As organisations look to empower consumers with alternative channels of communication and engagement, there will be a greater adoption of Conversational AI. The biggest challenge lies in getting the deployment right from the start. There are many vendors that are promoting their offerings around Conversational AI, and some enterprises that have rushed to invest have been disappointed with the outcome – no improvement in CX but at a higher cost. Organisations need to evaluate the entire design framework, plan where AI fits into the enterprise’s overall CX vision and understand what constitutes Conversational AI.
This whitepaper outlines the definition of Conversational AI and what tech buyers need to consider before embarking on a Conversational AI deployment. The data used in this paper is from the global Ecosystm CX and AI studies, that are live and can be accessed on the Ecosystm platform.
Click Below to Download the Whitepaper

(Clicking on this link will take you to Nuance website where you can download the Whitepaper)

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming embedded in financial services across consumer interactions and core business processes, including the use of chatbots and natural language processing (NLP) for KYC/AML risk assessment.
But what does AI mean for financial regulators? They are also consuming increasing amounts of data and are now using AI to gain new insights and inform policy decisions.
The efficiencies that AI offers can be harnessed in support of compliance within both financial regulation (RegTech) and financial supervision (SupTech). Authorities and regulated institutions have both turned to AI to help them manage the increased regulatory requirements that were put in place after the 2008 financial crisis. Ecosystm research finds that compliance is key to financial institutions (Figure 1).
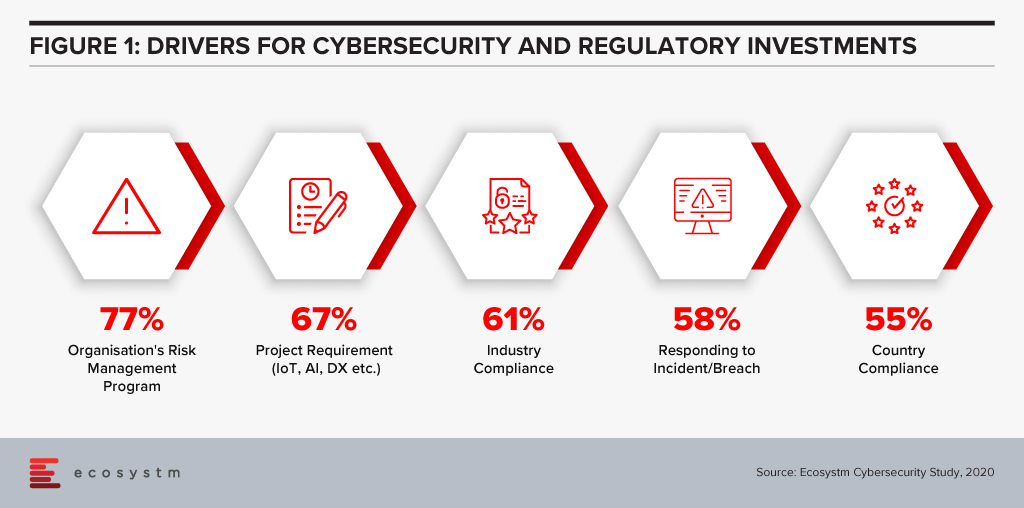
SupTech is maturing with more robust safeguards and frameworks, enabling the necessary advancements in technology implementation for AI and Machine Learning (ML) to be used for regulatory supervision. The Bank of England and the UK Financial Conduct Authority surveyed the industry in March 2019 to understand how and where AI and ML are being used, and their results indicated 80% of survey respondents were using ML. The most common application of SupTech is ML techniques, and more specifically NLP to create more efficient and effective supervisory processes.
Let us focus on the use of NLP, specifically on how it has been used by banking authorities for policy decision making during the COVID-19 crisis. AI has the potential to read and comprehend significant details from text. NLP, which is an important subset of AI, can be seen to have supported operations to stay updated with the compliance and regulatory policy shifts during this challenging period.
Use of NLP in Policy Making During COVID-19
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) coordinates at the international level, the work of national financial authorities and international standard-setting bodies in order to develop and promote the implementation of effective regulatory, supervisory and other financial sector policies. A recent FSB report delivered to G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors for their virtual meeting in October 2020 highlighted a number of AI use cases in national institutions.
We illustrate several use cases from their October report to show how NLP has been deployed specifically for the COVID-19 situation. These cases demonstrate AI aiding supervisory team in banks and in automating information extraction from regulatory documents using NLP.
De Nederlandsche Bank (DNB)
The DNB is developing an interactive reporting dashboard to provide insight for supervisors on COVID-19 related risks. The dashboard that is in development, enables supervisors to have different data views as needed (e.g. over time, by bank). Planned SupTech improvements include incorporating public COVID-19 information and/or analysing comment fields with text analysis.
Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)
MAS deployed automation tools using NLP to gather international news and stay abreast of COVID-19 related developments. MAS also used NLP to analyse consumer feedback on COVID-19 issues, and monitor vulnerabilities in the different customer and product segments. MAS also collected weekly data from regulated institutions to track the take-up of credit relief measures as the pandemic unfolded. Data aggregation and transformation were automated and visualised for monitoring.
US Federal Reserve Bank Board of Governors
One of the Federal Reserve Banks in the US is currently working on a project to develop an NLP tool used to analyse public websites of supervised regulated institutions to identify information on “work with your customer” programs, in response to the COVID-19 crisis.
Bank of England
The Bank developed a Policy Response Tracker using web scraping (targeted at the English versions of each authority/government website) and NLP for the extraction of key words, topics and actions taken in each jurisdiction. The tracker pulls information daily from the official COVID-19 response pages then runs it through specific criteria (e.g. user-defined keywords, metrics and risks) to sift and present a summary of the information to supervisors.
Market Implications
Even with its enhanced efficiencies, NLP in SupTech is still an aid to decision making and cannot replace the need for human judgement. NLP in policy decision is performing clearly defined information gathering tasks with greater efficiency and speed. But NLP cannot change the quality of the data provided, so data selection and choice are still critical to effective policy making.
For authorities, the use of SupTech could improve oversight, surveillance, and analytical capabilities. These efficiency gains and possible improvement in quality arising from automation of previously manual processes could be consideration for adoption.
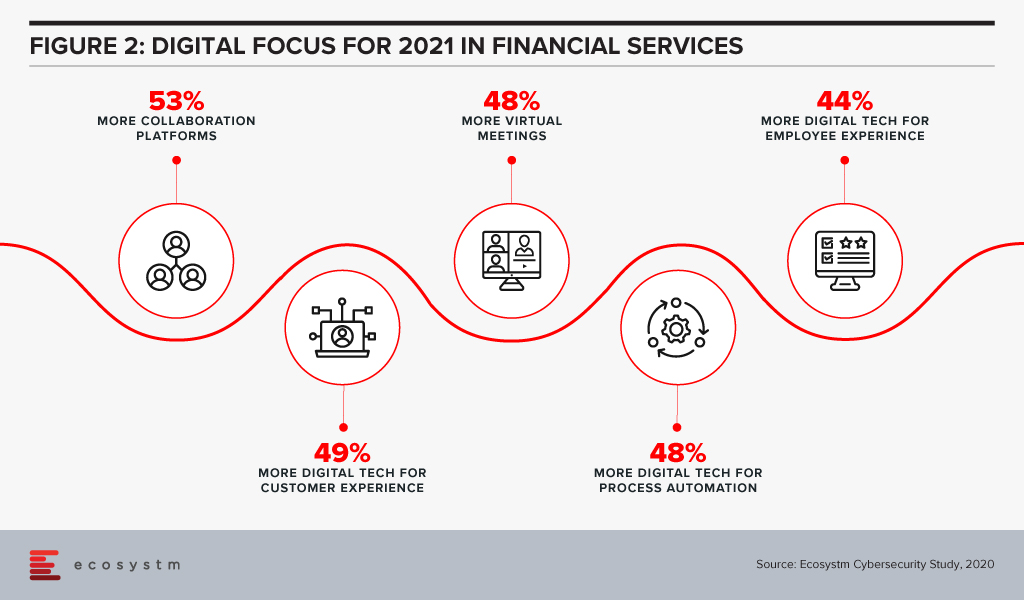
Attention will be paid in 2021 to focusing on automation of processes using AI (Figure 2).
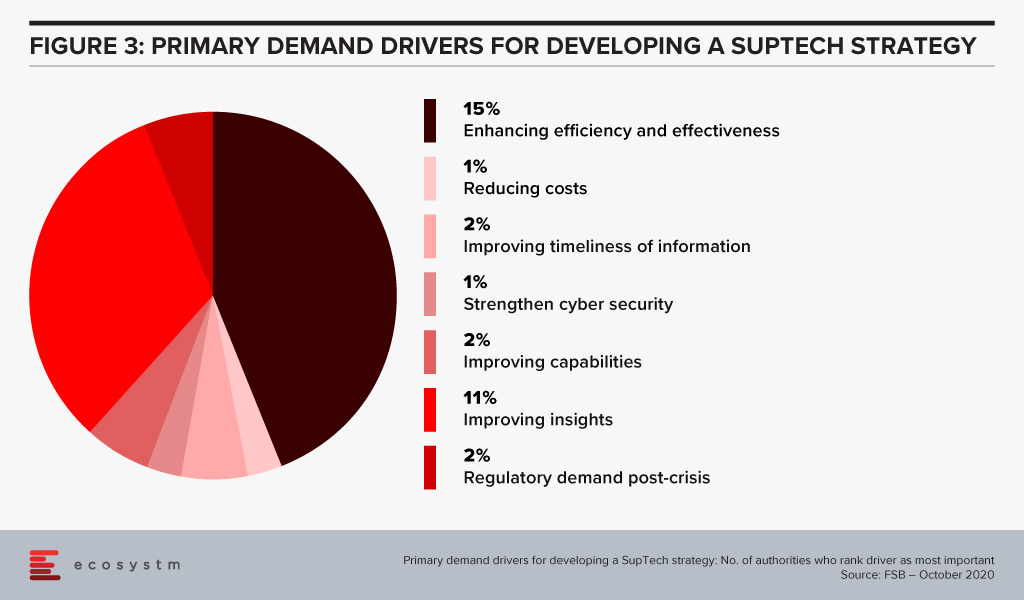
Based on a survey done by the FSB of its members (Figure 3), the majority of their respondents had a SupTech innovation or data strategy in place, with the use of such strategies growing significantly since 2016.
Summary
For more mainstream adoption, data standards and use of effective governance frameworks will be important. As seen from the FSB survey, SupTech applications are now used in reporting, data management and virtual assistance. But institutions still send the transaction data history in different reporting formats which results in a slower process of data analysing and data gathering. AI, using NLP, can help with this by streamlining data collection and data analytics. While time and cost savings are obvious benefits, the ability to identify key information (the proverbial needle in the haystack) can be a significant efficiency advantage.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit which will cover topics tied to creating infrastructure for a digital economy; and RegTech and SupTech policies to drive innovation and efficiencies in a co-Covid-19 world.

Five9, a cloud-based contact centre solutions provider announced the acquisition of intelligent virtual agent (IVA) platform provider, Inference Solutions for about USD 172 million. Five9 and Inference Solutions have been partnering for the last couple of years, with Five9 being a reseller for Inference Solutions’ IVA platform. The acquisition is expected to provide a boost to Five9’s AI portfolio, automate contact centre agent activities and provide AI-based omnichannel self-service solutions.
The need to drive greater automation in the contact centre is high on the agenda, and this acquisition demonstrates how important AI and automation is to contact centre modernisation. The old-fashioned ways of long wait times, being passed on through different menus on the IVR and being asked to repeat yourself through the older speech recognition engines is starting to not only frustrate customers but will become obsolete. Based on Ecosystm’s research, close to 60% of contact centres globally stated that investing in machine learning and AI is a top customer experience priority in the next 12 months.
Inference has come a long way since its inception at Telstra Labs
Inference Solutions (founded in 2005) was spun out of Telstra Labs. It has since expanded to the US and developed a suite of solutions in the IVA segment. They have a good partnership strategy with the leading telecom providers globally as well as the UC/contact centre vendors. Inference Solutions uses resellers such as service providers, UC, and contact centre software providers – and these include AT&T, Cisco (Broadsoft), Momentum Telecom, Nextiva, 8×8 and many others. The Inference Studio solution will see a new release in the next few months where the solution will come pre-built with the ability for the contact centre team to pre-load the contact centre conversations. These can be conversations that have been going on for 6 months or longer. The Studio solution will then be able to analyse and understand the underlying intent of the conversation, match the intent so that it can be used to auto train the bots accurately. That process of matching the intent and training is expensive and if you can automate some elements of that, it will bring the cost of the deployment down. Its solution integrates into NLP engines from Google, AWS, and IBM. In Australia they continue to work on patents in close partnerships with Melbourne University and RMIT. Throughout its journey, Inference has built a good base of customers in the US, UK, and Australia.
Five9 to accelerate on its vision of AI and Cloud
Contact centre modernisation is high on the agenda for many organisations and this will lead them to build AI and automation at the core of their customer strategies. The discussion spans across the CEO, Digital and Innovation, and the Contact Centre teams.
Five9 had acquired Whendu, an iPaaS platform provider empowering businesses and developers with no-code, visual application workflow tool, optimised for contact centres in November 2019, and Virtual Observer, an innovative provider of cloud-based workforce optimisation, also known as Workforce Engagement Management (WEM) in February of this year.
The pandemic has resulted in increased engagement of contact centres with customers. Companies are gradually looking for ways to automate tasks, deliver better communication, speech and text recognition, decipher languages, and implement solutions mimicking humans. As a solution to these challenges, IVAs are being viewed as efficient and effective digital workers for a modern contact centre. IVAs represent increased throughput, more accurate results, and better-informed agents.
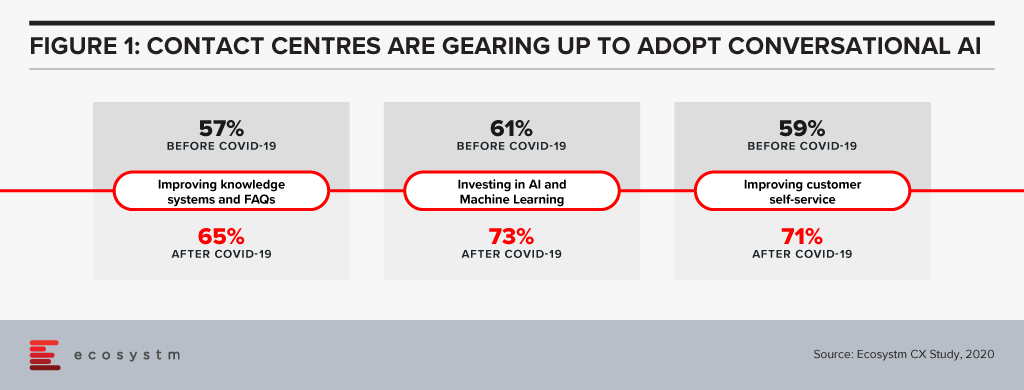
Successful use cases have shown that conversational AI can reduce calls and repetitive queries by 70-90%. IVRs with monolithic, complicated menus will start becoming unpopular and force contact centres to embark on a modernisation and automation strategy. If we evaluate the shift in priorities after COVID-19, we see that organisations are ramping up their self-service capabilities and their adopt of AI and machine learning (Figure 1).
The acquisition will give Five9 a foothold in the Asia Pacific region with an initial focus on the Australia market. The Australia market is by far the most advanced cloud contact centre market in the Asia Pacific. Five9 gains a team of staff that will help them fuel the contact centre modernisation discussion across the Asia Pacific. As the region has a complex market, the need to work with local carriers and partners will be critical for further expansion. Five9 has made an important acquisition in building in IVA capability into its CCaaS solution.
Click below to access insights from the Ecosystm Contact Centre Study on visibility into organisations’ priorities when running a Contact Centre (both in-house and outsourced models) and the technologies implemented and being evaluated

The Retail industry has had to do a sharp re-think of its digital roadmap and transformation journey – Ecosystm research shows that about 75% of retail organisations had to start, accelerate, or re-focus their digital transformation initiatives. However, that will not be enough as organisations move beyond survival to recovery – and future successes. While retailers will focus on the shift in customer expectations, a mere focus on customer experience will not be enough in 2021. Ecosystm Principal Advisors, Alan Hesketh and Alea Fairchild present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Retail & eCommerce in 2021.
This is a summary of the predictions, the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform here.
The Top 5 Retail & eCommerce Trends for 2021
- There Will Only be Omnichannel Retailers
The value of an omnichannel offer in Retail has become much clearer during the COVID-19 pandemic. Retailers that do not have the ability to deliver using the channel customers prefer will find it hard to compete. As the physical channel becomes less important new revenue opportunities will open up for businesses operating in adjacent market sectors – companies such as food and grocery wholesalers will increasingly sell direct to consumers, leveraging their existing online and distribution capabilities.
Most customers transact on mobile device – either a mobile phone or tablet. New capabilities will remove some of the barriers to using these mobile devices. For one, technologies such as Progressive Web Apps (PWA) and Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) will provide a better customer experience on mobile platforms than existing websites, while delivering a user experience at par or better than mobile apps. Also, as retailers become AI-enabled, machine learning engines will provide purchase recommendations through smartwatches or in-home, voice-enabled, smart devices.
- COVID-19 Will Continue to be an Influence Forcing Radical Shifts
In driving the economic recovery in 2021, we will see ‘glocal’ consumption – emphasis on local retailers and global players taking local actions to win the hearts and minds of local consumers. There will be significant actions within local communities to drive consumers to support local retailers. Location-based services (LBS) will be used extensively as consumers on the high street carry more LBS-enabled devices than ever before. Bluetooth beacon technology and proximity marketing will drive these efforts. Consumers will have to opt-in for this to work, so privacy and relationship management are also important to consider.
But people still want to “physically” browse, and design aesthetics of a store are still part of the attraction. In the next 18 months, the concept of virtual stores that are digital twins will take off, particularly in the holiday and Spring clearance sales. Innovators like Matterport can help local retailers gain a more global audience with a digital twin with a limited technological investment. At a minimum, Shopify or other intermediaries will be necessary for a digital shop window.
- The Industry will See Artificial Intelligence in Everything
AI will increase its impact on Retail with an uptake in two key areas.
- Customer interactions. Retail AI will use customer data to deliver much richer and targeted experiences. This may include the ability to get to a ‘segment of one’. Tools will include chatbots that are more functional and support for voice-based commerce using mobile and in-home edge devices. Also, in-store recognition of customers will become easier through enhanced device or facial recognition. Markets where privacy is less respected will lead in this area – other markets will also innovate to achieve the same outcomes without compromising privacy but will lag in their delivery. This mismatch of capability may allow early adopters to enter other geographic markets with competitive offers while meeting the privacy requirements of these markets.
- Supply chain and pricing capabilities. AI-based machine learning engines using both internal and increased sources of external data will replace traditional math-based forecasting and replenishment models. These engines will enable the identification of unexpected and unusual demand influencing factors, particularly from new sources of external data. Modelling of price elasticity using machine learning will be able to handle more complex models. Retailers using this capability will be in a better position to optimise their customer offers based on their pricing strategies. Supply chains will be re-engineered so products with high demand volatility are manufactured close to markets, and the procurement of products with stable demands will be cost-based.
- Distribution Woes Will Continue
Third party delivery platforms such as Wish and RoseGal are recruiting additional international non-Asian suppliers to expand their portfolios. Amazon and AliExpress are leaders here, but there are many niche eCommerce platforms taking up the slack due to the uneven distribution patterns from the ongoing economic situation. Expect to see a number of new entrants taking up niche spaces in the second half of 2021, sponsored by major retail product brands, to give Amazon a run for their money on a more local basis.
As the USPS continues to be under strain, delivery companies like FedEx in the US who partner with the USPS are already suffering from the USPS’s operational slowdown, in both their customer reputation and delivery speed. In 2021, COVID-19 – and workers’ unions – will continue to impact distribution activities. Increased spending in warehouse automation and new retail footprints such as dark stores will be seen to make up for worker shortfalls.
- China’s Retail Models Will Expand into Other Markets
China’s online businesses operate in a large domestic market that is comparatively free of international competitors. Given the scale of the domestic market, these online companies have been able to grow to become substantial businesses using advanced technologies. All the Chinese tech giants – among them Alibaba, ByteDance, DiDi Chuxing, and Tencent – are expanding internationally.
China’s rapidly recovering economy puts those businesses in a strong position to fund a competitive expansion into international markets using their domestic base, particularly with their Government’s promotion of the country’s tech sector. It is harder to impose restrictions on software-based businesses, unlike the approach that we have witnessed the US Government take for hardware companies such as Huawei – placing constraints on mobile phone components and operating systems.
These tech giants also have significant experience in a Big Data environment that provides little privacy protection, as well as leading-edge AI capabilities. While they will not be able to operate with the same freedom in global markets, and there will be other large challenges in translating Chinese experience to other markets – these tech players will be able to compete very effectively with incumbent global companies. Chinese companies also continue to raise capital from US stock exchanges with The Economist reporting Chinese listings have raised close to USD 17 billion since January 2020.

Ecosystm research finds that 47% of organisations re-evaluated cybersecurity risks and management making it the biggest measure undertaken by IT Teams when COVID-19 hit. There is no denying any more that cybersecurity is a key business enabler. This year witnessed cybercrime escalating in all parts of the world and several governments issued advisories warning enterprises and citizens of the increase in the threat landscape, during and post COVID-19. Against this backdrop, Ecosystm Advisors, Alex Woerndle, Andrew Milroy, Carl Woerndle and Claus Mortensen present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for Cybersecurity & Compliance in 2021.
This is a summary of the predictions, the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform here.
The Top 5 Cybersecurity & Compliance Trends for 2021
- There will be Further Expansion of M&A Activities Through 2021 and Beyond
As predicted last year, the market is set to witness mergers and acquisitions (M&As) to consolidate the market. The pandemic has slowed down M&A activities in 2020. However, the market remains fragmented and there is a demand for consolidation. As the cyber market continues to mature, we expect M&A activities to ramp up over the next couple of years especially once we emerge from COVID-19. Some organisations that understand the full impact of the shift to remote working and the threats it creates have embraced the opportunity to acquire, based on perceived value due to COVID-19. The recent acquisition of Asavie by Akamai Technologies is a case in point. Asavie’s platform is expected to strengthen Akamai’s IoT and mobile device security and management services.
- After a Year of Pandemic Leniency, Regulators will Get Stricter in 2021
The regulators in the EU appear to have gone through a period of relative leniency or less activity during the first few months of the pandemic and have started to increase their efforts after the summer break. Expect regulators – even outside the EU – to step up their enforcement activities in 2021 and seek larger penalties for breaches.
Governments continue to evolve their Compliance policies across broader sectors, which will impact all industries. As an example, in Australia, the Federal Government has made changes to its definition of critical infrastructure, which brings mandates to many more organisations. Governments have shown an acute awareness of the rise in cyber-attacks highlighted by several high-profile breaches reported in mainstream media. Insider threats – highlighted by Tesla, where an employee raised the allegations of bribery by unknown third parties in exchange for exfiltrating corporate information – will also lead regulators to double down on their enforcement activities.
- The Zero Trust Model Will Gain Momentum
Remote working has challenged the traditional network security perimeter model. The use of personal and corporate devices to access the network via public networks and third-party clouds is creating more opportunity for attackers. Organisations have started turning to a Zero Trust security model to mitigate the risk, applying advanced authentication and continuous monitoring. We expect the adoption of the Zero Trust model to gain momentum through 2021. This will also see an increase in managed services around active security monitoring such as Threat Detection & Response and the increased adoption of authentication technologies. With an eye on the future, especially around quantum computing, authentication technologies will need to continually evolve.
- The Endpoint Will be the Weakest Link
The attack surface continues to grow exponentially, with the increase in remote working, IoT devices and multicloud environments. Remote endpoints require the same, if not higher levels of security than assets that sit within corporate firewalls, and it will become very clear to organisations that endpoints are the most vulnerable. Remote workers are often using unsecure home Wi-Fi connections and unpatched VPNs, and are increasingly vulnerable to phishing attacks. IoT device passwords are often so weak that brute-force attackers can enter networks in milliseconds.
Although endpoint security can be dealt with through strict policies together with hardware or software authentication, the difficult part is to adopt an approach that retains a relatively high level of security without having a too negative an impact on the employee experience. Experience shows that if the security measures are too cumbersome, employees will find ways to circumvent them.
- Hackers Will Turn the Table on AI Security
Cybersecurity vendors are increasingly offering solutions that leverage AI to identify and stop cyber-attacks with less human intervention than is typically expected or needed with traditional security approaches. AI can enhance cybersecurity by better predicting attacks enabling more proactive countermeasures, shortening response times, and potentially saving cybersecurity investment costs. The problem is that the exact same thing applies to the hackers. By leveraging AI, the costs and efforts needed to launch and coordinate large hacker attacks will also go down. Hackers can automate their attacks well beyond the use of botnets, target and customise their attacks with more granularity than before and can effectively target the biggest weakness of any IT security system – people.
Already, phishing attacks account for many of the breaches we see today typically by employees being tricked into sharing their IT credentials via email or over the phone. As we move forward, these types of attacks will become much more sophisticated. Many of the deepfake videos we see have been made using cheap or free AI-enabled apps that are easy enough for even a child to use. As we move into 2021, this ability to manipulate both video and audio will increasingly enable attackers to accurately impersonate individuals.

Juniper Networks has entered into an agreement to acquire Massachusetts-based 128 Technology for USD 450 million that will enhance its AI-driven enterprise networking portfolio. The deal is expected to close by the end of 2020. The combined portfolio of 128 Technology’s Session Smart™ networking and Juniper’s Mist AI platform will bolster Juniper’s AI expertise in SD-WAN technology.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Ashok Kumar says, “Juniper Networks has been a major player in enterprise networking from the core to the edge of the network with SD-WAN, WLAN, and AI-driven applications aware network products. Juniper had strengthened their enterprise networks portfolio with the acquisition of WLAN vendor Mist Systems in 2019 which provided cloud-based management and an AI engine. With Juniper’s acquisition of 128 Technology the network transformation process in the industry will continue.”
The platform created by 128 Technology bases decisions on real-time sessions instead of legacy static systems and networking approaches. The newer system created through this by Juniper will use AI to automate sessions and policies for a full AI-driven WAN operation – from initial configuration to customisable actions across various levels, and AI-driven support.
In addition to this, the automation is expected to reduce overheads, minimise IT costs and deliver better client and user-experience through automated network optimised for client-to-cloud. The two companies also aim to optimise the network and user experiences for voice, 5G and collaboration. Juniper continues to evolve the enterprise networking portfolio adding to the acquisition of WLAN start up Mist Systems for USD 405 million last year. Juniper’s AI -driven SD-WAN and networking products and services for enterprises and end-users is a step towards smart LAN and WAN environments.
A recent study on The Future of the Secure Office Anywhere, conducted by Ecosystm on behalf of Asavie found that 56% of global organisations are looking to improve employee experience, as they look beyond the COVID-19 crisis. The feedback from over 1,000 business and technology leaders globally, also finds that 55% of the organisations are also focused on digital transformation. This will require a re-evaluation of enterprise network solutions, to give employees seamless access to company resources as they continue to work remotely.
“Enterprise communications is being transformed to a user-centric, session-oriented distributed model from a legacy network-oriented centralised WAN model. In the new remote working environment of Office Anywhere, the traditional use of VPN in combination with first-generation SD-WAN will become an impediment going forward. Enterprises will need to re-design networks to address each end-user’s unique needs and their access to applications and all business resources as though they were a Branch of One.”
IBM announced its intention to spin off its infrastructure services business as a separate public company, allowing Big Blue to focus on hybrid cloud and AI. The newly formed entity, temporarily named NewCo, will offer project and outsourcing services that currently fall under its GTS business unit. NewCo will have a staff of around 90,000 employees and is expected to earn revenue of about $19B. While GTS has experienced declining revenue for some time now, IBM believes that the split will unlock growth and put it on a path to recovery.
Once the Red Hat acquisition closed last year and the tag team of Jim Whitehurst and Arvind Krishna were announced, it became clear that IBM was gearing up to become a leaner, more agile leader in the hybrid cloud space. One of two possible courses seemed apparent – either wither away for years until IBM was small enough to become nimble, or take bold action. IBM has opted for the latter and is likely to be rewarded for it. The new IBM will have revenue of around $59B, well short of its peak at over $100B, but sacrificing turnover for margin and growth gives it a more positive long-term outlook.
Stripping back IBM to become smaller, faster growing, and more profitable, will help solve many of its greatest challenges. Significant investment into growth segments will become more palatable without the financial burden of the declining infrastructure services unit. The well-needed cultural change and drive to think like a start-up will become more practical in the new IBM.
NewCo to Build New Cloud Partnerships
IBM’s infrastructure services unit has had some great success in larger, complex, hybrid cloud deals recently – but at the lower end of the market there have been many head winds. Public cloud providers have eroded what was once a lucrative compute and storage services market. At the same time, application service providers, like Accenture, TCS, and HCL have been pivoting towards infrastructure. Untethering infrastructure services makes a turnaround story more likely, giving NewCo greater flexibility and speed, which clients have been crying out for.
The greatest benefit to NewCo will be the ability to freely partner with other cloud providers, like AWS, Microsoft, and Google. Although IBM has made noises about being willing to embrace its competitors, this was not necessarily implemented on the ground nor was it reciprocated.
It is no secret that GTS and GBS have had a rocky relationship since day one. The split will reassure clients that each of them is agnostic and relieve any internal pressure to partner unless it is best for the client. While elements of this decision look like the unfolding of a long-term strategy that began under Ginni Rometty, it does, however, leave open the question of why GTS and GBS were more closely integrated over the last few years. This also means IBM is moving in the opposite direction to its competitors, who are shifting towards offerings that cover the full stack of services from infrastructure up to applications.
What Lies Ahead for IBM
One detail that is not immediately certain is the fate of IBM security services, which could be integrated with security software at IBM, spun out with the rest of infrastructure services, or even split into consulting and delivery. An important differentiator for IBM has been its ability to build in security at the beginning of transformation projects making final placement a difficult decision.
It might be tempting to predict that next IBM would couple its Systems unit and Support Services to be spun off or sold although Mr. Krishna ruled that out. Over the long term, these are both financially underperforming units but there is an advantage to building the core infrastructure that critical workloads are run on.
Each new IBM CEO has had a make or break moment and Mr. Krishna has decided that his will come early. For the company to thrive for another 100 years it needed to place a big bet and it could not have come soon enough.

Telstra and Microsoft have extended their partnership to jointly build solutions harnessing the capabilities of AI, IoT, and Digital Twin technologies in Australia. The partnership will also enable both companies to work on sustainability, emission reduction, and digital transformation initiatives.
The adoption of cloud and 5G technology is already on the rise and creating opportunities across the globe. The Microsoft-Telstra partnership is set to bring together the capabilities of both providers for businesses in Australia and globally. Their focus on AI, IoT, cloud and 5G will enable Australia’s developers and independent software vendors (ISVs) to leverage AI with low latency 5G access to drive efficiency, and enhance decision making. This will also see practical applications and new solutions in areas like asset tracking, supply chain management, and smart spaces to enhance customer experience.
Technology Enhancing the Built Environment
Microsoft Azure and Telstra’s 5G capabilities will come together to develop new industry solutions – the combination of cloud computing power and telecom infrastructure will enable businesses and industries to leverage a unified IoT platform where they can get information through sensors, and perform real-time compute and data operations. Telstra and Microsoft will also build digital twins for Telstra’s customers and Telstra’s own commercial buildings which will be initially deployed at five buildings. Upon completion, the digital twin will enable Telstra to form a digital nerve centre and map physical environments in a virtual space based on real-world models and plot what-if scenarios.
Telstra CEO, Andy Penn says, “If you think about the physical world – manufacturing, cities, buildings, mining, logistics – the physical world hasn’t really been digitised yet. So, how do you digitise the physical world? Well, what you do is put sensors into physical assets. Those sensors can draw information around that physical asset, which you can then capture and then understand.”
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Mike Zamora finds the comment interesting and says, “It isn’t so much that the physical world is digitized – it is more about how digital tools enhance and enable the physical world to be more effective to help the occupier of the space. This has been the history of the physical space. There have been many ‘tools’ over time to help the physical world – the elevator in the late 1880s enabled office buildings to be taller; the use of steel improved structural support, allowing structural walls to be thinner and buildings taller. These two ‘tools’ enabled the modern skyscraper to be born. The HVAC system developed in the early 1900s, enabled occupants to be more comfortable inside a building year-round in any climate.”
“Digital tools (sensors, etc) are just the latest to be used to enhance the physical space for the occupant. Digital twins enable an idea to be replicated in 3D – prior to having to spend millions of dollars and hundreds of man hours to see if a new idea is viable. Its advent and use enable more experimentation at a lower cost and faster set up. This equates into a lower risk. It is a welcomed tool which will propel the experimentation in the physical world.”
Talking about emerging technologies, Zamora says, “Digital twins along with other digital tools, such as 3D printing, AI, drones with 4K cameras and others will enable the built environment to develop at a very quick pace. It is the pace that will be welcomed, as the built environment is typically a slow-moving asset (pardon the pun).”
“Expect the Built Environment developers, designers, investors, and occupiers to welcome the concept. It will allow them to dream of the possible.”
Telstra and Microsoft – Joint Goals
Telstra and Microsoft have partnered over the years over multiple projects. Last year, the companies partnered to bring Telstra’s eSIM functionality to Windows devices for data and wireless connectivity; they have also worked on Telstra Data Hub for secured data sharing between data producers, businesses and government agencies; and most recently collaborated on Telstra’s exclusive access to Xbox All Access subscription service to Australian gamers with the announcement of Microsoft’s Xbox Series X and Xbox Series S gaming consoles expected to release in November.
This announcement also sees them work jointly towards their sustainability goals. Both companies are committed to sustainability and addressing climate change. Earlier this year, Microsoft announced its plans to be carbon negative by 2030, while Telstra has also set a target to generate 100% renewable energy by 2025 and reducing its absolute carbon emissions by 50% by the same time. To enable sustainability, Telstra and Microsoft are exploring technology to reduce carbon emissions. This includes further adoption of cloud for operations and services, remote working, and piloting on real-time data reporting solutions.
Telstra also aims to leverage Microsoft technology for its ongoing internal digital transformation, adopting Microsoft Azure as its cloud platform to streamline operations, and infrastructure modernisation, including transition from legacy and on-premise infrastructure to cloud based applications.

Smarter buildings and public facilities have long been of interest to architects and developers. Innovators can see that the promise of intelligent data used for spatial design can transform how we work, live and play.
How can Big Data be used for intelligent building design? There are a consortia of companies trying to figure this out together. I will discuss the Building 4.0 Co-operative Research Centre (CRC) in Australia.
I have already been examining the new approaches to using big data in facilities management. This is done by developing smarter office spaces, embedded with devices employing Ambient Intelligence (AmI). Research looked at how the intelligent use of big data contributed to building an environment with greater energy efficiency, optimised space utilisation, enhanced workplace experience and occupants’ comfort. This includes sound masking, the use of lighting for enhance environments, and sensors for occupancy for hygiene controls.
Ambient Intelligence (AmI)
AmI refers to electronic environments that are sensitive and responsive to the presence of employees, residents or visitors. These environments can have ecosystems (pun intended) of different IoT devices communicating with each other.
There is a real emphasis here on edge computing, sensors and other IoT devices, and building intelligence into the edge for near real-time decision making closer to where the problem may sit. Ecosystm research finds that construction firms focus a significant amount of IoT investment for building management and energy management (Figure 1).
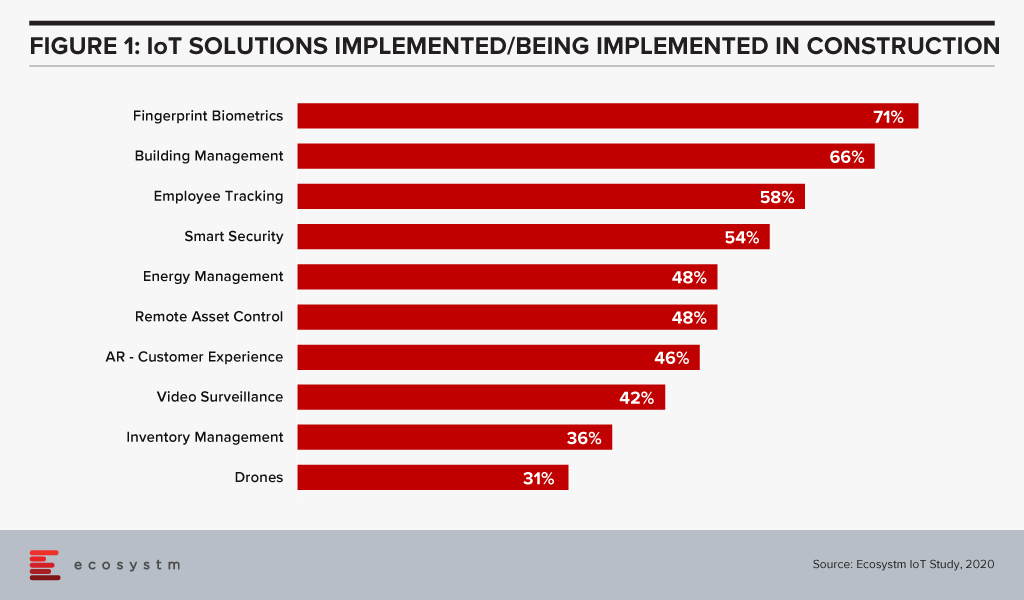
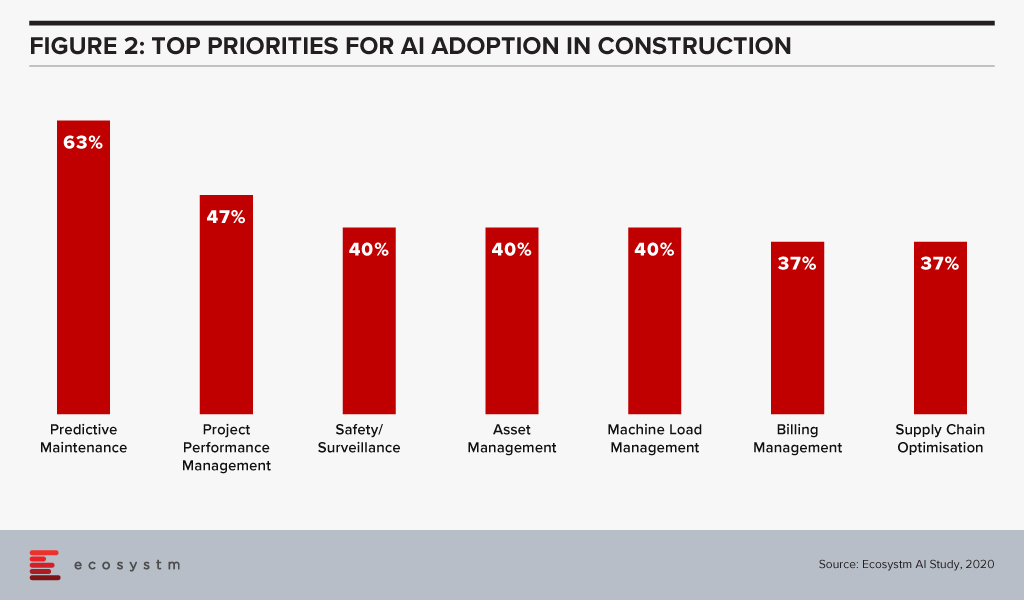
For example, if an HVAC system is on the verge of malfunction, the system could send a message for a repair intervention. When it comes to AI, predictive maintenance and surveillance are two of the leading use cases in the construction industry (Figure 2).
Building 4.0 Co-operative Research Centre (CRC)
In Australia, this push for sustainable and smarter building development is being driven by a consortium of companies looking at Big Data and infrastructure development for buildings. This year, the Building 4.0 Co-operative Research Centre (CRC) has been awarded a USD 19.5 million grant to focus on medium to long-term industry-led collaborations that can assist in driving the growth of new industries. The Australian building and construction industry is a major economic engine that contributes 13% of GDP and employs over 1.4 million Australians. Development of the Building 4.0 CRC makes sense and is timely given the current pandemic and economic conditions.
Part of its research program focus on develop new building processes and techniques through leveraging the latest technologies, data science and AI to ultimately improve all aspects of the key building phases. Their overall ecosystem is designed for enablement of several use cases (Figure 3).
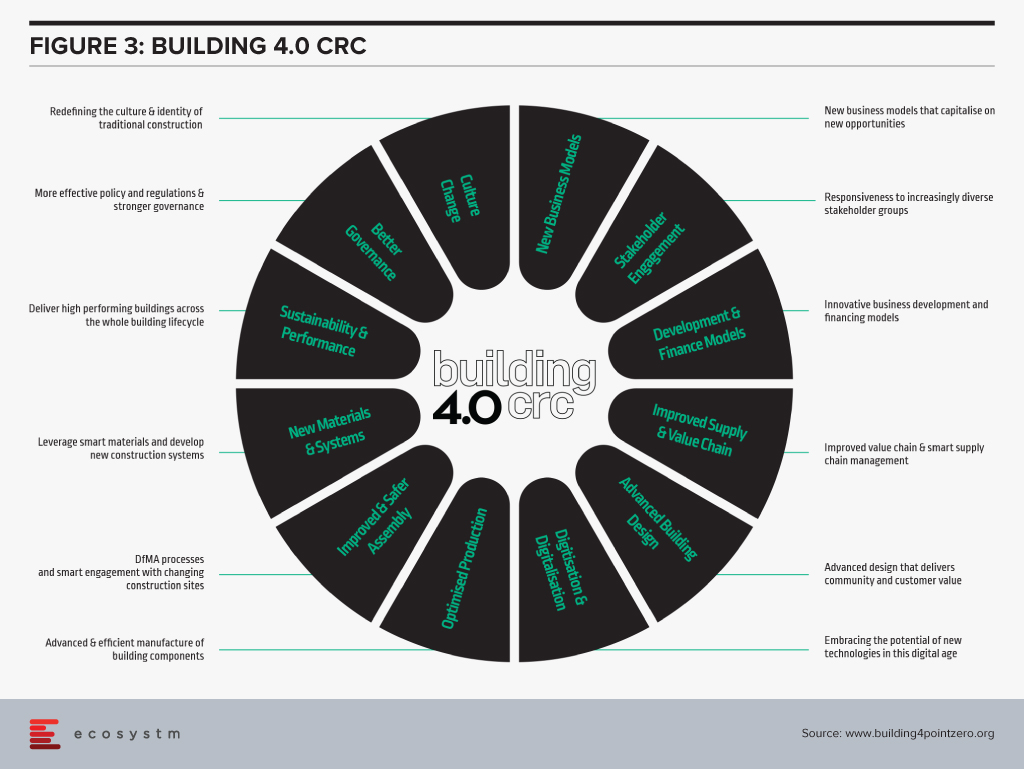
The Building 4.0 CRC’s principle aims are “to decrease waste; create buildings that are faster, cheaper, and smarter; and capture new opportunities by facilitating collaborative work between stakeholders across the whole value chain in cooperation with government and research organisations.”
Green Star, the rating system which was created by Green Building Council of Australia (GBCA) in 2003, rates the sustainability of buildings, fit outs and communities through Australia’s largest national, voluntary, holistic rating system. The GBCA is a partner organisation in the Building 4.0 CRC – as are many other major organisations in construction and trade, all pulling together here, for innovative efforts for the industry.
Where might the Building 4.0 CRC effort make an impact? Its collaborative structure of industry, academia, vocational trade organisation and governmental bodies harness innovative ideas to transmit them to transformative practices of industry and construction partners.
To be smarter, one must work smarter and more efficiently. A consortia such as this pulls the best minds together to try to accelerate industry efforts for intelligent design with data.











