Identifying and selecting a vendor for your tech project can be a daunting task – especially when it comes to emerging technologies or when implementing a tech solution for the first time. Organisations look for a certain degree of alignment with their tech vendors – in terms of products and pricing, sure, but also in terms of demonstrable areas of expertise and culture. Several factors are involved in the selection process – vendors’ ability to deliver, to match expected quality standards, to offer the best pricing, to follow the terms of the contract and so on. They are also evaluated based on favourable reviews from the tech buyer community.
Often businesses in a particular industry tend to have their unique challenges; for example, the Financial Services industries have their specific set of compliance laws which might need to be built into their CRM systems. Over the years, vendors have built on their industry expertise and have industry teams that can advise organisations on how their business requirements can be met through technology adoption. These experts speak in the language of the industry and understand their business and technology pain points. They are able to customise their product and service offerings to the needs of the industry for a single client – which can then be repeated for other businesses in that industry. Vendors arm themselves with a portfolio of industry use cases, especially when they are entering a new market – and this often gives them an upper hand at the evaluation stage. In the end, organisations want less customisations to keep the complexity and costs down.
Do organisations evaluate vendors on industry experience?
Ecosystm research finds that industry experience can be a significant vendor selection criterion for some tech areas (Figure 1), especially in emerging technologies such as AI. AI and automation applications and algorithms are considered to be distinctive to each industry. While a vendor may have the right certifications and a team of skilled professionals, there is no substitute for experience. With that in mind, a vendor with experience in building machine learning models for the Telecommunications industry might not be perceived as the right fit for a Utilities industry implementation.
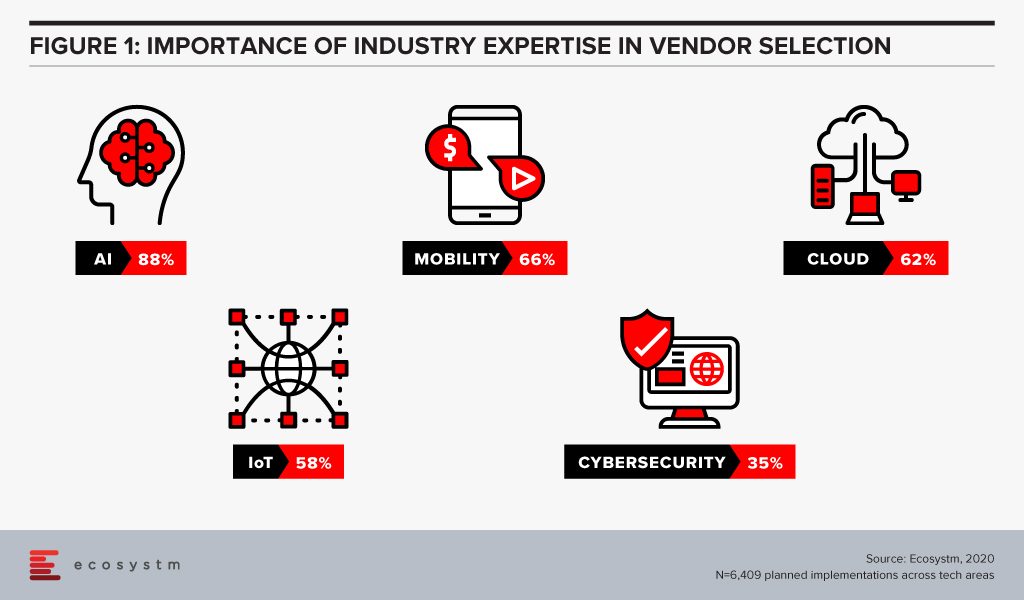
Whereas, we find that cybersecurity is at the other end of the spectrum, and organisations perceive that industry expertise is not required as network, applications and data protection requirements are not considered unique to any industry.
Is that necessarily the right approach?
Yes and no. If we look at the history of the ERP solution, as an example, we find that it was initially meant for and deeply entrenched in Manufacturing organisations. In fact, the precursor to modern-day ERP is the Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) software of the 1980s. Now, we primarily look at ERP as a cross-industry solution. Every business has taken lessons on inventory and supply chain management from the Manufacturing industry and has an enterprise-wide system. However, there are industries such as Hospitality and Healthcare that have their niche vendors who bundle in ERP features with their industry-specific solutions. This will be the general pattern that all tech solutions will follow: a) an industry use case will become popular; b) other industries will try to incorporate that solution, and in the process; c) create their own industry-specific customisations. It is important, therefore, for those who are evaluating emerging technologies to cast their net wide to identify use cases from other industries.
AI and automation is one such tech area where organisations should look to leverage cross-industry expertise. They should ask their vendors about their implementations in other allied industries and, in some cases, in industries that are not allied.
For cybersecurity, their approach should be entirely different. As companies move on from network security to more specific areas such as data security and emerging areas such as GRC communication, it will be important to evaluate industry experience. Data protection and compliance laws are often specific to industries – for example, while customer-focused industries are mandated on how to handle customer data, the Banking, Insurance, Healthcare and Public Sector industries have the need to store more sensitive data than other industries. They should look at solutions that have in-built checks and balances in place, incorporating their GRC requirements.
So, the answer to whether organisations should look for industry expertise in their vendors is that they should for more mature tech areas. An eCommerce company should look for industry experience when choosing a web hosting partner, but should look for experience in other industries such as Banking, when they are looking to invest in virtual assistants.
Are some industries more focused on industry experience than others?
Ecosystm research also sought to find out which industries look for industry expertise more than others (Figure 2). Surprisingly, there are no clear differences across industries. The Services, Healthcare and Public Sector industries emphasise marginally more on industry expertise – but the differences are almost negligible.
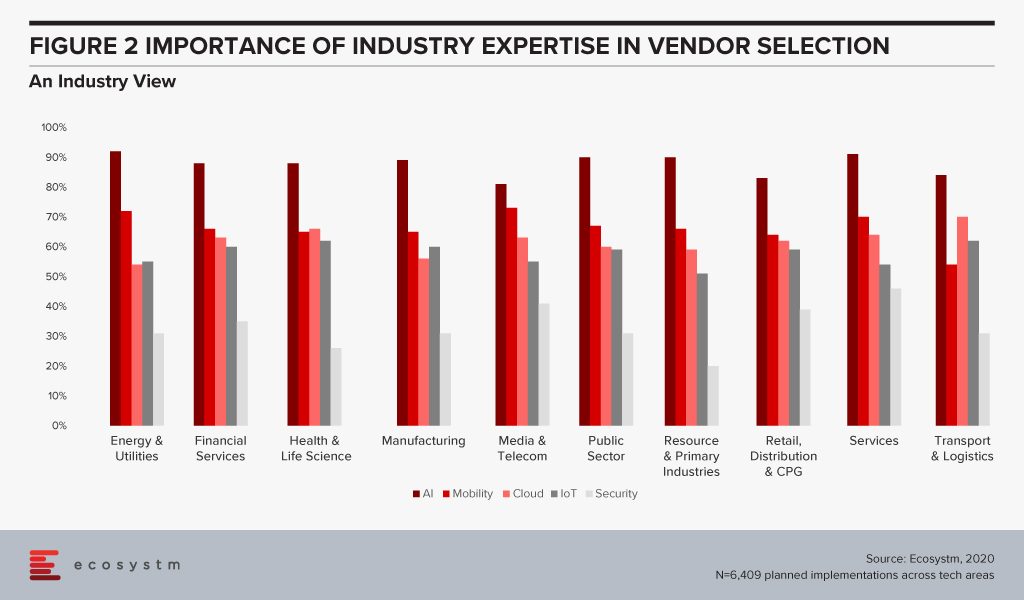
There are some differences when we look at specific tech areas, however. For example, industries that may be considered early adopters of IoT – Transportation, Manufacturing and Healthcare – tend to give more credit to industry experience because there are previous use cases that they can leverage. There are industries that are still formulating standards when it comes to IoT and they will be more open to evaluating vendors that have a successful solution for their requirement – irrespective of the industry.
The Healthcare Industry Example
Ecosystm Principal Analyst, Sash Mukherjee says, “In today’s fast-evolving technology market, it is important to go beyond use cases in only your industries and look for vendors that have a demonstrated history of innovation and experience in delivering measurable results, irrespective of the industry.” Mukherjee takes the example of the Healthcare industry. “No one vendor can provide the entire gamut of functionalities required for patient lifecycle management. In spite of recent trends of multi-capability vendors, hospitals need multiple vendors for the hospital information systems (HIS), ERP, HR systems, document management systems, auxiliary department systems and so on. For some areas such as electronic health records (EHR) systems, obviously industry expertise is paramount. However, if healthcare organisations continue to look for industry expertise and partner with the same vendors, they miss out on important learnings from other industries.”
Talking about industries that have influenced and will influence the Healthcare industry in the very near future, Mukherjee says, “Healthcare providers have learnt a lot from the Manufacturing industry – and several organisations have evaluated and implemented Lean Healthcare and Six Sigma to improve clinical outcomes. The industry has also learnt from the Retail and Hospitality industries on how to be customer focused. In the Top 5 Healthtech trends for 2020, I had pointed out the similarities between the Financial and Healthcare industries (stringent regulations, process-based legacy systems and so on). As the Healthcare industry focuses on value-based outcomes, governments introduce more regulations around accountability and transparency, and people expect the experience that they get out of their retail interactions, Healthtech start-ups will become as mainstream as Fintech start-ups.”
It is time for tech buyers to re-evaluate whether they are restricting themselves by looking at industry use cases, especially for emerging technologies. While less industry customisations mean easier deployments, it may also hamper innovation.
Enterprise mobility was a key area of focus for organisations for many years in the late 2000s and early 2010s. Many businesses invested significant amounts of money and time in helping their employees access the information they needed while on the go – until the consumer smartphone era drove our attention away from our employees. Now we are focused on providing the best mobile apps, websites and experiences possible.
The constant evolution of the capabilities of smartphones, along with the drive to offer an ever-improving customer experience (CX) has kept our attention firmly on our customers. However, smart businesses now understand that in order to offer a great CX, they need to keep their employees happy. And giving them access to the technology that delivers the right information at the right time is a key factor in achieving better employee experience.
“Investment in enterprise mobility tools and platforms is forecast to increase significantly over the next few years. And the COVID-19 pandemic may even see some of that spend accelerated as businesses look to better support their remote and work-from-home employees,” says Tim Sheedy, Ecosystm Principal Advisor.
What to Expect from this New Wave of Enterprise Mobility
#1 Growth of UEM Adoption
Sheedy adds,“Today, many businesses are empowering their employees by providing the best end-user computing experience that will drive the best outcome. This often sees them looking beyond a single device (phone, PC etc) towards the entire experience – including the application, interface, management and security of the experience.”
A robust unified endpoint management (UEM) solution provides IT teams with a transparent and traceable overview of all endpoints within the network as well as the power to manage all connected devices from a single platform. It maps out the network setup and structure by carrying out a complete inventory of all network devices, configurations, installed software, and the drivers for endpoint subsystems. Ecosystm research finds that more than 60% of global organisations have either adopted UEM or are evaluating it (Figure 1).
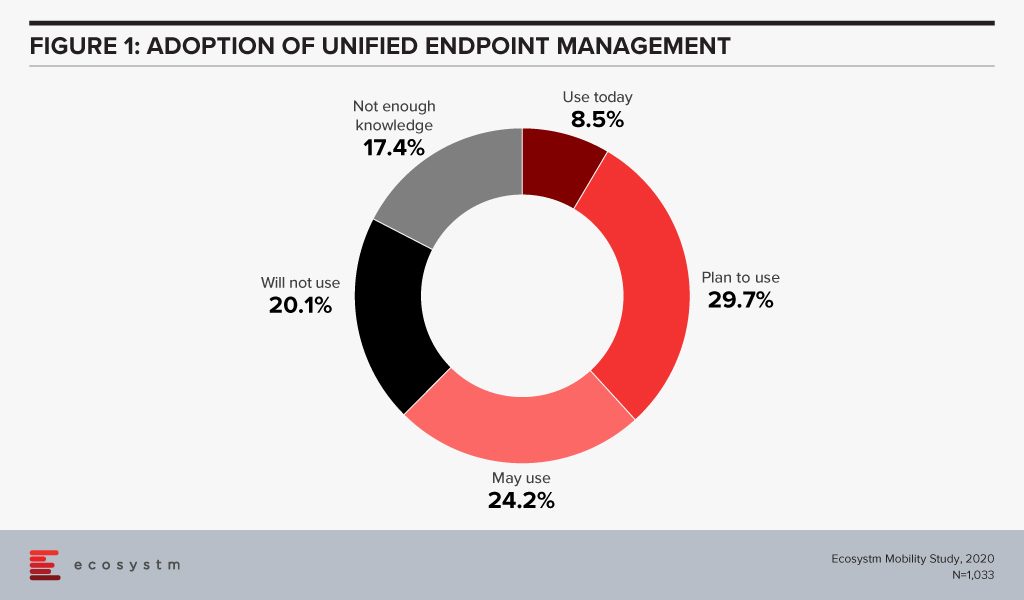
This trend will only go up with the rise in the number of devices organisations have to manage remotely. The workplace of the future will become exponentially digital and tech vendors will further strengthen their portfolio to offer UEM solutions.
#2 Greater C-Level Visibility in Mobility
In his report, The Enterprise Mobile Landscape in 2020, Sheedy notes that enterprise mobility decision, including the choice of devices supported often have C-level involvement (Figure 2). “A large government agency in Australia has had the Director General intervene in their mobility decisions to stamp his personal preference on decisions, and a CIO at a large bank makes sure that Apple devices are always preferred – even when it makes little business sense to do so!”
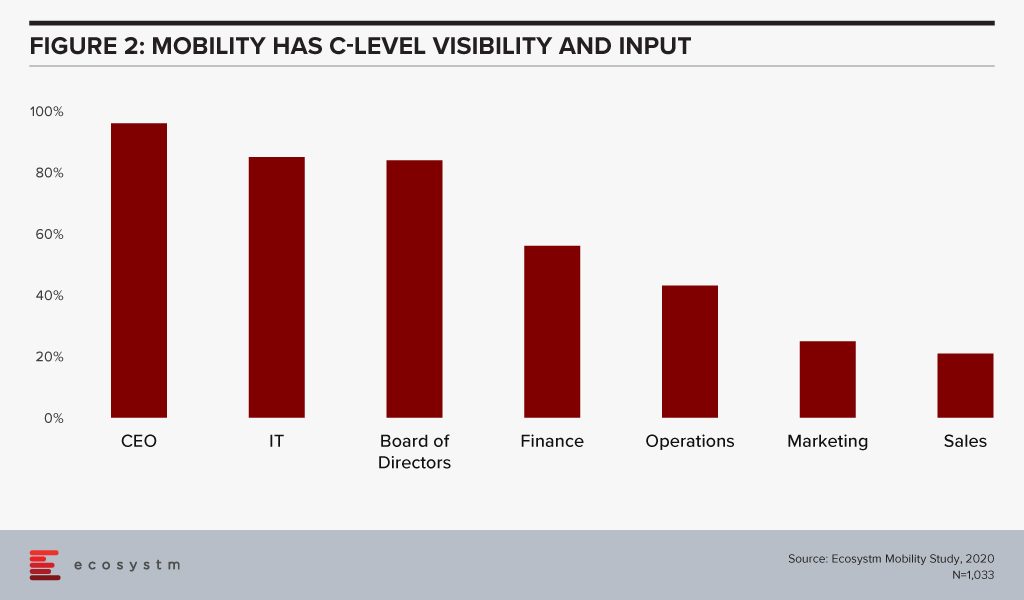
Choice of mobile devices is personal and most organisations have realised that. Less than a third of global organisations issue corporate devices and only 6% continue to believe that they can manage by only supporting corporate devices. However, nearly no organisation has gone fully BYOD either.
Apart from mobile device choice, mobility solutions also have to take into consideration the huge amounts of traffic it has to support. When organisations adopt a Mobile First Strategy it is an acknowledgement that it will involve multiple stakeholders, right from the inception of the vision. This is clearly a technology area where user experience and uptake is of importance. So, the mobility strategy should have senior level overview and input so that it can be a company-wide policy.
#3 There will be renewed interest in Mobile Security
Ecosystm research finds that the global adoption rate of mobile device management (MDM) solutions is about 44%, while only about 17% of organisations indicate the adoption of a Mobile Security solution focused on identity management, multilayered security and threat analysis.
Organisations are aware that mobility initiatives increase their risk profile (Figure 3). An enterprise mobility solution that allows people to work on their device and OS of choice and from where they choose to, will become increasingly important in the current milieu. But the threats to organisation are equally real.
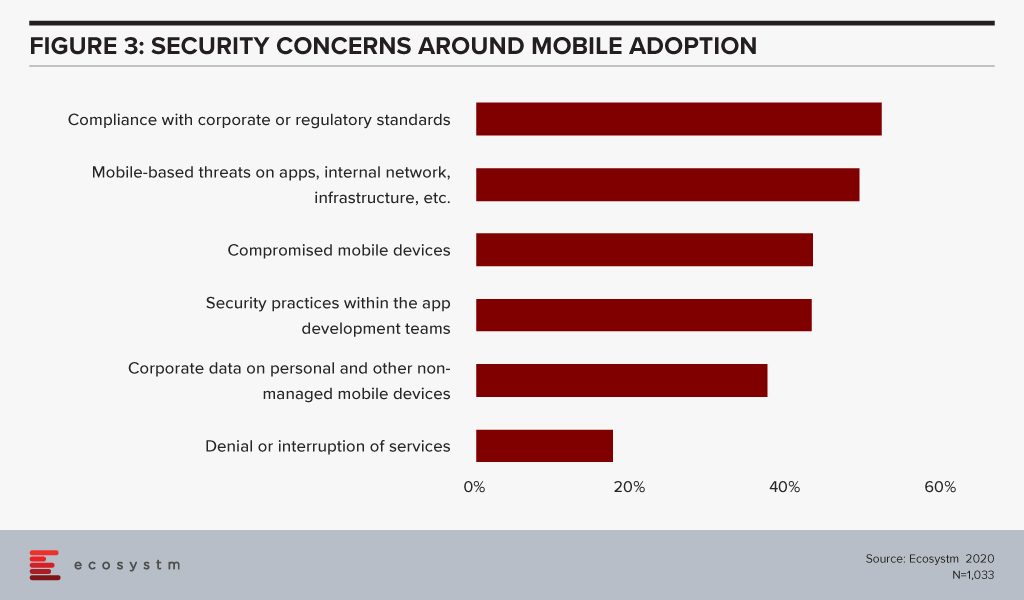
More than half of the organisations are concerned about compliance with corporate or regulatory standards in implementing mobility solutions. This is a good indication that the Mobile First strategy implementations have a strong compliance angle to them, both internally and for external agencies.
However, as Sheedy notes, it is still a challenge for the IT team. “Organisations provide one or two more operating systems that the IT team needs to manage, patch and secure. The mobile applications provide more entry points for would-be hackers and others to use and threaten the business. The devices and applications provide another set of user interface that need to be managed and governed to ensure regulatory compliance. They can also gather highly personal data (such as the location of customers when they are using – or not using – the application) so this data needs to be secured and governed.” As adoption matures, organisations will need to invest in niche Mobile Security solutions to combat their security concerns.
#4 Mobility will Drive SaaS Adoption
What organisations want most from their mobility solutions is cloud capabilities. One of the main reasons why organisations look for cloud capabilities is because mobile workloads tend to be unpredictable and cloud solutions are best equipped to handle the unexpected spikes. Most organisations also consider cloud solutions for a seamless integration with back-end systems and because a mobile workforce needs to make real-time decisions based on real-time data. Given the disparity of the data sources in a typical organisation, hosting on a neutral platform becomes more attractive. Also as organisations become more conscious about mobile security, cloud options also give them better traceability on remote device and data access.
However, conversely mobility will also drive the adoption of SaaS enterprise solutions and tools. Many businesses have mobilised their email, eCommerce platforms and unified communications and collaboration tools. But beyond that, organisations are not really empowering their employees to work on their mobile devices (Figure 4). This will have to – and will change – fast.

In his report, Make Remote Working Successful, Sheedy notes, “It goes without saying that your employees’ productivity levels will improve if they have access to the applications they need. And while many organisations already have enabled universal (or near-universal) application access from PCs and laptop computers, many of these applications should also be available from smartphones and tablets. This will allow your employees to work when they are on the move – not just when they are at home.”
It is time for organisations to re-evaluate their enterprise mobility if they have to remain productive in these difficult times, and beyond. Sheedy says, “Ultimately, our employee’s reliance on great mobile and targeted end-user computing experiences is increasing – and 5G services will only accelerate the transition away from traditional telephony, communications services and desktop applications. Businesses will need to continue to mobilise their enterprise systems to make them easier to use. Employees have now experienced great mobile apps and systems – and most enterprise mobility systems don’t stand up in that comparison.”

In our blog, Artificial Intelligence – Hype vs Reality, published last month we explored why the buzz around AI and machine learning have got senior management excited about future possibilities of what technology can do for their business. AI – starting with automation – is being evaluated by organisations across industries. Several functions within an organisation can leverage AI and the technology is set to become part of enterprise solutions in the next few years. AI is fast becoming the tool which empowers business leaders to transform their organisations. However, it also requires a rethink on data integration and analysis, and the use of the intelligence generated. For a successful AI implementation, an organisation will have to leverage other enabling technologies.
Technologies Enabling AI
IoT
Organisations have been evaluating IoT – especially for Industry 4.0 – for the better part of the last decade. Many organisations, however, have found IoT implementations daunting for various reasons – concerns around security, technology integration challenges, customisation to meet organisational and system requirements and so on. As the hype around what AI can do for the organisation increases, they are being forced to re-look at their IoT investments. AI algorithms derive intelligence from real-time data collected from sensors, remote inputs, connected things, and other sources. No surprise then that IoT Sensor Analytics is the AI solution that is seeing most uptake (Figure 1).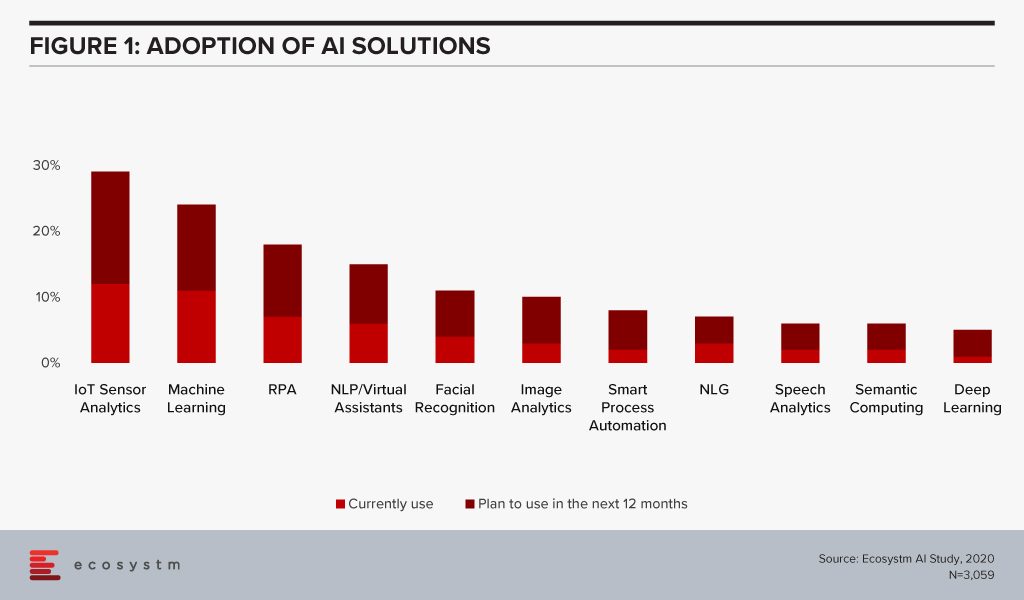
This is especially true for asset and logistics-driven industries such as Resource & Primary, Energy & Utilities, Manufacturing and Retail. Of the AI solutions, the biggest growth in 2020 will also come from IoT Analytics – with Healthcare and Transportation ramping up their IoT spend. And industries will also look at different ways they can leverage the IoT data for operational efficiency and improved customer experience (CX). For instance, in Transportation, AI can use IoT sensor data from a fleet to help improve time, cost and fuel efficiency – suggesting less congested routes with minimal stops through GPS systems, maintaining speeds with automated speed limiters – and also in predictive fleet maintenance.
IoT sensors are already creating – and will continue to create large amounts of data. As organisations look to AI-enabled IoT devices, there will be a shift from one-way transactions (i.e. collecting and analysing data) to bi-directional transactions (i.e. sensing and responding). Eventually, IoT as a separate technology will cease to exist and will become subsumed by AI.
Cloud
AI is changing the way organisations need to store, process and analyse the data to derive useful insights and decision-making practices. This is pushing the adoption of cloud, even in the most conservative organisations. Cloud is no longer only required for infrastructure and back-up – but actually improving business processes, by enabling real-time data and systems access.
Over the next decades, IoT devices will grow exponentially. Today, data is already going into the cloud and data centres on a real-time basis from sensors and automated devices. However, as these devices become bi-directional, decisions will need to be made in real-time as well. This has required cloud environments to evolve as the current cloud environments are unable to support this. Edge Computing will be essential in this intelligent and automated world. Tech vendors are building on their edge solutions and tech buyers are increasingly getting interested in the Edge allowing better decision-making through machine learning and AI. Not only will AI drive cloud adoption, but it will also drive cloud providers to evolve their offerings.
The global Ecosystm AI study finds that four of the top five vendors that organisations are using for their AI solutions (across data mining, computer vision, speech recognition and synthesis, and automation solutions) today, are also leading cloud platform providers (Figure 2).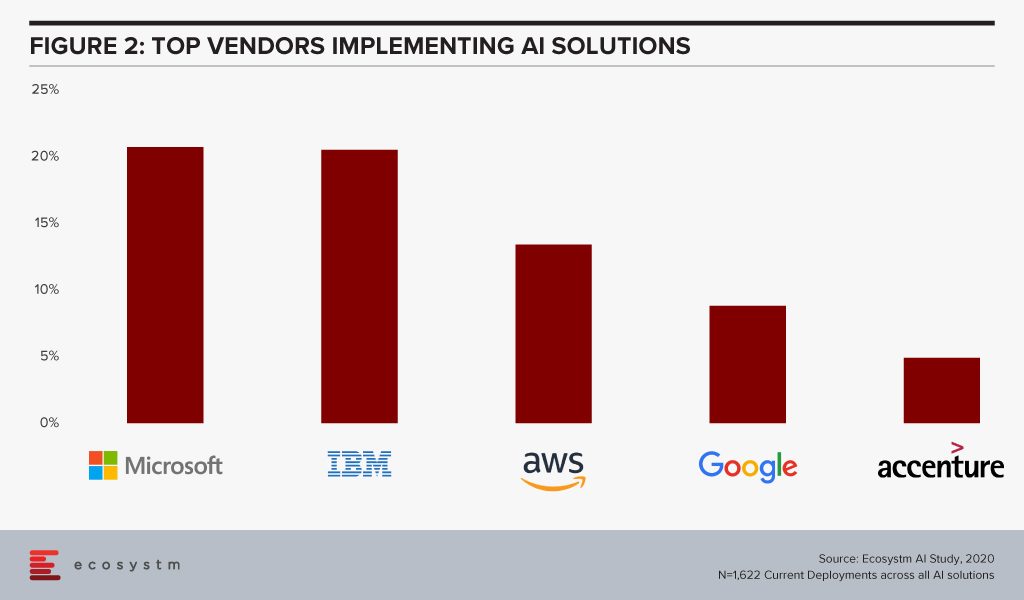
The fact that intelligent solutions are often composed of multiple AI algorithms gives the major cloud platforms an edge – if they reside on the same cloud environment, they are more likely to work seamlessly and without much integration or security issues. Cloud platform providers are also working hard on their AI capabilities.
Cybersecurity & AI
The technology area that is getting impacted by AI most is arguably Cybersecurity. Security Teams are both struggling with cybersecurity initiatives as a result of AI projects – and at the same time are being empowered by AI to provide more secure solutions for their organisations.
The global Ecosystm Cybersecurity study finds that one of the key drivers that is forcing Security Teams to keep an eye on their cybersecurity measures is the organisations’ needs to handle security requirements for their Digital Transformation (DX) projects involving AI and IoT deployments (Figure 3).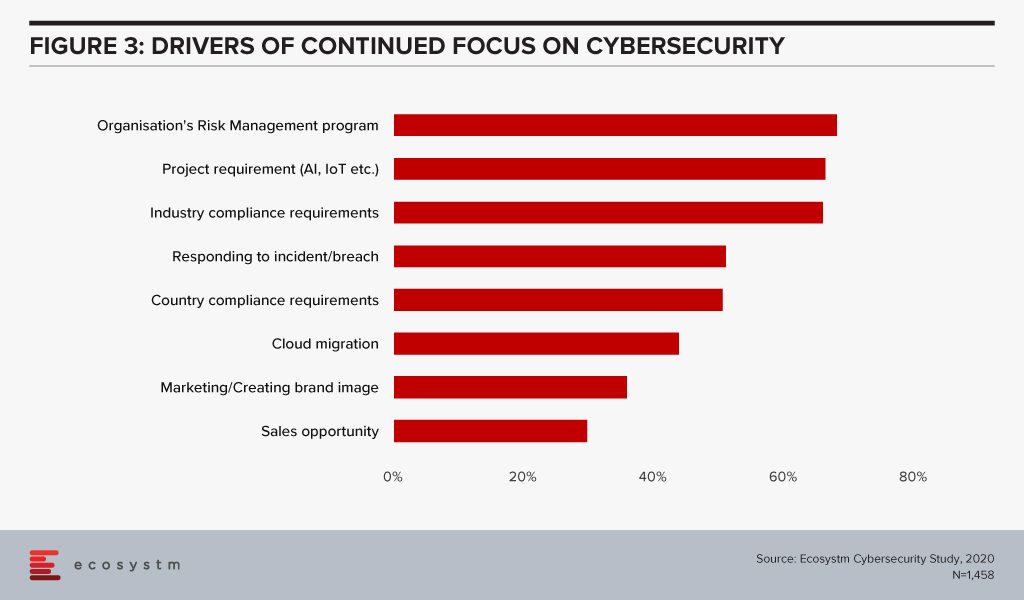
While AI deployments keep challenging Security Teams, AI is also helping cybersecurity professionals. Many businesses and industries are increasingly leveraging AI in their Security Operations (SecOps) solutions. AI analyses the inflow and outflow of data in a system and analyses threats based on the learnings. The trained AI systems and algorithms help businesses to curate and fight thousands of daily breaches, unsafe codes and enable proactive security and quick incident response. As organisations focus their attention on Data Security, SecOps & Incident Response and Threat Analysis & Intelligence, they will evaluate solutions with embedded AI.
AI and the Experience Economy
AI has an immense role to play in improving CX and employee experience (EX) by giving access to real-time data and bringing better decision-making capabilities.
Enterprise mobility was a key area of focus when smartphones were introduced to the modern workplace. Since then enterprise mobility has evolved as business-as-usual for IT Teams. However, with the introduction of AI, organisations are being forced to re-evaluate and revamp their enterprise mobility solutions. As an example, it has made mobile app testing easier for tech teams. Mobile automation will help automate testing of a mobile app – across operating systems (Figure 4). While more organisations tend to outsource their app development functions today, mobile automation reduces the testing time cycle, allowing faster app deployments – both for internal apps (increasing employee productivity and agility) and for consumer apps (improving CX).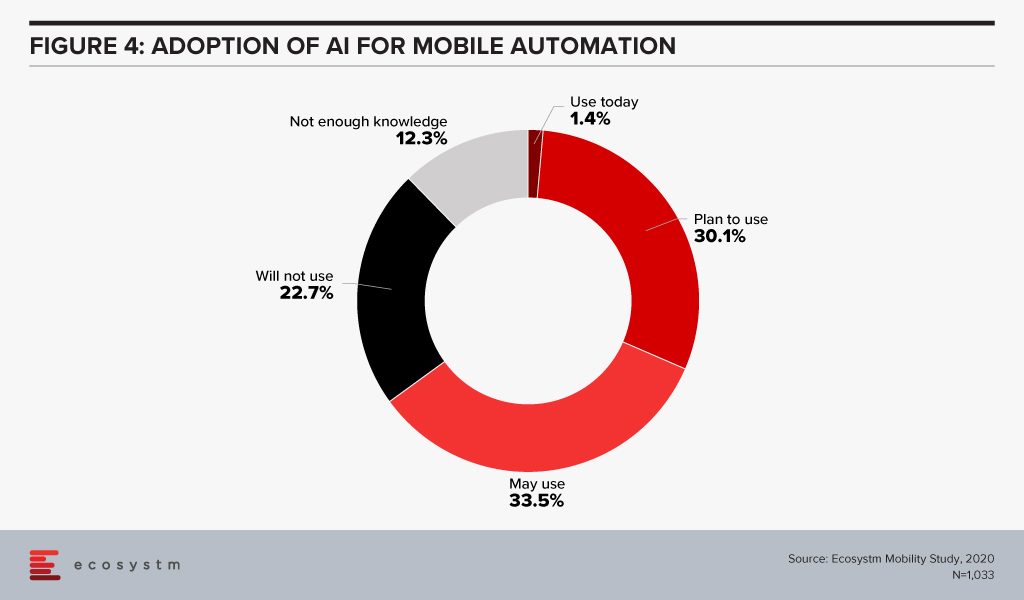
CX Teams within organisations are especially evaluating AI technologies. Visual and voice engagement technologies such as NLP, virtual assistants and chatbots enable efficient services, real-time delivery and better customer engagement. AI also allows organisations to offer personalised services to customers providing spot offers, self-service solutions and custom recommendations. Customer centres are re-evaluating their solutions to incorporate more AI-based solutions (Figure 5).
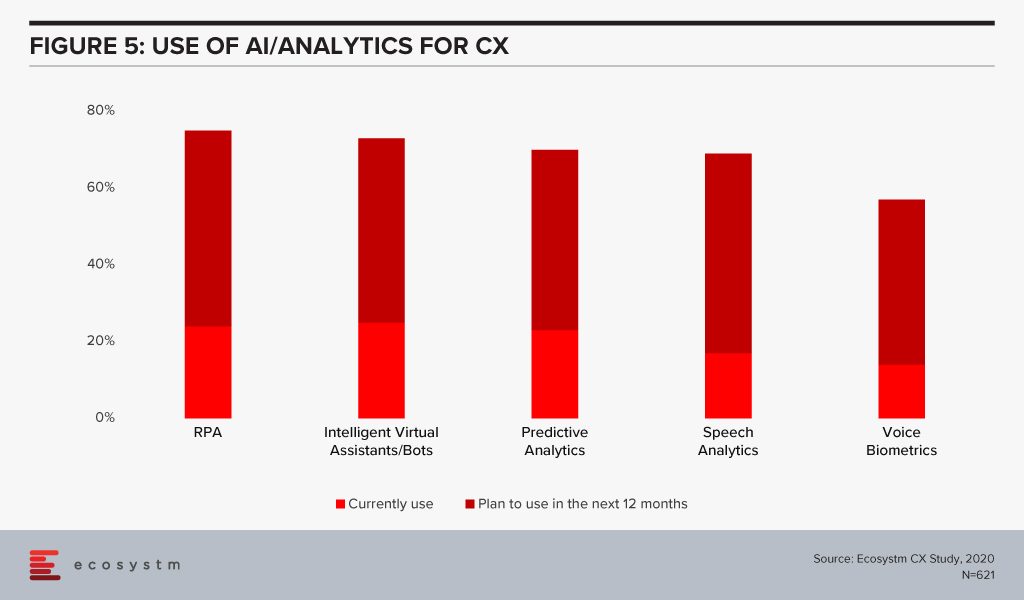
The buzz around AI is forcing tech teams to evaluate how AI can be leveraged in their enterprise solutions and at enabling technologies that will make AI adoption seamless. Has your organisation started re-evaluating other tech areas because of your AI requirements? Let us know in the comments below.

With the advancements in the technology landscape, the CIO’s role has become increasingly complex. One of the key challenges they face is in emerging and newer technology implementations, which require them to identify and partner with newer tech vendors. The common challenges that tech buyers face today include:
- The emergence of newer technologies that are catching the fancy of the C-suite and they are expected to adopt and deliver
- Getting management buy-in for IT investments (increasingly including discussions on ROI)
- Need to involve business stakeholders in tech decision-making
- Lack of sufficiently skilled internal IT
- Engagement with multiple tech vendors (including newer vendors that they have to establish a relationship with)
- Digital transformation projects that might require an overhaul (or at least a re-think) of IT systems
- Backdrop of compliance and risk management mandates
Many of these challenges will require the sourcing of new technology or a new tech partner and rethinking their vendor selection criteria. And selecting a tech vendor can be hard. The mere fact that there is an industry whose sole purpose is to help businesses select tech vendors goes to show the massive gap between what these providers sell and what businesses want. If there was easy alignment, the Tech Sourcing professionals and businesses would not have existed.
But over my time working with Tech Sourcing professionals, CIOs and business leaders, I have picked up on a few key factors that you should incorporate in your vendor selection process best practices. First and foremost, you are looking for a partner – someone who will be with you through the good and bad. Someone whose skills, products, services – and most importantly – culture, match your business and its needs.
I believe that the technology ecosystem is not really as competitive as we think. Yes, in practice Google competes with Microsoft in the office productivity space. But I often hear about companies moving from one to the other not for features, function or even price – but for a cultural match. Some traditional businesses were hoping Google can help them become more innovative, but in reality, their business culture smothered Google and meant they could not benefit from the difference in the ways of working. And I am not suggesting Microsoft is not innovative – more that Office represents the traditional ways of working – and perhaps can help a business take a more stepwise approach to change its own culture.
And I regularly hear about IT services deals (managed services, systems integration, consulting etc) going to the company that made the most sense from a cultural fit – where they were willing to take on the culture of their customer and embrace that way of working. In fact, I have been brought into many deals where a company hired a strategic consultant to create a new digital strategy or AI strategy, only to receive a document that is unworkable in their business and their culture.
So, I believe every strategic technology relationship should start and end with a cultural match. This company is a partner – not just a provider. How do you determine if they are a partner and measure cultural match? Well, that is the topic of an upcoming report of mine, so watch this space!
Questions You Should Ask Before Stepping in the Ring
There are also a number of questions that you should ask along with the partnership discussion:
- How will this solution change the organisation?
- What are the risks either way (of implementing or not implementing the solution)?
- Does the solution solve a key business problem?
- Is it likely to have more impact than the solution it is replacing?
- Where will the funding for the implementation come from?
- Have you calculated the ROI and the time to deployment?
- Have you baselined the current scenario so that you can measure improvement?
These can inform you of the business impact of the solution – and what you need to do to prepare for successful implementation (if you plan for success, you are more likely to be able to get faster benefits than if you do not plan for the change!)
Engagement Criteria for Your Shortlisting Process
In order to determine vendor selection process best practices, Ecosystm research tries to unearth the top criteria that organisations employ when shortlisting the vendors that they want to engage, across multiple technologies.
There is still a skills gap in internal IT and organisations want technical guidance from their Cloud and IoT vendors. With the plethora of options available in these tech areas, CIOs and IT teams also tend to look at the brand reputation when engaging with the vendor. Very often, organisations looking to migrate their on-prem solutions on the cloud engage with existing infrastructure providers or systems integrators for guidance, and existing relationships are significant. IoT solutions tend to be very industry-specific and a portfolio of specific industry use cases (actual deployments – not proofs of concept) can be impactful when selecting a vendor for planned deployments.
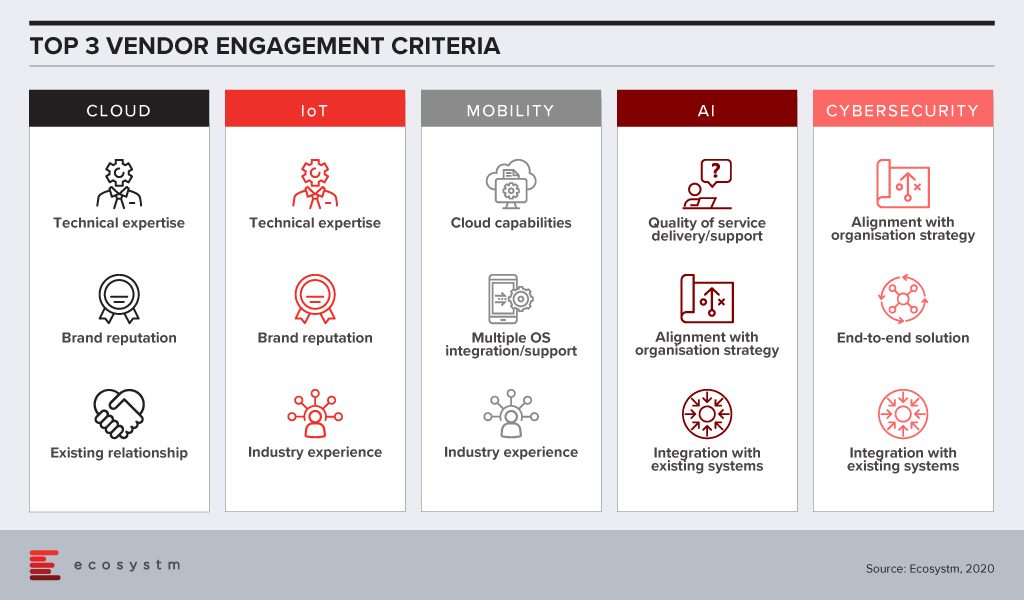
Artificial intelligence (AI) deployments are often linked with digital transformation (DX). Organisations look for a vendor that can understand the organisational strategy and customise the AI solutions to help the organisation achieve its goal. Adoption of AI is still at a nascent stage globally across all industries. Many organisations do not have the right skills, such as data scientists, yet. They appreciate that integration with internal systems will be key to reap the full benefits of the solutions, especially if the entire organisation has to benefit from the deployments. They also anticipate that they would have to have a continuous period of engagement with their vendors, right from identifying the right data set, data cleaning to the right algorithms that keep learning. Organisations will look at vendor partners who are known for delivering better customer experience.
This is true for cybersecurity solutions as well, as organisations are driven to continue their investments to adhere to the internal risk management requirements. Given how fragmented the cybersecurity landscape has become, organisations will also wish to engage with vendors that have an end-to-end offering, especially a managed security service provider (MSSP). Cybersecurity vendors are increasingly strengthening their partner ecosystem so that they can provide their client with the single-point-of-contact that they want.
Of the technologies mentioned in the figure, mobility is arguably the most mature. As organisations revisit their enterprise mobility solution as they go increasingly ‘Mobile First’, their requirements from their mobility vendors are more specific. They have decided over the years which OSs they want to support their enterprise applications and are looking for vendors with robust cloud offerings.
The vendor selection criteria will likely be different for each technology area. And as your knowledge and understanding of the technology increases, you should be able to drill the requirements down to the solution level, while making sure you engage with a vendor with the right culture.
Tim Sheedy’s upcoming report, ‘Best Practices for Vendor Evaluation and Selection’ is due to be published in February 2020.
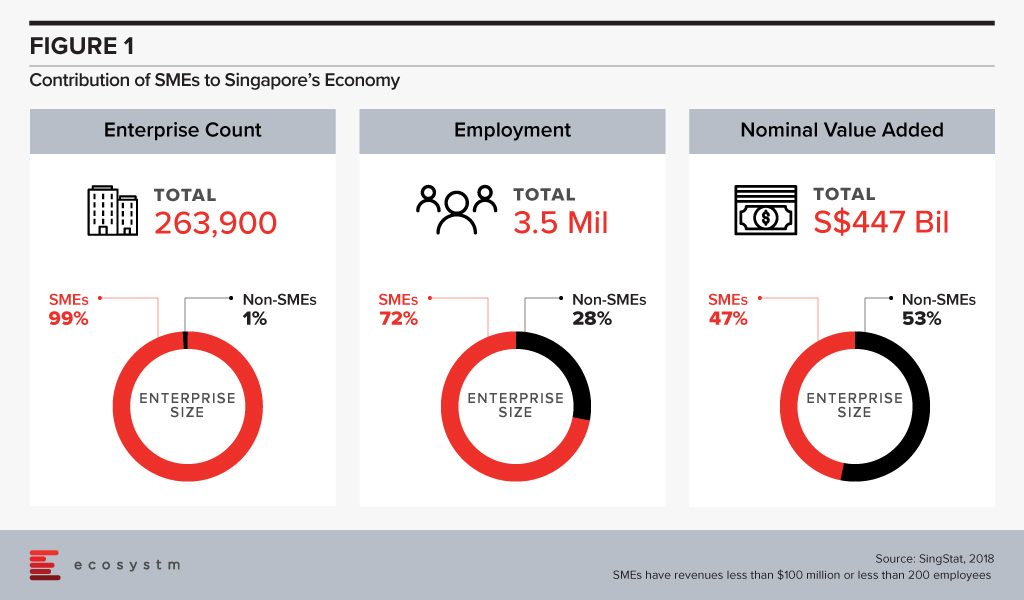
Singapore maintains its competitiveness through strong Government support and an environment that encourages trade and investments. The economy sees a huge contribution from start-ups and small and medium enterprises (SMEs), which receives financial incentives and technology guidance from the Government.
The success of SMEs in Singapore is at the core of national economic growth with approximately 261,000 SMEs contributing to nearly 50% of the country’s GDP.
A survey conducted by United Overseas Bank (UOB) in November 2019 illustrates that SMEs in Singapore are focusing on boosting productivity as they grapple with macro-economic and socio-political uncertainties this year. The UOB survey included 615 local SMEs with a revenue of less than S$100 million. Nearly half of the SMEs surveyed have a positive outlook for their business in 2020, while nearly a third are not so optimistic about it.
While cost reduction and new streams of revenue generation are top business priorities, more than half of the SMEs polled, mentioned increasing productivity as their top priority. Technology adoption has often been linked to an increase in productivity. SMEs in Singapore appear to be on the right track as currently 65% use digital solutions, mostly geared towards accounting, HR and customer relationship management. Digitalisation involves a widespread adoption of cloud and automation solutions. If we look at the key drivers of cloud adoption across all global organisations (Figure 2), we find that optimisation and productivity are key incentives.
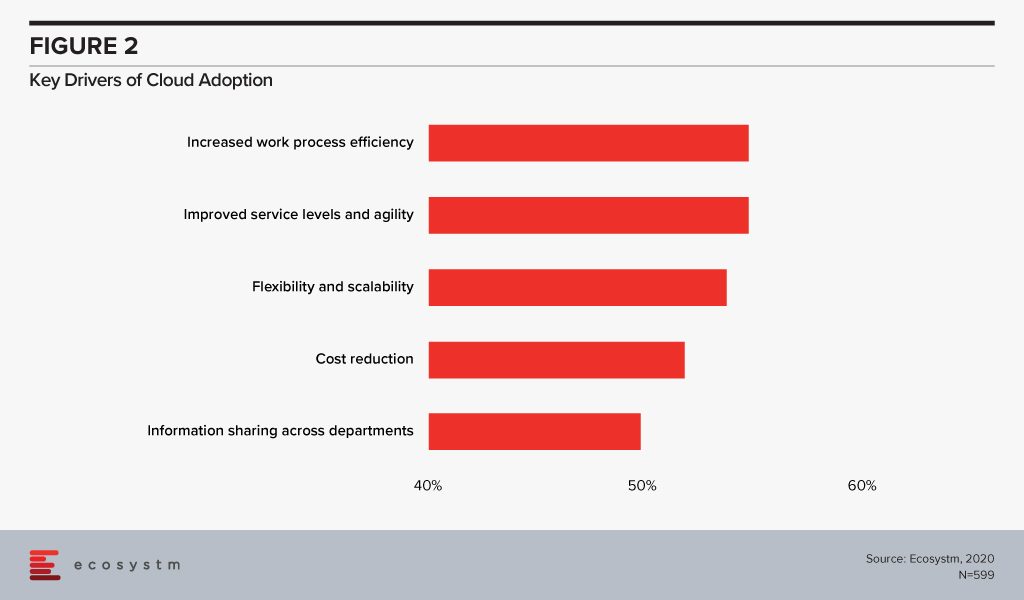
Interestingly, the UOB survey also finds that more than half of SMEs in Singapore have sustainability goals. Resource optimisation and energy efficiency will also see higher adoption of technology in the future.
Government Initiatives Empowering SMEs
Government agencies and industry bodies have always been proactive in empowering SMEs with technological knowledge. There are various programs and initiatives to promote digitalisation, which have made Singapore SMEs competitive at a global level.
The Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) is helping Singapore SMEs to scale and improve their digital capabilities, expand their network and go global through collaboration with multinational companies (MNCs). The SMEs Go Digital program launched in 2017, has seen an estimated 4,000 SMEs adopting pre-approved digital solutions.
Several organisations in Singapore – such as A*Star and Enterprise Singapore – have targeted programs for the SME community. One of the key challenges for SMEs that impacts their ability to invest in technology is a lack of internal IT skills. Initiatives such as the Technology Adoption Programme (TAP) recognise this and bring in multiple industry and technology stakeholders to translate new technologies into Ready-to-Go (RTG) solutions, aimed at SMEs.
Apart from technology, access to financing is a key factor that determines the success of an SME and remains a key focus of Singapore’s banking and financial sector. The digital wholesale licenses are also aimed at SME financing, especially targeting those that are unable to procure funds from traditional sources.
Technologies Enabling Digitalisation in Singapore SMEs
Cloud
As mentioned earlier, cloud is the key enabler of digitalisation, giving organisations the ability to access solutions anywhere and anytime. Ecosystm research shows that 80% of SMEs in Singapore use an IaaS solution, while more than 75% use a SaaS solution.
There are programs that boost cloud adoption in Singapore SMEs as well. As an example, SMECEN, developed by the Association of Small & Medium Enterprises (ASME), and supported by Enterprise Singapore, Accounting and Corporate Regulatory Authority (ACRA) and Inland Revenue Authority of Singapore (IRAS) is a SaaS solution with accounting, HR and compliance modules – integration with other business tools is on the cards.
AI/Automation
Digitalisation will eventually involve investments in Automation and AI. For Singapore, AI is a key technology as it continues to focus on IoT, smart buildings, smart electricity, autonomous electric vehicles and other smart city solutions. The Government is working to open up access to data and AI tools so everyone can experiment. It especially wants to encourage SMEs to adopt AI and work on government use cases.
Singapore SMEs are ramping up their AI investments, especially in IoT sensor analytics (27%), machine learning (21%) and robotic process automation (16%), according to the Ecosystm AI study. Their key short-term drivers are insights into the competition and enhanced internal process monitoring. However, in the longer term, they are looking at cost reduction and better profit margins.
Fintech
According to an OCBC survey in 2018, which polled 200 such companies, two-thirds of SMEs in Singapore are likely to go cashless by 2023. It is estimated that over 75% of Fintech transactions in Singapore are digital payments and it receives over a quarter of Fintech funding. Government initiatives such as FAST and SGQR, have opened up digital payment options for consumer use as well as for SMEs.
However, the UOB survey notes some concerns that SMEs have over digital payments adoption, including customer/supplier acceptance and security. This is an encouraging sign, which indicates that SMEs are not just adopting technology because of the hype – but are evaluating the pros and cons of tech adoption before embarking on a digitalisation project.

As organisations look to leverage better operational and business insights, adopting Cloud has become imperative for them, especially for those that intend to make use of other technologies like analytics and IoT. All the imperatives for moving to Cloud continue to grow stronger, while at least some of the reasons for resisting the trend are becoming indefensible. The key inhibitors continue to be security and data privacy concerns and back-up/connectivity issues. Also, as the Cloud ecosystem has matured, an important inhibitor has become cost considerations as many organisations are now evaluating whether the Cloud is indeed more cost-effective than on-premises options.
This article presents the Top 5 Cloud Trends for 2020 for the Cloud market in 2020. It is based on the latest data from the global Ecosystm Cloud, IoT and Cybersecurity studies, that are live and ongoing on the Ecosystm platform, and qualitative research by Ecosystm Principal Advisors Claus Mortensen and Craig Baty.
The Top 5 Cloud Trends for 2020
Here are the Top 5 Cloud Trends for 2020 that we believe will impact both businesses and consumers in 2020.
-
Major Cloud Providers Will Push for Open Source
Open Source has always played a big role in Cloud and as we move into 2020, its role will only grow bigger. Infrastructure and Platform Clouds may not have been dominated by Open Source in the past, but all major Cloud players such as AWS, Microsoft, and IBM have been focusing on Open Source recently.
In 2020, major cloud providers will switch to Open Source to create a development environment that can achieve more than they would be able to develop fully in-house.
-
Open Source will Drive the Adoption of Serverless Computing
Serverless computing is a cloud model where the Cloud provider runs and manages the server and the allocation of machine resources. Beyond just the individual servers, many vendors are now offering to totally replace the data centre with a virtual version that runs in the Cloud.
It has the potential to become a widely used solution for mid-range businesses. A dynamically scaled and priced data centre could offer them a much more flexible IT environment where they do not have to worry about capacity planning and scaling – even when compared to a more traditional Cloud environment.
-
Cloud and IoT Will Drive Edge Computing
Edge computing has been widely touted as a necessary component of a viable 5G setup, as it offers a more cost-effective and lower-latency set up than more traditional infrastructure. Also, with IoT being a major part of the business case behind 5G, the number of connected devices and endpoints is set to explode in the coming years, potentially overloading an infrastructure based fully on data centres for processing the data
Although some are touting Edge computing as the ultimate replacement of Cloud, we believe it will be complementary rather than a competing technology – at least in the foreseeable future and certainly as far as 2020 is concerned. Edge computing will allow Cloud providers to better cater to companies that need low latency, quick access to data and data processing. On the mobile side, it will allow them to push workloads to the handset, reducing the backend workload and potentially enhancing data privacy.
-
‘Cloud Creep’ Will Get Worse Before It Gets Better
What we have previously referred to as “shadow IT” is rapidly spreading – and worsening – as organisations move to the Cloud and many organisations are now suffering from what is referred to as “cloud creep”. There are several implications of cloud creep – the most significant ones being security issue and cost.
As the use of stand-alone Cloud services grows, the risk of sensitive data being used, stored and shared in non-compliant ways increases. As for cost, while LoB sourcing of Cloud services may save the strain on the IT department’s budget as the money may come from a different “bucket”, it makes it very difficult to get a true picture of the organisations total IT spend and it may mean that consolidation benefits from well-managed sourcing and usage cannot be achieved. A third and increasingly important factor is energy footprint and savings. A fall-out from cloud creep is increased “server sprawl” whereby virtual machines (VMs) and applications remain under-utilised, leading to poor productivity and proficiency.
-
Alliances and Partnerships Will be Formed as the Battle for the Top Heats Up
The global Cloud market has been consolidating around 5 players: AWS, Microsoft, Alibaba, Google and IBM. Nothing really suggests that this trend will change in 2020.
But even for the current top 5 players, their ability to compete will increasingly come down to their ability to expand their service capabilities beyond their current offerings. Ecosystm expects these players to further enhance their focus on expanding their services, management and integration capabilities through global and in-country partnerships. One particular area might be partnerships – focusing on Cloud migration between Clouds and from Cloud to on-premises.
Download Report: The Top 5 Cloud Trends For 2020
The full findings and implications of the report ‘Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Cloud Trends For 2020’ are available for download from the Ecosystm website. Signup for Free to download the report and gain insight into ‘the top 5 Cloud trends for 2020’, implications for tech buyers, implications for tech vendors, insights, and more resources. Download Link Below ?

The global cloud market is dominated by AWS, Microsoft, IBM, Google, and Alibaba, all of whom are strengthening their grip on the global market. Their continued dominance means that over time, organisations reliance on them will rise.
In order to reduce the dependency on American and Chinese cloud providers, and to counteract mounting data security and privacy concerns, France and Germany are drawing plans to strengthen Europe’s data infrastructure.
The countries announced a proposal to boost Europe’s cloud computing sector in the form of a homegrown, and government-backed, data infrastructure project to establish a safe and sovereign European data infrastructure.
Last month, France recruited tech companies Dassault Systemes – a French software company and OVH – a privately held French cloud computing company to provide plans to break the dominance of U.S. cloud companies.
To serve as an alternative to American and Chinese cloud providers and enable innovative business models, Germany and France have collaborated on developing the core concepts of the European cloud network, called Gaia-X, before trying to get other European countries to join early next year. As a part of Gaia-X, the cloud participants will be required to certify their customers’ information security – e.g. where it is stored and how it is processed. Germany has formed a broad alliance of associations and companies, including Siemens, SAP, Deutsche Bank and Deutsche Telekom for the European cloud project. Claus Mortensen, Principal Advisor at Ecosystm said, “the project is focusing on security at its core and the idea of certifying customers could further help ensure data security and data privacy.”
Mortensen continued, “so far, cloud uptake in Europe has trailed other regions – especially North America and a number of countries in Asia. Whether or not these projects will succeed depends on several factors: the political will behind the project, whether the process becomes overly complicated and lengthy and whether the different companies involved can cooperate when needed.”
Mortensen added, “there is nothing wrong with countries in the EU building cloud infrastructure and issuing tenders for private companies to build this infrastructure – as long as the tenders have followed EU rules and they provide non-discriminatory access to this infrastructure. In the end, it will come down to how the infrastructure is managed and who owns it.”
French and German government officials are set to meet this month, where other interested companies will be invited to provide their inputs. The aim is to create a governance structure for the initiative before the end of the year.
Another goal of pushing homegrown cloud platforms is to support European companies in their development of AI and algorithms and to help them protect against the marketplace which is becoming the domain of a few big vendors.
“The existing cloud giants have technical know-how and readiness, so competing with them will not be easy unless the project can differentiate in ways other than the typical selling points such as price, scalability, granularity, etc. The political backers of this project may be relying on the ‘Made in Europe’ case, but I doubt that will be enough to persuade the bulk of future potential customers” said Mortensen. “More choice is always good for customers and if an objective of this project is to increase cloud uptake in Europe, this would certainly help.”
In June 2019, Ecosystm conducted Roundtables in Sydney and Melbourne supported by our partner Delphix. IT and business executives from data-intensive industries in Australia came together to discuss how to overcome data-driven constraints and enable innovation by effectively managing and distributing data in a secure environment within organisations. These are the salient points that emerged from the sessions.
In the course of my facilitation, I realised that the key focus of the discussions was on how organisations today handle their biggest asset – data – and manage all the moving parts in large and diverse settings and in very traditional enterprises that are transitioning into data-driven “New Age” businesses.
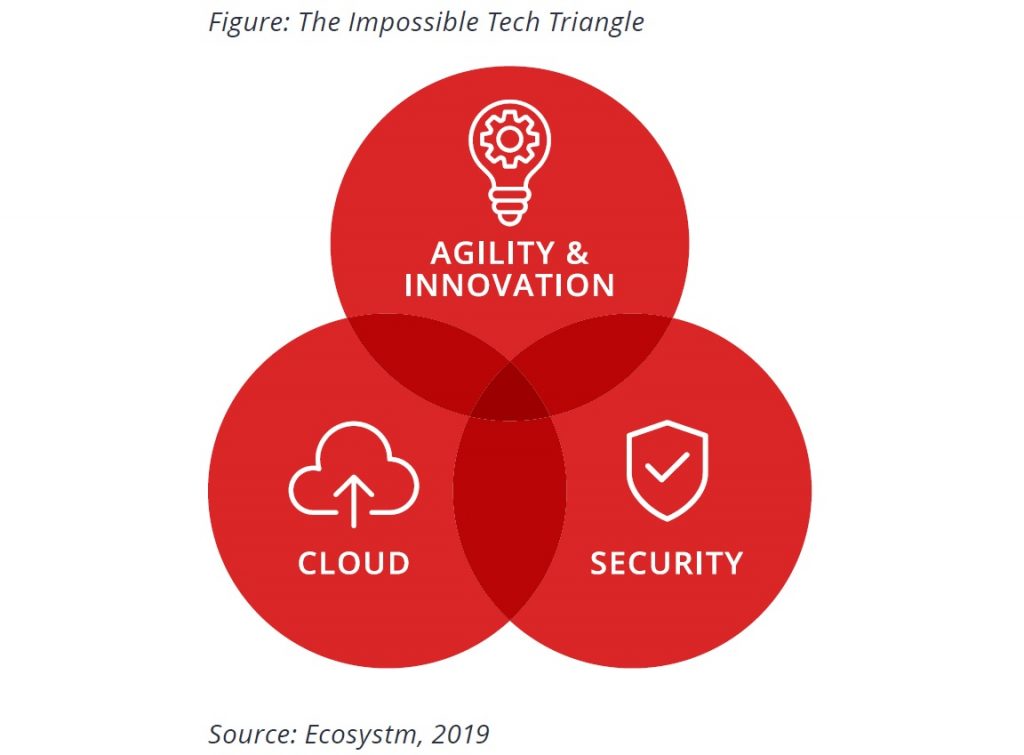
The Impossible Tech Triangle
Data has never been so prolific or strategic as it is today. Multiple sources of data generation and technologically savvy customers have seen a data explosion. Simultaneously, personalised services and data insights have seen a drive toward using the data for increased intelligence in most industries. The biggest risk organisations face and what CSOs and business leaders spend sleepless nights on, is significant disruption due to compromise. Moreover, the complexity of the technology platforms means that no organisation is 100% certain that they have it right and that they are managing the risk effectively.
Does this give rise to a similar situation as in Marketing and Advertising where the triangle of price, quality and speed appear to be unattainable by many organisations?
Key takeaways from the sessions
#1 Drivers & Challenges of Cloud adoption
The fact that discussions around agility and innovation can happen with the intensity it does today, is because organisations have embraced Cloud infrastructure and application development platforms and SaaS solutions.Every organisation’s Cloud journey is unique, driven by its discrete set of requirements. Organisations choosing cloud may not have the resources to build in-house systems – or may choose to migrate to the cloud for various reasons such as cost, productivity, cross-border collaboration or for compliance.
When embarking on a Cloud journey it is important to have a clear roadmap that involves instilling a Cloud-First culture and training the IT organisation in the right skills for the environment. Concerns around costs, security, and data ownership are still synonymous with Cloud, therefore, organisations can distill the workload from a cost angle before jumping on Cloud. It is important for organisations to appreciate when a Cloud option will not work out from a cost angle and to have the right cost considerations in place, because organisations that do a straight resource swapover on Cloud are likely to end up paying more.
Data ownership and data residency can also be challenging, especially from a compliance standpoint. For some, the biggest challenge is to know the status of their data residency. The challenges are not just around legacy systems but also in terms of defining a data strategy that can deliver the desired outcomes and managing risk effectively without ruining the opportunities and rewards that data utilisation can bring. Cloud transformation projects bring in data from multiple and disparate sources. A clear data strategy should manage the data through its entire lifecycle and consider aspects such as how the data is captured, stored, shared, and governed.
#2 Perception on Public Cloud Security
While security remains a key concern when it comes to Cloud adoption, Cloud is often regarded as a more secure option than on-premise. Cloud providers have dedicated security focus, constantly upgrade their security capabilities in response to newer threats and evolve their partner ecosystem. There is also better traceability with Cloud as every virtual activity can be tracked, monitored, and is loggable.
However, the Cloud is as secure as an organisation makes it. The Cloud infrastructure may be secure, but the responsibility of securing applications lies with the organisation. The perception that there is no need to supplement public Cloud security features can have disastrous outcomes. It is important to supplement the Cloud provider’s security with event-driven security measures within an organisation’s applications and cloud infrastructure. As developers increasingly leverage APIs, this need to focus on security, along with functionality and agility should be emphasised on. Organisations should be aware that security is a shared responsibility between the Cloud provider and the organisation.
#3 Viewing Security as a Business Risk – not IT Risk
The Executive Management and the Board may be involved in the Security strategy and GRC policies of an organisation. But a consistent challenge Security teams face is convincing the Board and Senior Management on the need for ongoing focus and investments on cybersecurity measures. Often, these investments are isolated from the organisation’s KPIs and are harder to quantify. But Security breaches do have financial and reputational impact on organisations. Mature organisations are beginning to view Security as a business risk requirement and not a matter of IT risk alone. One of the reasons why Senior Management and Boards do not understand the full potential of data breaches is because CISOs do not translate the implications in business terms. It is their responsibility to find ways to procure senior management buy-in, so that Security becomes part of the Strategy and the costs associated gets written into the cost of doing business.
Training sessions that educate the stakeholders on the basics of the risks associated with using knowledge systems can help. Simulation of actual cybersecurity events and scenario testing can bring home the operational issues around recovery, assessment and containment and it is important to involve senior stakeholders in these exercises. However, eventually the role of the CSO will evolve. It will become a business role and traverse Security across the entire organisation – physical as well as cybersecurity. This is when organisations will truly recognise investment in Security as a business requirement.
#4 Moving away from Compliance-driven Security Practices
Several organisations look at Security as part of their compliance exercise, and compliance is built into their organisational risk management programmes. Often, security practices are portrayed as a product differentiator and used as a marketing tool. An organisation’s Security strategy should be more robust than that and should not only be focused on ticking the right compliance boxes.
A focus on compliance often means that Security teams continually create policies and call out non-compliance rather than proactively contribute to a secure environment. Applications teams do not always have the right skills to manage Security. The focus of the Security team should not be on telling Applications teams what they are doing wrong and writing copious policies, procedures and standards, expecting others to execute on the recommendations. There should be a focus on automated policy-driven remediation that does not restrict the Applications team per se but focuses on unsafe practices, when they are detected. Their role is to work on the implementation and set up Security practices to help the Applications team do what they do best.
#5 Formulating the Right Incident Response Policy
In the Ecosystm Cybersecurity study, 73% of global organisations think that a data breach is inevitable – so organisations largely believe that “it is not about if, but when”. About 50% of global organisations have a cyber insurance policy or are evaluating one. This trend will only rise. Policy-driven incident response measures are an absolute requirement in all enterprises today. However, to a large extent even their incident response policies are compliance driven. 65% of the organisations appear to be satisfied with their current breach handling processes. It is important to keep evolving the process in the face of new threats.
Organisations should also be aware of the need for people management during an incident. Policies might be clear and adhered to, but it is substantially harder to train the stakeholders involved on how they will handle the breach emotionally. It extends to how an organisation manages their welfare both during an incident and long after the incident response has been closed off.
Over the two sessions, we explored how to achieve the ‘unattainable triangle’ of Cloud, Agility and Security. What I found interesting – yet unsurprising – is that discussions were heavily focussed on the role of Security. On the one hand, there is the challenge of the current threat landscape. On the other hand, Security teams are required to deliver a Cloud and an agile development strategy in tandem. This disconnect ultimately highlights the need for Security and data management to be embedded and managed from the very start, and not as an afterthought.
Here are some of the moments from the session –
As companies grapple with finding the right balance between managing multiple touchpoints and driving great customer experience (CX), the importance of getting the flow consistent – right communication to the client without spending too much time on re-directing calls or asking questions about a previous call or experience via a touchpoint – is becoming critical. The desire to impress a customer the first time they come into contact with a touchpoint is an area companies are looking to invest in. Using data as a means to understand customer sentiment before the call comes in will give the agent information to prepare them for making appropriate decisions during and after the call.
Case Study – Carsales
I was recently invited to an AWS Connect, Zendesk and Voice Foundry event in Sydney and it was great to hear from Carsales about how they re-invented CX. Prior to making the leap to deploying the solution from AWS Connect and Zendesk, they had been running their contact centre for years using a traditional contact centre platform. Some of the issues they have faced over the years included the following:
- Difficult and costly to customise
- Expensive support costs
- Expensive and difficult integrations
- Difficult to extract reporting
- Downtime for upgrades
- Difficult to use
These issues are common challenges posed by traditional contact centre platforms. High costs of maintenance and expensive integration costs are some of the challenges I hear of when speaking to end-users. The contact centre and CX industry are at an inflection point where organisations are evaluating how best to drive great CX and at the same time considering how to work with vendors that can help drive innovation in CX. Carsales eventually shortlisted 4 players before making the decision on which cloud provider to work with. They ended up working with Zendesk and AWS Connect.
Carsales recognised the need for a CX solution that could use the data they already have on their customers in Zendesk and Salesforce CRM systems to create a unique experience for each interaction. It was important for them to have a solution that would simplify data warehousing and analytics to make it easier to get a full view of the customer. By integrating the CRM application to AWS Connect as the CX orchestration engine. to bring the contact centre and CRM applications together helped Carsales deliver a personalised CX for their customers.
WHY AWS Connect?
These have come off the points mentioned by Carsales as to why they selected AWS Connect:
- Cloud-Based (accessible anywhere)
- No downtime for upgrades
- Access to Data (Lambda and APIs) via ZenDesk and Salesforce
- Easy UI
- Support from implementation partner Voice Foundry
- Affordable solution
- Access to great technology such as Speech to Text (Polly), Speech Recognition (Lex) and Analytics (Transcribe and Comprehend)
- Scalable and customisable call flows
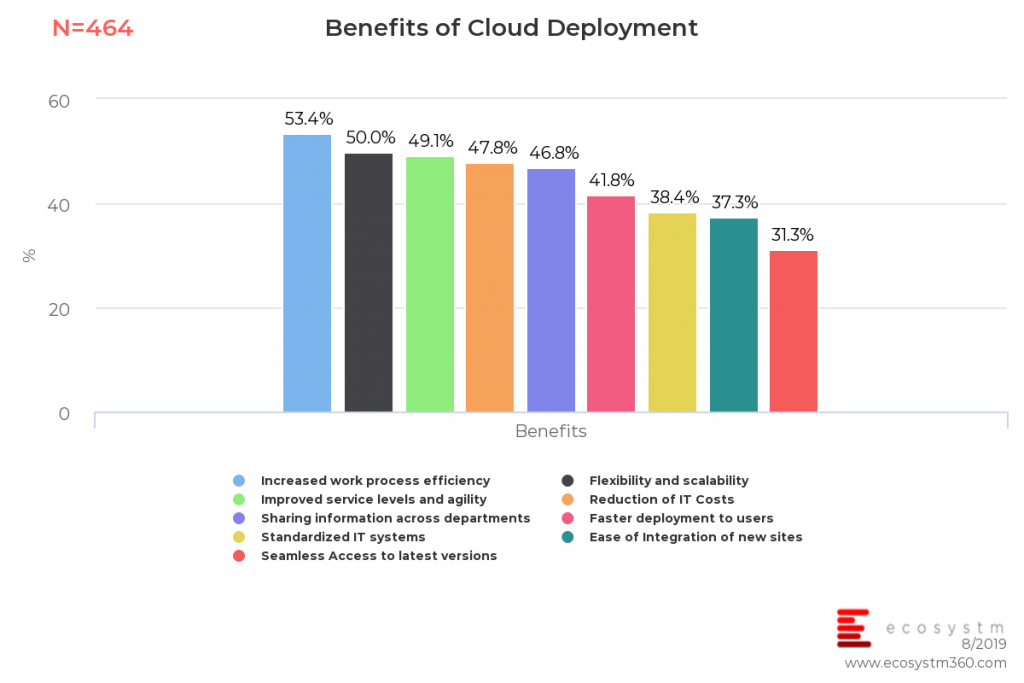
In the global Ecosystm Cloud study, as depicted by the chart below, about 53% of organisations state that increased work processes and efficiency are a key benefit of the cloud. Nearly half the organisations rate flexibility and scalability and improved service levels and agility as the main benefits of a cloud deployment.
Implementation Learnings
What Carsales found about the AWS Connect solution, is how changes can be made easily. Most configurations can be made by the contact centre staff and there is no need to go to IT. Their primary aim was to deliver a personalised CX by accessing data from other internal systems (CRM, proprietary databases, etc) and the solution addressed this need.
The advice that Carsales gives to others implementing a Cloud Contact Centre are:
- Ensure that you have invested in the network to support voice over IP.
- Make sure that your headsets are compatible to ensure full functionality.
- Engage with a partner rather than implementing the platform on your own. Although you can implement AWS Connect solution on your own, it can be difficult. Voice Foundry was a great implementation partner.
The Importance of Data-Driven CX
The market is witnessing a shift where organisations are looking for new and more agile platforms for CX. The challenges, as highlighted by Carsales – such as existing solutions being difficult and costly to customise – are some of the common challenges we are hearing from organisations about the limitations of traditional telephony and contact centre solutions. Whilst the traditional vendors still have a majority share of the market, that is changing. Some of the new cloud contact centre vendors are offering new and dynamic ways of driving a better experience for the users of the technology – from agents to those that manage the contact centre solution. The ability to add agents when needed has become easier (without intervention from IT) and cloud provides better security due to the multiple back-ups and redundancies it offers. The ability to reduce maintenance and customise applications with new agile methodologies and APIs are driving a new era in the contact centre market. The single most important area is deep analytics. The ability to have deep analytics to understand the customer better as a starting point before a call, during a call and after the call is critical. Artificial intelligence can be used to better understand customer sentiment and detect trends in customer data.
The shift from traditional contact centres to cloud contact centres is happening and no longer just with mid-market companies. Large organisations are making the shift to the cloud as the benefits are apparent. Implementing a data-driven culture is key to driving a personalised CX. The tight integration between CRM databases and the applications in the contact centre is becoming more important than ever.


















