There have been some long-term shifts in market dynamics in the telecom industry. Network traffic growth rates have accelerated; new business models emerged; and cloud services matured and spread to new verticals, applications and customer sizes. Networks are more important than ever. Revenue growth rates and profitability in the three segments – telecom, webscale, and carrier-neutral – have been stronger in recent quarters than anticipated.
Looking ahead, networks will increasingly revolve around data centres, which will continue to proliferate both at the core and edge.
Data centre innovation will be rapid, as webscalers push the envelope on network design and function, and telecom operators seek cheaper ways of running their networks. The telecom operator’s need for cost efficiency will increase as overhyped 5G-based opportunities fail to materialise in any big way. Carrier-neutral operators (CNNOs) will benefit from an ongoing wave of new capital which will help them transform to more integrated providers of “digital infrastructure” assets.
Read on to find out about
- The interdependence of network operators
- The growth potential of the telecom, webscale, and CNNO markets
- How webscalers such as Facebook and Alibaba are leveraging scale
- Acquisition and deals in the CNNO market such as the American Tower-CoreSite acquisition and the Digital Realty deal with Ciena.
- The growth of environmental consciousness in the telecom industry
Click here to download The Future of Telecom: Industry Outlook for 2022 and Beyond slides as a PDF.

Oracle is clearly prioritising a rapid expansion across the globe. The company is in a race to catch up with the big 3 (AWS, Google, and Microsoft), and recognises that many of their customers are eager to migrate to the cloud, and they have other options. Their strategy appears to be to rely on third-party co-location providers for most of their data centres, and build a single availability zone per region, at least to start.
Oracle Cloud Rollout Ramps Up
Let us consider the following:
- Oracle’s network spending level puts it in the range of other webscalers. Focusing only on the Network and IT portion of their CapEx, Oracle has now passed Alibaba. Oracle is also ahead of both IBM and Baidu, which are included in the “All others” category in Figure 1.
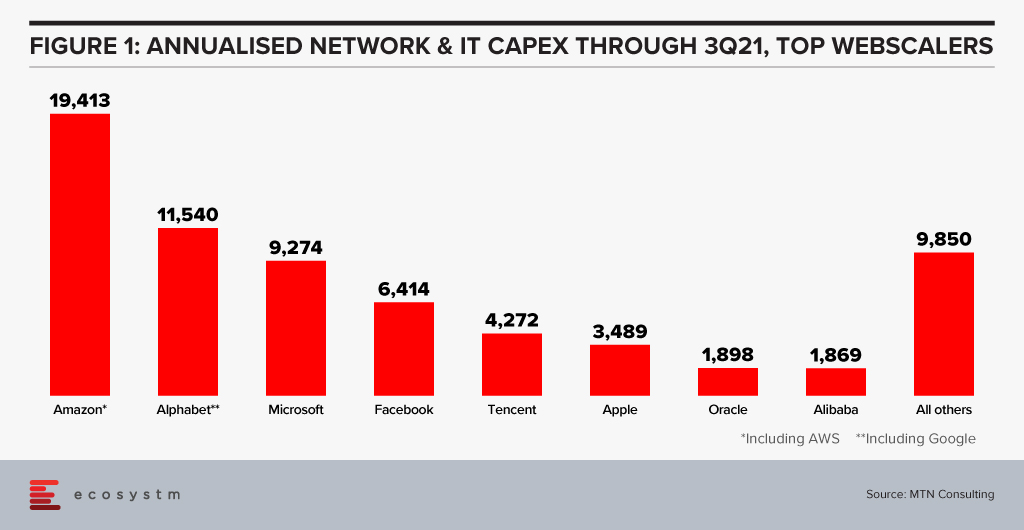
- The coverage of the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) is impressive. It has 36 regions today (some dedicated for government use), with a plan to reach 44 by year-end 2022. That compares to 27 overall for AWS, 65 for Azure, 29 for GCP; regional competitors Tencent and Huawei have 27 regions each, and Alibaba 25 regions. The downside is that Oracle has only one availability zone in most of its regions, while the Big 3 usually have 2 or 3 per region. Oracle needs to build out its local resiliency rapidly over the next year or two or risk losing business to the big 3, especially to AWS; but the company knows this and is budgeting CapEx aggressively to address the problem.
- Oracle’s initial reliance on leased facilities may be an interim step. The rapid growth of AWS, Azure, and GCP in the late 2010s was a surprise and Oracle started to see serious risks of losing customers to these cloud platforms. Building out their own cloud base on new data centres would have taken years and cost them business. So, Oracle did the smart thing and leaped into the cloud as fast as possible with the resources and time available. The company has scaled their OCI operations at an impressive rate. It expects capital expenditures to double YoY for the fiscal year ending May 2022, as it increases “data centre capacities and geographic locations to meet current and expected customer demand” for OCI.
- Finally, Oracle has invested heavily in designing the servers to be installed in its data centres (even if most of them are leased). Oracle was an early investor in Ampere Computing, which makes Arm-based processors, sidestepping the Intel ecosystem. In May 2021, Oracle rolled out its first Arm-based compute offering, OCI Ampere A1 Compute, based on the Ampere Altra processor. Oracle says this allows OCI customers to run “cloud-native and general-purpose workloads on Arm-based instances with significant price-performance benefits.” Microsoft and Tencent also deploy the Ampere Altra in some locations.
Reaching Global Scale
Once Oracle decided to launch into the cloud, its goal was to both grow revenues and also protect its legacy base from slipping away to the Big 3, which already had a growing global footprint. Oracle chose to quickly build cloud regions in its key markets, with the understanding that it would have to fill out individual regions as time passed. This is not that different from the big 3, in fact, but Oracle started its buildout much later. It also has lesser availability zones per region.
Oracle has not ignored this disparity. It recognises that reliability is key for its clients in trusting OCI. For example, the company emphasises that:
- Each Oracle Cloud region contains at least three fault domains, which are “groupings of hardware that form logical data centers for high availability and resilience to hardware and network failures.” Fault domains allow a customer to distribute instances so “the instances are not on the same physical hardware within a single availability domain.”
- OCI has a network of 70 “FastConnect” partners which offer dedicated connectivity to OCI regions and services (comparable to AWS DirectConnect)
- OCI and Microsoft Azure have a partnership allowing “joint customers” to run workloads across the two clouds, providing low latency, cross-cloud interconnect between OCI and Azure in eight specific regions. Customers can migrate existing applications or develop cloud native applications using a mix of OCI and Azure.
- Oracle allows customers to deploy OCI completely within their own data centers, with Dedicated Region and Exadata Cloud@Customer, deploy cloud services locally with public cloud-based management, or deploy cloud services remotely on the edge with Roving Edge Infrastructure.
- Further, Oracle clearly tries to differentiate around its Arm-based Ampere processors. Reliability is not necessarily the focus, though. The main focus is contrasting Ampere with the x86 ecosystem around overall price-performance, with highlights on power efficiency, scalability and ease of development.
Ultimately the market will decide whether Oracle’s approach makes it truly competitive with the big 3. The company continues to announce some big wins, including with Deutsche Bank, FedEx, NEC, Toyota, and Zoom. The latter is probably the company’s biggest cloud win given Zoom’s rise to prominence amidst the pandemic. Not surprisingly, Oracle’s recent Singapore cloud region launch was hosted by Zoom.
Conclusion
Over the long run, the webscale market is getting more concentrated in the hands of a few players; some companies tracked as webscalers, such as HPE and SAP, will fall by the wayside as they can’t keep up with the infrastructure spending requirements of being a top player. Oracle is aiming to remain in the race, however. CEO Larry Ellison addressed this in an earnings call, arguing the global cloud market is not just the “big 3” (AWS, Azure, and GCP), but is a “big 4” due in part to Oracle’s database strengths. Ellison also argued that the OCI is “much better for security, for performance, for reliability” and cost: “we’re cheaper.” The market will ultimately decide these things, but Oracle is off to a strong start. Its asset light approach to network buildout, and limited depth within regions, clearly have downfalls. But the company has a deep roster of long-term customers across many regions, and it is moving fast to secure their business as they migrate operations to the cloud.

The emergence of COVID-19 last year caused a rapid shift towards work and study from home, and a pickup in eCommerce and social media usage. Tech companies running large data centre-based “webscale” networks have eagerly exploited these changes. Already flush with cash, the webscalers invested aggressively in expanding their networks, in an effort to blanket the globe with rapid, responsive connectivity. Capital investments have soared. For the webscale sector, spending on data centres and related network technology accounts for over 40% of the total CapEx.
Here are the 3 key emerging trends in the data centre market:
#1 Top cloud providers drive webscale investment but are not alone
The webscale sector’s big cloud providers have accounted for much of the recent CapEx surge. AWS, Google, and Microsoft have been building larger facilities, expanding existing campuses and clusters, and broadening their cloud region footprint into smaller markets. These three account for just under 60% of global webscale tech CapEx over the last four quarters. Alibaba and Tencent have been reinforcing their footprints in China and expanding overseas, usually with partners. Numerous smaller cloud providers – notably Oracle and IBM – are also expanding their cloud services offerings and coverage.
Facebook and Apple, while they don’t provide cloud services, also continue to invest aggressively in networks to support large volumes of customer traffic. If we look at Facebook, the reason becomes clear: as of early 2021, they needed to support 65 billion WhatsApp messages per day, over 2 billion minutes of voice and video calls per day, and on a monthly basis their Messenger platform carries 81 billion messages.
The facilities these webscale players are building can be immense. For instance, Microsoft was scheduled to start construction this month on two new data centres in Des Moines Iowa, each of which costs over USD 1 billion and measures over 167 thousand square metres. And Microsoft is not alone in building these large facilities.

#2 Building it all alone is not an option for even the biggest players
The largest webscalers – Google, AWS, Facebook and Microsoft – clearly prefer to design and operate their own facilities. Each of them spends heavily on both external procurement and internal design for the technology that goes into their data centres. Custom silicon and the highest speed, most advanced optical interconnect solutions are key. As utility costs are a huge element of running a data centre, webscalers also seek out the lowest cost (and, increasingly, greenest) power solutions, often investing in new power sources directly. Webscalers aim to deploy facilities that are on the bleeding edge of technology. Nonetheless, in order to reach the far corners of the earth, they have to also rely on other providers’ network infrastructure. Most importantly, this means renting out space in data centres owned by carrier-neutral network operators (CNNOs) in which to install their gear.
The Big 4 webscalers do this as little as possible. For many smaller webscalers though, piggybacking on other networks is the norm. Of course, they want some of their own data centres – usually the largest ones closest to their main concentrations of customers and traffic generators. But leasing space – and functionalities like cloud on-ramps – in third-party facilities helps enormously with time to market.
Oracle is a case in point. They have expanded their cloud services business dramatically in the last few years and attracted some marquee names to their client list, including Zoom, FedEx and Cisco. To ramp up, Oracle reported a rise in CapEx, growing to USD 2.1 billion in the 12 months ended June 2021, which represents a 31% increase from the previous year. However, when compared to Microsoft’s spending this appears modest. Microsoft reported having spent USD 20.6 billion in the 12 months ended June 2021 – a 33% increase over the previous year – to help drive the growth of their Azure cloud service.
One reason behind Oracle’s more modest spending is how heavily the company has relied on colocation partners for their cloud buildouts. Oracle partners with Equinix, Digital Realty, and other providers of neutral data centre space to speed their cloud time to market. Oracle rents space in 29 Digital Realty locations, for instance, and while Equinix doesn’t quantify its partnership with Oracle, Oracle’s cloud regions across the globe access the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) via the Equinix Cloud Exchange Fabric. Oracle also works with telecom providers; their Dubai cloud region, launched in October 2020, is hosted out of an Etisalat owned data centre.
#3 Carrier-neutral data centre investment is surging in concert with webscale/cloud growth
As the webscale sector has raced to expand over the last 2 years, companies that specialise in carrier-neutral data centres have benefited. Industry sources estimate that as much as 50% or more of the cloud sector’s total data centre footprint is actually in these third-party data centres. That is unlikely to change, especially as some CNNOs are explicitly aiming to build out their networks in areas where webscalers have less incentive to devote resources. It’s not just about the webscalers’ need for space; the need for highly responsive, low latency networks is also key, and interconnection closer to the end-user is a driver.
Looking at the biggest publicly traded carrier-neutral providers in the data centre sector shows that their capacity has expanded significantly in the last few years (Figure 1)
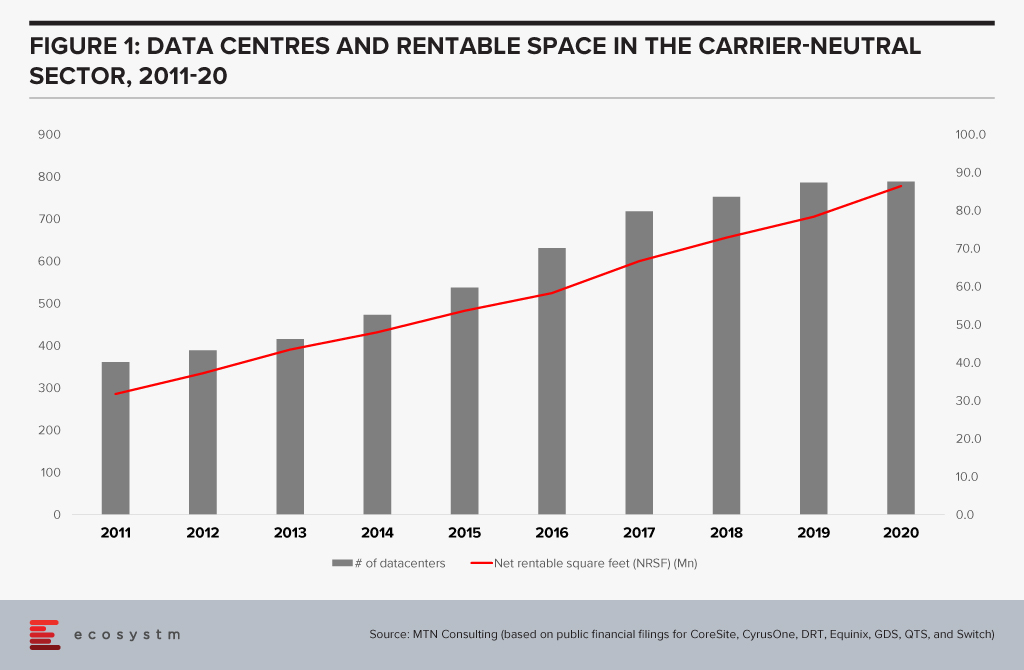
By my estimation, for the first 6 months of 2021, CapEx reported publicly for these CNNOs increased 18% against 1H20, to an estimated USD 4.1 Billion. Beyond the big public names, private equity investment is blossoming in the data centre market, in part aimed at capturing some of the demand growth generated by webscalers. Examples include Blackstone’s acquisition of QTS Realty Trust, Goldman Sachs setting up a data centre-focused venture called Global Compute Infrastructure; and Macquarie Capital’s strategic partnership with Prime Data Centers.
Some of this new investment target core facilities in the usual high-traffic clusters, but some also target smaller country markets (e.g. STT’s new Bangkok-based data centre), and the network edge (e.g. EdgeConneX, a portfolio company of private equity fund EQT Infrastructure).
EdgeConneX is a good example of the flexibility required by the market. They build smaller size facilities and deploy infrastructure closer to the edge of the network, including a PoP in Boston’s Prudential Tower. The company offers data centre solutions “ranging from 40kW to 40MW or more.” They have built over 40 data centres in recent years, including both edge data centres and a number of regional and hyperscale facilities across North America, Europe, and South America. Notably, EdgeConneX recently created a joint venture with India’s property group Adani – AdaniConneX – which looks to leverage India’s status of being the current hotspot for carrier-neutral data centre investment.
As enterprises across many vertical markets continue to adopt cloud services, and their requirements grow more stringent, the investment climate for new data centre capacity is likely to remain strong. Webscale providers will provide much of this capacity, but carrier-neutral specialists have an important role to play.

In this first edition of Ecosystm RNx we rank the Top 10 Global Cloud Vendors.
Ecosystm RNx is an objective vendor ranking based on in-depth and quantified ratings from technology decision-makers on the Ecosystm platform.
If you are an technology user, this Cloud Vendor ranking will help you evaluate your buying decisions based on key evaluation ratings by your peers across a number of key metrics and benchmarks, including customer experience.
If you are a Cloud Vendor, this is an opportunity to understand how your customers rate you on capabilities and their overall customer experience.

Alibaba has been actively expanding its global reach over the last year. There have been several announcements this year to indicate that the cloud provider is looking to benefit from the recent uptick in cloud adoption and support the global recovery initiatives. In April, Alibaba announced its plans to invest USD 28 billion, focusing on infrastructure and technologies related to operating systems, servers, chips and networks, over the next three years. Later in June, Alibaba announced the intention to recruit 5,000 people globally showing serious intentions to become a global cloud player. It is also strengthening capabilities in markets where they already have a strong market presence. By 2021 Alibaba intends to have 64 availability zones with 21 regions across the globe.
Consolidating Partnership with Equinix
Alibaba’s partnership with Equinix, the interconnection and data centre company dates back a few years. In 2017 the partnership started providing enterprises with direct, scalable access to Alibaba Cloud via the Equinix Cloud Exchange in 5 of their global data centres.
Last week the partnership was further strengthened by Equinix extending the reach of Alibaba Cloud via its network of Equinix Cloud Exchange Fabric (ECX Fabric) Cloud interconnection platform. The deal will widen Alibaba’s cloud reach in the US, EMEA, and the Asia Pacific region for customers to privately connect with Alibaba’s cloud. Under the partnership, Alibaba will integrate its API with Equinix ECX Fabric to facilitate direct and secured connections to Alibaba Cloud, across these regions:
- 9 US metros. Chicago, Dallas, Denver, Los Angeles, Miami, New York, Seattle, Silicon Valley and Washington DC
- 5 Asia Pacific hubs. Hong Kong, Jakarta, Singapore, Sydney and Tokyo
- 3 hubs in EMEA. Dubai, Frankfurt and London
The deal also gives Alibaba direct access to Equinix’s interconnected ecosystem of over 9,700 customers including enterprises, cloud and network operators, and IT service providers.
The Hybrid Cloud Push
In the last 18 months or so, the industry has seen a greater push in private/hybrid cloud or multi-cloud adoption. Ecosystm Principal Advisor Andrew Milroy says, “As enterprises move to hybrid cloud infrastructures, the world’s leading IaaS providers, including Alibaba Cloud, are expanding their private cloud and hybrid cloud services.”
Many of these IaaS providers may not have the capabilities to provide a hybrid cloud offering at a global level. Partnerships such as the one between Equinix and Alibaba Cloud may well be the solution. Milroy says, “Equinix offers interconnection services from multiple sites across the globe. These interconnection services are necessary for the provision of private and hybrid cloud services, on a global scale, offering the level of performance and security that organisations want.”
“In order to compete with AWS, GCP and Microsoft, Alibaba Cloud needs to be able to scale its private and hybrid cloud offerings globally. Equinix can enable them to do this. At the same time, Equinix will also benefit from Alibaba Cloud’s growth into newer markets, which will lead to an increased demand for its interconnection services.”
In the report, Ecosystm Predicts: The Top Healthcare Trends for 2020, we had noted the similarities between the healthcare and the financial services industries and that Healthtech will take lessons from the Fintech industry.
In the report, Ecosystm Principal Analyst, Sash Mukherjee said, “Fintech plays a significant role in driving greater inclusion, especially to drive the induction of the unbanked into the mainstream economy, give the underbanked more options to leverage the broader financial services available, and reduce disparity in the adoption of financial services by bridging the gender gap and differences based on ethnicity and socio-economic status. It is not hard to imagine a similar fate for Healthtech. As the industry focuses on value-based outcomes, governments put in more regulations around accountability and transparency in the industry, and people expect the customer experience that they get out of their retail interactions, Healthtech start-ups will become as mainstream as Fintech start-ups.”
However, Mukherjee notes that there might be some pitfalls in this journey, especially when organisations focus more on the technology and less on the actual application and benefits of the technology. “Innovators and start-ups need to align themselves early, with corporates and technology providers to gain a better understanding of the market and regulatory landscape.”
Singapore bringing key industry stakeholders together
The MoU between Alibaba Cloud, Pfizer and Singapore’s Fintech Academy announced yesterday, is a move in the right direction that promises to give early and necessary guidance to Healthtech start-ups. Under the newly formed Healthcare Fintech Alliance (HFA), Alibaba will provide infrastructural support and technological mentorship to the Healthtech and Fintech start-ups to help them leverage cloud, AI and other technologies for their future requirements. The Fintech Academy will guide these start-ups through talent management and venture building programs. Pfizer will provide thought leadership through its network of healthcare experts and opinion leaders, including guidance on commercialisation of the products and services. The Healthcare Fintech Alliance initiative will begin with a pilot in Singapore, Indonesia, and Vietnam before expanding to other regions – Malaysia and the Philippines.
Mukherjee says, “The healthcare industry, for all the cutting-edge research, that it represents, has been remarkably slow to transform. But the COVID-19 crisis has forced the industry to transform, without the luxury or time to think about it. While the implications on the life sciences and provider organisations is clearer, there has simultaneously emerged a need for transformation in the healthcare payer industry. There will be greater demand from consumers for micro-financing to tide over sudden healthcare crises and greater transparency in how these funds are managed. Again, there is an immense potential here for the industry to learn from Fintech.”
Healthcare Fintech Alliance Focus Areas
The focus areas for Healthcare Fintech Alliance shows the deep connection between Healthtech and Fintech.
- Healthcare Affordability. Micro-financing and other financial models involving patients, family members, payers, and other healthcare stakeholders
- Value Based Healthcare. Linking payment schemes to a drug’s effectiveness, health outcomes or utilisation
- Outcome Monitoring. Tracking and reporting of outcomes derived from patients, wearables, healthcare providers, R&D databases and real-world evidence.
- Personalised Healthcare. Using digital technology to tailor healthcare to individual needs
- Innovative Healthtech Devices. Driving adoption in digital tools, such as diagnostic tools linked to medicine access and reimbursement
- Population Health Management. Leveraging patient and associated data in a compliant way to better understand population health characteristics, for effective wellness programs, treatment protocols and cost management.
“Alliances such as these have potential benefits for the industry stakeholders such as Alibaba and Pfizer. Alibaba has been focusing on the Southeast Asia market – earlier in the month the Alibaba Cloud Philippines Ecosystem Alliance was formed to support digital transformation in start-ups and small and medium enterprises. Initiatives such as this is an effective way to associate themselves with the evolving start-up community in the region,” says Mukherjee. “Life sciences companies operate in an extremely competitive global market where they have to work on new products against a backdrop of competition from generics and global concern over rising healthcare expenditure. Against that backdrop, this alliance is the right go-to-market messaging for Pfizer as well.”
“However, the deepest positive impact of alliances such as these will be on the Healthcare industry as a whole. It makes concepts such as value-based healthcare, remote care and personalised healthcare achievable in the near future.”
As organisations stride towards digitalisation, re-evaluate their business continuity plans and define what the Future of Work will look for them, Cloud adoption is expected to surge. In June, there were several announcements that indicate the market is responding to this increased interest.
Cloud Providers Gearing up to Enable Economic Recovery
Global economies are slowly gearing up for a technology-led recovery phase and several organisations are taking advantage of the disruption to start or accelerate their digital transformation plans. Many are looking at this as a good opportunity to replace their legacy systems. Cloud providers are expected to lead from the front when it comes to helping the economy recover.
Government agencies have been immensely impacted by the COVID-19 crisis and will need to shift fast into the recovery mode. Salesforce launched a multi-tenant dedicated Cloud infrastructure for their US Federal, state and local government customers, government contractors, and federally funded research and development centres. Hosted on AWS GovCloud and FedRAMP compliant, it provides customers with a compliant and secure environment to deploy Salesforce’s CRM platform and industry solutions. The launch is expected to empower government agencies with the ability to deliver better services, scale to unprecedented demands and connect to citizens on their channel of choice.
Initiatives such as the UK Crown Commercial Service (CCS) and Google Cloud agreement will also help in the recovery phase. This allows qualified public sector agencies to avail of a discounted price for their Google Cloud deployments. Earlier in the year CCS entered into a price arrangement with Microsoft as well. If Cloud has to be the vehicle for economic recovery, such arrangements will benefit cash-strapped public sector organisations.
The recovery will also require the entire technology ecosystem to engage not only with large enterprises but also small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Alibaba Cloud announced an investment of US$ 283 million to revamp its global partner program. They plan to introduce new partner-customer communication processes to enhance response time and bring more opportunities to independent software vendors (ISVs) managed service providers (MSPs) and system integrators (SIs) as partners.
Europe Emerging as a Cloud Hub
As a fallout of the current political scenario, Europe is pushing for more cloud independence and to become an innovation hub as a vendor-neutral network for cloud computing providers and their customers.
GAIA-X Foundation is a federated data infrastructure project initiated to build a unified system of cloud and data services to be protected by EU Laws – including GDPR, the free flow of non-personal data regulation and the Cybersecurity Act. France and Germany kicked off the GAIA-X cloud project last year and the system is open for participation to national and European initiatives for exchange of data across industries and services such as AI, IoT and data analytics. GAIA-X took another step towards becoming a real option for European organisations with the establishment as a legal entity in June. Various organisations – including Dassault, Orange, Siemens, SAP, Atos, Scaleway and Deutsche Telekom are a part of this non-profit platform, working together on Cloud applications, high-performance computing as well as edge systems. The project is expecting to release a working model by early 2021 and will be further enhanced in phases.
Global Cloud leaders are also focusing on expanding their presence in Europe. In February, Microsoft announced a new data centre in Spain leveraging Telefónica infrastructure. In a similar move, Google Cloud announced its plans to expand in the region in partnership with Telefónica. Telefonica and Google are expected to jointly work on Spain’s digitalisation through edge infrastructure and 5G for consumers and telecom infrastructure.
Cloud Providers Bolstering their Cybersecurity Capabilities
2020 has witnessed a host of cybersecurity threats and data breaches. While Cloud providers have always evolved their cybersecurity capabilities, it has become important for them to become vocal about these measures to build trust in the industry.
To complement the Microsoft Azure IoT security, Microsoft acquired IoT security specialist CyberX, last month. The acquisition will enable greater security for the IoT devices connected to the Microsoft network and will help their customers to gain visibility through a map of devices thus allowing them to gather information on security risks associated with thousands of sensors and connected devices. This will enhance smart grid, smart manufacturing and digital assets and profiles and reduce vulnerabilities across production and supply chain.
In another move which will benefit the ISV and SI ecosystem, NetFoundry’s zero trust networking API is now available on RapidAPI. RapidAPI’s marketplace enables developers to easily find, connect to, and manage the APIs they need to build a range of applications. Now the ISV and developer community can access NetFoundry’s software-only, zero trust models on RapidAPI.
More Partnerships between Software/Industry Solutions Providers and Cloud Providers
The COVID-19 crisis has had a far-reaching impact on several industries. The technologies that are expected to see the most uptake are IoT and Future of Work technologies.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “COVID-19 has brought to the fore the need for managing risks better. And the key to managing risks is to have better visibility and drive data-driven decisions; the sweet spot for IoT technologies.”
Last week, Microsoft and Hitachi announced a strategic alliance to accelerate the digital transformation of the Manufacturing and Logistics industries across Southeast Asia, Japan and North America. The first solutions are expected to be made available in Thailand as early as this month. Hitachi brings to the table their industry solutions, such as Lumada, and their IoT-ready industrial controllers HX Series. These solutions will be fully integrated with the Microsoft cloud platform, leveraging Azure, Dynamics 365 and Microsoft 365.
Another sector that has seen significant disruption is Real Estate. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Andrew Milroy in his blog Proptech: Driving Digital Transformation in the Wake of COVID-19 sees a real opportunity for the sector to transform. “Many activities within the property ecosystem have remained unchanged for decades. There are several opportunities for digital engagement and automation in this sector, ranging from the use of robots in construction to the ‘uberisation’ of the residential property customer journey.”
June saw Honeywell and SAP partner to create a joint cloud-based solution based on Honeywell Forge and SAP cloud. The cloud solution is aimed at real estate operators and customers providing aggregated financial and operational insights in real-time. The solution leverages the Honeywell Forge autonomous buildings solution and the SAP Cloud for Real Estate solution, enabling facility managers and building owners to reposition their real estate portfolios through parameters such as cost savings and energy efficiency and help improve the tenant experience.
As organisations struggle to maintain operations during the ongoing crisis, there has been an exponential increase in employees working from home and relying on the Future of Work technologies. Ecosystm principal Advisor, Audrey William says, “During the COVID-19 pandemic, people have become reliant on voice, video and collaboration tools and even when things go back to normal in the coming months, the blended way of work will be the norm. There has been a surge of video and collaboration technologies. The need to have good communication and collaboration tools whether at home or in the office has become a basic expectation especially when working from home. It has become non-negotiable.”
AWS and Slack announced a multi-year partnership to collaborate on solutions to enable the Workplace of the Future. This will give Slack users the ability to manage their AWS resources within Slack, as well as replace Slack’s voice and video call features with AWS’s Amazon Chime. And AWS will be using Slack for their internal communication and collaboration.
Delivering excellent customer experience in the midst of the crisis has proved to be difficult for organisations. Customer care centres have been especially impacted by high volumes of customer interactions – through voice and non-voice channels. This will see a major rise in adoption of cloud contact centre solutions. Contact centre providers are ramping up their capabilities in anticipation. Genesys selected AWS as their preferred cloud partner to deliver new features to customers and build a global and secure infrastructure.
The industry can expect more news from Cloud providers in the next few months as they ramp up their capabilities and channel their go-to-market messaging.
Gain access to more insights from the Ecosystm Cloud Study

As far back as in 2018, Tencent had set its eyes on the business customer, starting a Cloud and Smart Industries business group (CSIG). Since then it has not lost focus on what businesses need and has continued to evolve its offerings. Late last year, Tencent Meeting , a video-conferencing app for its enterprise business was launched. This was a savvy move, as it came right after Zoom was blocked from the China market forcing local users to search for in-country alternatives.
Tencent’s Go-to-Market Strategy
Talking about Tencent’s go-to-market strategy, Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Niloy Mukherjee says, “The current leader in the video-conferencing space, Zoom is not available in China so that market alone can sustain an offering like Tencent Meeting. With the popularity of WeChat, Tencent has a huge opportunity to combine conferencing on the desktop and the mobile and I see that as an advantage for Tencent when compared to other players in the market.”
In another savvy move, as enterprises grapple with remote employees and video-conferencing solution grow in importance, Tencent rolled out its video-conferencing solution for the global market. VooV Meeting, the global version of the domestic app Tencent Meeting, was launched in over 100 countries including the larger Asia Pacific markets such as Malaysia, Hong Kong, Singapore and Japan.
Mukherjee says, “At this particular moment in time, the COVID-19 crisis has suddenly brought video-conferencing front and centre. While people are now resorting to it out of compulsion, they are likely to discover that this is a great way to work. As bandwidths and connectivity improve across countries, video-conferencing emerges as a really viable solution. Organisations will soon realise that this technology can help save tremendous amounts of travel and facility rental costs. So, usage is likely to grow exponentially – and it is not a bad time at all for Tencent to enter this market.”
The Video-Conferencing Market is Heating up
The video-conferencing market continues to grow and providers such as Zoom, Microsoft, Google, and Slack have made many of their offerings free. In the current milieu industries such as healthcare, education and professional services are using unprecedented video collaboration tools, both internally and for customer interactions.
Zoom is gaining global popularity with stock prices rising 28% in the last month in an otherwise under-performing global market. Zoom continues to evolve user-friendly features such as the virtual background, forcing other conferencing providers such as Microsoft to emulate them. Microsoft Teams has also seen a steep rise in popularity, with the company reporting over 50% rise in chat volume in the last month.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Audrey William says, “Expanding the capabilities beyond video will be critical for a larger market share. Zoom is now expanding its offering to include calling capabilities with Zoom phone. Beyond video, collaboration platforms are growing in importance and Microsoft Teams, as an example, has made the platform feature-rich across voice, video and collaboration capabilities. Users will want features that will make chat, video, voice and collaboration sessions rich and intuitive. If the experience is not good, they will find another platform to use. It will all come down to user experience!”
Tencent is by no means the only tech organisation from China that is eyeing the global market. Recently, Alibaba launched a free international collaboration platform based on their productivity app Dingtalk for medical professionals to share information and advice on prevention and treatment of COVID-19. In a boost to Tencent however, the United Nations (UN) announced that they will be using VooV Meeting to host their online conversations, especially for their initiatives to mark their 75th anniversary – UN75. Not only will the UN use Tencent’s video-conferencing capabilities, they will also leverage other Tencent offerings such as WeChat Work, and Tencent AI SI.
William thinks that the market might be crowded and Tencent will face some challenges. “Tencent’s challenge is that it is entering an established market. To make a mark, it will have to continue to innovate on features, focus on platform security and ensure that the experience is seamless. Tencent announced in January that the solution can support 300 attendees simultaneously. To sustain this and make a bigger push internationally, it will need to work with local partners to help take this product to market.”
“With all the options around, people will not use VooV Meeting just because it is free – they will if they find the features to be unique and the experience brilliant.”
Mukherjee adds, “Tencent is one of the most admired companies in China – it is a top pick for most graduates as their preferred employer and is seen as a better company to work for than other big players in China. This is a reflection of its strong corporate culture and continuing success. Tencent has, so far, had a good track record of competing with the likes of Alibaba and I believe that they will move quickly to muscle in and take a leadership space in the global video-conferencing market.”
Two things happened recently that 99% of the ICT world would normally miss. After all microprocessor and chip interconnect technology is quite the geek area where we generally don’t venture into. So why would I want to bring this to your attention?
We are excited about the innovation that analytics, machine learning (ML) and all things real time processing will bring to our lives and the way we run our business. The data center, be it on an enterprise premise or truly on a cloud service provider’s infrastructure is being pressured to provide compute, memory, input/output (I/O) and storage requirements to take advantage of the hardware engineers would call ‘accelerators’. In its most simple form, an accelerator microprocessor does the specialty work for ML and analytics algorithms while the main microprocessor is trying to hold everything else together to ensure that all of the silicon parts are in sync. If we have a ML accelerator that is too fast with its answers, it will sit and wait for everyone else as its outcomes squeezed down a narrow, slow pipe or interconnect – in other words, the servers that are in the data center are not optimized for these workloads. The connection between the accelerators and the main components becomes the slowest and weakest link…. So now back to the news of the day.
A new high speed CPU-to-device interconnect standard, the Common Express Link (CXL) 1.0 was announced by Intel and a consortium of leading technology companies (Huawei and Cisco in the network infrastructure space, HPE and Dell EMC in the server hardware market, and Alibaba, Facebook, Google and Microsoft for the cloud services provider markets). CXL joins a crowded field of other standards already in the server link market including CAPI, NVLINK, GEN-Z and CCIX. CXL is being positioned to improve the performance of the links between FPGA and GPUs, the most common accelerators to be involved in ML-like workloads.
Of course there were some names that were absent from the launch – Arm, AMD, Nvidia, IBM, Amazon and Baidu. Each of them are members of the other standards bodies and probably are playing the waiting game.
Now let’s pause for a moment and look at the other announcement that happened at the same time. Nvidia and Mellanox announced that the two companies had reached a definitive agreement under which Nvidia will acquire Mellanox for $6.9 billion. Nvidia puts the acquisition reasons as “The data and compute intensity of modern workloads in AI, scientific computing and data analytics is growing exponentially and has put enormous performance demands on hyperscale and enterprise datacenters. While computing demand is surging, CPU performance advances are slowing as Moore’s law has ended. This has led to the adoption of accelerated computing with Nvidia GPUs and Mellanox’s intelligent networking solutions.”
So to me it seems that despite Intel working on CXL for four years, it looks like they might have been outbid by Nvidia for Mellanox. Mellanox has been around for 20 years and was the major supplier of Infiniband, a high speed interconnect that is common in high performance workloads and very well accepted by the HPC industry. (Note: Intel was also one of the founders of the Infiniband Trade Association, IBTA, before they opted to refocus on the PCI bus). With the growing need for fast links between the accelerators and the microprocessors, it would seem like Mellanox persistence had paid off and now has the market coming to it. One can’t help but think that as soon as Intel knew that Nvidia was getting Mellanox, it pushed forward with the CXL announcement – rumors that have had no response from any of the parties.
Advice for Tech Suppliers:
The two announcements are great for any vendor who is entering the AI, intense computing world using graphics and floating point arithmetic functions. We know that more digital-oriented solutions are asking for analytics based outcomes so there will be a growing demand for broader commoditized server platforms to support them. Tech suppliers should avoid backing or picking one of either the CXL or Infiniband at the moment until we see how the CXL standard evolves and how nVidia integrates Mellanox.
Advice for Tech Users:
These two announcements reflect innovation that is generally so far away from the end user, that it can go unnoticed. However, think about how USB (Universal Serial Bus) has changed the way we connect devices to our laptops, servers and other mobile devices. The same will true for this connection as more and more data is both read and outcomes generated by the ‘accelerators’ for the way we drive our cars, digitize our factories, run our hospitals, and search the Internet. Innovation in this space just got a shot in the arm from these two announcements.




























