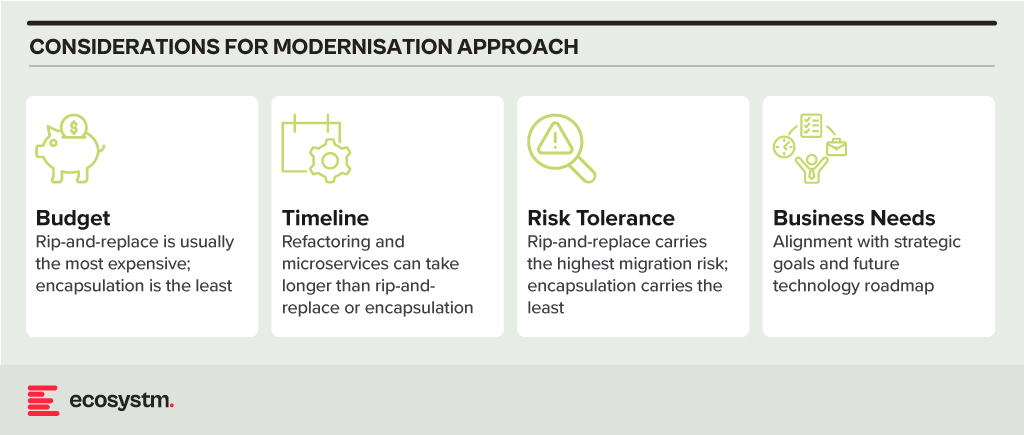
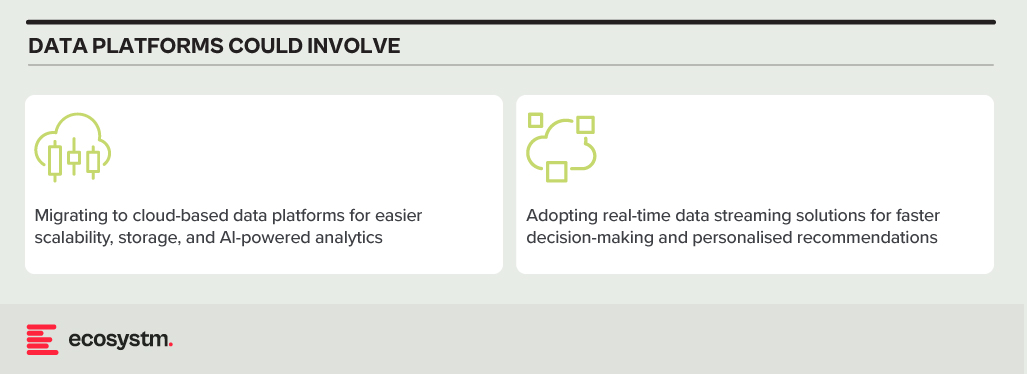
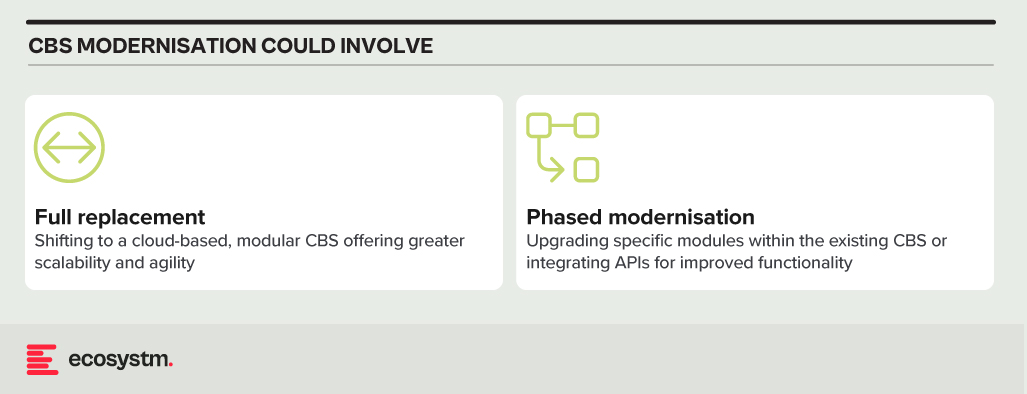
Digital Transformation. Rapid technological advancements and changing customer preferences are driving BFSI organisations to undergo digital transformation initiatives. However, legacy systems and processes hinder their ability to innovate and adapt to digital trends quickly. Transitioning to modern, agile architectures while ensuring uninterrupted services and minimal disruption to customers is a complex undertaking for many BFSI organisations.
Customer Education and Communication. Financial products and services can be complex, and customers often require guidance to make informed decisions. Sales & Support teams in BFSI organisations struggle to effectively educate their customers about the features, benefits, and risks associated with various products. Clear and transparent communication regarding fees, terms, and conditions is essential for building trust and maintaining customer satisfaction. Balancing regulatory requirements with the need for transparent communication can be challenging.
5 Ways to Empower Sales & Support Teams in BFSI
BFSI organisations in Asia Pacific often overlook technology enablement for the empowerment of their Sales & Support and other customer engagement teams. Key measures to empower these teams include upskilling for role flexibility and offering competitive remuneration for better employee retention.
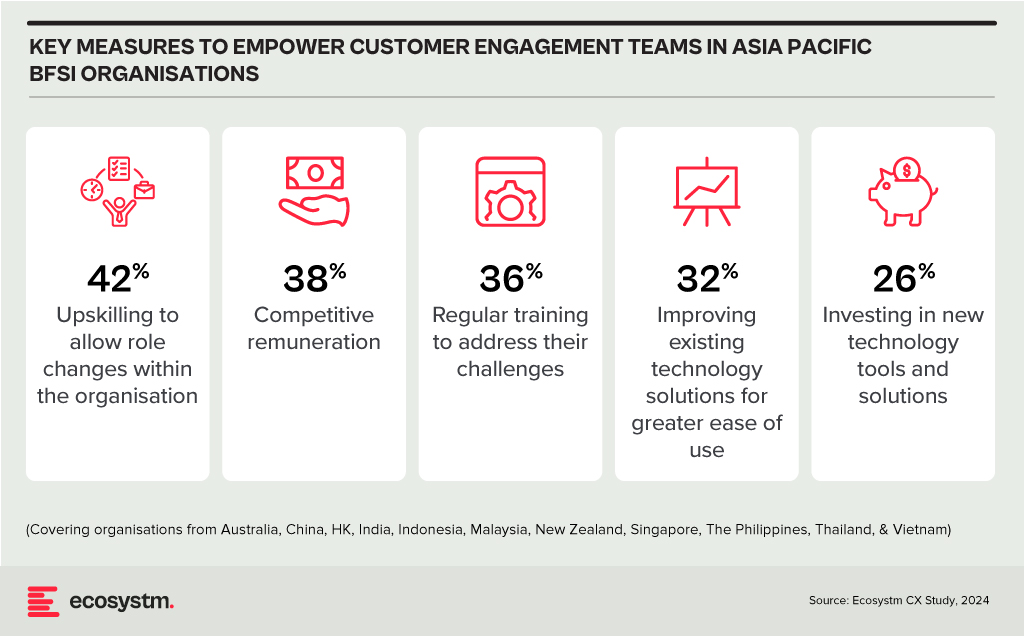
Organisations should prioritise upgrading Sales & Support tools and solutions to address the team’s key pain points.
#1 Boost Customer Engagement with Omnichannel Support
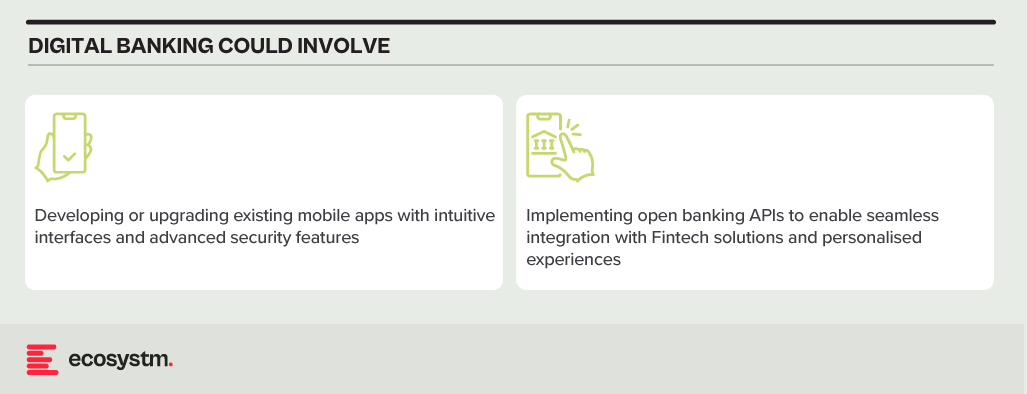
BFSI organisations need to work on a suite of API-driven solutions to create a comprehensive omnichannel presence. This enables engagement with customers via their preferred channels, such as SMS, email, voice, chat, or video. Such flexibility enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty by ensuring personalised and convenient interactions. This includes capabilities such as the ability to deploy messaging and voice services to dispatch timely account activity alerts, secure transactions with two-factor authentication, and deliver customised financial advice through chatbots or direct communications.
#2 Streamline Customer Service with AI and Virtual Assistants
Integrating AI and virtual assistants allows BFSI companies to automate standard inquiries and transactions, freeing Sales & Support teams to tackle more sophisticated customer needs. These AI tools can interpret and process natural language, facilitating conversational interactions with automated services. This boosts efficiency and shortens response times, elevating the customer engagement experience. Also, consistently integrating these virtual assistants across various channels ensures a uniform customer experience – and brand image.
#3 Enhance Security Measures and Compliance Standards
Adhering to stringent security and compliance requirements is essential for BFSI organisations. A secure platform complies with critical global and country-level standards and regulations. The voice and video communication services must include comprehensive encryption, protecting all customer interactions. There is also a need to have a suite of tools for monitoring and auditing communications to meet compliance requirements, allowing BFSI organisations to protect sensitive data while providing secure communication options.
#4 Leverage Insights for Personalised Customer Interactions
BFSI organisations must focus on aggregating, harmonising, and scrutinising customer interactions across various channels. This holistic view of customer behaviour allows for more targeted and personalised services, enhancing customer engagement and loyalty. By leveraging insights into customers’ interaction histories, preferences, and financial objectives, companies can customise their outreach and recommendations, improving upselling, cross-selling, and retention strategies.
#5 Increase Operational Efficiency with Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based communication solutions offer BFSI organisations the scalability and flexibility needed to respond swiftly to market shifts and customer demands. This adaptability is vital for fostering growth in a dynamic industry. A customisable solution supports organisations in refining their operations, from automating workflows to integrating CRM systems, enabling Sales & Support teams to operate more smoothly and effectively. Cloud technology helps reduce operational expenses, elevate service quality, and spur innovation.
Digital communication and collaboration tools have the power to revolutionise BFSI, enhancing engagement, security, and efficiency. Through APIs, AI, and cloud, organisations can meet evolving market needs, driving growth and innovation. Embracing these solutions ensures competitiveness and agility in a changing landscape.