Banks, insurers, and other financial services organisations in Asia Pacific have plenty of tech challenges and opportunities including cybersecurity and data privacy management; adapting to tech and customer demands, AI and ML integration; use of big data for personalisation; and regulatory compliance across business functions and transformation journeys.
Modernisation Projects are Back on the Table
An emerging tech challenge lies in modernising, replacing, or retiring legacy platforms and systems. Many banks still rely on outdated core systems, hindering agility, innovation, and personalised customer experiences. Migrating to modern, cloud-based systems presents challenges due to complexity, cost, and potential disruptions. Insurers are evaluating key platforms amid evolving customer needs and business models; ERP and HCM systems are up for renewal; data warehouses are transforming for the AI era; even CRM and other CX platforms are being modernised as older customer data stores and models become obsolete.
For the past five years, many financial services organisations in the region have sidelined large legacy modernisation projects, opting instead to make incremental transformations around their core systems. However, it is becoming critical for them to take action to secure their long-term survival and success.
Benefits of legacy modernisation include:
- Improved operational efficiency and agility
- Enhanced customer experience and satisfaction
- Increased innovation and competitive advantage
- Reduced security risks and compliance costs
- Preparation for future technologies
However, legacy modernisation and migration initiatives carry significant risks. For instance, TSB faced a USD 62M fine due to a failed mainframe migration, resulting in severe disruptions to branch operations and core banking functions like telephone, online, and mobile banking. The migration failure led to 225,492 complaints between 2018 and 2019, affecting all 550 branches and required TSB to pay more than USD 25M to customers through a redress program.
Modernisation Options
- Rip and Replace. Replacing the entire legacy system with a modern, cloud-based solution. While offering a clean slate and faster time to value, it’s expensive, disruptive, and carries migration risks.
- Refactoring. Rewriting key components of the legacy system with modern languages and architectures. It’s less disruptive than rip-and-replace but requires skilled developers and can still be time-consuming.
- Encapsulation. Wrapping the legacy system with a modern API layer, allowing integration with newer applications and tools. It’s quicker and cheaper than other options but doesn’t fully address underlying limitations.
- Microservices-based Modernisation. Breaking down the legacy system into smaller, independent services that can be individually modernised over time. It offers flexibility and agility but requires careful planning and execution.
Financial Systems on the Block for Legacy Modernisation
Data Analytics Platforms. Harnessing customer data for insights and targeted offerings is vital. Legacy data warehouses often struggle with real-time data processing and advanced analytics.
CRM Systems. Effective customer interactions require integrated CRM platforms. Outdated systems might hinder communication, personalisation, and cross-selling opportunities.

Payment Processing Systems. Legacy systems might lack support for real-time secure transactions, mobile payments, and cross-border transactions.

Core Banking Systems (CBS). The central nervous system of any bank, handling account management, transactions, and loan processing. Many Asia Pacific banks rely on aging, monolithic CBS with limited digital capabilities.
Digital Banking Platforms. While several Asia Pacific banks provide basic online banking, genuine digital transformation requires mobile-first apps with features such as instant payments, personalised financial management tools, and seamless third-party service integration.
Modernising Technical Approaches and Architectures
Numerous technical factors need to be addressed during modernisation, with decisions needing to be made upfront. Questions around data migration, testing and QA, change management, data security and development methodology (agile, waterfall or hybrid) need consideration.
Best practices in legacy migration have taught some lessons.
Adopt a data fabric platform. Many organisations find that centralising all data into a single warehouse or platform rarely justifies the time and effort invested. Businesses continually generate new data, adding sources, and updating systems. Managing data where it resides might seem complex initially. However, in the mid to longer term, this approach offers clearer benefits as it reduces the likelihood of data discrepancies, obsolescence, and governance challenges.
Focus modernisation on the customer metrics and journeys that matter. Legacy modernisation need not be an all-or-nothing initiative. While systems like mainframes may require complete replacement, even some mainframe-based software can be partially modernised to enable services for external applications and processes. Assess the potential of modernising components of existing systems rather than opting for a complete overhaul of legacy applications.
Embrace the cloud and SaaS. With the growing network of hyperscaler cloud locations and data centres, there’s likely to be a solution that enables organisations to operate in the cloud while meeting data residency requirements. Even if not available now, it could align with the timeline of a multi-year legacy modernisation project. Whenever feasible, prioritise SaaS over cloud-hosted applications to streamline management, reduce overhead, and mitigate risk.
Build for customisation for local and regional needs. Many legacy applications are highly customised, leading to inflexibility, high management costs, and complexity in integration. Today, software providers advocate minimising configuration and customisation, opting for “out-of-the-box” solutions with room for localisation. The operations in different countries may require reconfiguration due to varying regulations and competitive pressures. Architecting applications to isolate these configurations simplifies system management, facilitating continuous improvement as new services are introduced by platform providers or ISV partners.
Explore the opportunity for emerging technologies. Emerging technologies, notably AI, can significantly enhance the speed and value of new systems. In the near future, AI will automate much of the work in data migration and systems integration, reducing the need for human involvement. When humans are required, low-code or no-code tools can expedite development. Private 5G services may eliminate the need for new network builds in branches or offices. AIOps and Observability can improve system uptime at lower costs. Considering these capabilities in platform decisions and understanding the ecosystem of partners and providers can accelerate modernisation journeys and deliver value faster.
Don’t Let Analysis Paralysis Slow Down Your Journey!
Yes, there are a lot of decisions that need to be made; and yes, there is much at stake if things go wrong! However, there’s a greater risk in not taking action. Maintaining a laser-focus on the customer and business outcomes that need to be achieved will help align many decisions. Keeping the customer experience as the guiding light ensures organisations are always moving in the right direction.

As they continue to promote innovation in the Financial Services industry, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) introduced the Financial Sector Technology and Innovation Scheme 3.0 (FSTI 3.0) earlier this week, pledging up to SGD 150 million over three years. FSTI 3.0 aims to boost innovation by supporting projects that use cutting-edge technologies or have a regional scope, while strengthening the technology ecosystem in the industry. This initiative includes three tracks:
- Enhanced Centre of Excellence track to expand grant funding to corporate venture capital entities
- Innovation Acceleration track to support emerging tech based FinTech solutions, and
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) FinTech track to accelerate ESG adoption in fintech
Additionally, FSTI 3.0 will continue to support areas like AI, data analytics, and RegTech while emphasising talent development. We can expect to see transformative financial innovation through greater industry collaboration.
MAS’ Continued Focus on Innovation
Over the years, the MAS has consistently been a driving force behind innovation in the Financial Services industry. They have actively promoted and supported technological advancements to enhance the industry’s competitiveness and resilience.
The FinTech Regulatory Sandbox framework offers a controlled space for financial institutions and FinTech innovators to test new financial products and services in a real-world setting, with tailored regulatory support. By temporarily relaxing specific regulatory requirements, the sandbox encourages experimentation, while ensuring safeguards to manage risks and uphold the financial system’s stability. Upon successful experimentation, entities must seamlessly transition to full compliance with relevant regulations.
Innovation Labs serve as incubators for new ideas, fostering a culture of experimentation and collaboration. They collaborate with disruptors, startups, and entrepreneurs to develop groundbreaking solutions. Labs like Accenture Innovation Hub, Allianz Asia Lab, Aviva Digital Garage, ANZ Innovation Lab, and AXA Digital Hive drive create prototypes, and roll out market solutions.
Building an Ecosystem
Partnerships between financial institutions, technology companies, startups, and academia contribute to Singapore’s economic growth and global competitiveness while ensuring adaptive regulation in an evolving landscape. By creating a vibrant ecosystem, MAS has facilitated knowledge exchange, collaborative projects, and the development of innovative solutions. For instance, in 2022, MAS partnered with United Nations Capital Development Fund (UNCDF) to build digital financial ecosystems for MSMEs in emerging economies.
This includes supporting projects that address environmental, social, and governance (ESG) concerns within the financial sector. For instance, MAS worked with the People’s Bank of China to establish the China-Singapore Green Finance Taskforce (GFTF) to enhance collaboration in green and transition finance. The aim is to focus on taxonomies, products, and technology to support the transition to a low-carbon future in the region, co-chaired by representatives from both countries.
MAS has also promoted Open Banking and API Frameworks to encourage financial institutions to adopt open banking practices enabling easier integration of financial services and encouraging innovation by third-party developers. This also empowers customers to have greater control over their financial data while fostering the development of new financial products and services by FinTech companies.
Regulators in Asia Pacific Taking a Proactive Approach
While Singapore is at the forefront of financial innovations, other regulatory and government bodies in Asia Pacific are also taking on an increasingly proactive role in nurturing innovation. This stance is being driven by a twofold objective – to accelerate economic growth through technological advancements and to ensure that innovative solutions align with regulatory requirements and safeguard consumer interests.
Recognising the potential of fintech to enhance financial services and drive economic growth, the Hong Kong Monetary Authority (HKMA) established the Fintech Facilitation Office (FFO) to facilitate communication between the fintech industry and traditional financial institutions. The central bank’s Smart Banking Initiatives, including the Faster Payment System, Open API Framework, and the Banking Made Easy initiative that reduces regulatory frictions help to enhance the efficiency and interoperability of digital payments.
The Financial Services Agency of Japan (FSA) has been actively working on creating a regulatory framework to facilitate fintech innovation, including revisions to existing laws to accommodate new technologies like blockchain. In 2020, FSA launched the Blockchain Governance Initiative Network (BGIN) to facilitate collaboration between the government, financial institutions, and the private sector to explore the potential of blockchain technology in enhancing financial services.
The Central Bank of the Philippines (Bangko Sentral ng Pilipinas – BSP) has launched an e-payments project to overcome challenges hindering electronic retail purchases, such as limited interbank transfer facilities, high bank fees, and low levels of trust among merchants and consumers. The initiative included the establishment of the National Retail Payment System, a framework for retail payment, and the introduction of automated clearing houses like PESONet and InstaPay. These efforts have increased the percentage of retail purchases made electronically from 1% to over 10% within five years, demonstrating the positive impact of effective cooperation and innovative policies in driving a shift towards a cash-lite economy.
The promotion of fintech innovation highlights a collective belief in its potential to transform finance and boost economies. As regulations adapt for technologies like blockchain and open banking, the Asia Pacific region is promoting collaboration between traditional financial institutions and emerging fintech players. This approach underscores a commitment to balance innovation with responsible oversight, ensuring that advanced financial solutions comply with regulatory standards.

The appetite to adopt Open Banking solutions has increased, largely expedited by the pandemic. As consumers look for more digital engagements and better rates and services, they are more open to giving third-party providers access to their financial information that has traditionally been held by their banks.
The success of Open Banking initiatives depends on the Banking and FinTech ecosystem coming together to create an end-to-end digital architecture.
This Ecosystm Snapshot discusses some of the evolving trends in Open Banking, such as product differentiation by FinTechs to address a competitive market; the banking industry’s need to adopt digital and foster innovation; market entry by other industry leaders; and the need for trust in Open Banking adoption.
We cover recent announcements by companies such as Lloyd’s Bank, Mastercard, Batelco Financial Services, CarFinance 247, Credit Kudos, Prometeo, APImetrics and tomato pay.

Woolworths have announced the adoption of a new Software-as-a-Service capability from One Door to support the quality and compliance of their in-store merchandising. There are some valuable lessons from this announcement for other retailers.
The power of data, particularly as the capability of specialist AI tools improves, continues to help retailers improve their offering to customers.
SaaS Capabilities Offer Performance Improvements
Woolworths are working on improving the compliance of product merchandising in-store using One Door Visual Merchandising solution.
One Door will improve the accuracy of data available to both the in-store teams and for the central supermarket merchandising team. The supply chain in Woolworths is already highly automated but getting the shelf presence right is dependent on the quality of data being captured. While store teams already use a range of electronic tools to capture this information, the compliance with store planograms and visual merchandising standards has been difficult to automate.
One Door’s solution provides a single source of this information in an easy to use digital format. The AI tools that One Door have developed appear to be able to show the degree of compliance of the actual shelf layout and stock position.
For store teams, One Door will simplify tracking layout changes by highlighting them and making the data available on the shop floor. This should deliver productivity benefits to the store – benefits that can be reinvested in new activities or on better customer service.
Store teams will be able to verify that third party merchandisers are compliant. Major product manufacturers often use their own merchandising teams in supermarkets and One Door will provide a simple mechanism to verify they have done their jobs properly.
The central merchandise teams will be able to quickly get data-driven feedback on how the stores are making planned changes, as well as verifying the quality of compliance with their store layouts.
All of these factors should mean that the product that is available in-store is presented in the manner that the merchandising teams have defined, and the customers will see a more consistent presentation of products.
Integration is Critical for Rapid Deployment
Effective integration with existing systems and new cloud capabilities is critical to support the real-time operation in Retail.
The ability to introduce and scale up new capabilities that can be delivered by cloud services such as One Door will only be effective if integration is simple and quick. This requires compatibility at a number of levels including data semantics and the ability to exchange data effectively. Woolworths have been growing their capability for managing and supporting APIs that will make this integration smoother.
In addition, the cloud service providers have made the development of integration capabilities an investment priority.
The introduction of One Door is showing how the company can integrate new capability and introduce it to almost 10% of their stores as a pilot capability, with the full deployment to be completed across their chain during 2022.
Other retailers who don’t have this capability to integrate cloud services quickly, reliably and cost-effectively are going to lag companies that have invested to achieve this capability.
CIOs and CDOs should be leading their organisations in the development of a rich and scalable set of APIs to enable the integration of this type of high-value specialised solution.
Deployment without Consistent Architectures will be Complex
Rapid deployment of new capabilities requires a well-architected cloud, network, and edge infrastructure – and a well-trained team.
It is highly likely that the deployment of the One Door solution will be delivered over the existing Woolworths infrastructure. The capability is delivered from the cloud, with little or no deployment costs or time required. With the existing network and hybrid cloud capabilities that Woolworths have developed this type of rollout will be a relatively simple technical activity.
The integration of the service into the Woolworths environment is likely to be the most complex activity to make sure accurate data is exchanged.
It doesn’t take long to identify a wide range of different digital initiatives that Woolworths are pursuing. With the platform that they have established, they are well-positioned to take advantage of new capabilities as start-ups and existing suppliers develop them.
Every retailer needs to maintain their focus on their digital capabilities. As companies such as One Door develop AI-based enhancements, CIOs and their teams need to be ready to integrate these capabilities quickly.
Strong architectures for both infrastructure and digital services are needed to achieve these outcomes.
Recommendations for Retailers
Retail organisations continue to find new ways to leverage the power of the data that they are able to collect. The flexibility that SaaS developments deliver will be essential to maintaining an organisation’s competitive positioning.
CIOs and their teams need to lead their organisations and ecosystems by:
- Identifying new SaaS capabilities that support the strategic positioning of their companies
- Preparing their environments by supporting a rich set of APIs to support the rapid integration of these new capabilities
- Developing and maintaining strong architectures that provide organisations a solid framework to develop within
Checkout Alan’s previous insight on Woolworths micro automation technology adopted to speed up the fulfilment of online grocery orders

Last week Zoom announced a USD 100 million Zoom Apps Fund to promote the development of Zoom’s ecosystem of Zoom applications, integrations, video, developer tools, and hardware.
As part of Zoom Apps Fund, the company will invest in a portfolio of companies that are promoting and innovating on Zoom’s video conferencing platform. The portfolio companies will receive initial investments between USD 250,000 and USD 2.5 million to build solutions. To support the practice, Zoom is providing its tools and expertise to various start-ups, entrepreneurs, and industry players to build applications and integrate Zoom’s functionality and native interface in their products.
In March, Zoom introduced an SDK designed to help programmers embed Zoom functionality inside their applications. Zoom SDK is a component of Zoom Developer platform which includes SDKs, APIs, webhooks, chatbots, and distribution for applications and integration. Last year Zoom launched Zoom Apps and Zoom Marketplace at its Zoomtopia virtual conference to bring applications and productivity into the Zoom experience.
Zoom is not alone in evolving their Unified communications as a service (UCaaS) capabilities and market. Tencent rolled out their video conferencing solution for the global market, Facebook expanded their offerings in videoconferencing applications through the integration of new features, Google announced a series of upgrades and innovations to better support the flexibility needs of frontline and remote workers in Google Workspaces, and Microsoft introduced Viva that aims to bring together communications, knowledge, learning, resources, and insights together.

“Ecosystm research shows that 50% of organisations will continue to increase use of collaboration platforms and tools in 2021. However, if videoconferencing remains just a tool to log in to for meetings without purpose-built workflows and functionality that suit worker profiles, then it will start losing its attractiveness. Vendors need to work on user interface, UX, the lighting, security, audio quality and many other aspects that draws users to the platform.
The big question is what next for videoconferencing vendors? How can engineering teams innovate to build the capabilities organisations want when they use drawing tools, share images, have chats and discussions within collaboration platforms? How do you make the experience real so employees can “live and breathe” in the environment?
Zoom investing in understanding what apps and workflows are suited for a particular vertical or business is fundamental to the future of video and collaboration and will be a big game changer.”

“Zoom is continuing to expand the markets in which they operate and investing in start-ups increases their opportunities to grow as a platform. Their App Marketplace already offers a rich source of innovations, with Zoom themselves appearing to develop integration with market leaders such as Salesforce and HubSpot in the CRM category. This has led to Zoom integrations in close to 80 CRM products – including integrations developed in-house by Salesforce and HubSpot to supplement Zoom capabilities.
They are promoting an open web and audio-conferencing platform that does not limit users to the walled-garden approach of competitors such as Microsoft Teams.
Zoom’s strategy creates the opportunity for CIOs to access a widely used, rich functionality, digital collaboration channel – one they can integrate seamlessly into their existing digital channels knowing that their customers are likely to be highly familiar with the user experience.”
Get more insights on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and technology areas that will see innovations, as organisations get into the recovery phase.

The disruption that we faced in 2020 has created a new appetite for adoption of technology and digital in a shorter period. Crises often present opportunities – and the FinTech and Financial Services industries benefitted from the high adoption of digital financial services and eCommerce. In 2021, there will be several drivers to the transformation of the Financial Services industry – the rise of the gig economy will give access to a larger talent pool; the challenges of government aid disbursement will be mitigated through tech adoption; compliance will come sharply back into focus after a year of ad-hoc technology deployments; and social and environmental awareness will create a greater appetite for green financing. However, the overarching driver will be the heightened focus on the individual consumer (Figure 1).
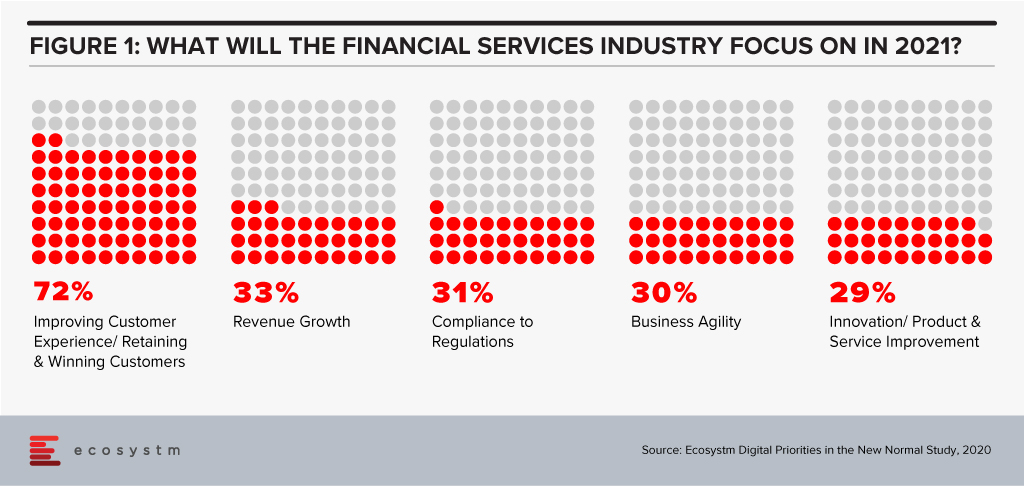
2021 will finally see consumers at the core of the digital financial ecosystem.
Ecosystm Advisors Dr. Alea Fairchild, Amit Gupta and Dheeraj Chowdhry present the top 5 Ecosystm predictions for FinTech in 2021 – written in collaboration with the Singapore FinTech Festival. This is a summary of the predictions; the full report (including the implications) is available to download for free on the Ecosystm platform.
The Top 5 FinTech Trends for 2021
#1 The New Decade of the ‘Empowered’ Consumer Will Propel Green Finance and Sustainability Considerations Beyond Regulators and Corporates
We have seen multiple countries set regulations and implement Emissions Trading Systems (ETS) and 2021 will see Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) considerations growing in importance in the investment decisions for asset managers and hedge funds. Efforts for ESG standards for risk measurement will benefit and support that effort.
The primary driver will not only be regulatory frameworks – rather it will be further propelled by consumer preferences. The increased interest in climate change, sustainable business investments and ESG metrics will be an integral part of the reaction of the society to assist in the global transition to a greener and more humane economy in the post-COVID era. Individuals and consumers will demand FinTech solutions that empower them to be more environmentally and socially responsible. The performance of companies on their ESG ratings will become a key consideration for consumers making investment decisions. We will see corporate focus on ESG become a mainstay as a result – driven by regulatory frameworks and the consumer’s desire to place significant important on ESG as an investment criterion.
#2 Consumers Will Truly Be ‘Front and Centre’ in Reshaping the Financial Services Digital Ecosystems
Consumers will also shape the market because of the way they exercise their choices when it comes to transactional finance. They will opt for more discrete solutions – like microfinance, micro-insurances, multiple digital wallets and so on. Even long-standing customers will no longer be completely loyal to their main financial institutions. This will in effect take away traditional business from established financial institutions. Digital transformation will need to go beyond just a digital Customer Experience and will go hand-in-hand with digital offerings driven by consumer choice.
As a result, we will see the emergence of stronger digital ecosystems and partnerships between traditional financial institutions and like-minded FinTechs. As an example, platforms such as the API Exchange (APIX) will get a significant boost and play a crucial role in this emerging collaborative ecosystem. APIX was launched by AFIN, a non-profit organisation established in 2018 by the ASEAN Bankers Association (ABA), International Finance Corporation (IFC), a member of the World Bank Group, and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS). Such platforms will create a level playing field across all tiers of the Financial Services innovation ecosystem by allowing industry participants to Discover, Design and rapidly Deploy innovative digital solutions and offerings.
#3 APIfication of Banking Will Become Mainstream
2020 was the year when banks accepted FinTechs into their product and services offerings – 2021 will see FinTech more established and their technology offerings becoming more sophisticated and consumer-led. These cutting-edge apps will have financial institutions seeking to establish partnerships with them, licensing their technologies and leveraging them to benefit and expand their customer base. This is already being called the “APIficiation” of banking. There will be more emphasis on the partnerships with regulated licensed banking entities in 2021, to gain access to the underlying financial products and services for a seamless customer experience.
This will see the growth of financial institutions’ dependence on third-party developers that have access to – and knowledge of – the financial institutions’ business models and data. But this also gives them an opportunity to leverage the existent Fintech innovations especially for enhanced customer engagement capabilities (Prediction #2).
#4 AI & Automation Will Proliferate in Back-Office Operations
From quicker loan origination to heightened surveillance against fraud and money laundering, financial institutions will push their focus on back-office automation using machine learning, AI and RPA tools (Figure 3). This is not only to improve efficiency and lower risks, but to further enhance the customer experience. AI is already being rolled out in customer-facing operations, but banks will actively be consolidating and automating their mid and back-office procedures for efficiency and automation transition in the post COVID-19 environment. This includes using AI for automating credit operations, policy making and data audits and using RPA for reducing the introduction of errors in datasets and processes.
There is enormous economic pressure to deliver cost savings and reduce risks through the adoption of technology. Financial Services leaders believe that insights gathered from compliance should help other areas of the business, and this requires a completely different mindset. Given the manual and semi-automated nature of current AML compliance, human-only efforts slow down processing timelines and impact business productivity. KYC will leverage AI and real-time environmental data (current accounts, mortgage payment status) and integration of third-party data to make the knowledge richer and timelier in this adaptive economic environment. This will make lending risk assessment more relevant.
#5 Driven by Post Pandemic Recovery, Collaboration Will Shape FinTech Regulation
Travel corridors across border controls have started to push the boundaries. Just as countries develop new processes and policies based on shared learning from other countries, FinTech regulators will collaborate to harmonise regulations that are similar in nature. These collaborative regulators will accelerate FinTech proliferation and osmosis i.e. proliferation of FinTechs into geographies with lower digital adoption.
Data corridors between countries will be the other outcome of this collaboration of FinTech regulators. Sharing of data in a regulated environment will advance data science and machine learning to new heights assisting credit models, AI, and innovations in general. The resulting ‘borderless nature’ of FinTech and the acceleration of policy convergence across several previously siloed regulators will result in new digital innovations. These Trusted Data Corridors between economies will be further driven by the desire for progressive governments to boost the Digital Economy in order to help the post-pandemic recovery.


















