Telstra and Microsoft have extended their partnership to jointly build solutions harnessing the capabilities of AI, IoT, and Digital Twin technologies in Australia. The partnership will also enable both companies to work on sustainability, emission reduction, and digital transformation initiatives.
The adoption of cloud and 5G technology is already on the rise and creating opportunities across the globe. The Microsoft-Telstra partnership is set to bring together the capabilities of both providers for businesses in Australia and globally. Their focus on AI, IoT, cloud and 5G will enable Australia’s developers and independent software vendors (ISVs) to leverage AI with low latency 5G access to drive efficiency, and enhance decision making. This will also see practical applications and new solutions in areas like asset tracking, supply chain management, and smart spaces to enhance customer experience.
Technology Enhancing the Built Environment
Microsoft Azure and Telstra’s 5G capabilities will come together to develop new industry solutions – the combination of cloud computing power and telecom infrastructure will enable businesses and industries to leverage a unified IoT platform where they can get information through sensors, and perform real-time compute and data operations. Telstra and Microsoft will also build digital twins for Telstra’s customers and Telstra’s own commercial buildings which will be initially deployed at five buildings. Upon completion, the digital twin will enable Telstra to form a digital nerve centre and map physical environments in a virtual space based on real-world models and plot what-if scenarios.
Telstra CEO, Andy Penn says, “If you think about the physical world – manufacturing, cities, buildings, mining, logistics – the physical world hasn’t really been digitised yet. So, how do you digitise the physical world? Well, what you do is put sensors into physical assets. Those sensors can draw information around that physical asset, which you can then capture and then understand.”
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Mike Zamora finds the comment interesting and says, “It isn’t so much that the physical world is digitized – it is more about how digital tools enhance and enable the physical world to be more effective to help the occupier of the space. This has been the history of the physical space. There have been many ‘tools’ over time to help the physical world – the elevator in the late 1880s enabled office buildings to be taller; the use of steel improved structural support, allowing structural walls to be thinner and buildings taller. These two ‘tools’ enabled the modern skyscraper to be born. The HVAC system developed in the early 1900s, enabled occupants to be more comfortable inside a building year-round in any climate.”
“Digital tools (sensors, etc) are just the latest to be used to enhance the physical space for the occupant. Digital twins enable an idea to be replicated in 3D – prior to having to spend millions of dollars and hundreds of man hours to see if a new idea is viable. Its advent and use enable more experimentation at a lower cost and faster set up. This equates into a lower risk. It is a welcomed tool which will propel the experimentation in the physical world.”
Talking about emerging technologies, Zamora says, “Digital twins along with other digital tools, such as 3D printing, AI, drones with 4K cameras and others will enable the built environment to develop at a very quick pace. It is the pace that will be welcomed, as the built environment is typically a slow-moving asset (pardon the pun).”
“Expect the Built Environment developers, designers, investors, and occupiers to welcome the concept. It will allow them to dream of the possible.”
Telstra and Microsoft – Joint Goals
Telstra and Microsoft have partnered over the years over multiple projects. Last year, the companies partnered to bring Telstra’s eSIM functionality to Windows devices for data and wireless connectivity; they have also worked on Telstra Data Hub for secured data sharing between data producers, businesses and government agencies; and most recently collaborated on Telstra’s exclusive access to Xbox All Access subscription service to Australian gamers with the announcement of Microsoft’s Xbox Series X and Xbox Series S gaming consoles expected to release in November.
This announcement also sees them work jointly towards their sustainability goals. Both companies are committed to sustainability and addressing climate change. Earlier this year, Microsoft announced its plans to be carbon negative by 2030, while Telstra has also set a target to generate 100% renewable energy by 2025 and reducing its absolute carbon emissions by 50% by the same time. To enable sustainability, Telstra and Microsoft are exploring technology to reduce carbon emissions. This includes further adoption of cloud for operations and services, remote working, and piloting on real-time data reporting solutions.
Telstra also aims to leverage Microsoft technology for its ongoing internal digital transformation, adopting Microsoft Azure as its cloud platform to streamline operations, and infrastructure modernisation, including transition from legacy and on-premise infrastructure to cloud based applications.

Last year Microsoft announced it was developing a new version of Flight Simulator which caught many of us by surprise. Flight Simulator? Really? The last launch of a new version of the game was in 2006 – 14 years ago, now!! How does something come back after all these years?
Now that it has launched about a week ago, the initial feedback has been extremely positive and it appears that Microsoft has a winner here. An analysis even claims that it will spur $2.6 billion in hardware sales of PCs, game accessories and the like!
I wanted to unpeel the onion a bit to take a closer look at what is going on and discovered a world of interesting developments around this product.
My first thoughts on hearing the announcement was that Microsoft, who has been steadily losing the battle of consoles to Sony’s PlayStation platform, was reviving this old favourite to resuscitate its drooping share.
Not a bad move. Flight Simulator has a core of die-hard fans – it even boasts of professional pilots who play the game as relaxation. It has a long history and a captive fan community. But it is old. That loyal community is not part of the demographic that a gaming company would normally look at today.
The other interesting aspect to consider is the COVID-19 situation this year. Obviously, Microsoft did not know this at the time they embarked on this project but the pandemic has turned everything on its head – hardware sales are through the roof – including accessories, at a time when people have been homebound and looking for entertainment within the four walls of one’s abode. The Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal study finds that 76% of organisations increased their hardware investments when the crisis hit – and 67% of organisations expect their hardware spending to go up in 2020-21. And that is only on the enterprise side of things. On the consumer side, at this point joysticks are in short supply – a trend that seems to have been accelerated by the Microsoft launch last week, interestingly – and so are PCs. The PC vendors are all enjoying a bumper year of growth. This is an ideal time to launch a really cool new version of the game.
Microsoft’s Bigger Game
The reality however is that while Flight Simulator will add to the revenue and also give Xbox One a fillip, Microsoft is probably after a much bigger “game” (excuse the pun!). The company has called its ‘Xbox Game Pass’ the Netflix of the gaming market. With multiple cloud-based gaming platforms having been launched – many with subscription services – the battle is on to decide the winners in a relatively new space. To this end, Microsoft has announced an intention to make Game Pass available across different devices – XBox console, PCs, tablets, phones. Having a title like Flight Simulator available through Game Pass, will act as a key hook to get customers to sign up for the subscription.
The new Flight Simulator version has been developed using AI and real-world imagery brought in with data from Bing Maps. With the newly added realistic scenery, it also seems like a great fit for use with the HoloLens Virtual Reality headsets. In one shot Microsoft is showcasing their lead in areas of technology which are likely to prove attractive to developers in a big way. I believe that this is a way for them to entice more developers on to Azure and to Microsoft cloud to develop their games – “AI SDKs anyone? Virtual Reality tools anyone?”
What seems at first glance like the launch of a new “future is here” version of a great game will turn out to be a possible big swing at multiple targets by Microsoft – at leadership in gaming with Game Pass; at reviving Xbox fortunes; at leadership in game development platforms, with Azure packing AI services, Bing Maps, AR/VR tools, among other technologies to move more development on to the Microsoft cloud. In the process Microsoft launched a highly enjoyable game and got closer to their ultimate aim to indeed become the Netflix of gaming.
Great move Microsoft! Tip: This could also give them a foothold in the virtual travel and virtual vacations market! That would be a hot seller in these times.
We continue to receive responses from the tech buyer community on the impact of COVID-19 on Digital Transformation initiatives, and the early business and technology measures that were implemented to combat the crisis. As the months go by, it is becoming apparent that organisations have implemented the early measures and are now looking ahead to their journey to recovery.
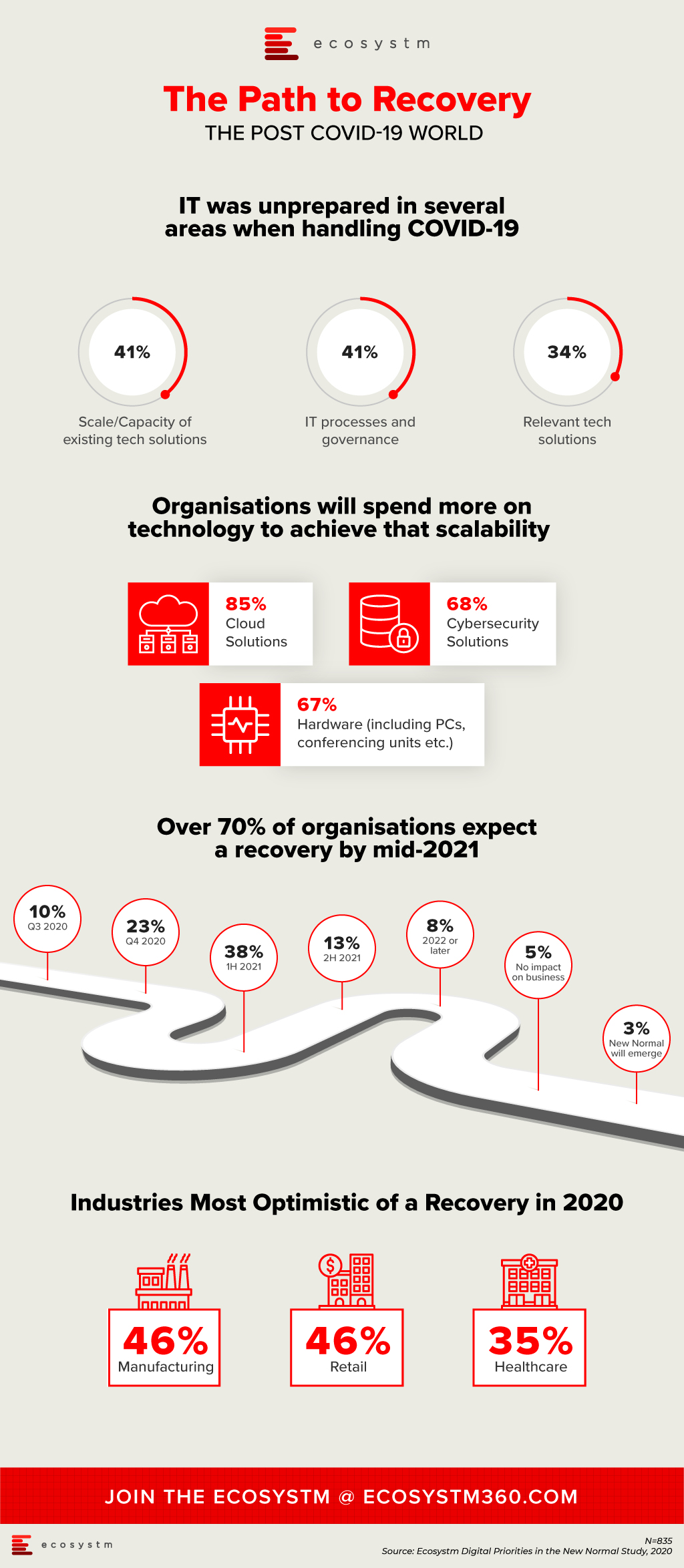
IT Teams realised that even if they had the right technology solutions, they were unprepared for the scale or capacity to extend these technology offerings to handle the sudden and enormous changes required to manage the crisis. Their cloud business applications, cybersecurity and collaboration solutions were simply not sufficient to meet the needs of the remote workforce. As organisations become more conscious of business continuity planning (BCP) for future eventualities, they will boost their technology capabilities, over the next 12 months.
Another area the study aims to explore is how optimistic is the business outlook, when it comes to expecting a return to normalcy. Only 3% of organisations are expecting a New Normal that is very different from where things were at the beginning of the year. About a third of organisations are expecting a return to normalcy by the end of the year, while the majority expect to recover by the middle of 2021. Also, some industries are more optimistic of a recovery than others. As an example, 35% of healthcare organisations expect a return to normalcy by the end of the year. This is a positive indicator, given that the industry has been in the forefront of the crisis, for nearly 6 months now.
More insights on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and technology areas that will see continued investments, as organisations get into the recovery phase, can be found in the Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study.
As organisations stride towards digitalisation, re-evaluate their business continuity plans and define what the Future of Work will look for them, Cloud adoption is expected to surge. In June, there were several announcements that indicate the market is responding to this increased interest.
Cloud Providers Gearing up to Enable Economic Recovery
Global economies are slowly gearing up for a technology-led recovery phase and several organisations are taking advantage of the disruption to start or accelerate their digital transformation plans. Many are looking at this as a good opportunity to replace their legacy systems. Cloud providers are expected to lead from the front when it comes to helping the economy recover.
Government agencies have been immensely impacted by the COVID-19 crisis and will need to shift fast into the recovery mode. Salesforce launched a multi-tenant dedicated Cloud infrastructure for their US Federal, state and local government customers, government contractors, and federally funded research and development centres. Hosted on AWS GovCloud and FedRAMP compliant, it provides customers with a compliant and secure environment to deploy Salesforce’s CRM platform and industry solutions. The launch is expected to empower government agencies with the ability to deliver better services, scale to unprecedented demands and connect to citizens on their channel of choice.
Initiatives such as the UK Crown Commercial Service (CCS) and Google Cloud agreement will also help in the recovery phase. This allows qualified public sector agencies to avail of a discounted price for their Google Cloud deployments. Earlier in the year CCS entered into a price arrangement with Microsoft as well. If Cloud has to be the vehicle for economic recovery, such arrangements will benefit cash-strapped public sector organisations.
The recovery will also require the entire technology ecosystem to engage not only with large enterprises but also small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Alibaba Cloud announced an investment of US$ 283 million to revamp its global partner program. They plan to introduce new partner-customer communication processes to enhance response time and bring more opportunities to independent software vendors (ISVs) managed service providers (MSPs) and system integrators (SIs) as partners.
Europe Emerging as a Cloud Hub
As a fallout of the current political scenario, Europe is pushing for more cloud independence and to become an innovation hub as a vendor-neutral network for cloud computing providers and their customers.
GAIA-X Foundation is a federated data infrastructure project initiated to build a unified system of cloud and data services to be protected by EU Laws – including GDPR, the free flow of non-personal data regulation and the Cybersecurity Act. France and Germany kicked off the GAIA-X cloud project last year and the system is open for participation to national and European initiatives for exchange of data across industries and services such as AI, IoT and data analytics. GAIA-X took another step towards becoming a real option for European organisations with the establishment as a legal entity in June. Various organisations – including Dassault, Orange, Siemens, SAP, Atos, Scaleway and Deutsche Telekom are a part of this non-profit platform, working together on Cloud applications, high-performance computing as well as edge systems. The project is expecting to release a working model by early 2021 and will be further enhanced in phases.
Global Cloud leaders are also focusing on expanding their presence in Europe. In February, Microsoft announced a new data centre in Spain leveraging Telefónica infrastructure. In a similar move, Google Cloud announced its plans to expand in the region in partnership with Telefónica. Telefonica and Google are expected to jointly work on Spain’s digitalisation through edge infrastructure and 5G for consumers and telecom infrastructure.
Cloud Providers Bolstering their Cybersecurity Capabilities
2020 has witnessed a host of cybersecurity threats and data breaches. While Cloud providers have always evolved their cybersecurity capabilities, it has become important for them to become vocal about these measures to build trust in the industry.
To complement the Microsoft Azure IoT security, Microsoft acquired IoT security specialist CyberX, last month. The acquisition will enable greater security for the IoT devices connected to the Microsoft network and will help their customers to gain visibility through a map of devices thus allowing them to gather information on security risks associated with thousands of sensors and connected devices. This will enhance smart grid, smart manufacturing and digital assets and profiles and reduce vulnerabilities across production and supply chain.
In another move which will benefit the ISV and SI ecosystem, NetFoundry’s zero trust networking API is now available on RapidAPI. RapidAPI’s marketplace enables developers to easily find, connect to, and manage the APIs they need to build a range of applications. Now the ISV and developer community can access NetFoundry’s software-only, zero trust models on RapidAPI.
More Partnerships between Software/Industry Solutions Providers and Cloud Providers
The COVID-19 crisis has had a far-reaching impact on several industries. The technologies that are expected to see the most uptake are IoT and Future of Work technologies.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “COVID-19 has brought to the fore the need for managing risks better. And the key to managing risks is to have better visibility and drive data-driven decisions; the sweet spot for IoT technologies.”
Last week, Microsoft and Hitachi announced a strategic alliance to accelerate the digital transformation of the Manufacturing and Logistics industries across Southeast Asia, Japan and North America. The first solutions are expected to be made available in Thailand as early as this month. Hitachi brings to the table their industry solutions, such as Lumada, and their IoT-ready industrial controllers HX Series. These solutions will be fully integrated with the Microsoft cloud platform, leveraging Azure, Dynamics 365 and Microsoft 365.
Another sector that has seen significant disruption is Real Estate. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Andrew Milroy in his blog Proptech: Driving Digital Transformation in the Wake of COVID-19 sees a real opportunity for the sector to transform. “Many activities within the property ecosystem have remained unchanged for decades. There are several opportunities for digital engagement and automation in this sector, ranging from the use of robots in construction to the ‘uberisation’ of the residential property customer journey.”
June saw Honeywell and SAP partner to create a joint cloud-based solution based on Honeywell Forge and SAP cloud. The cloud solution is aimed at real estate operators and customers providing aggregated financial and operational insights in real-time. The solution leverages the Honeywell Forge autonomous buildings solution and the SAP Cloud for Real Estate solution, enabling facility managers and building owners to reposition their real estate portfolios through parameters such as cost savings and energy efficiency and help improve the tenant experience.
As organisations struggle to maintain operations during the ongoing crisis, there has been an exponential increase in employees working from home and relying on the Future of Work technologies. Ecosystm principal Advisor, Audrey William says, “During the COVID-19 pandemic, people have become reliant on voice, video and collaboration tools and even when things go back to normal in the coming months, the blended way of work will be the norm. There has been a surge of video and collaboration technologies. The need to have good communication and collaboration tools whether at home or in the office has become a basic expectation especially when working from home. It has become non-negotiable.”
AWS and Slack announced a multi-year partnership to collaborate on solutions to enable the Workplace of the Future. This will give Slack users the ability to manage their AWS resources within Slack, as well as replace Slack’s voice and video call features with AWS’s Amazon Chime. And AWS will be using Slack for their internal communication and collaboration.
Delivering excellent customer experience in the midst of the crisis has proved to be difficult for organisations. Customer care centres have been especially impacted by high volumes of customer interactions – through voice and non-voice channels. This will see a major rise in adoption of cloud contact centre solutions. Contact centre providers are ramping up their capabilities in anticipation. Genesys selected AWS as their preferred cloud partner to deliver new features to customers and build a global and secure infrastructure.
The industry can expect more news from Cloud providers in the next few months as they ramp up their capabilities and channel their go-to-market messaging.
Gain access to more insights from the Ecosystm Cloud Study

I’m really excited to launch our AI and Automation VendorScope! This new tool can help technology buyers understand which vendors are offering an exceptional customer experience, which ones have momentum and which are executing and delivering on their promised capabilities. The positioning of vendors in Ecosystm VendorScopes is independent of analyst bias or opinion or vendor influence – customers directly rate their suppliers in our ongoing market benchmarks and assessments.
The Evolution of the AI Market
The AI market has evolved significantly over the past few years. It has gone from a niche, poorly understood technology, to a mainstream one. Projects have moved from large, complex, moonshot-style “change the world” initiatives to small, focused capabilities that look to deliver value quickly. And they have moved from primarily internally focused projects to delivering value to customers and partners. Even the current pandemic is changing the lens of AI projects as 38% of the companies we benchmarked in Asia Pacific in the Ecosystm Business Pulse Study, are recalibrating their AI models for the significant change in trading conditions and customer circumstances.
Automation has changed too – from a heavily fragmented market with many specific – and often very simple tools – to comprehensive suites of automation capabilities. We are also beginning to see the use of machine learning within the automation platforms as this market matures and chases after the bigger automation opportunities where processes are not only simplified but removed through intelligent automation.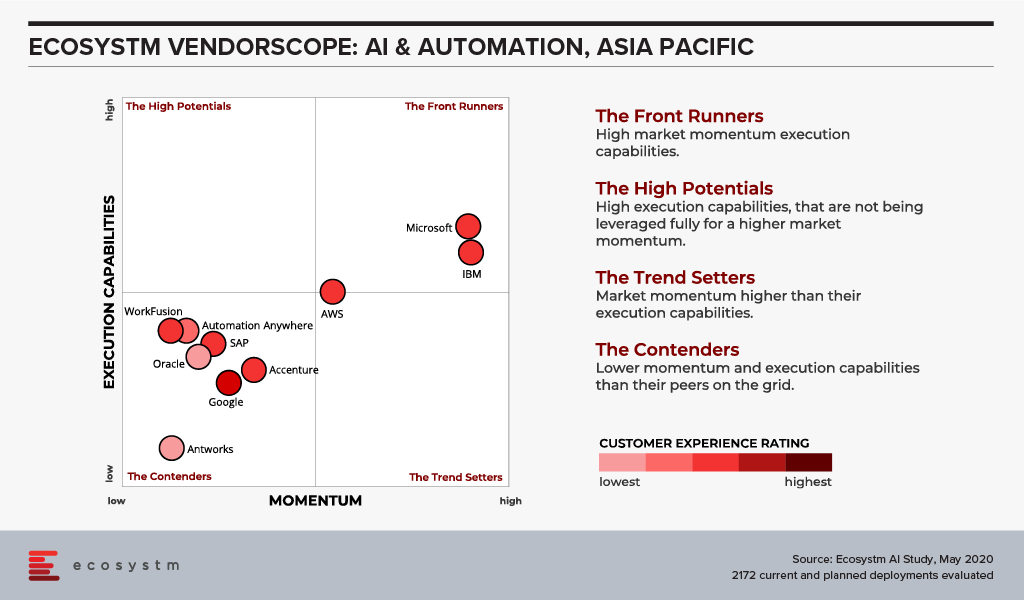
Cloud Platform Providers Continue to Lead
But what has changed little over the years is the dominance of the big cloud providers as the AI leaders. Azure, IBM and AWS continue to dominate customer mentions and intentions. And it is in customer mentions that the frontrunners in the VendorScope – Microsoft and IBM – set themselves apart. Not only are they important players today – but existing customers AND non-customers plan to use their services over the next 12-24 months. This gives them the market momentum over the other players. Even AWS and Google – the other two public cloud giants – who also have strong AI offerings – didn’t see the same proportions of customers and prospects planning to use their AI platforms and tools.
While Microsoft and IBM may have stolen the lead for now, they cannot expect the challengers to sit still. In the last few weeks alone we have seen several major launches of AI capabilities from some providers. And the Automation vendors are looking to new products and partnerships to take them forward.
Without the market momentum, Microsoft and IBM would still stand above the rest of the pack – just not as dramatically! Both companies are not just offering the AI building blocks, but also offer smart applications and services – this is possibly what sets them apart in an era where more and more customers want their applications to be smart out-of-the-box (or out-of-the-cloud). The appetite for long, expensive AI projects is waning – fast time to value will win deals today.
The biggest change in AI over the next few years will hopefully be more buyers demanding that their applications are smart out-of-the-box/cloud. AI and Automation shouldn’t be expensive add-ons – they should form the core of smart applications – applications that work for the business and for the customer. Applications that will deliver the next generation of employee and customer experiences.
Ecosystm Vendorscope: AI & Automation
Signup for Free to access the Ecosystm Vendorscope: AI & Automation report.

Contact centres across industries are being challenged by the current crisis because of the high volume of inbound interactions – through voice and non-voice channels. This has been further compounded by the need to move most of their customer care agents to their homes, especially in countries that have implemented strict social distancing and lockdown measures. This is particularly challenging for the public sector because they are having to respond to an influx of citizen queries regarding COVID-19 specifically (including test centres and availability) and other related areas (information on trade and travel, economic stimulus and so on).
Public Sector Focus on Citizen Experience
Ecosystm research reveals that public sector organisations are hugely focused on citizen experience (Figure 1). But other priorities include employee experience and innovation in their service provision.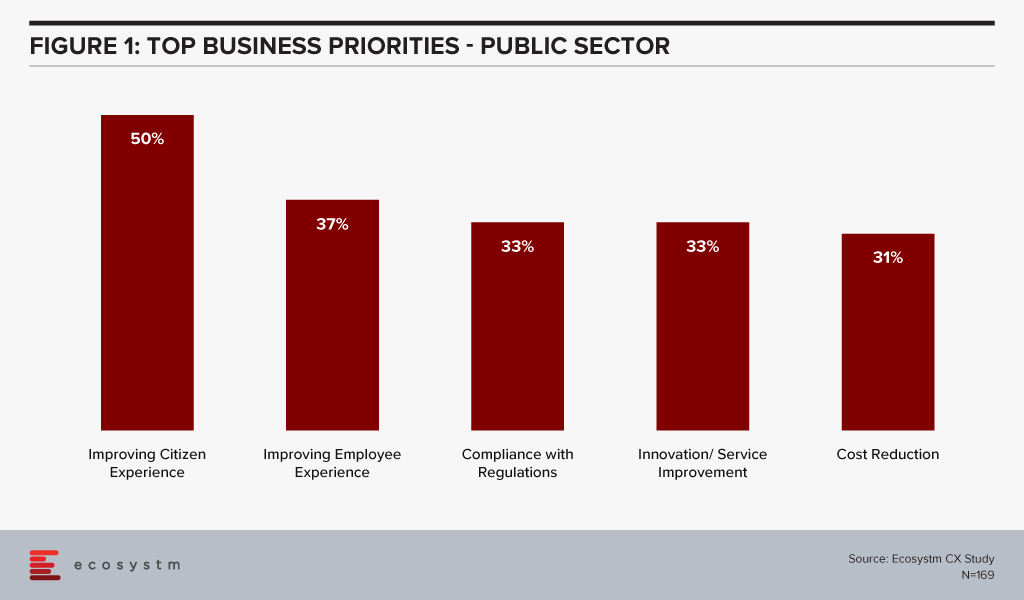
Being able to provide better and innovative service to citizens in a compliant manner is key for every public sector organisation. This has led to governments driving the uptake of cloud solutions, such as the New Zealand Government’s directive to public sector organisations that public cloud services are preferred over traditional IT systems, in order to enhance citizen experiences, streamline operations and create new delivery models. In 2018, the Singapore Government had announced the intention to use commercial cloud services in the public sector. This was fueled as much by the need to overhaul ageing infrastructure, as it was to provide exceptional citizen experience.
Public Sector Adopting Cloud Contact Centres
While the private sector is often quicker in their adoption of digital technologies for better customer experience (CX), the adoption in the public sector can be challenging due to various concerns such as legacy systems, privacy, national security, inter-departmental dependency and more. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Audrey William says, “Most cloud contact centre solution providers today have the highest level of security wraps and certifications including country-level certifications. However, verticals such as Government, have remained concerned about security. This has not allowed them to innovate as fast as some of the other sectors on leveraging some of the best-in-class customer experience technologies.”
In the US, MAXIMUS, a government services provider company and Genesys recently announced a partnership to set up the MAXIMUS Genesys Engagement Platform, an integrated, cloud-based omnichannel contact centre solution. This was driven by the government requirement for public sector organisations to provide seamless customer experiences similar to those offered in the private sector. The platform is certified by the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP). FedRAMP promotes the adoption of secure cloud services across the US Federal Government, in partnership with federal agencies, cloud service providers and 3rd party assessment organisations and provides the standards for security and risk assessment.
This is in line with what we see in the Ecosystm data. Government agencies that use contact centres are increasingly evaluating cloud options, with 17% saying that they operate fully on the cloud (Figure 2). While this may be difficult for all public sector organisations, with mandates around data location and security, a majority are partially on the cloud.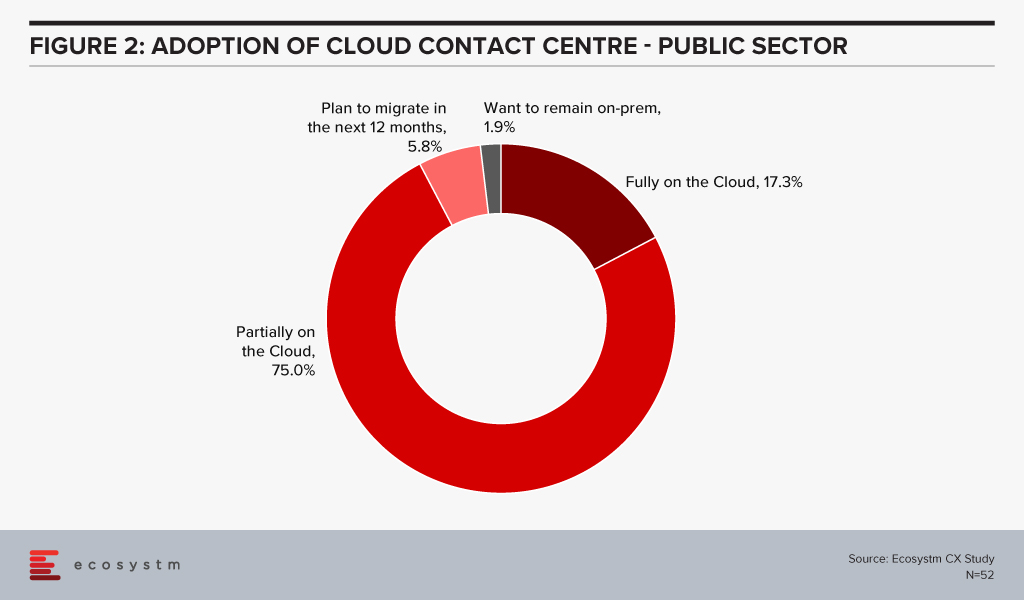
There are several benefits to using the cloud model including the ability to make changes and scale up/down without much customisation or professional services (which can come in handy for a quick re-alignment of the workforce) and manage seasonal spikes. Additionally, cloud solutions allow almost instantaneous access to new features and easy testing of proofs of concept. Public sector organisations are fast realising the value of cloud contact centres.
William sees the FedRAMP certification having immense potential. “FedRamp provides a secured environment for any service that is rolled out as this involves multiple levels of security. Citizens expect a more personalised service through chat, Twitter, mobile, social messaging channels like WhatsApp and many more. However, they also want to feel safe when providing personal information and want to know that the platform that holds their data is secure. When they know that security is at the highest level, they will be more open to providing personal data.”
Managing an Omnichannel Experience
Over half of public sector organisations in the Ecosystm CX study mentioned that they are driving an omnichannel experience for their customers. This has become especially relevant today, as organisations have the need to reduce the call volumes for their contact centres – through non-voice services and customer self-service. The MAXIMUS Genesys Engagement Platform will leverage Genesys Engage, which provides integrated features and functionalities across multiple channels through a single voice and digital user interface. Solutions such as these provide the ability to integrate calls, emails, chats, messages and social comments into one connected platform.
William says, “The cloud platform can help with the highest level of efficiency, scale and speed by integrating multiple channels on a single platform, for more connected customer experience. Government departments will look to leverage capabilities such as Conversational AI, in-app mobile messaging, SMS, email and voice calls within a multi secure environment. Citizens have high expectations from government departments – they expect fast, reliable and efficient service and automation. It would be difficult for governments to provide that level of service without leveraging cloud contact centre technology. That is the only way to move away from inefficient traditional architectures.”
Speaking about the adoption of cloud contact centres in the Asia Pacific region, William says, “Despite initiatives like Australia’s Digital Transformation Agency, the adoption has been relatively low in the public sector. But that has been changing fast with the COVID-19 situation forcing some government departments to move almost immediately to the cloud allowing easier changes to call workflows and other dynamic services that may have to be addressed on a daily basis.”

The opportunities that can be created by 5G continue to excite businesses and consumers alike. As 5G rollouts gather pace, new consumer experiences and business models emerge. For consumers, enhanced mobile broadband offers superior experience, driving the consumption of much more data-rich content and the more widespread application of emerging technologies such as augmented reality (AR). For businesses, the low latency, higher bandwidth, and the ability to handle massive machine type communications promised by 5G create opportunities for a dizzying array of uses cases, usually linked to IoT technology.
As enterprise use cases like autonomous driving, remote surgery and software-defined factories are enabled by 5G, the impact of cybersecurity breaches becomes much greater. Breaches can potentially have a catastrophic impact – they could lead to serious damage to or the destruction of sensitive critical infrastructures, such as power stations and transportation systems.
Security vulnerabilities associated with 5G are underpinned by a change in network architecture. The latency benefits of 5G require a more distributed architecture to enable use cases which require real-time data processing. This leads to the virtualisation of higher-level network functions formerly performed by physical appliances. So 5G networks will necessarily create a greatly expanded attack surface. If an attacker gains control of the software managing the networks, they can also control the network and potentially cause chaos.
One of the major benefits of 5G is massively increased bandwidth. This is also a huge benefit for attackers. An increase in available bandwidth makes it much easier to generate attack traffic from compromised connected devices and vulnerable networks. As volumetric DDoS attacks grow in terms of frequency, magnitude, and sophistication, traditional defences such as out-of-band scrubbing centres and manual interventions become inadequate and expensive.
In a 5G World, Security Postures must be Agile and not Act as a Bottleneck to Performance
5G use cases require a radical shift in cybersecurity posture and a new set of security considerations. Networks managed by enterprises and service providers need to scale up to handle larger capacity requirements and scale out to accommodate the increased demands of edge computing and the growing volumes of IoT endpoints. Security infrastructure must change accordingly with upgrades to both physical and virtual components. Importantly, security postures must also be sufficiently agile to change with new requirements while ensuring that security does not act as a bottleneck to network performance.
A common response to the increasing complexity of distributed cloud and IoT environments – where existing tools cannot always detect new and emerging threats – is to deploy brand new security tools. This seems like a great solution but can lead to significant problems and compromise security. Over time, the deployment of multiple security tools creates an estate of siloed security products, sometimes reporting to their own dashboards. Although this management challenge is typically being addressed by service providers and large enterprises, most commonly with SIEM, they must continually ensure that there is provision for the centralisation of security alerts, so that cybersecurity staff do not face the challenge of monitoring multiple consoles and cross-referencing between disparate screens and information formats. Applying security policy changes is a laborious and time-consuming task in a multi-dashboard environment – representing a security threat in its own right.
In the case of large volumetric attacks, redirecting suspicious traffic to scrubbing centres adds latency and imposes a significant financial burden, since mitigation costs are directly tied to the volume of the data traffic. Large enterprises and service providers should consider adopting new DDoS protection approaches that incorporate AI, real-time analysis, and telemetry to automate a more intelligent and cost-effective detection and mitigation process.
Different Policies Required to Reflect Specific Needs of Each Use Case
5G allows mobile service providers to partition their network resources, to address a diverse set of use cases with differing performance and functional requirements. These varying service performance profiles have a direct impact on security protocol choices and policy implementation. For instance, the service in one use case, such as a Smart City application, may require extremely long device battery life, which constrains the security protocol in some other way (e.g., how often re-authentication is performed). In another example, the use case may be very privacy-sensitive, requiring unusually intensive security procedures (e.g., very frequent reallocation of temporary identities).
The complexity associated with securing highly distributed and virtualised networks powered by 5G, will grow enormously and be hampered by an ever-increasing skills shortage. The only way to address these challenges is to create an intelligent security infrastructure that is sufficiently agile to scale with the network and use AI to detect, contain and eliminate threats. Security managers will need a unified view of all assets – physical and virtual – so that multiple security policies can be enforced and managed.
CEOs have an active role to play in an organisation’s transformation needs and journey – including in the technology decisions. Last month we spoke about why CEOs should get involved in their organisation’s IoT investments. Now, we look at Cloud – which has been a part of the CIO’s purview so far. Under the current circumstances, most organisations are actively pushing to go digital and the internal discussions will often revolve around empowering remote employees and digital customers. All the technologies that are being evaluated by organisations today have Cloud as their pillar. Increasingly, we see organisations adopt the hybrid and the multi-cloud. And organisations may not have the capabilities – technological and skills – to support the complexity of their Cloud environment. While a CEO does not have to understand the technology fully, it is important to understand the business impact of the technology.
Why should a CEO get involved in and have visibility into an organisation’s Cloud investments? There are a few important reasons.
#1 Cloud is not a cost-saving measure – it will enable you to transform
Organisations have matured in their Cloud adoption and no longer evaluate the benefits of Cloud only in terms of shifting CapEx to OpEx. If we look at the benefits of Cloud adoption, reduction of IT costs is not even in the top 3 benefits that organisations are seeking from Cloud anymore. Operational efficiency and collaboration emerge as key benefits (Figure 1) – while some companies still move to the Cloud for the savings, they stay there for other benefits.
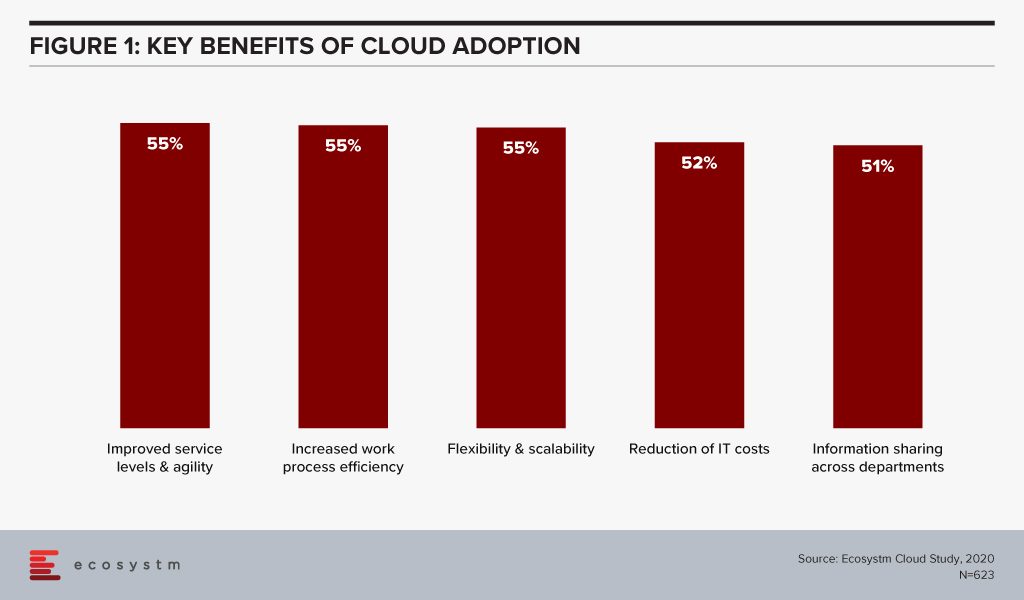
This requires organisations to think of Cloud as a technology empowering their infrastructure and services. Cloud acts as an enabler for ease of doing business, real-time data access for productivity increase, and process automation. This impacts the entire organisation. It also involves prioritising the needs of certain functions over others – definitely not what a CIO should have to do.
If we look at just Cloud storage as an example, organisations can no longer have individual functions and their associated shadow IT teams having their own Cloud storage (and collaboration). This often turns out to be more expensive and there is a lack of consolidated view and management. While organisations forge ahead with the dream of having real-time information sharing across functions, a CIO has to consider the entire organisation’s technological and business needs – a CEO is the best person to guide the CIO in translating the organisation’s vision into IT priorities.
#2 In fact Cloud adoption may not cut costs at all!
Organisations are also re-evaluating the cost benefits of Cloud. Investing in a Cloud infrastructure with a short-term view on the investments involved has led to instances of Cloud solutions being brought back in-house because of rising costs. While security, data privacy and integration remain the key challenges of Cloud adoption (Figure 2), over a third of the organisations find Cloud more expensive than traditional licensing or owning the hardware.
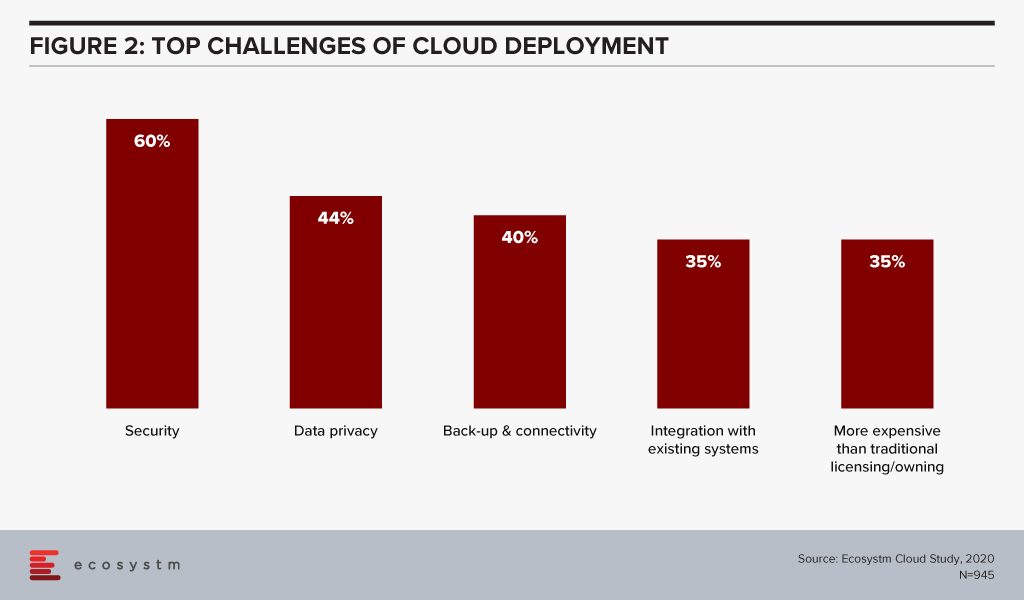
Organisations find that the cost considerations do not stop after the adoption or migration. As businesses use Cloud to scale, there are several aspects that require constant re-evaluation and often further investments – cybersecurity measures, continuous data protection (CDP), disaster recovery management, rightsizing capacity, software and database licenses and day-to-day maintenance, to name a few. In addition to this, the cost of finding and recruiting a team of professionals to manage and maintain the Cloud environment also adds up to the OpEx.
If the CIO is talking about a Cloud migration for cost benefits only, the CEO and the CFO need to step in to evaluate that all factors have been taken into consideration. Moreover, the CIO may not have full visibility of how and where the organisation is looking to scale up or down. It is the CEO’s responsibility to share that vision with the CIO to guide Cloud investments.
#3 Cloud will increasingly be part of all tech adoption considerations
In this disruptive world, CEOs should explore possibilities and understand the technical capabilities which can give organisations an edge over their competitors. It is then up to the CIOs to implement that vision with this larger context in mind. As organisations look to leverage emerging technologies, organisations will adopt Cloud to optimise their resources and workloads.
AI is changing the way organisations need to store, process and analyse the data to derive useful insights and decision-making practices. This is pushing the adoption of Cloud, even in the most conservative organisations. Cloud is no longer only required for infrastructure and back-up – but actually improving business processes, by enabling real-time data and systems access. Similarly, IoT devices will grow exponentially. Today, data is already going into the Cloud and data centres on a real-time basis from sensors and automated devices. However, as these devices become bi-directional, decisions will need to be made in real-time as well. Edge Computing will be essential in this intelligent and automated world. Cloud platform vendors are building on their edge solutions and tech buyers are increasingly getting interested in the Edge allowing better decision-making through machine learning and AI.
In view of the recent global crisis, we will see a sharp uptake of Cloud solutions across tech areas. IaaS will remain the key area of focus in the near future, especially Desktop-as-as-Service. Organisations will also look to evaluate more SaaS solutions, in order to empower a mobile and remote workforce. This will allow the workforce of the future to stay connected, informed and make more decisions. More than ever, CEOs have to drive business growth with innovative products and services – not understanding the capabilities and challenges of Cloud adoption and the advancements in the technology can be a serious handicap for CEOs.
#4 Your IT Team may be more complacent about Cloud security than you think
Another domain that requires the CEO’s attention is cybersecurity. The Cloud is used for computing operations and to store data including, intellectual property rights, financial information, employee details and other sensitive data. Cybersecurity breaches have immense financial and reputational implications and IT Teams cannot solely be responsible for it. Cybersecurity has become a Board-level conversation and many organisations are employing a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) who reports directly into the CEO. Cybersecurity is an aspect of an organisation’s risk management program.
Evaluating the security features of the Cloud offerings, therefore, becomes an important aspect of an IT decision-maker’s job. While security remains a key concern when it comes to Cloud adoption, Cloud is often regarded as a more secure option than on-premise. Cloud providers have dedicated security focus, constantly upgrade their security capabilities in response to newer threats and evolve their partner ecosystem. There is also better traceability with the Cloud as every virtual activity can be tracked, monitored, and logged. Ecosystm research finds that more than 40% of IT decision-makers think the Public Cloud has enough security measures and does not need complementing (Figure 3).
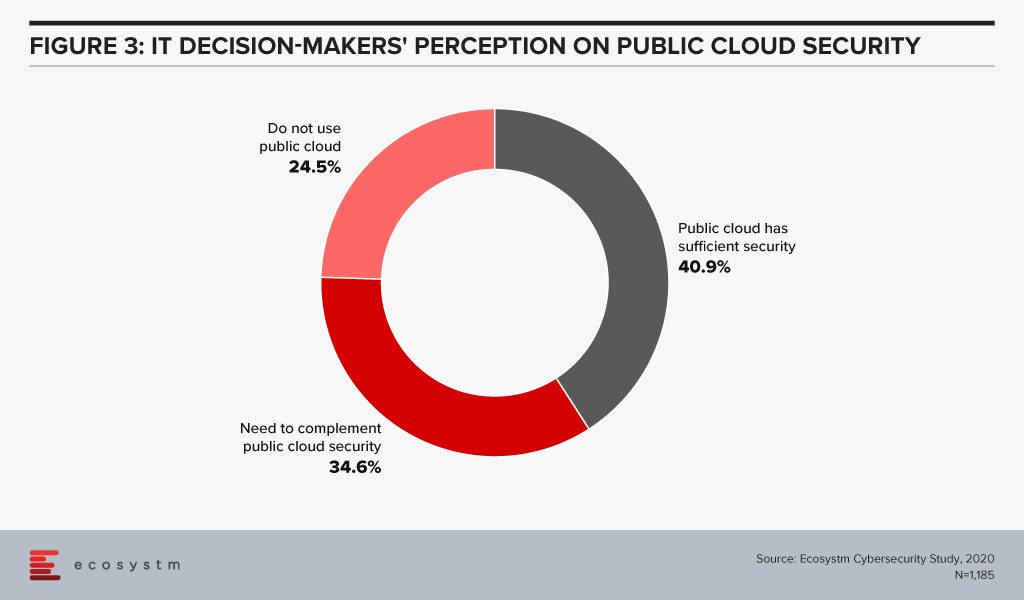
However, the Cloud is as secure as an organisation makes it. The perception that there is no need to supplement Public Cloud security features can have disastrous outcomes. It is important to supplement the Cloud provider’s security with event-driven security measures within an organisation’s applications and cloud interface.
It is the job of the CEO – through the CISO – to evaluate how cyber ready the IT Team really is. Do they know enough about shared responsibility? Do they have full cognizance of the SLAs of their Cloud providers? Do they have sufficient internal cybersecurity skills? Do they understand that data breaches can have cost and reputational impacts? As cybersecurity breaches begin to have more financial implications than ever and can derail an organisation, a CEO should have visibility of the risks of the organisation’s Cloud adoption.
Cloud is no longer just a technological decision – it is a business decision and takes into account the organisation’s vision. A full visibility of the Cloud roadmap – including the pitfalls, the risks and the immense potential – will empower a CEO immensely.

Governments face multiple challenges which are further getting highlighted by the ongoing global crisis. They have to manage the countries’ financial performances, reducing fiscal deficits. Every economy – whether emerging or mature – face challenges in bridging economic and social divides and ensuring equal access to infrastructure across the population. Most governments have challenges associated with the changes in demographics – whether because of rapid urbanisation, a fast ageing population or those associated with immigration policies.
Government agencies have the task of ensuring reliable public service, keeping their citizens safe, and striving for cost optimisation. In this constantly evolving world, agencies need to rely on technology to manage ever-growing citizen expectations and rising costs. Several government agencies have started their digital transformation (DX) journey replacing their legacy systems to transform the way they deliver services to their citizens.
Drivers of Transformation in Public Sector
Creating cross-agency synergies
Government agencies have access to enormous quantities of citizen data. But much of that data resides with individual agencies, often with no real synergies between them. For improved cost management and better utilisation of the data, it is imperative for governments to think of cross-agency collaboration systems and tools which give the larger entity a better visibility of their resources, contracts and citizen information. This involves, developing procedures, frameworks and working beyond their limited boundaries, leveraging technology to share information, applications, platform and processes. While this has been in discussion for nearly a decade now, most government agencies still work in departmental siloes and find it hard to work as a networked entity. The Ecosystm AI study finds that nearly three-quarters of public sector organisations find data access a challenge for their AI projects.
Improving citizen engagement
Increasingly, citizens are becoming tech-savvy and are expecting digital services from their government agencies. Not only that, but they are also ready to have conversations with agencies and provide feedback on matters of convenience and public safety. With the popularity of social media, citizens now have the capability to take their feedback to a wider open forum, if the agency fails to engage with them. Public sector organisations have to streamline and automate the services they provide, including payments, and provide real-time services that require collaborative feedback and increased participation from citizens. Smart governments are successfully able to leverage their citizen engagement to use open data platforms – Data.gov and data.gov.uk, are allowing communities to target and solve problems for which governments do not have the bandwidth. With citizen centricity and open government policies, there is also an ever-increasing need for greater accountability and transparency.
Managing project performance and costs
Most government projects involve several stakeholders and are complex in terms of the data, infrastructure and investments required. To take better decisions in terms of project complexity, risks and investments, public sector agencies need to have a structured project management framework, using an optimum mix of physical. technical, financial and human resources. In an environment where citizens expect more accountability and transparency, and where projects are often funded by citizens’ taxes, running these projects become even more complicated. Government agencies struggle to get funding, optimise costs (especially in projects that run over multiple years and political environments), and demonstrate some form of ROI. There is also an overwhelming requirement to detect and prevent frauds.
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for public sector, that are focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). It is very clear that the key areas of focus are cost optimisation (including fraud detection and project performance management) and having access to better data to provide improved citizen services (such as public safety and predicting citizen behaviour).
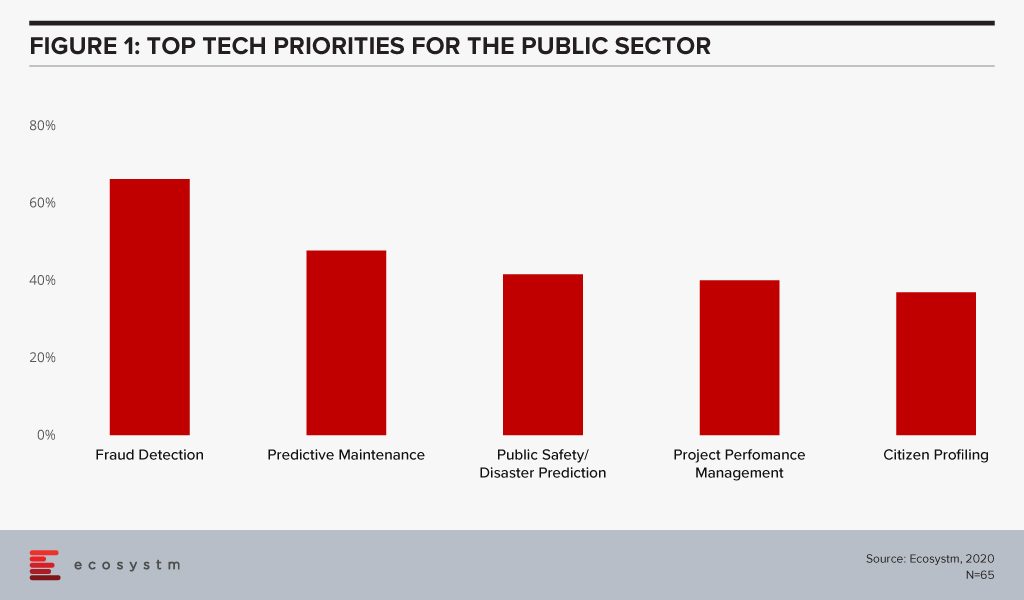
Technology as an Enabler of Public Sector transformation
Several emerging technologies are being used by government agencies as they look towards DX in the public sector.
The Push to Adopt Cloud
To prepare for the data surge that governments are facing and will continue to face, there is a push towards replacing legacy systems and obsolete infrastructure. The adoption of cloud services for data processing and storage is helping governments to provide efficient services, improve productivity, and reduce maintenance costs. Moreover, cloud infrastructure and services help governments provide open citizen services. The Government of India has built MeghRaj, India’s national cloud initiative to host government services and applications including local government services to promote eGovernance and better citizen services. The New Zealand Government has sent a clear directive to public sector organisations that public cloud services are preferred over traditional IT systems, in order to enhance customer experiences, streamline operations and create new delivery models. The objective is to use public cloud services for Blockchain, IoT, AI and data analytics.
Transparency through Communication & Collaboration technologies
Since the 1990s, the concept of eGovernment has required agencies to not only digitise citizen services but also work on how they communicate better with their citizens. While earlier modes of communication with citizens were restricted to print, radio or television, digital government initiatives have introduced more active communication using mobile applications, discussion forums, online feedback forms, eLearning, social media, and so on. Australia’s Just Ask Once allows citizens to access information on various government services at one place for better accessibility. More and more government agencies are implementing an omnichannel communication platform, which allows them to disseminate information across channels such as web, mobile apps, social media and so on. In the blog The Use of Technology in Singapore’s COVID-19 Response, Ecosystm analysts spoke about the daily updates shared by the Government through mobile phones. Demonstrating cross-agency collaboration, the information disseminated comes from multiple government agencies – the same channel is also used to drip-feed hygiene guidelines and the evolving government policies on travel, trade and so on.
AI & Automation for Process Efficiency and Actionable Intelligence
Governments are focusing on leveraging centralised resources and making processes smarter through the adoption of AI platforms. Initiatives such as the Singapore Government’s concept of Single Sources of Truth (SSOT), where all decision-making agencies have access to the same data, is the first step in efficient AI adoption. Singapore’s government agencies also have three data aggregators – Trusted Centers (TCs). This enables initiatives such as Vault-Gov.SG which allows government officials to browse a metadata catalogue and download sample data to run exploratory analytics. To push the adoption of AI, several governments are focusing on roadmaps and strategies such as Singapore’s National AI Strategies to transform the country by 2030, and the Government of Australia’s AI Roadmap and framework to help in the field of industry, science, energy, and education.
The first step of AI adoption is often through automation tools, such as virtual assistants and chatbots. The US Citizen and Immigration Service (USCIS) introduced an AI powered chatbot Emma to better support citizens through self-service options and reduce the workload of their customer service agents. The department of Human Services in Australia rolled out various chatbots named Roxy, Sam, Oliver, Charles and the most latest in progress PIPA (Platform Independent Personal Assistant) to provide information on various services and assist on queries.
Real-time data access with IoT
Governments have the responsibility of enforcing law and order, infrastructure management and disaster management. Real-time information data access is key to these initiatives. IoT sensors are being used in various government applications in object detection, and risk assessment in cities as well as remote areas. For example, IoT-enabled traffic monitoring and surveillance systems are embedded to provide real-time updates and continuous monitoring that can be used to solve issues, as well as provide real-time information to citizens. In a futuristic step, the US Department of Transportation (USDOT) is working with auto manufacturers on embedding vehicle to vehicle communication capabilities in all vehicles to avoid collision with emergency braking and vehicle speed monitoring. In an effort to promoting smart city initiatives and for infrastructure maintenance, New Zealand has installed smart cameras with automated processing capabilities, and IoT based street lighting system. IoT has tremendously benefited the supply chain and logistics sector. The US Army’s Logistics Support Activity (LOGSA) is using IoT for one of the Government’s biggest logistics systems. and military hardware with on-board sensors to analyse data directly from the vehicles for better asset maintenance. Again like in AI, there is a need for a clear roadmap for government adoption of emerging technologies, especially considering the safety and ethics angle. The Government of UK has introduced IoTUK, a program to help the public sector and private enterprises to come together and develop IoT technologies considering aspects such as privacy, security, and reliability.
Blockchain enabled Traceability & Transparency
Moving paper-based systems to digitised systems makes processes efficient to a degree. However, more is required for full traceability and transparency. Managing the data flow and safeguarding the information is vital for government organisations, especially as there is an increase in cross-agency collaboration. Government agencies and departments across the globe are increasingly collaborating using Blockchain technology, while at the same time maintaining the security of the data. For instance, in Georgia, the government department of Land, Property and Housing Management is using Blockchain to maintain land and property records. The blockchain-based land registry allows speedier approvals with no involvement of paperwork or multi-party signatures on physical documents. This is enhancing service quality while offering better security measures as the data is digitally stored in the National Agency of Public Registry’s land title database. Estonia is using Blockchain to protect their digital services such as electronic health records, legal records, police records, banking information, covering data and devices from attacks, misuse, and corruption.
Technology-led digital transformation has become the norm for public sector organisations across both emerging and mature economies. However, agencies need to create clear roadmaps and frameworks, including RoI considerations (which may not only be financial but should include citizen experience) and avoid ad-hoc implementations. The key consideration that government agencies should keep in mind is citizen security and ethics when adopting emerging technologies.