The global economy remains fragile due to multiple factors; and banking organisations will need to weather the storm. While large and well-capitalised banks are expected to fare better, there is a need for the industry to pursue new sources of value beyond traditional boundaries.
Banking industry leaders should be bold, proactive, and envision possibilities beyond current uncertainties. Technology has a key role to play in turning their innovation and resiliency goals into reality.
Read on to find out how the National Australia Bank, the Scottish National Investment Bank, the ANZ Bank, the Swiss National Bank, Mastercard, and the French banking group Crédit Agricole are leading the charge in driving innovation within the banking industry by investing in new technologies and exploring business models to better serve their customers.
Download ‘The Future of Banking’ as a PDF

Leading Banking and Financial Services organisations play a crucial role in financing sustainability transition. They have the infrastructure and resources to kickstart their own sustainability journey. But beyond that, they also have a greater role in building a sustainable value chain.
This extends to helping the traditional economy to transition; green investments to promote organisations with the right intentions; and empowering their customers to make environmentally-friendly choices.
As a technology leader in BFSI, you are an integral part of your organisation’s sustainability journey. Here are 5 ways in which BFSI tech leaders can support their organisations to turn sustainability intentions into reality.
Align tech with business goals and strategy. Think like a business leader and understand larger goals beyond technology deployments to empower your team.
View reporting as more than a checklist. You are in an ideal position to demonstrate the value of data insights beyond reporting mandates to the leadership team – link them to larger business outcomes.
Build intelligence into your facilities and assets. Consider investing in an intelligent enterprise asset management solution to automate asset and infrastructure management, remotely monitor and manage asset operations, and achieve sustainable business outcomes.
Automate your infrastructure allocation. You are increasingly using FinOps tools and other predictive analytics dashboards for cost and resource optimisation – extend the use for greater energy efficiency.
Understand your organisation’s unique sustainability journey. Seek independent opinion from third parties to empower your organisation to take the first step in the sustainability strategy, derive insights from data assets, and create market differentiation.
Read on to find more.
Download 5 Sustainability Actions for BFSI Tech Leaders as a PDF

The appetite to adopt Open Banking solutions has increased, largely expedited by the pandemic. As consumers look for more digital engagements and better rates and services, they are more open to giving third-party providers access to their financial information that has traditionally been held by their banks.
The success of Open Banking initiatives depends on the Banking and FinTech ecosystem coming together to create an end-to-end digital architecture.
This Ecosystm Snapshot discusses some of the evolving trends in Open Banking, such as product differentiation by FinTechs to address a competitive market; the banking industry’s need to adopt digital and foster innovation; market entry by other industry leaders; and the need for trust in Open Banking adoption.
We cover recent announcements by companies such as Lloyd’s Bank, Mastercard, Batelco Financial Services, CarFinance 247, Credit Kudos, Prometeo, APImetrics and tomato pay.

In this Insight, guest author Anupam Verma talks about the technology-led evolution of the Banking industry in India and offers Cloud Service Providers guidance on how to partner with banks and financial institutions. “It is well understood that the banks that were early adopters of cloud have clearly gained market share during COVID-19. Banks are keen to adopt cloud but need a partnership approach balancing innovation with risk management so that it is ‘not one step forward and two steps back’ for them.”

India has been witnessing a digital revolution. Rapidly rising mobile and internet penetration has created an estimated 1 billion mobile users and more than 600 million internet users. It has been reported that 99% of India’s adult population now has a digital identity in the form of Aadhar and a large proportion of the adult Indians have a bank account.
Indians are adapting to consume multiple services on the smartphone and are demanding the same from their financial services providers. COVID-19 has accelerated this digital trend beyond imagination and is transforming India from a data-poor to a data-rich nation. This data from various alternate sources coupled with traditional sources is the inflection point to the road to financial inclusion. Strong digital infrastructure and digital footprints will create a world of opportunities for incumbent banks, non-banks as well as new-age fintechs.
The Cloud Imperative for Banks
Banks today have an urgent need to stay relevant in the era of digitally savvy customers and rising fintechs. This journey for banks to survive and thrive will put Data Analytics and Cloud at the front and centre of their digital transformation.
A couple of years ago, banks viewed cloud as an outsourcing infrastructure to improve the cost curve. Today, banks are convinced that cloud provides many more advantages (Figure 1).
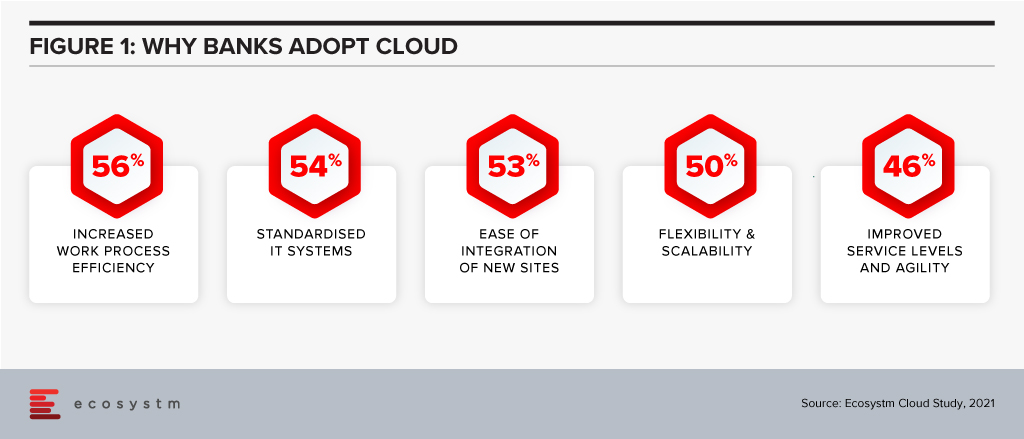
Banks are also increasingly partnering with fintechs for applications such as KYC, UI/UX and customer service. Fintechs are cloud-native and understand that cloud provides exponential innovation, speed to market, scalability, resilience, a better cost curve and security. They understand their business will not exist or reach scale if not for cloud. These bank-fintech partnerships are also making banks understand the cloud imperative.
Traditionally, banks in India have had concerns around data privacy and data sovereignty. There are also risks around migrating legacy systems, which are made of monolithic applications and do not have a service-oriented architecture. As a result, banks are now working on complete re-architecture of the core legacy systems. Banks are creating web services on top of legacy systems, which can talk to the new technologies. New applications being built are cloud ready. In fact, many applications may not connect to the core legacy systems. They are exploring moving customer interfaces, CRM applications and internal workflows to the cloud. Still early days, but banks are using cloud analytics for marketing campaigns, risk modelling and regulatory reporting.
The remote working world is irreversible, and banks also understand that cloud will form the backbone for internal communication, virtual desktops, and virtual collaboration.

Strategy for Cloud Service Providers (CSPs)
It is estimated that India’s public cloud services market is likely to become the largest market in the Asia Pacific behind only China, Australia, and Japan. Ecosystm research shows that 70% of banking organisations in India are looking to increase their cloud spending. Whichever way one looks at it, cloud is likely to remain a large and growing market. The Financial Services industry will be one of the prominent segments and should remain a focus for cloud service providers (CSPs).
I believe CSPs targeting India’s Banking industry should bucket their strategy under four key themes:
- Partnering to Innovate and co-create solutions. CSPs must work with each business within the bank and re-imagine customer journeys and process workflow. This would mean banking domain experts and engineering teams of CSPs working with relevant teams within the bank. For some customer journeys, the teams have to go back to first principles and start from scratch i.e the financial need of the customer and how it is being re-imagined and fulfilled in a digital world.
CSPs should also continue to engage with all ecosystem partners of banks to co-create cloud-native solutions. These partners could range from fintechs to vendors for HR, Finance, business reporting, regulatory reporting, data providers (which feeds into analytics engine).
CSPs should partner with banks for experimentation by providing test environments. Some of the themes that are critical for banks right now are CRM, workspace virtualisation and collaboration tools. CSPs could leverage these themes to open the doors. API banking is another area for co-creating solutions. Core systems cannot be ‘lifted & shifted’ to the cloud. That would be the last mile in the digital transformation journey. - Partnering to mitigate ‘fear of the unknown’. As in the case of any key strategic shift, the tone of the executive management is important. A lot of engagement is required with the entire senior management team to build the ‘trust quotient’ of cloud. Understanding the benefits, risks, controls and the concept of ‘shared responsibility’ is important. I am an AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner and I realise how granular the security in the cloud can be (which is the responsibility of the bank and not of the CSP). This knowledge gap can be massive for smaller banks due to the non-availability of talent. If security in the cloud is not managed well, there is an immense risk to the banks.
- Partnering for Risk Mitigation. Regulators will expect banks to treat CSPs like any other outsourcing service providers. CSPs should work with banks to create robust cloud governance frameworks for mitigating cloud-related risks such as resiliency, cybersecurity etc. Adequate communication is required to showcase the controls around data privacy (data at rest and transit), data sovereignty, geographic diversity of Availability Zones (to mitigate risks around natural calamities like floods) and Disaster Recovery (DR) site.
- Partnering with Regulators. Building regulatory comfort is an equally important factor for the pace and extent of technology adoption in Financial Services. The regulators expect the banks to have a governance framework, detailed policies and operating guidelines covering assessment, contractual consideration, audit, inspection, change management, cybersecurity, exit plan etc. While partnering with regulators on creating the framework is important, it is equally important to demonstrate that banks have the skill sets to run the cloud and manage the risks. Engagement should also be linked to specific use cases which allow banks to effectively compete with fintech’s in the digital world (and expand financial access) and use cases for risk mitigation and fraud management. This would meet the regulator’s dual objective of market development as well as market stability.
Financial Services is a large and growing market for CSPs. Fintechs are cloud-native and certain sectors in the industry (like non-banks and insurance companies) have made progress in cloud adoption. It is well understood that the banks that were early adopters of cloud have clearly gained market share during COVID-19. Banks are keen to adopt cloud but need a partnership approach balancing innovation with risk management so that it is ‘not one step forward and two steps back’ for them.
The views and opinions mentioned in the article are personal.
Anupam Verma is part of the Leadership team at ICICI Bank and his responsibilities have included leading the Bank’s strategy in South East Asia to play a significant role in capturing Investment, NRI remittance, and trade flows between SEA and India.

If you are a digital leader in the Financial Services industry (FSI), you have already heard this from your customers: ‘Why is it that Netflix and Amazon can make more relevant and personalised offers than my bank or wealth manager?’ Digital first players are obsessed with using data to understand their customer’s commercial and consumer behaviour. Financial Services will need to become just as obsessed with personalisation of offerings and services if they want to remain relevant to their customers. Ecosystm research finds that leveraging data to offer personalised service and product offerings to their clients is the leading digital priority in more than 50% of FSI organisations.
Banks, particularly, are both in a strong position and have a strong incentive to offer this personalisation. Their retail customers’ expectations are now shaped by the experience they have received from their favorite digital first firms, and they are making it increasingly clear that they expect personalised offerings from their banks. Furthermore, they are well positioned as a facilitator of commercial relationships between two segments of customers – consumers and merchants. The amount of data they hold on consumer interactions is comprehensive – and more importantly they are a trusted custodian of their customers’ data and privacy.
The Barriers to Personalisation
So, what is stopping them? Here are three insights from over 12 years of experience driving digitisation of Financial Services:
- Systems Legacy. Often the data and core banking systems do not allow for easy access and analysis of the required data across the data sets required (eg. Consumers and Merchants).
- Investment Priorities. There is still a significant investment happening in compliance and modernisation of core banking systems. Too often the focus of these programs can be myopic, and banks miss the opportunity to solve multiple pain points with their investments driven by overly focused problem statements.
- Culture and Purpose. Are banks stuck in a paradigm of their own making – defining their business models by what has served them well in the past? Will Amazon think about its provision of working capital to their small and medium business partners the same way as a bank does?
Vendor Focus – Crayon Data
Thankfully, there is a new breed of tech vendors who is making it easier for banks to drive personalisation of their offerings and connect customers from across segments. Crayon Data is a good example, with their maya.ai engine unearthing the preferences of customers and matching them to offerings from qualified merchants. It benefits all parties:
- The Consumer receives relevant offers, is served from discovery to fulfillment on a single platform and all personal data and information guarded by their bank.
- For Merchants, it allows them to reach the right customers at the right moment, develop valuable marketing and insights and all this directly from their bank partner’s platform.
- For Banks, it provides a scalable model for offer acquisition and easily configurable and measurable consumer engagement.
maya.ai leverages patented AI to create a powerful profile of each customer based on their buying habits and comparing these with millions of other consumers drawn in from their unstructured data sets and graph-based methodology. They then use their algorithms to assist their Financial Services client to make relevant offerings from qualified merchants to consumers in the right channel, at the right moment. All of this is done without exposing personal client information, as the data sets are based on behaviour rather than identity.

Conclusion
There are significant considerations for banks in offering these types of capabilities, such as:
- Privacy. While the technology operates on non-identifiable information, the perception of clients being ‘stalked’ by their bank in order to drive business to a merchant is one that would need to be managed carefully.
- Consumer opt-out. The ability for customers to opt out of this type of service is critical.
- Consumer financial wellbeing. It may be in the best interests of some consumer to not receive merchant offers, for instance where they are managing to a strict budget. These considerations can be baked into the overall customer journey (eg. prompts when the consumer is nearing their self-imposed monthly budget for a category), but care will need to be taken to keep customers’ best interests at heart.
While there are multiple challenges to overcome, the fact remains that personalisation is quickly becoming a core expectation for consumers. How will banks respond, and will we see AI use cases like Crayon Data become more prominent?

As the Knowledge Partner for the Singapore Fintech Festival, Ecosystm has a finger on the pulse of the Financial Services industry.
In this Ecosystm Bytes, we focus on how the Banking industry will look in the decade ahead, why it continues to struggle with compliance and customer experience, and where technology is helping.
Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 FinTech Trends for 2021
In 2021, one of the prevalent shifts we are witnessing in banking services is the switch towards automation to enhance the services and customer experience. Want to know more? Create your free account on the Ecosystm platform to access The Top 5 FinTech Trends for 2021 and more from the Ecosystm Predicts Series.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming embedded in financial services across consumer interactions and core business processes, including the use of chatbots and natural language processing (NLP) for KYC/AML risk assessment.
But what does AI mean for financial regulators? They are also consuming increasing amounts of data and are now using AI to gain new insights and inform policy decisions.
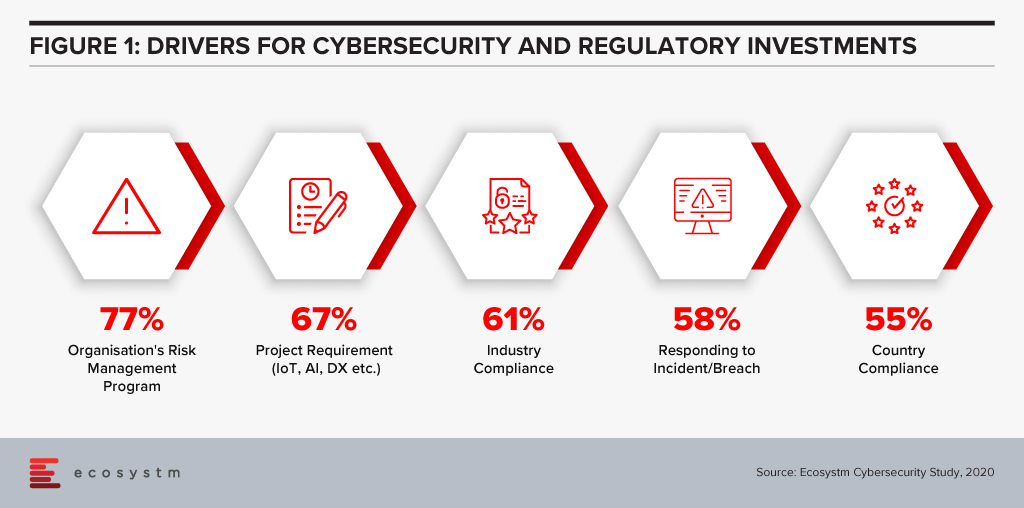
The efficiencies that AI offers can be harnessed in support of compliance within both financial regulation (RegTech) and financial supervision (SupTech). Authorities and regulated institutions have both turned to AI to help them manage the increased regulatory requirements that were put in place after the 2008 financial crisis. Ecosystm research finds that compliance is key to financial institutions (Figure 1).
SupTech is maturing with more robust safeguards and frameworks, enabling the necessary advancements in technology implementation for AI and Machine Learning (ML) to be used for regulatory supervision. The Bank of England and the UK Financial Conduct Authority surveyed the industry in March 2019 to understand how and where AI and ML are being used, and their results indicated 80% of survey respondents were using ML. The most common application of SupTech is ML techniques, and more specifically NLP to create more efficient and effective supervisory processes.
Let us focus on the use of NLP, specifically on how it has been used by banking authorities for policy decision making during the COVID-19 crisis. AI has the potential to read and comprehend significant details from text. NLP, which is an important subset of AI, can be seen to have supported operations to stay updated with the compliance and regulatory policy shifts during this challenging period.
Use of NLP in Policy Making During COVID-19
The Financial Stability Board (FSB) coordinates at the international level, the work of national financial authorities and international standard-setting bodies in order to develop and promote the implementation of effective regulatory, supervisory and other financial sector policies. A recent FSB report delivered to G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors for their virtual meeting in October 2020 highlighted a number of AI use cases in national institutions.
We illustrate several use cases from their October report to show how NLP has been deployed specifically for the COVID-19 situation. These cases demonstrate AI aiding supervisory team in banks and in automating information extraction from regulatory documents using NLP.
De Nederlandsche Bank (DNB)
The DNB is developing an interactive reporting dashboard to provide insight for supervisors on COVID-19 related risks. The dashboard that is in development, enables supervisors to have different data views as needed (e.g. over time, by bank). Planned SupTech improvements include incorporating public COVID-19 information and/or analysing comment fields with text analysis.
Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)
MAS deployed automation tools using NLP to gather international news and stay abreast of COVID-19 related developments. MAS also used NLP to analyse consumer feedback on COVID-19 issues, and monitor vulnerabilities in the different customer and product segments. MAS also collected weekly data from regulated institutions to track the take-up of credit relief measures as the pandemic unfolded. Data aggregation and transformation were automated and visualised for monitoring.
US Federal Reserve Bank Board of Governors
One of the Federal Reserve Banks in the US is currently working on a project to develop an NLP tool used to analyse public websites of supervised regulated institutions to identify information on “work with your customer” programs, in response to the COVID-19 crisis.
Bank of England
The Bank developed a Policy Response Tracker using web scraping (targeted at the English versions of each authority/government website) and NLP for the extraction of key words, topics and actions taken in each jurisdiction. The tracker pulls information daily from the official COVID-19 response pages then runs it through specific criteria (e.g. user-defined keywords, metrics and risks) to sift and present a summary of the information to supervisors.
Market Implications
Even with its enhanced efficiencies, NLP in SupTech is still an aid to decision making and cannot replace the need for human judgement. NLP in policy decision is performing clearly defined information gathering tasks with greater efficiency and speed. But NLP cannot change the quality of the data provided, so data selection and choice are still critical to effective policy making.
For authorities, the use of SupTech could improve oversight, surveillance, and analytical capabilities. These efficiency gains and possible improvement in quality arising from automation of previously manual processes could be consideration for adoption.
Attention will be paid in 2021 to focusing on automation of processes using AI (Figure 2).
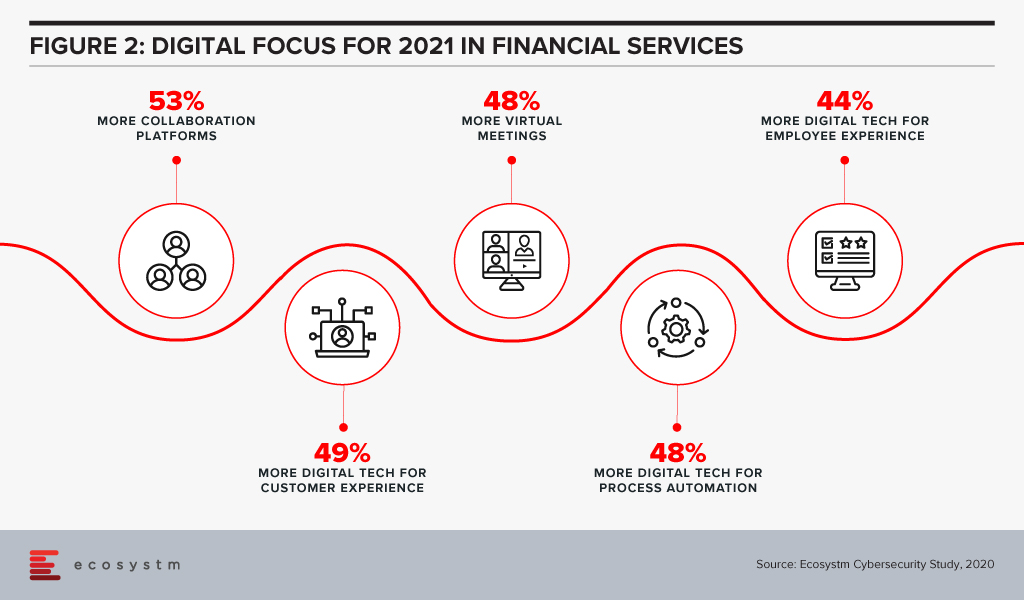
Based on a survey done by the FSB of its members (Figure 3), the majority of their respondents had a SupTech innovation or data strategy in place, with the use of such strategies growing significantly since 2016.
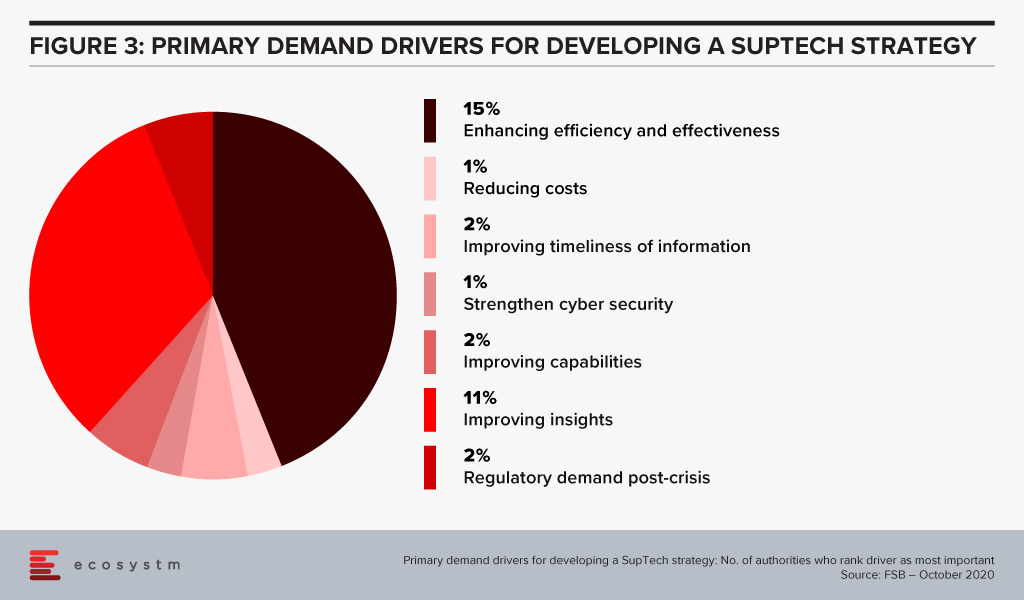
Summary
For more mainstream adoption, data standards and use of effective governance frameworks will be important. As seen from the FSB survey, SupTech applications are now used in reporting, data management and virtual assistance. But institutions still send the transaction data history in different reporting formats which results in a slower process of data analysing and data gathering. AI, using NLP, can help with this by streamlining data collection and data analytics. While time and cost savings are obvious benefits, the ability to identify key information (the proverbial needle in the haystack) can be a significant efficiency advantage.
Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit
For more insights, attend the Singapore FinTech Festival 2020: Infrastructure Summit which will cover topics tied to creating infrastructure for a digital economy; and RegTech and SupTech policies to drive innovation and efficiencies in a co-Covid-19 world.

We are in the midst of an economic and social crisis. COVID-19 will have far-reaching effects on organisations and how they do business. It is expected to drive more investments in Fintech, especially in digital payments, as more organisations and consumers adopt eCommerce. Countries will also have to re-think the ways they trade with other countries, as travel restrictions continue. This is expected to boost the Fintech industry and July was witness to how Fintech organisations, financial institutions and governments are gearing up to leverage Fintech in their path to economic and social recovery.
Financial Industry Seeing More Open Banking Initiatives
The banking industry is fast moving towards collaboration and openness. July saw several initiatives that take the industry closer to open banking.
Late last year, South Korea piloted an open banking system with participation from local banks and lenders. The Financial Services Commission (FSC), South Korea’s top financial regulator reported in July that the initiative had participation from 72 companies including commercial banks and Fintech firms with 20 million subscribers using the open banking services.
Australia introduced an open banking initiative, monitored by the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC). From July, Australia’s banking customers can share their financial and banking data with accredited businesses under Consumer Data Right Act to access a better suite of financial applications.
There is global expansion as well. Railsbank, a global open banking platform with a presence in Southeast Asia introduced their services in the US market. The company will offer Banking-as-a Service, Cards-as-a Service and Credit Card-as-a-Service in the US market. Khaleeji Commercial Bank (KHCB), an Islamic bank in Bahrain, launched their open banking service enabling a customer to link their bank accounts with other banks and manage through the ‘Khaleeji 360’ platform. The portal allows clients to view all their bank accounts, automate operations and conduct banking through a unified platform.
Financial Institutions Increasing Partnerships with Fintech
Financial institutions no longer look at Fintech as competition. They appreciate that customers are at the centre of their entire operation – and Fintech services can and will provide them with the solutions they need. As financial institutions re-think their transformation journeys and face increasingly stringent regulations, they no longer have the option of ignoring Fintechs.
American Express, Visa, Mastercard and Discover came together to roll out a global standard. The big four’s advanced digital checkout solution Click to Pay is an online checkout system based on EMV Secure Remote Commerce (SRC) to make online payments across websites, mobile applications and connected devices, frictionless.
With an aim to unify payment solutions, a group of 16 major European banks launched the European Payment Initiative (EPI) to create a unified pan-European payment solution leveraging Instant Payments/SEPA Instant Credit Transfer (SCT Inst), including a card, e-wallet and P2P payments.
We also saw financial institutions strengthen their cross-border payment services in July. Deutsche Bank partnered with Airwallex to offer virtual account collections and API-enabled foreign exchange services in Japan and Hong Kong. The service will enable merchants and traders to transact through virtual accounts and APIs without opening bank accounts in foreign markets. Mastercard and Bank of China partnered to enhance cross-border business payments into China. This will enable global businesses to send payments to China while accessing real-time exchange rates, reduce the need for unnecessary documentation between merchants, and reduce transaction hassles and costs.
Fintechs Facilitating Cross-border Trade
Seamless cross-border financial transactions will be key to economic recovery, whether easy remittance or the ability to reach a larger market and be able to trade beyond borders.
July saw the formalisation of the Digital Economy Partnership Agreement (DEPA) between New Zealand, Chile and Singapore, to facilitate end-to-end digital trade, which includes establishing digital identities, paperless trade and the development of Fintech solutions to support it. The initiative also intends to allow cross-border data flow and give access to necessary government data to small and medium enterprises (SMEs) enabling them to be digital-ready to explore newer markets.
Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) signed an MoU with Jiaozi Fintech Dreamworks based in China opening new opportunities for innovation and trade. The agreement will enable Fintech companies based in both cities to access each other’s markets. Primarily established to facilitate the ‘Belt and Road’ initiative, it is a critical component of the DIFC’s 2024 strategy to strengthen relationships with the international financial community and increase access to the South-South corridor. Over the last few years, DIFC has been associated with over 200 Fintech organisations, and last month invested in four Fintech startups through their accelerator program. The agreement with Jiaozi will look at collaboration opportunities in Blockchain, AI and Cloud and will facilitate cross-border workshops and training programs.
Continuing Interests in Emerging Economies
Fintechs have been a means to bring about financial inclusion and are increasingly being used to target the unbanked and underbanked. Emerging economies continue to be attractive for Fintech organisations and global financial institutions.
With much of Malaysia’s economy dependent on foreign workers, Instapay, regulated by the Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM), announced a collaboration with Mastercard, to provide e-wallet accounts to the migrant workers. The widespread use of e-wallets by the migrant worker community will bring benefits to both workers, as well as their employers. Interestingly, Fintech providers in emerging economies are also looking to expand into other emerging markets. Malaysia’s GHL Group received approval from Philippines Securities and Exchange Commission to operate a lending business through their new unit, GHL Philippines Financing Services. GHL has been diversifying its business and has been operating its lending business in Malaysia and Thailand since 2019.
Crown Agent Bank, a wholesale foreign exchange and cross-border payment services based in the UK, partnered with South Africa’s biometric-based payment company, Paycode. Together the companies are aiming to reach 100 million unbanked customers where Crown Agents Bank will use their FX and payment services to bolster Paycode’s product offering and support financial inclusion across Sub-Saharan Africa.
India and Indonesia in the Asia Pacific continue to be popular markets because of the huge proportion of the unbanked population. Rapyd, a UK based global B2B Fintech-as-as-service provider partnered with major Indian e-payment providers – including Paytm, PhonePe, PayU, Citibank, DBS Bank, HDFC Bank, BharatPay, and Unimoni to launch an all-in-one payments solution that spans credit and debit cards, UPI, wallets, and cash. New registrations for digital banking in Indonesia are on the rise and Fintech startup Akulaku is capitalising on the potential digital banking overhaul to offer affordable and comprehensive financial services to consumers.
Fintechs benefiting other industries
The Fintech revolution has shown the path to several other industries – Healthcare and Agriculture are some of the industries that are hoping to benefit from Fintech organisations and their innovations. The MoU between Alibaba Cloud, Pfizer and Singapore’s Fintech Academy announced earlier in July, promises to give early and necessary guidance to Healthtech start-ups, and shows the deep connection between Healthtech and Fintech. In the Philippines, in an effort to improve financial services for farmers, AgriNurture acquired Fintech firm Pay8. By leveraging Pay8 e-wallet services, farmers will be able to access online payment services. This will enable the largely unbanked farmer community to become an active part of the economy.
The technology that these industries are looking to benefit from is Blockchain. South Korea brought Blockchain to their healthcare industry for better data management and storage. The 3 major telecommunications providers in the country – KT, SK Telecom and mobile carrier LG U+ – have also collaborated with KB Insurance to launch the blockchain-based mobile notification service (MNS) by matching customer data to their mobile subscription information. Oxfam Ireland – a charity organisation based in Ireland, received a sum of USD 1.18 million from the European Commission for a Blockchain-based pilot. The company is working on a project -The UnBlocked Cash – to help disaster-affected communities receive cash-based entitlements with more efficiency and traceability.
Fintech will continue to be a cornerstone of economic and social recovery in the future, and the financial industry will see more collaborations between Fintech organisations, financial institutions and governments. Other industries will continue to take learnings from Fintech.

AI is powering products, processes, strategies and customer experience in the Banking industry.
The banking industry is all geared up to embrace Artificial Intelligence (AI), to address its business requirements. In general, banks are struggling to implement smart services within their compliance framework, and have an incomplete view of their customer needs from their legacy systems. However, the industry continues to be reliant on legacy systems, largely because of the involvement of too many complex platforms, technologies, and systems which make migration or integration cumbersome.
Meanwhile, modern Digital Banks are aligning their services to customer needs by embedding AI and machine learning within their existing systems. The banking industry’s experimentation with AI is opening new opportunities for improving customer experience (CX).
“We are not too far away from a day where traditional enterprise applications are no longer relevant. The purpose of those traditional systems was to simplify, codify, and automate business and customer processes. But in the mid-term future, we will have a time where the entire process is intelligent – where the system/application creates the best business process for the customer on the fly”, says Tim Sheedy, Principal Advisor, Ecosystm.
Elevating CX and Security
Banks are being transformed through AI adoption, especially in areas such as process automation, cyber security (especially in threat analysis and intelligence, and fraud/transaction security) and better information sharing systems for both their corporate and retail customers.
Business Solutions being Addressed by AI in Banking
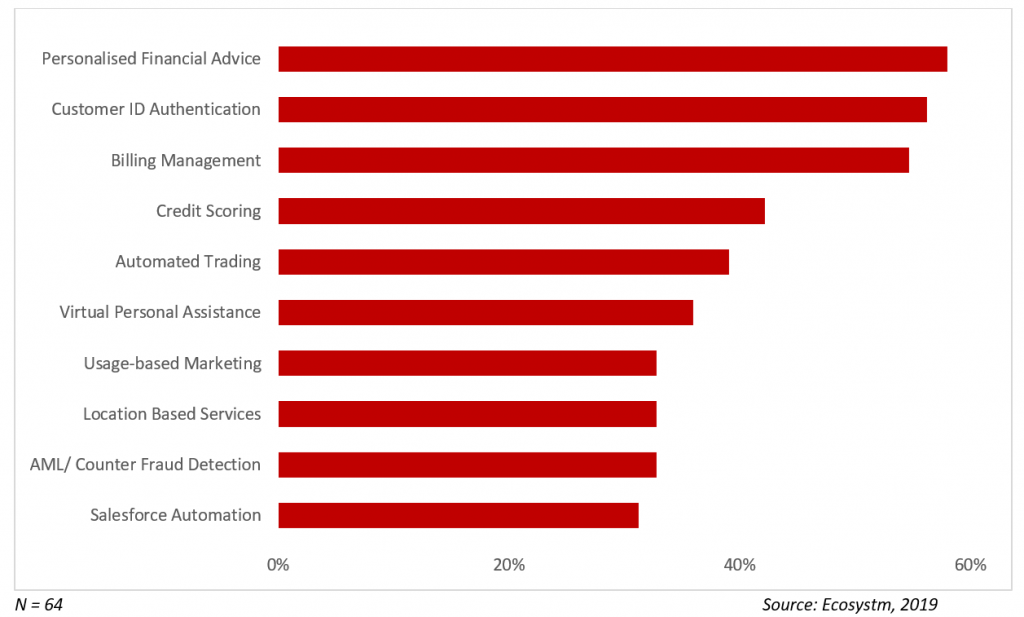
Customer Experience
Customer Service is one of the core banking applications. Adoption of technologies such as virtual assistants and natural language processing (NLP) techniques is redefining CX in the banking industry.
“With emerging technologies setting a new bar for personalisation and value-add, banks looking to stay ahead of the curve simply cannot afford to ignore them,” says Jannat Maqbool, Principal Advisor, Ecosystm.
Personalised financial advice is another area where banks are taking advantage of AI applications. While it might be a perception that AI will reduce the human touch when it comes to CX, in reality, it provides more accurate and timely assistance. For instance, Bank of America has built an AI virtual assistant, “Erica” which actively assists 25 million clients on its mobile platform. Erica searches for past transactions and informs customers on their credit scores and connects with them to provide analytics and information on their account.
Marketing Automation
As profit margins decrease in the Banking sector, and Fintech technologies become more mainstream, banks need to ramp up their marketing initiatives, to remain competitive. AI is helping banks to optimise their marketing dollars. Machine learning algorithms can analyse customers’ entire banking journey involving interactions, transactions, location history, and usage patterns to develop insights and make marketing decisions with unprecedented accuracy. Decisions on a range of marketing initiatives across product improvement, new products and services offerings, and targeted marketing keeping in view customers’ financial goals will be automated. This will impact the profit margin as sales cycles shorten, and customers banking journeys become more satisfying.
Process Automation
There are certain functions in banks which require a lot of manual labour such as billing, generation of reports, account opening operations, KYC, etc. AI is transforming the banking industry with data-driven processes and decision making to automate tasks such as billings, credit scoring, compliance reports and so on. This not only reduces the dependence on tedious manual processes but also creates mechanisms to reduce errors. These errors not only make the organisation less efficient but also has financial ramifications. UBS, as an example, has introduced robots to its workforce, mainly at the back offices, designed to execute more manual and repetitive tasks. This essentially means meeting the right tasks with more speed and accuracy.
Fraud Management
AI improves with data and learns behavioural patterns. Banks are utilising this data or claims management and fraud detection. The AI platform evaluates on certain parameters such as when and how a customer typically accesses services and manage their money – more importantly, how they do not. They are designed to flag transactions with missing information and can alert the bank staff to irregular transactions and suspicious activities to prevent fraud. Increasingly this is evolving a chain of an automated process, without the involvement of banking staff or customer complaints.
Banks have a difficult job delivering better service while remaining compliant, and AI-driven AML and KYC initiatives, helps prevent fraud, and flag suspicious activities such as money laundering.
Market Trends
Current Focus on AI – The banking industry’s focus on customer service and automating manual processes is reflected in the top AI solutions that they are currently adopting. Chatbots and virtual assistants are being improved through natural language generation (NLG) and speech analytics capabilities. Process automation through RPA is being integrated into the organisations’ digital journeys due to its relative ease of deployment and measurable ROI.
Current & Planned Adoption of AI Solutions in Banking
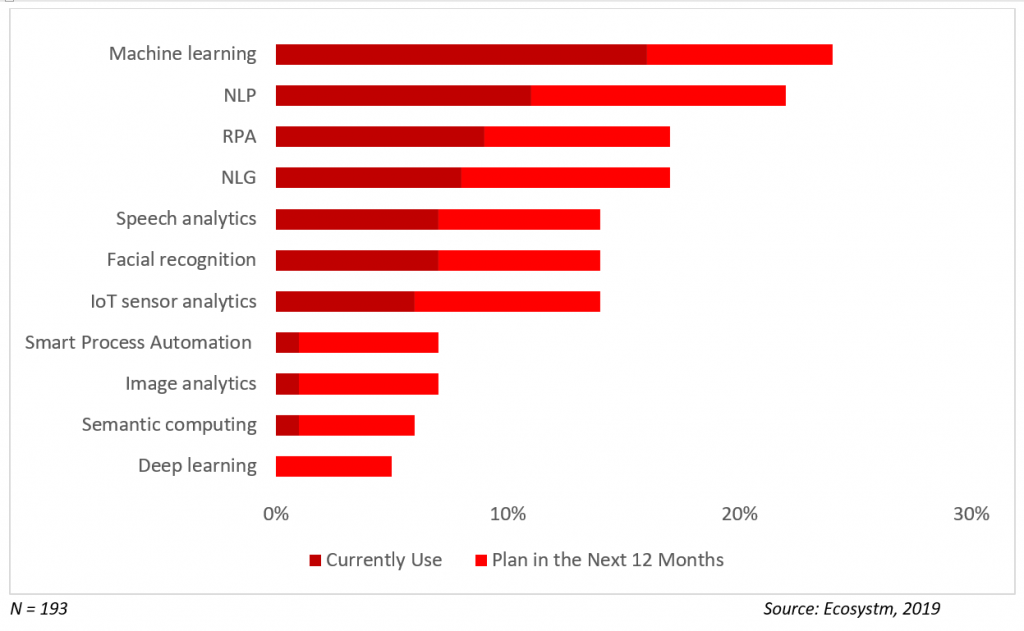
Future Focus on AI – Banks will continue to focus on CX and strengthening the capabilities of their customer service team through AI. Niche solutions such as facial recognition will also improve their front-end operations, especially in customer identity authentication. Banks will also go beyond customer management to asset management, with AI-enabled IoT systems.
What’s Next?
AI is fast evolving and there are some excellent opportunities for banks to explore on what AI has to offer. Banks are working on feeding data into AI systems with advanced algorithms to better understand their customers and improve their services. Banks should focus on getting quality inputs on inquiries, interactions, transactions or another way that can collect insights.
Consumers are looking for operations and systems that are simple to operate and directed towards them. The greatest potential for AI in banking is to deliver personalised and automated services to consumers in a cost-effective and efficient way.
AI is allowing banks to do quicker operations at much lower cost, what remains to be seen is how banks further leverage AI to extend its products and services offerings.