In this Insight, our guest author Anupam Verma talks about how the Global Capability Centres (GCCs) in India are poised to become Global Transformation Centres. “In the post-COVID world, industry boundaries are blurring, and business models are being transformed for the digital age. While traditional functions of GCCs will continue to be providing efficiencies, GCCs will be ‘Digital Transformation Centres’ for global businesses.”

India has a lot to offer to the world of technology and transformation. Attracted by the talent pool, enabling policies, digital infrastructure, and competitive cost structure, MNCs have long embraced India as a preferred destination for Global Capability Centres (GCCs). It has been reported that India has more than 1,700 GCCs with an estimated global market share of over 50%.
GCCs employ around 1 million Indian professionals and has an immense impact on the economy, contributing an estimated USD 30 billion. US MNCs have the largest presence in the market and the dominating industries are BSFI, Engineering & Manufacturing, Tech & Consulting.
GCC capabilities have always been evolving
The journey began with MNCs setting up captives for cost optimisation & operational excellence. GCCs started handling operations (such as back-office and business support functions), IT support (such as app development and maintenance, remote IT infrastructure, and help desk) and customer service contact centres for the parent organisation.
In the second phase, MNCs started leveraging GCCs as centers of excellence (CoE). The focus then was product innovation, Engineering Design & R&D. BFSI and Professional Services firms started expanding the scope to cover research, underwriting, and consulting etc. Some global MNCs that have large GCCs in India are Apple, Microsoft, Google, Nissan, Ford, Qualcomm, Cisco, Wells Fargo, Bank of America, Barclays, Standard Chartered, and KPMG.
In the post-COVID world, industry boundaries are blurring, and business models are being transformed for the digital age. While traditional functions of GCCs will continue to be providing efficiencies, GCCs will be “Digital Transformation Centres” for global businesses.
The New Age GCC in the post-COVID world
On one hand, the pandemic broke through cultural barriers that had prevented remote operations and work. The world became remote everything! On the other hand, it accelerated digital adoption in organisations. Businesses are re-imagining customer experiences and fast-tracking digital transformation enabled by technology (Figure 1). High digital adoption and rising customer expectations will also be a big catalyst for change.
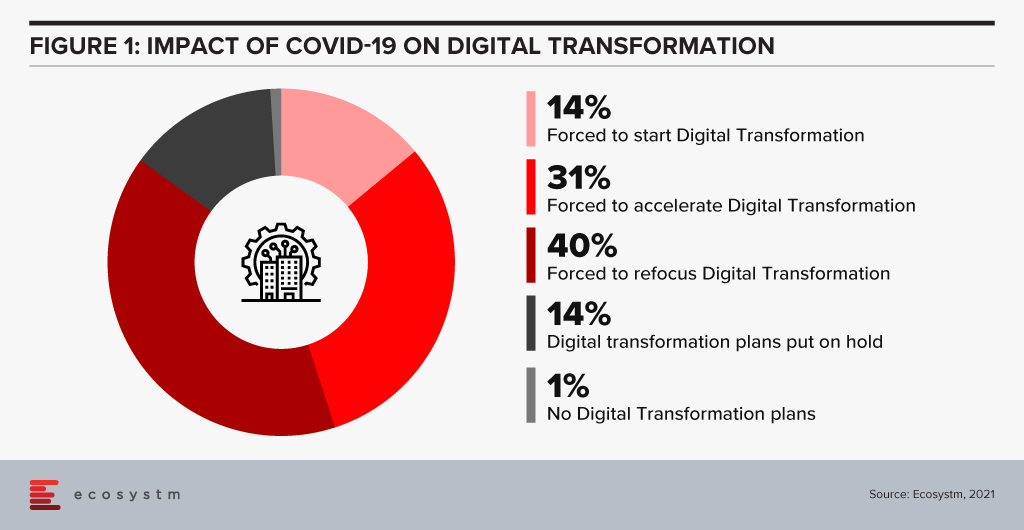
In last few years, India has seen a surge in talent pool in emerging technologies such as data analytics, experience design, AI/ML, robotic process automation, IoT, cloud, blockchain and cybersecurity. GCCs in India will leverage this talent pool and play a pivotal role in enabling digital transformation at a global scale. GCCs will have direct and significant impacts on global business performance and top line growth creating long-term stakeholder value – and not be only about cost optimisation.
GCCs in India will also play an important role in digitisation and automation of existing processes, risk management and fraud prevention using data analytics and managing new risks like cybersecurity.
More and more MNCs in traditional businesses will add GCCs in India over the next decade and the existing 1,700 plus GCCs will grow in scale and scope focussing on innovation. Shift of supply chains to India will also be supported by Engineering R & D Centres. GCCs passed the pandemic test with flying colours when an exceptionally large workforce transitioned to the Work from Home model. In a matter of weeks, the resilience, continuity, and efficiency of GCCs returned to pre-pandemic levels with a distributed and remote workforce.
A Final Take
Having said that, I believe the growth spurt in GCCs in India will come from new-age businesses. Consumer-facing platforms (eCommerce marketplaces, Healthtechs, Edtechs, and Fintechs) are creating digital native businesses. As of June 2021, there are more than 700 unicorns trying to solve different problems using technology and data. Currently, very few unicorns have GCCs in India (notable names being Uber, Grab, Gojek). However, this segment will be one of the biggest growth drivers.
Currently, only 10% of the GCCs in India are from Asia Pacific organisations. Some of the prominent names being Hitachi, Rakuten, Panasonic, Samsung, LG, and Foxconn. Asian MNCs have an opportunity to move fast and stay relevant. This segment is also expected to grow disproportionately.
New age GCCs in India have the potential to be the crown jewel for global MNCs. For India, this has a huge potential for job creation and development of Smart City ecosystems. In this decade, growth of GCCs will be one of the core pillars of India’s journey to a USD 5 trillion economy.
The views and opinions mentioned in the article are personal.
Anupam Verma is part of the Senior Leadership team at ICICI Bank and his responsibilities have included leading the Bank’s strategy in South East Asia to play a significant role in capturing Investment, NRI remittance, and trade flows between SEA and India.

Last week I wrote about the need to remove hype from reality when it comes to AI. But what will ensure that your AI projects succeed?
It is quite obvious that success is determined by human aspects rather than technological factors. We have identified four key organisational actions that enable successful AI implementation at scale (Figure 1).
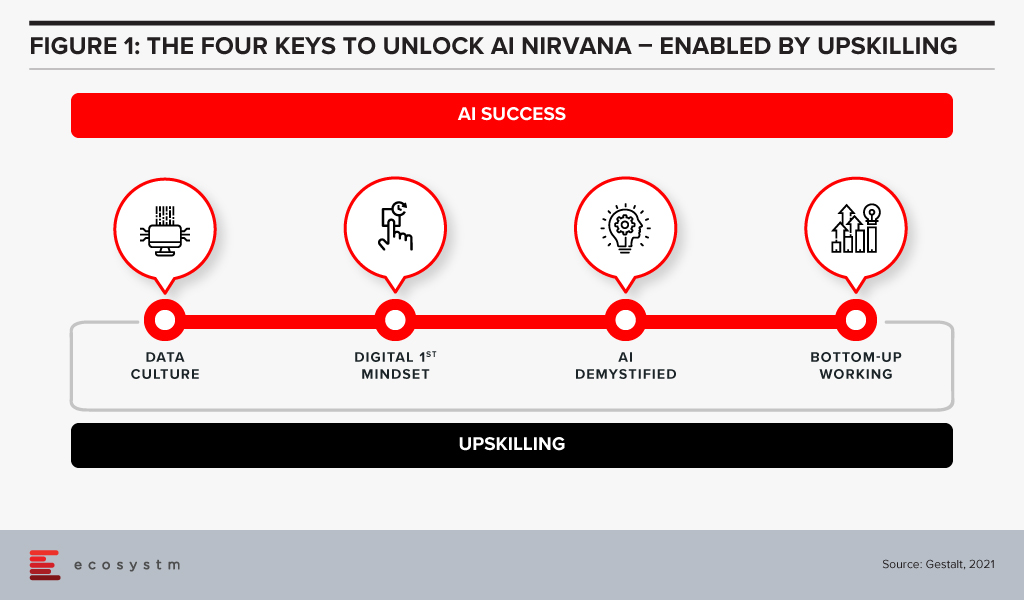
#1 Establish a Data Culture
The traditional focus for companies has been on ensuring access to good, clean data sets and the proper use of that data. Ecosystm research shows that only 28% of organisations focused on customer service, also focus on creating a data-driven organisational culture. But our experience has shown that culture is more critical than having the data. Does the organisation have a culture of using data to drive decisions? Does every level of the organisation understand and use data insights to do their day-to-day jobs? Is decision-making data-driven and decentralised, needing to be escalated only when there is ambiguity or need for strategic clarity? Do business teams push for new data sources when they are not able to get the insights they need?
Without this kind of culture, it may be possible to implement individual pieces of automation in a specific area or process, applying brute force to see it through. In order to transform the business and truly extract the power of AI, we advise organisations to build a culture of data-driven decision-making first. That organisational mindset, will make you capable implementing AI at scale. Focusing on changing the organisational culture will deliver greater returns than trying to implement piecemeal AI projects – even in the short to mid-term.
#2 Ingrain a Digital-First Mindset
Assuming a firm has passed the data culture hurdle, it needs to consider whether it has adopted a digital-first mindset. AI is one of many technologies that impact businesses, along with AR/VR, IoT, 5G, cloud and Blockchain to name a few. Today’s environment requires firms to be capable of utilising a variety of these technologies – often together – and possessing a workforce capable of using these digital tools.
A workforce with the digital-first mindset looks for a digital solution to problems wherever appropriate. They have a good understanding of digital technologies relevant to their space and understand key digital methodologies – such as Customer 360 to deliver a truly superior customer experience or Agile methodologies to successfully manage AI at scale.
AI needs business managers at the operational levels to work with IT or AI tech teams to pinpoint processes that are right for AI. They need to make an estimation based on historical data of what specific problems require an AI solution. This is enabled by the digital-first mindset.
#3 Demystify AI
The next step is to get business leaders, functional leaders, and business operational teams – not just those who work with AI – to acquire a basic understanding of AI.
They do not need to learn the intricacies of programming or how to create neural networks or anything nearly as technical in nature. However, all levels from the leadership down should have a solid understanding of what AI can do, the basics of how it works, how the process of training data results in improved outcomes and so on. They need to understand the continuous learning nature of AI solutions, getting better over time. While AI tools may recommend an answer, human insight is often needed to make a correct decision off this recommendation.
#4 Drive Implementation Bottom-Up
AI projects need alignment, objectives, strategy – and leadership and executive buy-in. But a very important aspect of an AI-driven organisation that is able to build scalable AI, is letting projects run bottom up.
As an example, a reputed Life Sciences company embarked on a multi-year AI project to improve productivity. They wanted to use NLP, Discovery, Cognitive Assist and ML to augment clinical proficiency of doctors and expected significant benefits in drug discovery and clinical trials by leveraging the immense dataset that was built over the last 20 years.
The company ran this like any other transformation project, with a central program management team taking the lead with the help of an AI Centre of Competency. These two teams developed a compelling business case, and identified initial pilots aligned with the long-term objectives of the program. However, after 18 months, they had very few tangible outcomes. Everyone including doctors, research scientists, technicians, and administrators, who participated in the program had their own interpretation of what AI was not able to do.
Discussion revealed that the doctors and researchers felt that they were training AI to replace themselves. Seeing a tool trying to mimic the same access and understanding of numerous documents baffled them at best. They were not ready to work with AI programs step-by-step to help AI tools learn and discover new insights.
At this point, we suggested approaching the project bottom-up – wherein the participating teams would decide specific projects to take up. This developed a culture where teams collaborated as well as competed with each other, to find new ways to use AI. Employees were shown a roadmap of how their jobs would be enhanced by offloading routine decisions to AI. They were shown that AI tools augment the employees’ cognitive capabilities and made them more effective.
The team working on critical trials found these tools extremely useful and were able to collaborate with other organisations specialising in similar trials. They created the metadata and used ML algorithms to discover new insights. Working bottom-up led to a very successful AI deployment.
We have seen time and again that while leadership may set the strategy and objectives, it is best to let the teams work bottom-up to come up with the projects to implement.
#5 Invest in Upskilling
The four “keys” are important to build an AI-powered, future-proof enterprise. They are all human related – and when they come together to work as a winning formula is when organisations invest in upskilling. Upskilling is the common glue and each factor requires specific kinds of upskilling (Figure 2).
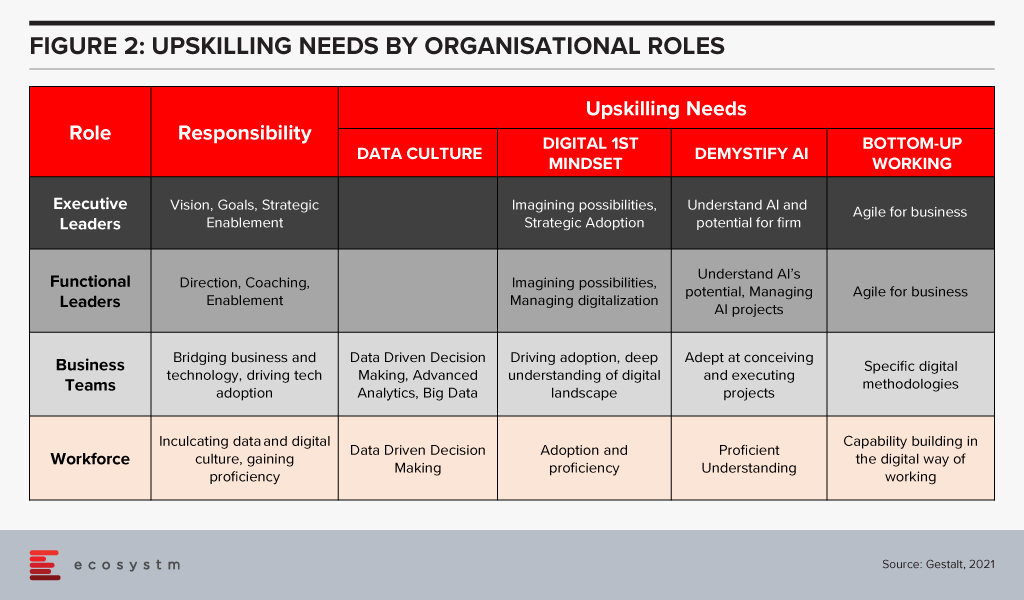
Upskilling needs vary by organisational level and the key being addressed. The bottom line is that upskilling is a universal requirement for driving AI at scale, successfully. And many organisations are realising it fast – Bosch and DBS Bank are some of the notable examples.
How much is your organisation invested in upskilling for AI implementation at scale? Share your stories in the comment box below.
Written with contributions from Ravi Pattamatta and Ratnesh Prasad

Moving from a product or regional focus to an industry focus appears to be the “strategy du jour” for many technology vendors today. For some it is a new strategy – with the plan to improve customer focus and increase growth; for others it is the pendulum moving back to where they were five or ten years ago as they bounce from being industry-centric to product-centric to geography-centric and back again.
Getting your industry focus right is much harder than it seems – and has to be timed with client needs and market opportunity. The need to focus on the industry varies for different technology products, services and capabilities. For example, most technology buyers want their vendors to understand what their business does and how they add value to customers – that is a given and industry-aligned Sales teams make a lot of sense. Many tech buyers also want certain software functions to align directly to their processes – there is little appetite to customise ERP and financial suites to specific industry needs and processes – and tech vendors should support these out-of-the-box or cloud needs.
Industry Solutions May Not Drive Competitive Advantage
If the industry solution you are selling is the same as what any of their competitors can buy from you, then organisations get the exact same benefit as the market – no more, no less. For example, about 10-15 years ago, large telecom providers around the globe made significant investments in CRM platforms (often from Siebel) – bringing in one of a few large global systems integrators to deploy their standard processes and systems. These CRMs were supposed to provide business and customer benefit, and drive competitive advantage. And while they did deliver positive change (often at SIGNIFICANT cost!) when every telecom provider was using the same solution with the same or similar processes, any competitive advantage was lost.
Industry Solutions are Often the Sign of a Mature Market
The widely accepted hypothesis is that the technology innovation and adoption happens in waves. The market has 5-7 year waves of innovation, followed by 5-7 year waves of deployment, adoption and consolidation.
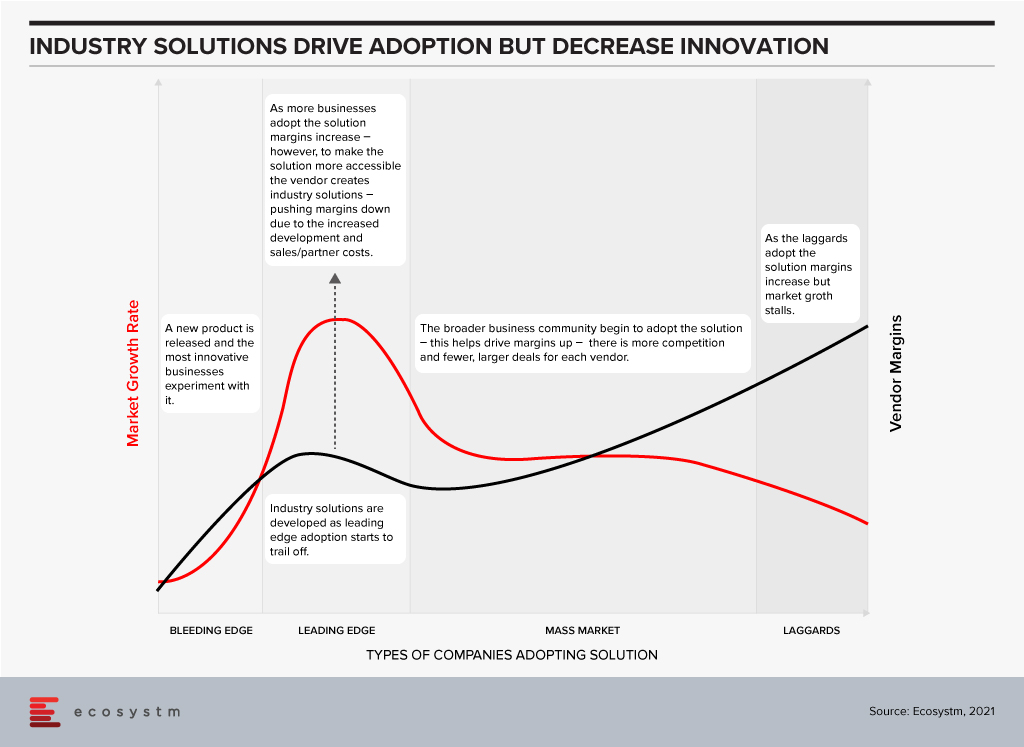
The Innovation Phase. In this stage new companies emerge, new products or services are launched and leading/bleeding edge companies embrace these new technologies to drive competitive advantage and business growth. They experiment with new technologies that drive new business capabilities – sometimes failing, but always pushing the envelope for business innovation and forging the path for mass market adoption. In this stage there is often little demand for industry solutions – as both the providers and buyers of the solutions are still working out where the business benefit is; where the technology might be able to drive change or help them get ahead of competitors. If you examine the growth of a company such as Salesforce, you see that the early stage products are targeted towards a generic market – customers are expected to customise the solution based on their needs and individual requirements. In 2002 I worked for a challenger telecom provider that had deployed a traditional Peoplesoft CRM capability, and I was part of the team that brought Salesforce into the business – and as a cloud-based solution, we saw the competitive advantage was the pace at which we could customise the product (by excluding IT teams and processes). However, the solution was a “one-size-fits-all” product. The innovation stage is typically characterised by high growth of smaller vendors and technology service providers who challenge the status quo.
The Deployment, Adoption and Consolidation Phase. This stage of market growth is when the mass market starts to adopt these solutions. Many of these buyers walk the paths that have been forged before them by the more innovative, leading edge businesses. This stage typically sees less innovation, less experimentation, and more standard deployments. To make the solutions more palatable and easier to sell to the mass market tech vendors typically pre-configure or customise the solutions to specific needs – for business teams, roles or industries. It is usually in this stage of market growth and deployment that the industry solutions see significant interest and adoption. This is where the mass market gets access to the business benefits the more innovative businesses received many years earlier (and often profited from in this time). In my example of the Salesforce deployment in 2002, over the following years many partners started to create industry solutions, and eventually Salesforce themselves sold industry-specific solutions – or at least targeted certain products and capabilities at specific industries and provided accelerated deployment models to drive advantage at a faster rate. The deployment and consolidation stage of market growth is typically characterised by steady, slow growth across the entire market as benefits are being driven to all providers (product vendors and solutions or implementation providers). Legacy providers either play catch up or suffer declining business as they realise the solution they sell no longer provides the business and customer the benefits that it used to.
Industry Focus Should be Aligned to Customer Segments, Solution Type and Geography
The decision to sell industry-focused solutions should be driven by the type of solution you are selling; the business benefit you are promising; and the type of business you are targeting the solution towards. Businesses that are more innovative will still buy some pre-configured, industry-specific solutions that don’t differentiate their business or drive competitive advantage. But where they expect competitive advantage, they need to stand apart – to be the only business with that capability.
It is also worth understanding that an innovation in one market might be standard practice in another (and vice-versa). Countries across the globe and specifically here in Asia Pacific have different approaches to technology and innovation. China and parts of Southeast Asia are often innovators – pushing the boundaries of new and emerging tech to do things we never thought possible (in the same way Silicon Valley traditionally has done). Australia and India are traditional markets that adopt industry solutions after they have been tried and tested by others. Innovation in Japan seems to happen in stages and at pace but only once every 10-15 years or so. New Zealand and Singapore are generally more nimble economies where businesses often have to be innovative to gain global competitive advantage quickly.
Evidence indicates that the rate of innovation is increasing across the entire region – even in the less innovative economies. The window for industry solutions is much smaller regardless of location – as the next new innovation is just around the corner. Even the large, traditionally less agile businesses are driving innovation programs – for example, many of the big financial services “dinosaurs” such as DBS and Commonwealth Bank often win tech innovation awards and offer market-leading customer experiences.
Use this lens to better develop your industry approach. The depth of your industry solution or capability will dictate the opportunities that you will drive based on the type of customer and technology stage. Do you want to drive innovation or efficiency in your clients? Do you want to win the big “safer” deals – but be thought of as a technology solution provider; or win the smaller deals in companies that will become the market leaders of tomorrow – and be considered a market leader and king maker? Understanding your own business goals, the current sales and delivery capabilities, and the capacity to change will help your company create a go-to-market strategy that suits your current and future customers and will likely dictate the growth rate of your business over the next 5-7 years.
Keep yourself abreast with the latest industry trends
Ecosystm market insights, data, and reports are jam-packed with industry analysis and digital trends across several industry verticals to help you keep tabs on the fast-paced world of tech.

Woolworths have announced the adoption of a new Software-as-a-Service capability from One Door to support the quality and compliance of their in-store merchandising. There are some valuable lessons from this announcement for other retailers.
The power of data, particularly as the capability of specialist AI tools improves, continues to help retailers improve their offering to customers.
SaaS Capabilities Offer Performance Improvements
Woolworths are working on improving the compliance of product merchandising in-store using One Door Visual Merchandising solution.
One Door will improve the accuracy of data available to both the in-store teams and for the central supermarket merchandising team. The supply chain in Woolworths is already highly automated but getting the shelf presence right is dependent on the quality of data being captured. While store teams already use a range of electronic tools to capture this information, the compliance with store planograms and visual merchandising standards has been difficult to automate.
One Door’s solution provides a single source of this information in an easy to use digital format. The AI tools that One Door have developed appear to be able to show the degree of compliance of the actual shelf layout and stock position.
For store teams, One Door will simplify tracking layout changes by highlighting them and making the data available on the shop floor. This should deliver productivity benefits to the store – benefits that can be reinvested in new activities or on better customer service.
Store teams will be able to verify that third party merchandisers are compliant. Major product manufacturers often use their own merchandising teams in supermarkets and One Door will provide a simple mechanism to verify they have done their jobs properly.
The central merchandise teams will be able to quickly get data-driven feedback on how the stores are making planned changes, as well as verifying the quality of compliance with their store layouts.
All of these factors should mean that the product that is available in-store is presented in the manner that the merchandising teams have defined, and the customers will see a more consistent presentation of products.
Integration is Critical for Rapid Deployment
Effective integration with existing systems and new cloud capabilities is critical to support the real-time operation in Retail.
The ability to introduce and scale up new capabilities that can be delivered by cloud services such as One Door will only be effective if integration is simple and quick. This requires compatibility at a number of levels including data semantics and the ability to exchange data effectively. Woolworths have been growing their capability for managing and supporting APIs that will make this integration smoother.
In addition, the cloud service providers have made the development of integration capabilities an investment priority.
The introduction of One Door is showing how the company can integrate new capability and introduce it to almost 10% of their stores as a pilot capability, with the full deployment to be completed across their chain during 2022.
Other retailers who don’t have this capability to integrate cloud services quickly, reliably and cost-effectively are going to lag companies that have invested to achieve this capability.
CIOs and CDOs should be leading their organisations in the development of a rich and scalable set of APIs to enable the integration of this type of high-value specialised solution.
Deployment without Consistent Architectures will be Complex
Rapid deployment of new capabilities requires a well-architected cloud, network, and edge infrastructure – and a well-trained team.
It is highly likely that the deployment of the One Door solution will be delivered over the existing Woolworths infrastructure. The capability is delivered from the cloud, with little or no deployment costs or time required. With the existing network and hybrid cloud capabilities that Woolworths have developed this type of rollout will be a relatively simple technical activity.
The integration of the service into the Woolworths environment is likely to be the most complex activity to make sure accurate data is exchanged.
It doesn’t take long to identify a wide range of different digital initiatives that Woolworths are pursuing. With the platform that they have established, they are well-positioned to take advantage of new capabilities as start-ups and existing suppliers develop them.
Every retailer needs to maintain their focus on their digital capabilities. As companies such as One Door develop AI-based enhancements, CIOs and their teams need to be ready to integrate these capabilities quickly.
Strong architectures for both infrastructure and digital services are needed to achieve these outcomes.
Recommendations for Retailers
Retail organisations continue to find new ways to leverage the power of the data that they are able to collect. The flexibility that SaaS developments deliver will be essential to maintaining an organisation’s competitive positioning.
CIOs and their teams need to lead their organisations and ecosystems by:
- Identifying new SaaS capabilities that support the strategic positioning of their companies
- Preparing their environments by supporting a rich set of APIs to support the rapid integration of these new capabilities
- Developing and maintaining strong architectures that provide organisations a solid framework to develop within
Checkout Alan’s previous insight on Woolworths micro automation technology adopted to speed up the fulfilment of online grocery orders

Hitachi announced their plans to acquire US based software development company GlobalLogic for an estimated USD 9.6 billion, including debt repayment. The transaction is expected to close by end of July, after which GlobalLogic will function under Hitachi’s Global Digital Holdings.
GlobalLogic was founded in 2000, and the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board and Swiss investment firm Partners Group have 45% of ownership; with the remainder owned by the company’s management.
Hitachi’s Business Portfolio Expansion
The acquisition of GlobalLogic is a part of Hitachi’s move to focus and extend the range of Hitachi’s digital services business. As Hitachi aims to expand from electronics hardware to concentrate on digital services, they are looking to benefit from GlobalLogic’s range of expertise – from chips to cloud services. Silicon Valley-based GlobalLogic has a presence in 14 countries with more than 20,000 employees and 400 active clients in industries including telecommunications, healthcare, technology, finance and automotive. This will also expand Hitachi’s network outside Japan by providing them access to a global customer base and will boost their software and solutions platforms, including Hitachi IoT portfolio and data analytics.
The GlobalLogic deal follows another big acquisition of ABB’s power grid business by Hitachi in July 2020 to focus on clean energy and distributed energy frontiers. This makes Hitachi one of the largest global grid equipment and service providers in all regions.
Hitachi is also planning to divest parts of their portfolio such as Hitachi Metals, their chemical unit and their medical equipment business.
Ecosystm Comments

“Hitachi’s move to acquire GlobalLogic is very interesting and is in line with the growing trend of global Operation Technology (OT) vendors riding the wave of Industry 4.0 and ‘Product as a Service’ models – essentially, to move up the margin ladder with more digital services added on to their already established equipment business. Siemens, Schneider Electric, Panasonic, ABB, Hitachi and Johnson Controls are some of the prominent vendors who have taken pole positions in their respective industry domains, in this race to digitally transform their businesses and business models. Last year, Panasonic made a very similar move, taking a 20% equity stake in Blue Yonder, a leading supply chain software provider.
With rapid advancements in computing and communications (5G), it is now possible to converge the IT (Information Technology supporting enterprise information flows), the OT (Operational Technology – machine level control of the physical equipment), and the ET (Engineering Technology in the Product Design and Development space such as CAD, CAM, PDM etc.) domains. Three worlds that were separate till now. The convergence of these three worlds enables high impact use cases in automation, product, process, and business model innovation in almost all sectors, such as autonomous vehicles, energy efficient buildings, asset tracking and monitoring, and predictive and prescriptive maintenance. For the OT vendors therefore, it becomes critical to acquire IT and ET capabilities to become successful in the new cyber physical world. Most OT vendors are choosing to acquire these capabilities through strategic partnerships (such as Siemens with Atos and SAP; Panasonic with Blue Yonder) or acquisitions (such as Hitachi and GlobalLogic) rather than develop such capabilities organically in completely new domains.“

The ways we connect, create, collaborate in our workplaces has seen major shifts in the last year. And the tech industry has continually supported that shift as they create new capabilities and upgrade existing ones. Technology providers will continue to revamp their product offerings to support the increase in adoption of the hybrid work model work – a fusion of remote and in-office. In the Top 5 Future of Work Trends for 2021, Ecosystm had predicted, “Every major digital workspace provider (such as Microsoft, Google, Zoom, Cisco, AWS and so on) will broaden their digital workplace capabilities and integrate them more effectively, making them easier to procure and use. Instead of a “tool-centric” approach to getting work done (chat vs video vs document sharing vs online meetings vs whiteboards and so on), it will become a platform play.”
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Ravi Bhogaraju says, “It is becoming clear that companies and individuals are grappling with three issues – the changing size and composition of the workforce; the productivity of those who are driving the businesses; and attracting, reskilling and engaging the broader workforce.” These are the challenges that tech providers will have to help organisations with.
Google Upgrades its Collaboration Platform
The Google Workspace was launched in October last year, and last week saw the tech giant announce a series of upgrades and innovations to better support the flexibility needs of frontline and remote workers.
Workspace is Google’s office productivity suite comprising video conferencing, cloud storage, collaboration tools, security and management controls built into a cohesive environment. The new features announced by Google Workspaces include Focus Time to avoid distractions by limiting notifications, recurring out-of-office and location indicators to make colleagues aware if the person is working from home or office, support for Google voice assistant in workplaces, second-screen experiences to support multiple devices, and features for frontline workers designed to help mobile employees collaborate and communicate better with the rest of the organisation. Google is also working on a trimmed down version of Google Workspace – Google Workspace Essentials – which will provide support for Chat, Jamboard, and Calendar. Workspace is estimated to have 2.6 billion monthly active users.
Bhogaraju says, “One of the issues that is fast emerging as significant is not just the employee experience or customer experience but the complexity of the digital workplace as platforms introduce newer and advanced features. In the end, there has to be simplicity, clarity, and a clear focus on the goals – not just an overload of features that makes life more complex for the employee. It would be critical to enable these features thoughtfully and reskill staff adequately so that the adoption and impact to business process is felt in their day-to-day activities.”
Workspace Transformation across Industries
With many of Google’s employees and developers working remotely, the company has first-hand experience of the challenges of remote working and is leveraging the experience. Google Workspace is also working on custom solutions for various industries. In Retail for example, Woolworths, rolled out Google Workspace and Chrome for geographically dispersed teams to collaborate in real-time and adopt custom-made applications linked to global servers to allow managers to log and address tickets from the shop floor itself. Similarly in Aviation, All Nippon Airways uses Google Workspace to allow pilots, cabin attendants, HR and finance staff to communicate and collaborate in real-time across the globe, using Google Meet, Google Docs, Google Sheets and Google Slides from their PCs, smartphones or tablets. Google retains its focus on the Education industry – Google Workspace Education Fundamentals is free for all qualifying institutions. Solutions such as Google’s Classroom, Teach from Anywhere hub, roster sync, mobile grading and EdTech tools aim to enable better learning and teaching experience for students and educators.
Tech Companies Revamping their Collaboration Offerings
With more companies rethinking their work policies, leaders in the collaboration space are also stepping up their game to evolve their offerings for the hybrid norm. Microsoft’s Viva unifies the experience across Teams and Microsoft 365 for employee communications, wellbeing, learning and knowledge discovery. Similarly, Zoom too has upgraded and integrated various utility, sharing, and management features to support a hybrid workforce. Tech companies are being forced to invest in creating next-generation tools to stay relevant, as Future of Work models continue to shift and evolve.
As tech companies evolve their capabilities, Bhogaraju warns organisations on how they should leverage them. “While technology companies continue to deliver feature rich suites – in reality the uptake and embedding of these programs into the day-to-day business processes is still in its early stages. Business, HR and IT teams continue to struggle. They tend to operate within independent thought silos and there is limited consensus on which feature is really needed and how it can add to the productivity and efficiency. Without this crucial context and an effective change management program – they remain rich features and not impactful ones.”
The hybrid workplace model is gaining popularity in 2021. Check out Ecosytsm’s top 5 Future of Work Trends For 2021. Signup for Free to download the report.

In the recently published the Top 5 Cybersecurity & Compliance Trends for 2021 report Ecosystm predicts that 2021 is when M&As will ramp up in earnest to consolidate the fragmented cybersecurity market. The pandemic has slowed down M&A activities in 2020. Early signs of what we can expect from the market when we emerge from COVID-19 can be seen in the recent acquisition of Asavie by Akamai Technologies. The market is realising the full implication of the shift to remote working and the potential of increased cyber threats – and this acquisition is a sign that larger vendors will continue to strengthen their cybersecurity capabilities by acquiring vendors, with complementary capabilities.
Asavie Enabling the Secure Office Anywhere
Asavie, headquartered in Ireland, offers a global platform that manages the security, performance, and access policies for mobile and internet-connected devices. Asavie delivers secure access to business resources for a mobile workforce – without requiring installation and management of client software. Increasing mobile workloads and Office Anywhere trends mean that the enterprise private network is no longer just PCs/laptops. All enterprise endpoints must be considered to be a part of the enterprise network – and security and authentication solutions must be able to handle this. Organisations will need to explore options where they can give seamless access to their employees without straining their IT and cybersecurity teams – a rapidly installable, scalable, and cloud-managed solution will become a necessity.
More than ever before, enterprises will have to treat all endpoints as branches of the organisation, and the Future of Work goes beyond enabling home offices. The Global CXO Study: The Future of the Secure Office Anywhere finds that 66% of IT and business leaders think of multiple locations, when they think of Office Anywhere. Employees will work wherever they get the best work experience and are most productive. Future work patterns will require that all endpoints are considered as extended branches of the organisation. This involves the ability to extend the enterprise WAN – with speed, flexibility, and security in mind – whether it is a temporary or a home office, an ad-hoc point of sales or an employee on the go. Every employee or device should be treated like a Branch of One.
Ecosystm Comments

“Akamai has been diversifying away from its well-known content delivery network (CDN) offering and has successfully built its security business offering in recent years. In 2019, the company nearly doubled its security revenue to USD 849 million from just USD 488 million in 2017. In their 3rd quarter financial results reported in end October 2020, the Cloud Security Solutions revenue was US$266 million, up 23% year-over-year.”
“The move into the mobile security segment has been timely for Akamai as enterprise application and content is moving from behind the firewall to the cloud; adding to the criticality of the cybersecurity threat management. The COVID-19 pandemic has further driven the onboarding of businesses and consumers alike, adding to significant addressable market opportunities.”
“The acquisition of Asavie is a strategic move. Asavie’s solution effectively extends the enterprise security management to incorporate mobile devices as a ‘Branch of One’ enabling CIOs and CISOs to manage security and policies the same way as traditional enterprise network resources. The growth of 5G will further drive IoT devices and a myriad of applications and use cases which will provide for a significant growth opportunity for Akamai – the acquisition of Asavie is a positive move to support this trend.”
Akamai Strengthens Intelligent Edge Capabilities
Asavie’s mobile, IoT and security solutions will integrate with Akamai’s Security and Personalisation Services (SPS) product line sold to carrier partners that embed the solution within the technology bundle sold to their subscribers. With the Asavie acquisition, Akamai intends to help their carrier partners address enterprise and mid-market customer demand for IoT and mobile device security and management services.
Ecosystm Comments

“The addition of Asavie to Akamai’s SPS product line provides synergy for the company to expand into new addressable markets for the remote workforce and internet-connected devices to deliver superior experience in a multi-cloud environment. The Global CXO Study conducted by Ecosystm found that three quarters of the organisations rate mobile security as an important or very important part of their digital transformation strategy. Secure mobile experiences will be a core element of the enterprise going forward in the post COVID-19 business environment – driven by employee needs for mobile services and corporate resources from remote locations, with superior identity and policy management, in a frictionless manner.”
“There is an opportunity for mobile service providers and mobile virtual network operators (MVNOs) to leverage the Asavie solution combined with Akamai’s strength at the edge with over 1,500 networks worldwide to offer cloud-based value-added cybersecurity services. The Global CXO Study also found that scaling of endpoint security was a major pain point for half the organisations with more than 100 branches. Service providers can become the enabler by offering services for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to dynamically adapt their network and security services to fluctuating demand conditions.”

“Although Akamai does offer CDN services for the SME segment, the company heavily relies on service providers and carriers to address this segment in the CDN, cloud security and its burgeoning IoT Edge offerings. Asavie’s market approach is similar and its products and services portfolio appears to complement Akamai’s very well, making it a very good fit for the company. Not only will it enhance Akamai’s SME positioning on the secure connectivity space, but it will also boost its offerings for carriers in the IoT space.”
“Carriers have had a checkered history at best, in understanding and making the most of data services. Mobile Internet took off because of smartphone manufacturers (Apple) and Internet companies – not through carrier offerings. Although carriers appear to be more proactive and forward-looking with regards to IoT, they should not expect to have the foresight to see what services and business cases will make 5G and IoT truly profitable. Rather, their main focus should be on enabling the secure and flexible infrastructure that can ultimately enable others to develop the use cases. The next logical step would then be for carriers to develop IoT orchestration platforms that can manage much larger parts of the IoT value chain. If they succeed in this (and even if they don’t) it could result in a major boost for Akamai’s CDN business.”
“In other words, carriers need help with IoT and to that end, Akamai’s acquisition of Asavie may strengthen its ability to support carriers to reach that goal.”
The full findings and implications of The top 5 Cybersecurity & Compliance Trends For 2021 are available for download from the Ecosystm platform. Sign up for Free to download the report.

Five9, a cloud-based contact centre solutions provider announced the acquisition of intelligent virtual agent (IVA) platform provider, Inference Solutions for about USD 172 million. Five9 and Inference Solutions have been partnering for the last couple of years, with Five9 being a reseller for Inference Solutions’ IVA platform. The acquisition is expected to provide a boost to Five9’s AI portfolio, automate contact centre agent activities and provide AI-based omnichannel self-service solutions.
The need to drive greater automation in the contact centre is high on the agenda, and this acquisition demonstrates how important AI and automation is to contact centre modernisation. The old-fashioned ways of long wait times, being passed on through different menus on the IVR and being asked to repeat yourself through the older speech recognition engines is starting to not only frustrate customers but will become obsolete. Based on Ecosystm’s research, close to 60% of contact centres globally stated that investing in machine learning and AI is a top customer experience priority in the next 12 months.
Inference has come a long way since its inception at Telstra Labs
Inference Solutions (founded in 2005) was spun out of Telstra Labs. It has since expanded to the US and developed a suite of solutions in the IVA segment. They have a good partnership strategy with the leading telecom providers globally as well as the UC/contact centre vendors. Inference Solutions uses resellers such as service providers, UC, and contact centre software providers – and these include AT&T, Cisco (Broadsoft), Momentum Telecom, Nextiva, 8×8 and many others. The Inference Studio solution will see a new release in the next few months where the solution will come pre-built with the ability for the contact centre team to pre-load the contact centre conversations. These can be conversations that have been going on for 6 months or longer. The Studio solution will then be able to analyse and understand the underlying intent of the conversation, match the intent so that it can be used to auto train the bots accurately. That process of matching the intent and training is expensive and if you can automate some elements of that, it will bring the cost of the deployment down. Its solution integrates into NLP engines from Google, AWS, and IBM. In Australia they continue to work on patents in close partnerships with Melbourne University and RMIT. Throughout its journey, Inference has built a good base of customers in the US, UK, and Australia.
Five9 to accelerate on its vision of AI and Cloud
Contact centre modernisation is high on the agenda for many organisations and this will lead them to build AI and automation at the core of their customer strategies. The discussion spans across the CEO, Digital and Innovation, and the Contact Centre teams.
Five9 had acquired Whendu, an iPaaS platform provider empowering businesses and developers with no-code, visual application workflow tool, optimised for contact centres in November 2019, and Virtual Observer, an innovative provider of cloud-based workforce optimisation, also known as Workforce Engagement Management (WEM) in February of this year.
The pandemic has resulted in increased engagement of contact centres with customers. Companies are gradually looking for ways to automate tasks, deliver better communication, speech and text recognition, decipher languages, and implement solutions mimicking humans. As a solution to these challenges, IVAs are being viewed as efficient and effective digital workers for a modern contact centre. IVAs represent increased throughput, more accurate results, and better-informed agents.
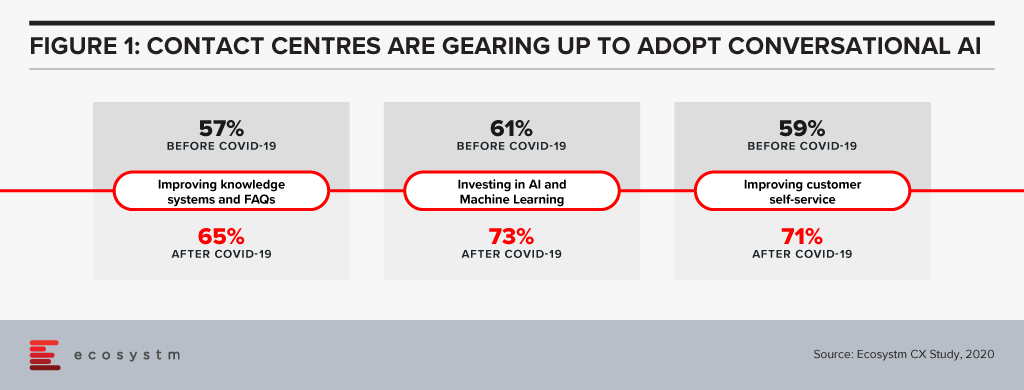
Successful use cases have shown that conversational AI can reduce calls and repetitive queries by 70-90%. IVRs with monolithic, complicated menus will start becoming unpopular and force contact centres to embark on a modernisation and automation strategy. If we evaluate the shift in priorities after COVID-19, we see that organisations are ramping up their self-service capabilities and their adopt of AI and machine learning (Figure 1).
The acquisition will give Five9 a foothold in the Asia Pacific region with an initial focus on the Australia market. The Australia market is by far the most advanced cloud contact centre market in the Asia Pacific. Five9 gains a team of staff that will help them fuel the contact centre modernisation discussion across the Asia Pacific. As the region has a complex market, the need to work with local carriers and partners will be critical for further expansion. Five9 has made an important acquisition in building in IVA capability into its CCaaS solution.
Click below to access insights from the Ecosystm Contact Centre Study on visibility into organisations’ priorities when running a Contact Centre (both in-house and outsourced models) and the technologies implemented and being evaluated

Authored by Alea Fairchild and Audrey William
Video conferencing company Zoom hosted its virtual Zoomtopia user conference lasts week. Given the attention the company has received as the de-facto standard video communication service for the many stranded work-from-home folks, Zoom has been using the event to launch a number of new products. This includes bringing into general availability its OnZoom events platform and marketplace, and introducing Zapps which brings apps from other providers into the Zoom experience.
ZaaP!
In this age of work-from-home connectivity, we are all asked to multi-platform depending on customer preference, company standards and choice of scale-out from a licensing perspective. But will video-led unified communications help position Zoom to be the infrastructure platform of choice of the workforce? Will Zoom as a Platform (ZaaP!) become a well-used phrase to discuss unified collaboration infrastructures?
The agenda of Zoomtopia, covering healthcare, government, financial services, sales engagement, blending learning in education, mindfulness, CSR, and a whole gambit of other vertical topics, demonstrates a virtual play to highlight use cases where other platforms have focused on the horizontal aspect of productivity.
If you compare Microsoft’s horizontal approach with Cisco’s networking approach, both come from places of productivity. Zoom, being video-led and UC oriented, comes from a place of communication and collaboration. Is collaboration now the real driver for the future of work?
Zoom connects the dots with these two product introductions. Zapps is designed to link productivity tools directly into the Zoom experience for user access to multiple applications from the platform. OnZoom allows hosts to run one-time events or event series with up to 100 or 1,000 attendees (depending on their license) and sell tickets for them. Zoom is also integrating the ability to receive donations through events via Pledgeling. Think a combination of EventBrite meeting GoFundMe meeting Facebook Events.
Zooming Ahead
With the wide variety of activities during this social distancing period around the world that have been Zoom-powered, familiarity leads to experimentation and early adoption.
Without using the word ‘portal’ – Zoom as a Platform (ZaaP!) enforces the drive for a main infrastructure for live interaction via video as the main means of communication over written material or pre-recorded media materials. And many of us are video-led, more than ever.
Zoom is scaling rapidly. When it started out many years ago, they were known as a company that offered video sessions for free and everyone was wondering who this new kid on the block was. In a span of a few years, they have become a powerhouse.
The announcement of OnZoom is something that marketeers will take note of. Many marketeers are Zoom users but could be using other platforms for hosting events. The solution will have in-built tools for selling tickets, scheduling, gifting tickets, promotional activities, etc. Zoom is thinking about video and layering that with added functionality to run a large-scale event. You can see them going into using AI to churn out rich analytics on attendees, attendance rates, effectiveness of campaigns and so on. All of a sudden it is about hosting an event with in-built rich features plus analytics so events can be run better. They are reaching a new audience and making it a fully built all-purpose solution for event organisers and marketeers.
Security Front and Centre
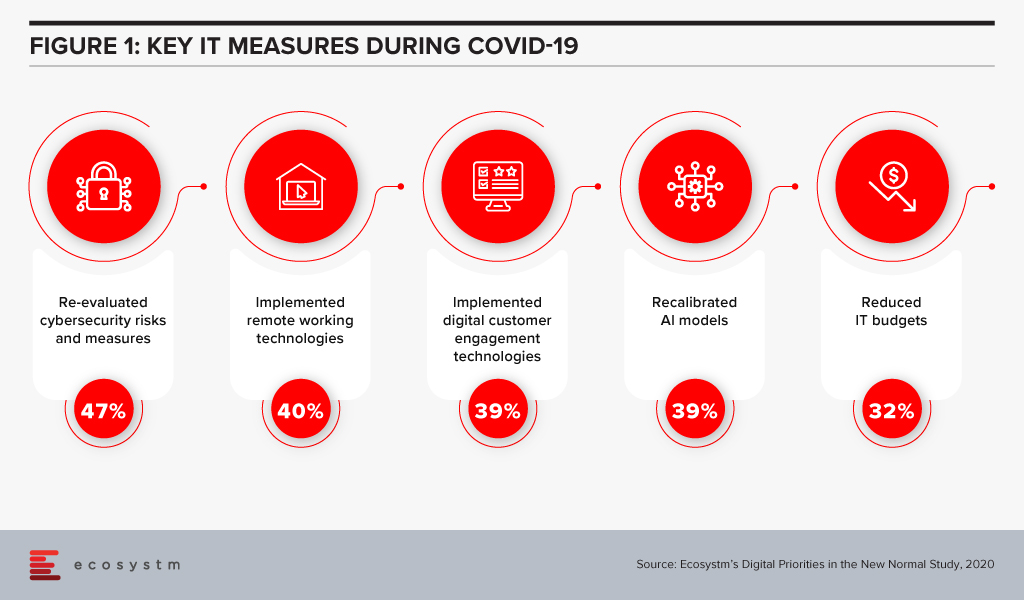
Ecosystm research shows that security has been a key component in organisation’s COVID-19 responses – and rightly so (Figure 1).
While Zoom received some negative publicity this year around security, they were quick to admit the issues and made incremental changes in the subsequent months including an acquisition. With E2EE, no third party including Zoom is provided with access to the meeting’s private keys. Zoom’s E2EE ensures that communication between meeting participants using Zoom applications is encrypted using cryptographic keys known only to the devices of those participants. Zoom is starting to penetrate larger accounts and the security aspect is important as it is the top of the mind discussion for every business leader.
Ecosystm Comments
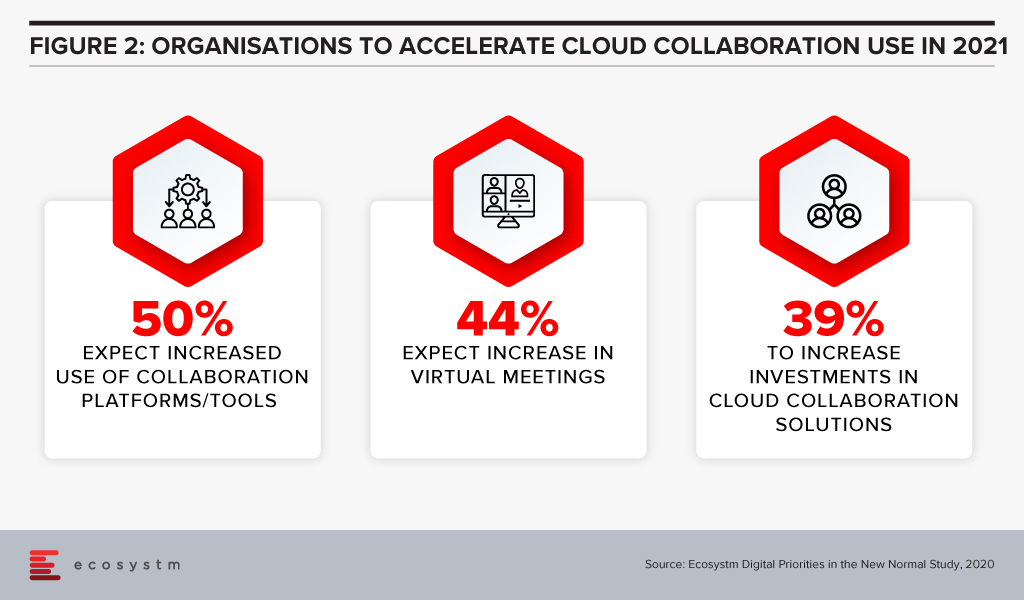
With the hybrid work model evolving between home and work, and work patterns changing, one thing that is going to stay is the use of video and collaboration tools and it is only going to accelerate (Figure 2).
What Zoom is doing well is how they take workflows and APIs seriously, making productivity flow into UC and UX, and not the other way around.
With longer work hours becoming a norm, growing instances of emotional stress and mental fatigue, UX becomes paramount. Knowledge workers want to seamlessly move between workflows and still find the experience simple and not tiring. Zoom is building on that vision as a platform enabler and infrastructure provider.











