In this Insight, guest author Anupam Verma talks about the technology-led evolution of the Banking industry in India and offers Cloud Service Providers guidance on how to partner with banks and financial institutions. “It is well understood that the banks that were early adopters of cloud have clearly gained market share during COVID-19. Banks are keen to adopt cloud but need a partnership approach balancing innovation with risk management so that it is ‘not one step forward and two steps back’ for them.”

India has been witnessing a digital revolution. Rapidly rising mobile and internet penetration has created an estimated 1 billion mobile users and more than 600 million internet users. It has been reported that 99% of India’s adult population now has a digital identity in the form of Aadhar and a large proportion of the adult Indians have a bank account.
Indians are adapting to consume multiple services on the smartphone and are demanding the same from their financial services providers. COVID-19 has accelerated this digital trend beyond imagination and is transforming India from a data-poor to a data-rich nation. This data from various alternate sources coupled with traditional sources is the inflection point to the road to financial inclusion. Strong digital infrastructure and digital footprints will create a world of opportunities for incumbent banks, non-banks as well as new-age fintechs.
The Cloud Imperative for Banks
Banks today have an urgent need to stay relevant in the era of digitally savvy customers and rising fintechs. This journey for banks to survive and thrive will put Data Analytics and Cloud at the front and centre of their digital transformation.
A couple of years ago, banks viewed cloud as an outsourcing infrastructure to improve the cost curve. Today, banks are convinced that cloud provides many more advantages (Figure 1).
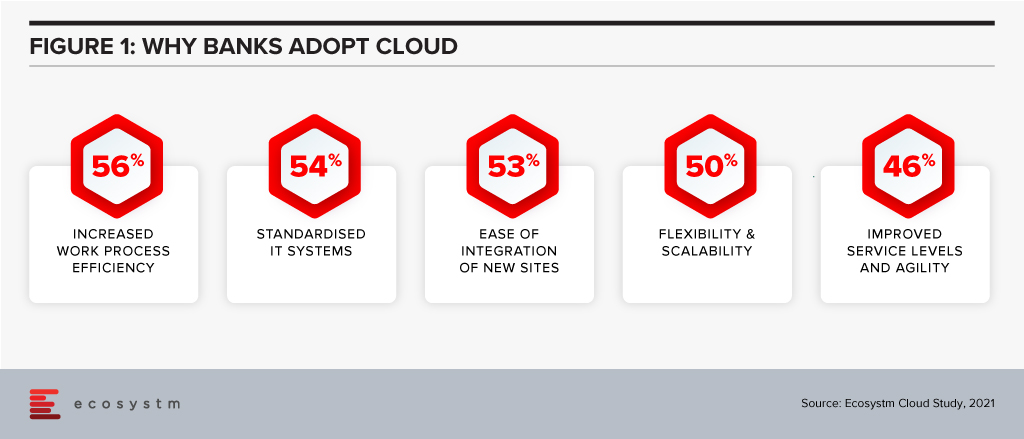
Banks are also increasingly partnering with fintechs for applications such as KYC, UI/UX and customer service. Fintechs are cloud-native and understand that cloud provides exponential innovation, speed to market, scalability, resilience, a better cost curve and security. They understand their business will not exist or reach scale if not for cloud. These bank-fintech partnerships are also making banks understand the cloud imperative.
Traditionally, banks in India have had concerns around data privacy and data sovereignty. There are also risks around migrating legacy systems, which are made of monolithic applications and do not have a service-oriented architecture. As a result, banks are now working on complete re-architecture of the core legacy systems. Banks are creating web services on top of legacy systems, which can talk to the new technologies. New applications being built are cloud ready. In fact, many applications may not connect to the core legacy systems. They are exploring moving customer interfaces, CRM applications and internal workflows to the cloud. Still early days, but banks are using cloud analytics for marketing campaigns, risk modelling and regulatory reporting.
The remote working world is irreversible, and banks also understand that cloud will form the backbone for internal communication, virtual desktops, and virtual collaboration.

Strategy for Cloud Service Providers (CSPs)
It is estimated that India’s public cloud services market is likely to become the largest market in the Asia Pacific behind only China, Australia, and Japan. Ecosystm research shows that 70% of banking organisations in India are looking to increase their cloud spending. Whichever way one looks at it, cloud is likely to remain a large and growing market. The Financial Services industry will be one of the prominent segments and should remain a focus for cloud service providers (CSPs).
I believe CSPs targeting India’s Banking industry should bucket their strategy under four key themes:
- Partnering to Innovate and co-create solutions. CSPs must work with each business within the bank and re-imagine customer journeys and process workflow. This would mean banking domain experts and engineering teams of CSPs working with relevant teams within the bank. For some customer journeys, the teams have to go back to first principles and start from scratch i.e the financial need of the customer and how it is being re-imagined and fulfilled in a digital world.
CSPs should also continue to engage with all ecosystem partners of banks to co-create cloud-native solutions. These partners could range from fintechs to vendors for HR, Finance, business reporting, regulatory reporting, data providers (which feeds into analytics engine).
CSPs should partner with banks for experimentation by providing test environments. Some of the themes that are critical for banks right now are CRM, workspace virtualisation and collaboration tools. CSPs could leverage these themes to open the doors. API banking is another area for co-creating solutions. Core systems cannot be ‘lifted & shifted’ to the cloud. That would be the last mile in the digital transformation journey. - Partnering to mitigate ‘fear of the unknown’. As in the case of any key strategic shift, the tone of the executive management is important. A lot of engagement is required with the entire senior management team to build the ‘trust quotient’ of cloud. Understanding the benefits, risks, controls and the concept of ‘shared responsibility’ is important. I am an AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner and I realise how granular the security in the cloud can be (which is the responsibility of the bank and not of the CSP). This knowledge gap can be massive for smaller banks due to the non-availability of talent. If security in the cloud is not managed well, there is an immense risk to the banks.
- Partnering for Risk Mitigation. Regulators will expect banks to treat CSPs like any other outsourcing service providers. CSPs should work with banks to create robust cloud governance frameworks for mitigating cloud-related risks such as resiliency, cybersecurity etc. Adequate communication is required to showcase the controls around data privacy (data at rest and transit), data sovereignty, geographic diversity of Availability Zones (to mitigate risks around natural calamities like floods) and Disaster Recovery (DR) site.
- Partnering with Regulators. Building regulatory comfort is an equally important factor for the pace and extent of technology adoption in Financial Services. The regulators expect the banks to have a governance framework, detailed policies and operating guidelines covering assessment, contractual consideration, audit, inspection, change management, cybersecurity, exit plan etc. While partnering with regulators on creating the framework is important, it is equally important to demonstrate that banks have the skill sets to run the cloud and manage the risks. Engagement should also be linked to specific use cases which allow banks to effectively compete with fintech’s in the digital world (and expand financial access) and use cases for risk mitigation and fraud management. This would meet the regulator’s dual objective of market development as well as market stability.
Financial Services is a large and growing market for CSPs. Fintechs are cloud-native and certain sectors in the industry (like non-banks and insurance companies) have made progress in cloud adoption. It is well understood that the banks that were early adopters of cloud have clearly gained market share during COVID-19. Banks are keen to adopt cloud but need a partnership approach balancing innovation with risk management so that it is ‘not one step forward and two steps back’ for them.
The views and opinions mentioned in the article are personal.
Anupam Verma is part of the Leadership team at ICICI Bank and his responsibilities have included leading the Bank’s strategy in South East Asia to play a significant role in capturing Investment, NRI remittance, and trade flows between SEA and India.

Many years ago – back in 2003 – I spent some quality time with BMC at their global analyst event in Phoenix, Arizona and they introduced the concept of “Business Service Management” (BSM). I was immediately a convert – that businesses can focus their IT Service Management initiatives on the business and customer services that the technology supports. Businesses that use BSM can have an understanding of the impact and importance of technology systems and assets because there is a direct link between these assets and the systems they support. A router that supports a customer payment platform suddenly becomes a much higher priority than one that supports an employee expense platform.
But for most businesses, this promise was never delivered. Creating a BSM solution became a highly manual process – mapping processes, assets, and applications. Many businesses that undertook this challenge reported that by the time they had mapped their processes, the map was out of date – as processes had changed; assets had been retired, replaced, or upgraded; software had been moved to the cloud or new modules had been implemented; and architectures had changed. Effectively their BSM mapping was often a pointless task – sometimes only delivering value in the slow to change systems – back-end applications and infrastructure that delivers limited value and has a defined retirement date.
The Growth of Digital Business Strategies
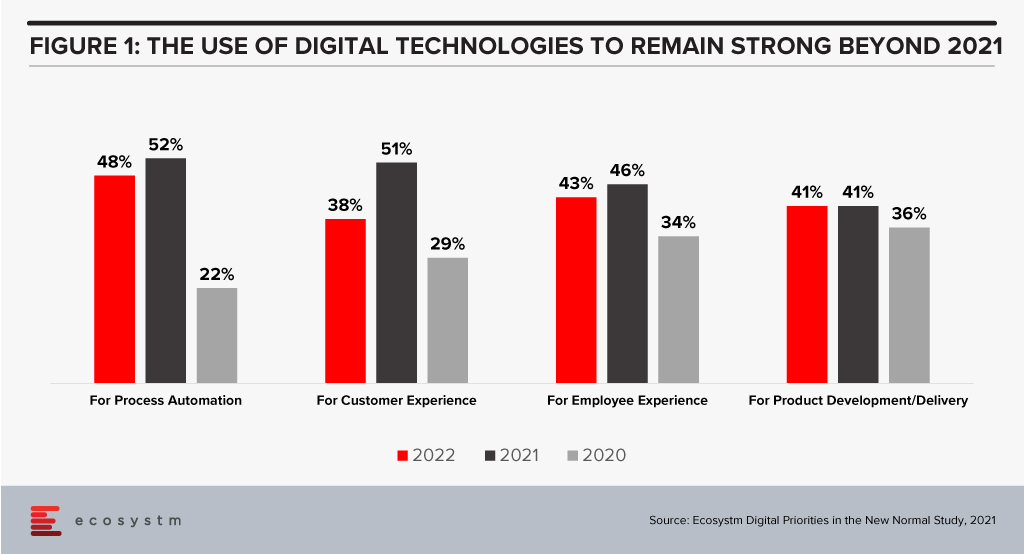
Our technology systems are becoming more important than ever as digital business strategies are realised and digital interactions with customers, employees, and partners significantly increase. Many businesses expect their digital investments to remain strong well into 2022 (Figure 1). More than ever, we need to understand the link between our tech systems and the business and customer services they support.
I recently had the opportunity to attend a briefing by ServiceNow regarding their new “AI-Powered Service Operations” that highlighted their service-aware CMDB – adding machine learning to their service mapping capabilities. The upgraded offering has the ability to map entire environments in hours or minutes – not months or weeks. And as a machine learning capability, it is only likely to get smarter – to learn from their customers’ use of the service and begin to recognise what applications, systems, and infrastructure are likely to be supporting each business service.
This heralds a new era in service management – one where the actual business and customer impact of outages is known immediately; where the decision to delay an upgrade or fix to a known problem can be made with a full understanding of the impacts. At one of my previous employers, email went down for about a week. It was finally attributed to an upgrade to network equipment that sat between the email system and the corporate network and the internet. The tech teams were scratching their heads for days as there was no documented link between this piece of hardware and the email system. The impact of the outage was certainly felt by the business – but had it happened at the end of the financial year, it could have impacted perhaps 10-20% of the business bookings as many deals came in at that time.
Being able to understand the link between infrastructure, cloud services, applications, databases, middleware and business processes and services is of huge value to every business – particularly as the percentage of business through digital channels and touchpoints continues to accelerate.

Focused on Digital Transformation? It is now more about how fast you can react to market shifts by using specific infrastructural resources.
This period is about digital acceleration. Cloud automation, artificial intelligence (AI), robotic process automation (RPA) and machine learning are all means to accelerate using infrastructure scalability.
Digital acceleration addresses the pace of change
Enterprises are searching to find unique and innovative ways to leverage cloud infrastructures with automation and intelligence. This is both to modernise and to optimise business processes while decreasing expenses. The speed at which the economic landscape has changed during the pandemic has removed debates on cloud usage:
- Remote work from home (WFH) with the need for video conferencing and collaboration tools has been supported by cloud
- Record amounts of SPAM and hacking attempts during the pandemic have leveraged cloud implementations for key security controls
- Tracking apps and classification and encryption of personally identifiable information (PII) via mobile devices are using cloud technology for greater automation and use of AI
Bandwidth and capacity are needed now. The ability to pivot, turn and shoot forward is critical to surviving and thriving in today’s radically changed marketplace. Cloud enablement can deliver enhanced customer experiences, monetise data assets, and can create new revenue streams by enabling new business models.
Cloud enablement explained
Digital acceleration is driven by cloud enablement, amplifying the enterprise value in the infrastructural investment.
Cloud enablement is an ongoing operational model. It incorporates orchestration, correctly organising teams, and a shift away from thinking only about platforms. The cloud platform is now a launchpad, not the main choice that has to be made. Orchestration is around the business and the business model, not just the technology.
Creating a cloud enablement strategic vision can identify where you need to go. It can provide the necessary requirements for expertise along the journey and deliver rapid, meaningful automation services engagements to deliver unbreakable delivery pipelines and agile cloud operations.
But this also involves managing and adjusting on the fly. Initial platform decisions, rolling out countless configuration changes and adjusting to new cloud investments make cloud enablement a tricky road to manage. Enterprises need to be cloud-smart towards their own business model and their strategy. Whatever configuration (on-prem, hybrid, private, public) combination works is dependent on many factors, including industry, size of the enterprise, employee resources and location.
The goal is implementing secure, flexible, scalable, and cost-effective cloud solutions. To do this requires regular cloud enablement audits as to the state of play and measuring successes.
Building and maintaining modern IT
Modern IT is hybrid and all the pieces that collect and manage the data need to be properly and securely managed. Just as technological (and economic) disruption has generally led to automation and the elimination of outdated processes, it has also always created new ideas and innovations.
One way to make your organisation more data-centric and digital is to selectively invest in those technology choices that are most adaptable and flexible to business needs. Data is the most strategic of assets and can be empowered by increasingly sophisticated intelligent operations. Process automation and AI help put that data to work by adding valued intelligence and encapsulating information.
Hybrid cloud coordination automated
Hybrid cloud coordination is an increasing enterprise demand, particularly in the Asia Pacific region, leading to enhanced data centres with joint customer support like the new Tokyo interconnection with Oracle and Microsoft Azure. The key to successfully monitoring a distributed cloud ecosystem is not only in gathering data on usage; it’s about knowing which questions to ask to make it more efficient and effective. This includes tracking connectivity speeds, creating common technical support and using single sign-on for better security. Here both AI and automation can help.
In Asia Pacific, the multi-cloud theme is being promoted heavily among integration providers with solutions that can plug into multiple clouds with virtual machine usage. Enterprises value enabled automated orchestration between cloud platforms. There will be a continued need for integrated tools across public and private clouds. This includes advanced analytics and AI as important aspects of an IT infrastructural investment.
Your choice of vendor for AI & Automation
In my opinion, AWS has the broadest AI service capabilities in the Asia Pacific cloud/ AI space, when compared to Microsoft, Google, and IBM. AWS provides users with pre-trained AI services for computer vision, language, recommendations, and forecasting to build, train, and deploy machine learning models at scale.
The Ecosystm VendorScope (Figure 1) rates the leading AI & Automation vendors in Asia Pacific based solely on quantifiable feedback from those who actually procure technology. It becomes clear from the responses that many organisations still start their AI journey through Automation. 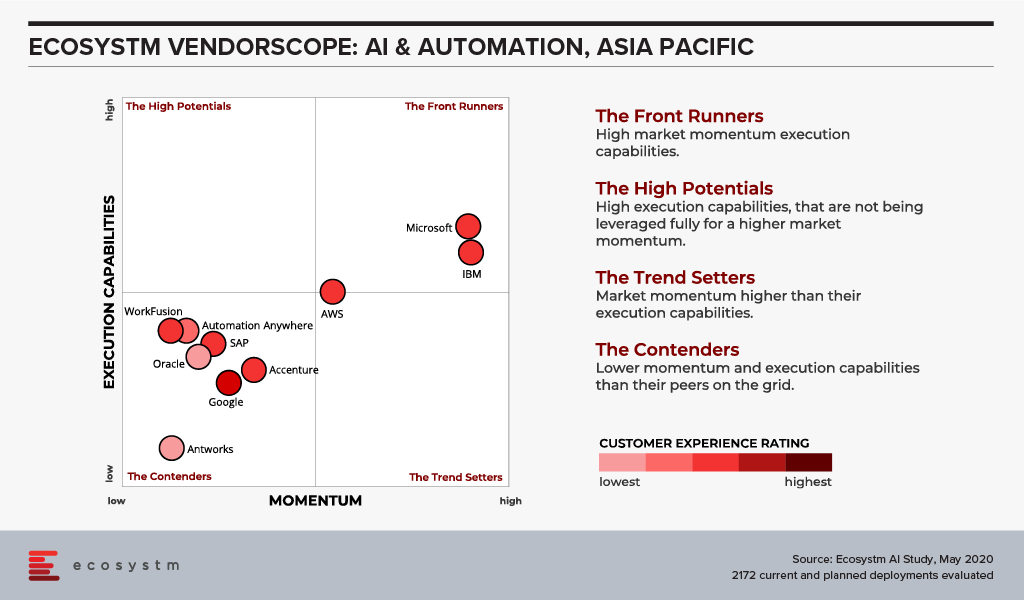
Most organisations understand the importance of leveraging AI to gain competitive advantage. But they do not necessarily know where to start. The secret is that AI is about intelligent process automation, and the firms who understand this are not the ones automating tasks. The use of RPA with vendors such as Antworks, WorkFusion, Arago and Automation Anywhere, leverages automated reasoning using knowledge-based problem-solving engines. These vendors add RPA to AI, not the other way around.
And domain-specific service providers have been creating the synergies for enterprises to link intelligent automation software and industry knowledge to create the necessary end-to-end workflows. An innate understanding of the specific business process is key to leveraging intelligent automation.
Focusing on developing a modern data supply chain process, with actionable analytics insights built into the infrastructure, can aid the development of self-service business intelligence capabilities along with visual data discovery solutions.
Cloud enablement solutions generate maximum business value by enabling IT with scalability and flexibility. This can reduce maintenance and security costs. A focus on cloud intelligence and scalability allows IT departments to concentrate more on innovative solutions, insights and systems that drive significant business growth. Now is the time, and speed is of the essence.
Ecosystm Vendorscope: AI & Automation
Sign up for Free to download the Ecosystm Vendorscope: AI & Automation report.





