Customer feedback is at the heart of Customer Experience (CX). But it’s changing. What we consider customer feedback, how we collect and analyse it, and how we act on it is changing. Today, an estimated 80-90% of customer data is unstructured. Are you able and ready to leverage insights from that vast amount of customer feedback data?
Let’s begin with the basics: What is VoC and why is there so much buzz around it now?
Voice of the Customer (VoC) traditionally refers to customer feedback programs. In its most basic form that means organisations are sending surveys to customers to ask for feedback. And for a long time that really was the only way for organisations to understand what their customers thought about their brand, products, and services.
But that was way back then. Over the last few years, we’ve seen the market (organisations and vendors) dipping their toes into the world of unsolicited feedback.
What’s unsolicited feedback, you ask?
Unsolicited feedback simply means organisations didn’t actually ask for it and they’re often not in control over it, but the customer provides feedback in some way, shape, or form. That’s quite a change to the traditional survey approach, where they got answers to questions they specifically asked (solicited feedback).
Unsolicited feedback is important for many reasons:
- Organisations can tap into a much wider range of feedback sources, from surveys to contact centre phone calls, chats, emails, complaints, social media conversations, online reviews, CRM notes – the list is long.
- Surveys have many advantages, but also many disadvantages. From only hearing from a very specific customer type (those who respond and are typically at the extreme ends of the feedback sentiment), getting feedback on the questions they ask, and hearing from a very small portion of the customer base (think email open rates and survey fatigue).
- With unsolicited feedback organisations hear from 100% of the customers who interact with the brand. They hear what customers have to say, and not just how they answer predefined questions.
It is a huge step up, especially from the traditional post-call survey. Imagine a customer just spent 30 min on the line with an agent explaining their problem and frustration, just to receive a survey post call, to tell the organisation what they just told the agent, and how they felt about the experience. Organisations should already know that. In fact, they probably do – they just haven’t started tapping into that data yet. At least not for CX and customer insights purposes.
When does GenAI feature?
We can now tap into those raw feedback sources and analyse the unstructured data in a way never seen before. Long gone are the days of manual excel survey verbatim read-throughs or coding (although I’m well aware that that’s still happening!). Tech, in particular GenAI and Large Language Models (LLMs), are now assisting organisations in decluttering all the messy conversations and unstructured data. Not only is the quality of the analysis greatly enhanced, but the insights are also presented in user-friendly formats. Customer teams ask for the insights they need, and the tools spit it out in text form, graphs, tables, and so on.
The time from raw data to insights has reduced drastically, from hours and days down to seconds. Not only has the speed, quality, and ease of analysis improved, but many vendors are now integrating recommendations into their offerings. The tools can provide “basic” recommendations to help customer teams to act on the feedback, based on the insights uncovered.
Think of all the productivity gains and spare time organisations now have to act on the insights and drive positive CX improvements.
What does that mean for CX Teams and Organisations?
Including unsolicited feedback into the analysis to gain customer insights also changes how organisations set up and run CX and insights programs.
It’s important to understand that feedback doesn’t belong to a single person or team. CX is a team sport and particularly when it comes to acting on insights. It’s essential to share these insights with the right people, at the right time.
Some common misperceptions:
- Surveys have “owners” and only the owners can see that feedback.
- Feedback that comes through a specific channel, is specific to that channel or product.
- Contact centre feedback is only collected to coach staff.
If that’s how organisations have built their programs, they’ll have to rethink what they’re doing.
If organisations think about some of the more commonly used unstructured feedback, such as that from the contact centre or social media, it’s important to note that this feedback isn’t solely about the contact centre or social media teams. It’s about something else. In fact, it’s usually about something that created friction in the customer experience, that was generated by another team in the organisation. For example: An incorrect bill can lead to a grumpy social media post or a faulty product can lead to a disgruntled call to the contact centre. If the feedback is only shared with the social media or contact centre team, how will the underlying issues be resolved? The frontline teams service customers, but organisations also need to fix the underlying root causes that created the friction in the first place.
And that’s why organisations need to start consolidating the feedback data and democratise it.
It’s time to break down data and organisational silos and truly start thinking about the customer. No more silos. Instead, organisations must focus on a centralised customer data repository and data democratisation to share insights with the right people at the right time.
In my next Ecosystm Insights, I will discuss some of the tech options that CX teams have. Stay tuned!

Banks, insurers, and other financial services organisations in Asia Pacific have plenty of tech challenges and opportunities including cybersecurity and data privacy management; adapting to tech and customer demands, AI and ML integration; use of big data for personalisation; and regulatory compliance across business functions and transformation journeys.
Modernisation Projects are Back on the Table
An emerging tech challenge lies in modernising, replacing, or retiring legacy platforms and systems. Many banks still rely on outdated core systems, hindering agility, innovation, and personalised customer experiences. Migrating to modern, cloud-based systems presents challenges due to complexity, cost, and potential disruptions. Insurers are evaluating key platforms amid evolving customer needs and business models; ERP and HCM systems are up for renewal; data warehouses are transforming for the AI era; even CRM and other CX platforms are being modernised as older customer data stores and models become obsolete.
For the past five years, many financial services organisations in the region have sidelined large legacy modernisation projects, opting instead to make incremental transformations around their core systems. However, it is becoming critical for them to take action to secure their long-term survival and success.
Benefits of legacy modernisation include:
- Improved operational efficiency and agility
- Enhanced customer experience and satisfaction
- Increased innovation and competitive advantage
- Reduced security risks and compliance costs
- Preparation for future technologies
However, legacy modernisation and migration initiatives carry significant risks. For instance, TSB faced a USD 62M fine due to a failed mainframe migration, resulting in severe disruptions to branch operations and core banking functions like telephone, online, and mobile banking. The migration failure led to 225,492 complaints between 2018 and 2019, affecting all 550 branches and required TSB to pay more than USD 25M to customers through a redress program.
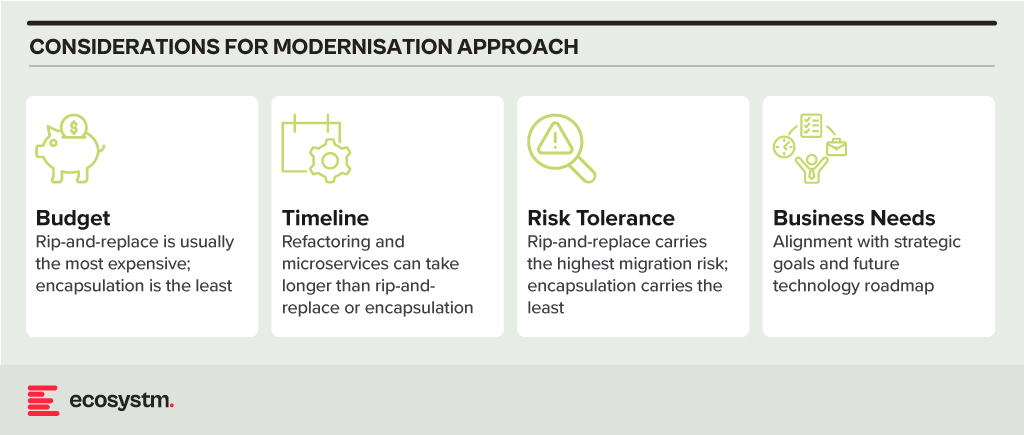
Modernisation Options
- Rip and Replace. Replacing the entire legacy system with a modern, cloud-based solution. While offering a clean slate and faster time to value, it’s expensive, disruptive, and carries migration risks.
- Refactoring. Rewriting key components of the legacy system with modern languages and architectures. It’s less disruptive than rip-and-replace but requires skilled developers and can still be time-consuming.
- Encapsulation. Wrapping the legacy system with a modern API layer, allowing integration with newer applications and tools. It’s quicker and cheaper than other options but doesn’t fully address underlying limitations.
- Microservices-based Modernisation. Breaking down the legacy system into smaller, independent services that can be individually modernised over time. It offers flexibility and agility but requires careful planning and execution.
Financial Systems on the Block for Legacy Modernisation
Data Analytics Platforms. Harnessing customer data for insights and targeted offerings is vital. Legacy data warehouses often struggle with real-time data processing and advanced analytics.
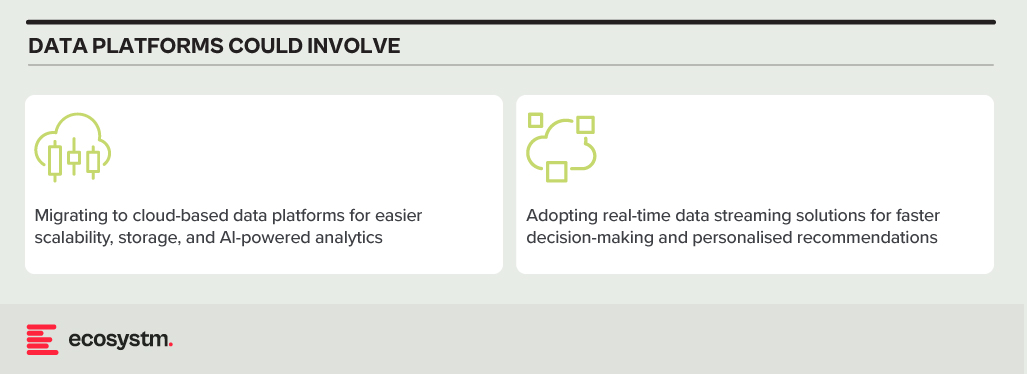
CRM Systems. Effective customer interactions require integrated CRM platforms. Outdated systems might hinder communication, personalisation, and cross-selling opportunities.

Payment Processing Systems. Legacy systems might lack support for real-time secure transactions, mobile payments, and cross-border transactions.

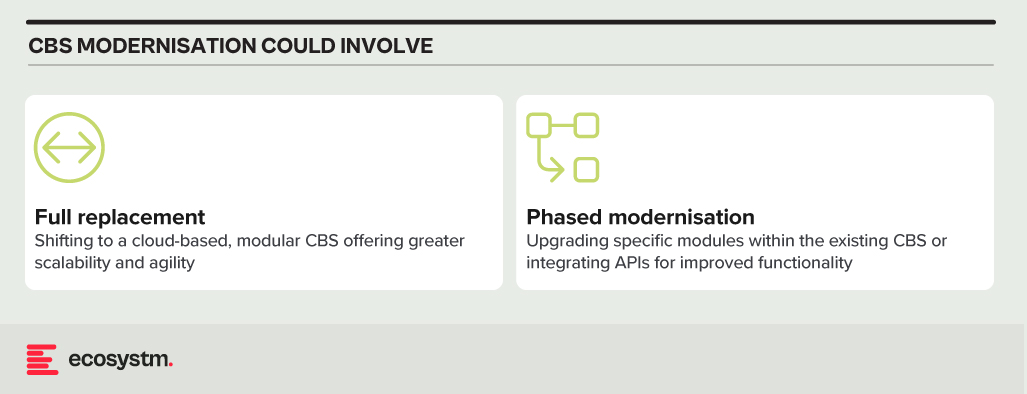
Core Banking Systems (CBS). The central nervous system of any bank, handling account management, transactions, and loan processing. Many Asia Pacific banks rely on aging, monolithic CBS with limited digital capabilities.
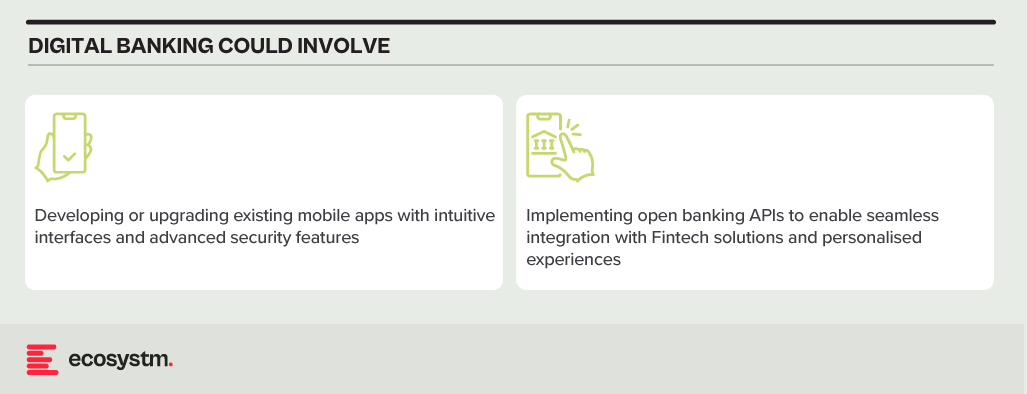
Digital Banking Platforms. While several Asia Pacific banks provide basic online banking, genuine digital transformation requires mobile-first apps with features such as instant payments, personalised financial management tools, and seamless third-party service integration.
Modernising Technical Approaches and Architectures
Numerous technical factors need to be addressed during modernisation, with decisions needing to be made upfront. Questions around data migration, testing and QA, change management, data security and development methodology (agile, waterfall or hybrid) need consideration.
Best practices in legacy migration have taught some lessons.
Adopt a data fabric platform. Many organisations find that centralising all data into a single warehouse or platform rarely justifies the time and effort invested. Businesses continually generate new data, adding sources, and updating systems. Managing data where it resides might seem complex initially. However, in the mid to longer term, this approach offers clearer benefits as it reduces the likelihood of data discrepancies, obsolescence, and governance challenges.
Focus modernisation on the customer metrics and journeys that matter. Legacy modernisation need not be an all-or-nothing initiative. While systems like mainframes may require complete replacement, even some mainframe-based software can be partially modernised to enable services for external applications and processes. Assess the potential of modernising components of existing systems rather than opting for a complete overhaul of legacy applications.
Embrace the cloud and SaaS. With the growing network of hyperscaler cloud locations and data centres, there’s likely to be a solution that enables organisations to operate in the cloud while meeting data residency requirements. Even if not available now, it could align with the timeline of a multi-year legacy modernisation project. Whenever feasible, prioritise SaaS over cloud-hosted applications to streamline management, reduce overhead, and mitigate risk.
Build for customisation for local and regional needs. Many legacy applications are highly customised, leading to inflexibility, high management costs, and complexity in integration. Today, software providers advocate minimising configuration and customisation, opting for “out-of-the-box” solutions with room for localisation. The operations in different countries may require reconfiguration due to varying regulations and competitive pressures. Architecting applications to isolate these configurations simplifies system management, facilitating continuous improvement as new services are introduced by platform providers or ISV partners.
Explore the opportunity for emerging technologies. Emerging technologies, notably AI, can significantly enhance the speed and value of new systems. In the near future, AI will automate much of the work in data migration and systems integration, reducing the need for human involvement. When humans are required, low-code or no-code tools can expedite development. Private 5G services may eliminate the need for new network builds in branches or offices. AIOps and Observability can improve system uptime at lower costs. Considering these capabilities in platform decisions and understanding the ecosystem of partners and providers can accelerate modernisation journeys and deliver value faster.
Don’t Let Analysis Paralysis Slow Down Your Journey!
Yes, there are a lot of decisions that need to be made; and yes, there is much at stake if things go wrong! However, there’s a greater risk in not taking action. Maintaining a laser-focus on the customer and business outcomes that need to be achieved will help align many decisions. Keeping the customer experience as the guiding light ensures organisations are always moving in the right direction.

Organisations are moving beyond digitalisation to a focus on building market differentiation. It is widely acknowledged that customer-centric strategies lead to better business outcomes, including increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, competitiveness, growth, and profitability.
AI is the key enabler driving personalisation at scale. It has also become key to improving employee productivity, empowering them to focus on high-value tasks and deepening customer engagements.
Over the last month – at the Salesforce World Tour and over multiple analyst briefings – Salesforce has showcased their desire to solve customer challenges using AI innovations. They have announced a range of new AI innovations across Data Cloud, their integrated CRM platform.
Ecosystm Advisors Kaushik Ghatak, Niloy Mukherjee, Peter Carr, and Sash Mukherjee comment on Salesforce’s recent announcements and messaging.
Read on to find out more.
Download Ecosystm VendorSphere: Salesforce AI Innovations Transforming CRM as a PDF

Since early 2020 nearly all organisations have strengthened their online presence and commerce abilities – irrespective of their industry. They have come to terms with the fact that the ability to win and retain customers, is largely linked to the digital customer experience (CX) they are able to deliver.
They have invested heavily in their CX roadmaps and technologies; but will find themselves solving for the same challenges they have faced the last 2 years – continued growth of digital experiences; gaining insights from customer data; customer churn; and catering to customer channel preferences.
2022 will be the time to consolidate and build the capabilities required to analyse the immense amount of customer data that they have access to – to finally be able to offer personalised customer experience.
Read on to find out what Ecosystm Advisors Audrey William and Tim Sheedy think will be the leading CX trends in 2022.
Click here to download Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Trends for Customer Experience in 2022 as a PDF

The term “intranet” won’t die. It should. I don’t think I have ever seen a good intranet in 24 years since I first started writing about business intranets in 1997 (yes – by writing about this market I was a part of the problem!). I’d even argue that there is no such concept as a “good intranet” – as it is an inherently flawed idea. An intranet effectively tries to bring together all the stuff that employees don’t access or don’t want to access and puts it somewhere that employees might actually use.
Intranets don’t help employees do their jobs
Why don’t we access these systems? Because they are generally not “core” to our jobs. Employees will find and access the systems and applications that are core to getting their jobs done – even if they are terrible to use (even in this “designed for humans, SaaS-world” there are still plenty of core systems that are terrible to use). Some companies try to integrate their intranet and core applications; making employees access the intranet to login to their essential apps. This might make life easier for IT responsible for deploying, managing and securing the applications. It also excites HR as they hope that along the way to accessing these systems, a “schmear” of company culture or information might rub off on them. But many employees quickly work out ways around these systems by bookmarking sites or using dedicated applications.
One of the reasons that company intranets are generally so poor is because they don’t actually help people do their job. There are often no guided processes or checklists to ensure follow through on tasks. Remember how many salespeople didn’t (or still don’t) use the CRM system because it didn’t help them actually sell? Well, intranets suffer from the same problem.
Some software providers looked to solve this problem by bringing the company intranet and core application together into a single interface. Salesforce has limited success with Chatter – but many users of Chatter spent much of their energy telling employees they “weren’t using Chatter the right way” – which sounds awfully like a design problem, not a user one.
Now is a good time to review your company intranet
Why now? Because the big collaboration players (Microsoft in particular) are improving their offerings in this space, creating partnerships, and painting a vision of a world where employees might actually WANT to access company intranets.
Which brings me to Microsoft Viva. We wrote about Viva when it was initially launched as a concept and businesses (and more importantly, their employees) can now experience the capabilities. Viva helps resolve some of the challenges with business intranets:
- It makes some of the collaboration systems more usable and insightful
- It actually provides outcomes for employees (through the learning module in particular)
- It integrates with existing processes and exposes these application-centric processes through Teams
At the same time, it is trying to be a “cultural change agent” by having a single place to go to view company news and announcements. This is similar to many company intranets, and like many of them, is likely to be an abandoned sideshow – the only time many employees visit it will be when they are forced to – like when the CEO sends an all-company email saying that there is an announcement on the company intranet that everyone needs to see. Which is the digital equivalent of posting you a letter to inform you that you have an email!
The challenge for Viva is that employees need to be using Teams to get the most out of it – and I don’t just mean “using Teams for chat and calling” but using the collaboration elements effectively – ALL the time. And the challenge with this is that (a) many employees don’t EVER use these features of Teams (or use them sporadically), and (b) some companies (and teams within companies) have multiple platforms for collaboration and sharing (Slack, Trello, Basecamp, Jira etc).
But either way, Viva looks like a positive step forward for collaboration – and more importantly, it gives businesses some guidelines on how to improve their existing intranet.

How to Make your Intranet work?
Integrate the work that people have KPIs on, with collaboration and intranet systems
Design processes so the intranet makes it EASIER for people to do their jobs – by removing unnecessary handing of information, copying and pasting, multiple levels of authentication and moving between many applications or screens. Leave requests or approving invoices have already been integrated into email – so managers can click a button in the email to send the approval. But what if there were a page on the intranet where all the leave requests or approvals for funding or payment were in a single spot? What if the system provided insight around these requests (such as Mary Singh only has 1 day leave left, or Company ABC takes 90 days to pay on average)? And if all leave requests could be approved with a single click, it actually makes the employees life easier.
Build processes into the systems to solve employee pain points
Many intranets are ostensibly used for helping employees find each other or find experts on specific topics. But they don’t guide this process – they just say “there’s lots of information here – use the search tool and good luck!”. Design guided processes for outcomes people actually want to achieve. Survey your employees to find out what they’d like the intranet to help them achieve – and build some employee journey maps across various roles to understand the challenges and pain points. If it makes sense, use the intranet to help resolve those pain points.
Make your existing tools more powerful and easier to use
Your employees generally want to collaborate. Don’t get me wrong – many don’t wake up each morning thinking that they’d love to share some documents with unknown team members today – but they do want to work together more easily than they do today. So take a look at what stops them from achieving this and look to solve those problems by making existing tools more powerful and easier to use. Adding analytics helps employees and their managers better manage their time and their interactions. Automating file sharing and discovery will help employees find the information they need without adding additional work for the content creator.
Businesses need to think of their intranets as “places to get things done”
Too many intranets seem to be designed for 4pm on Friday afternoon versus 9am Monday morning. And if this is yours, then don’t be surprised that employees don’t use it that often or give it little time. The more you can use an intranet to make employees lives easier, the more likely that you will be creating a resource which improves the productivity and happiness of the employees you serve.

As economies around the world are beginning to recover from the recessions and slowdowns caused by the pandemic, we are beginning to witness, what I like to call, the “Great Bounce Forward”.
Why the Great Bounce Forward? Because too many businesses, journalists and economists are talking about businesses “bouncing back”. But there is no bounce back. We are bouncing into the “economic unknown”. The trading conditions we see today are nothing like what they were at the beginning of 2020. While many people refer to the “new normal” I have heard few talks about how they are or will benefit from these new market conditions.
Bouncing back may not be relevant as we negotiate the economic unknown – it is time to evaluate how we can bounce forward!
Leaping Ahead Through Digital First
Customer interactions have changed – digital-first is now a requirement – and many customers expect a personalised and optimised experience. Many companies are starting to personalise experiences today – thinking they are “delighting customers” through personalised transactions and journeys. But you don’t delight customers by giving them what they want – you disappoint them if you don’t offer a true personalised experience.
Digital changes are coming thick and fast. For example, Australia Post has announced that online sales are currently 20% higher than what they were at the previous highest peak in December 2020. Yes – much of Australia is in a lockdown, but online sales are dwarfing what they were during lockdowns in 2020.
But it is not just about offering online sales. In the digital world, customers now expect to be able to track packages, get alerts when they are delivered, and have access to easy and free returns. Again – if you don’t do this today, you are creating poor customer experiences and are most likely losing business to those that offer great experiences.
Here is what organisations are witnessing:
The need to evolve their CRM solution. Salespeople expect the CRM to give them insights on who to sell to, why to sell to them and what approach will work best. CRM systems that don’t provide this analysis are letting businesses and salespeople down.
Analytics has to be turned into actions. More businesses are telling their analytics partners to stop telling them what to do, and just do it! Automating the outcomes of BI and analytics is beginning to be expected.
Ease of use has become essential. Interactions and processes need to be intelligent and easy to automate. We no longer throw teams of people at challenges – we automate the outcomes and use technology to deliver entirely new experiences without teams of employees pulling strings behind the scenes.
Process and technology changes happen quickly and seamlessly. We have been taught this by Zoom, Microsoft, AWS and Google. If you aren’t doing this today, you are behind the market and behind the expectations of your employees and customers.
Ecosystems are emerging to enable this agility and innovation. We can now innovate with a growing range of partners. Companies can partner for a single sale and move on. Start-ups are being embraced by dinosaurs, and competitors are becoming partners. More companies than ever are involving their own customers in their innovation processes. Ecosystems are changing the ability of technology and business teams to offer new and improved services to customers and employees.

Time for a Shift in Organisational Culture
Seemingly, the world changed overnight. But many of these changes have been in the works for years. It just took a global crisis to highlight how important they are and how much organisations need to change to embrace these opportunities. The only thing holding businesses back from thriving in the Great Bounce Forward are their people and culture. If you can embrace these changes, your businesses will move forward and emerge as different companies to the ones that entered the pandemic in early 2020. You’ll be more open, agile, innovative and digitally aware. You’ll be able to move in new, unheralded directions, driving improved customer, shareholder, or citizen value.
So stop thinking about how your business will bounce back. Make plans for it to bounce forward into the unknown.

New ‘as-a-service’ products are continuing to expand the options that are available to organisations, fragmenting the functionality used across many technology providers. Choosing the right products is getting more and more difficult – kind of like trying to choose your VOD service at home.
How many VOD networks do you use?
Do you remember the time when your access to video content was through either broadcast TV or cable TV? And when a regular trip to the video store was part of life? And you had to watch programs when the networks scheduled them?
Most programming was only available through one of those media, particularly if you wanted to see the latest series or movies. In some countries, we paid a TV license fee that partly paid for the government-funded free-to-air network. For those with access to cable or satellite TV, we paid a monthly fee for a smorgasbord of channels, most of which we never watched.
Today, we still have those options, but an explosion of video-on-demand (VOD) options has occurred. Each of them requires a separate contract that users rarely read. So we have little knowledge of what these services have contracted to deliver or how they will use our data. But we have an amazing range of content available if we want.
At least most are monthly services that we can cancel at short notice unless you take advantage of the price reduction for subscribing for a year or longer.
How many as-a-service products are you choosing?
Translate this to an organisation that is increasingly using as-a-service products. Choosing a service to use has much more complex requirements, there are more options available and happens more frequently.
If we think the domestic landscape for video is complicated, the options for as-a-service are significantly more fragmented. The most frequently used approach to selecting VOD services is to choose those that offer the content you want to see.
Choosing the appropriate as-a-service offering is much harder as the functional, security, integration and pricing requirements are much more complex than wanting to see a particular movie or drama series.
Suppliers of these services do not make it easy to understand what you get for your money. They decide to bundle or unbundle functions depending on a mix of factors to differentiate themselves for customers. This makes value and price comparisons difficult.
For example, there is a myriad of CRM suppliers out there offering a complex matrix of pricing and functionality options. And in each case, there is often an ecosystem of suppliers providing different pieces of functionality. No one provider delivers all the functionality that we desire.
Organisations wanting to choose as-a-service products need to be very clear on which requirements are the most important to them, and how well each supplier meets those specific needs. They cannot afford to be distracted by less valuable features.
It is extremely unlikely that one tech vendor will be able to provide all the desired features. Increasingly, other vendors will supplement the core functionality with niche features. So the selection has to take into account the ecosystem around the core as-a-service functionality.

Recommendations
Tech buyers should make sure they have a clear definition and priority for the features that they require for each purpose. Added to this they need to be very clear what they want in a single package, and what they are prepared to purchase from a wider ecosystem. Both need to be part of the selection criteria.
Once implemented, changing as-a-service products is a much more difficult proposition than switching VOD providers.
Tech vendors need to stay away from confusion marketing to make it possible for buyers to understand what they are getting. They need to help customers gain a clear understanding of any ecosystem they participate in, and what this means for the buyer.
The consequences of getting this choice right are dramatically more important than choosing the VOD provider with the programming you want.
And we know how difficult that choice has become.

Moving from a product or regional focus to an industry focus appears to be the “strategy du jour” for many technology vendors today. For some it is a new strategy – with the plan to improve customer focus and increase growth; for others it is the pendulum moving back to where they were five or ten years ago as they bounce from being industry-centric to product-centric to geography-centric and back again.
Getting your industry focus right is much harder than it seems – and has to be timed with client needs and market opportunity. The need to focus on the industry varies for different technology products, services and capabilities. For example, most technology buyers want their vendors to understand what their business does and how they add value to customers – that is a given and industry-aligned Sales teams make a lot of sense. Many tech buyers also want certain software functions to align directly to their processes – there is little appetite to customise ERP and financial suites to specific industry needs and processes – and tech vendors should support these out-of-the-box or cloud needs.
Industry Solutions May Not Drive Competitive Advantage
If the industry solution you are selling is the same as what any of their competitors can buy from you, then organisations get the exact same benefit as the market – no more, no less. For example, about 10-15 years ago, large telecom providers around the globe made significant investments in CRM platforms (often from Siebel) – bringing in one of a few large global systems integrators to deploy their standard processes and systems. These CRMs were supposed to provide business and customer benefit, and drive competitive advantage. And while they did deliver positive change (often at SIGNIFICANT cost!) when every telecom provider was using the same solution with the same or similar processes, any competitive advantage was lost.
Industry Solutions are Often the Sign of a Mature Market
The widely accepted hypothesis is that the technology innovation and adoption happens in waves. The market has 5-7 year waves of innovation, followed by 5-7 year waves of deployment, adoption and consolidation.
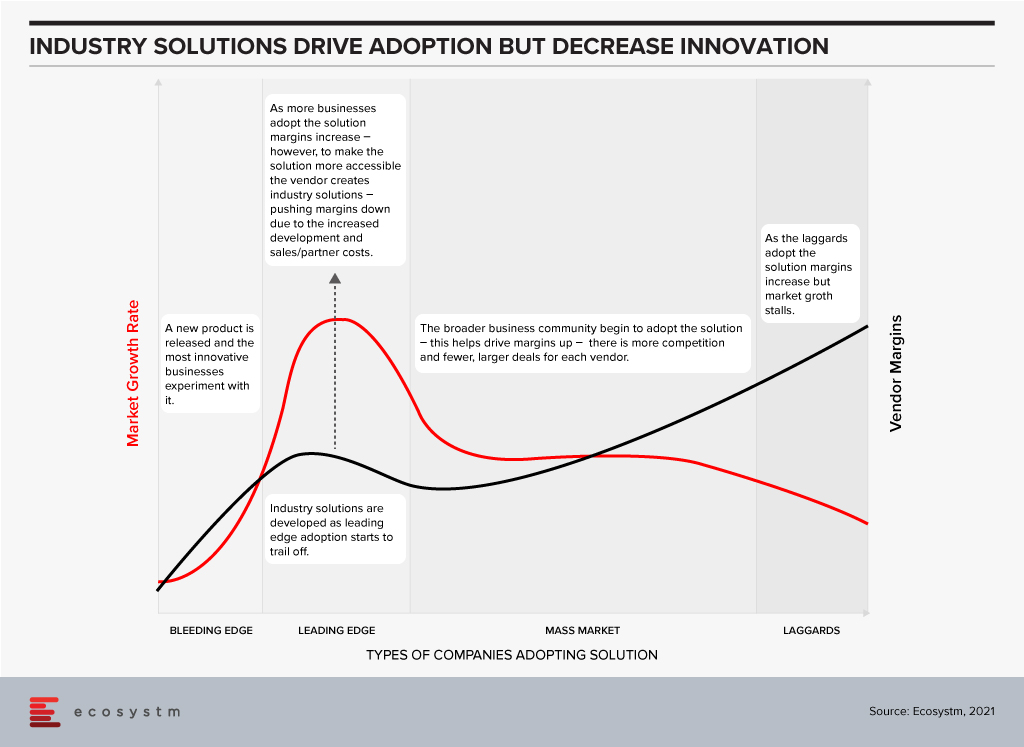
The Innovation Phase. In this stage new companies emerge, new products or services are launched and leading/bleeding edge companies embrace these new technologies to drive competitive advantage and business growth. They experiment with new technologies that drive new business capabilities – sometimes failing, but always pushing the envelope for business innovation and forging the path for mass market adoption. In this stage there is often little demand for industry solutions – as both the providers and buyers of the solutions are still working out where the business benefit is; where the technology might be able to drive change or help them get ahead of competitors. If you examine the growth of a company such as Salesforce, you see that the early stage products are targeted towards a generic market – customers are expected to customise the solution based on their needs and individual requirements. In 2002 I worked for a challenger telecom provider that had deployed a traditional Peoplesoft CRM capability, and I was part of the team that brought Salesforce into the business – and as a cloud-based solution, we saw the competitive advantage was the pace at which we could customise the product (by excluding IT teams and processes). However, the solution was a “one-size-fits-all” product. The innovation stage is typically characterised by high growth of smaller vendors and technology service providers who challenge the status quo.
The Deployment, Adoption and Consolidation Phase. This stage of market growth is when the mass market starts to adopt these solutions. Many of these buyers walk the paths that have been forged before them by the more innovative, leading edge businesses. This stage typically sees less innovation, less experimentation, and more standard deployments. To make the solutions more palatable and easier to sell to the mass market tech vendors typically pre-configure or customise the solutions to specific needs – for business teams, roles or industries. It is usually in this stage of market growth and deployment that the industry solutions see significant interest and adoption. This is where the mass market gets access to the business benefits the more innovative businesses received many years earlier (and often profited from in this time). In my example of the Salesforce deployment in 2002, over the following years many partners started to create industry solutions, and eventually Salesforce themselves sold industry-specific solutions – or at least targeted certain products and capabilities at specific industries and provided accelerated deployment models to drive advantage at a faster rate. The deployment and consolidation stage of market growth is typically characterised by steady, slow growth across the entire market as benefits are being driven to all providers (product vendors and solutions or implementation providers). Legacy providers either play catch up or suffer declining business as they realise the solution they sell no longer provides the business and customer the benefits that it used to.
Industry Focus Should be Aligned to Customer Segments, Solution Type and Geography
The decision to sell industry-focused solutions should be driven by the type of solution you are selling; the business benefit you are promising; and the type of business you are targeting the solution towards. Businesses that are more innovative will still buy some pre-configured, industry-specific solutions that don’t differentiate their business or drive competitive advantage. But where they expect competitive advantage, they need to stand apart – to be the only business with that capability.
It is also worth understanding that an innovation in one market might be standard practice in another (and vice-versa). Countries across the globe and specifically here in Asia Pacific have different approaches to technology and innovation. China and parts of Southeast Asia are often innovators – pushing the boundaries of new and emerging tech to do things we never thought possible (in the same way Silicon Valley traditionally has done). Australia and India are traditional markets that adopt industry solutions after they have been tried and tested by others. Innovation in Japan seems to happen in stages and at pace but only once every 10-15 years or so. New Zealand and Singapore are generally more nimble economies where businesses often have to be innovative to gain global competitive advantage quickly.
Evidence indicates that the rate of innovation is increasing across the entire region – even in the less innovative economies. The window for industry solutions is much smaller regardless of location – as the next new innovation is just around the corner. Even the large, traditionally less agile businesses are driving innovation programs – for example, many of the big financial services “dinosaurs” such as DBS and Commonwealth Bank often win tech innovation awards and offer market-leading customer experiences.
Use this lens to better develop your industry approach. The depth of your industry solution or capability will dictate the opportunities that you will drive based on the type of customer and technology stage. Do you want to drive innovation or efficiency in your clients? Do you want to win the big “safer” deals – but be thought of as a technology solution provider; or win the smaller deals in companies that will become the market leaders of tomorrow – and be considered a market leader and king maker? Understanding your own business goals, the current sales and delivery capabilities, and the capacity to change will help your company create a go-to-market strategy that suits your current and future customers and will likely dictate the growth rate of your business over the next 5-7 years.
Keep yourself abreast with the latest industry trends
Ecosystm market insights, data, and reports are jam-packed with industry analysis and digital trends across several industry verticals to help you keep tabs on the fast-paced world of tech.

Last week Zoom announced a USD 100 million Zoom Apps Fund to promote the development of Zoom’s ecosystem of Zoom applications, integrations, video, developer tools, and hardware.
As part of Zoom Apps Fund, the company will invest in a portfolio of companies that are promoting and innovating on Zoom’s video conferencing platform. The portfolio companies will receive initial investments between USD 250,000 and USD 2.5 million to build solutions. To support the practice, Zoom is providing its tools and expertise to various start-ups, entrepreneurs, and industry players to build applications and integrate Zoom’s functionality and native interface in their products.
In March, Zoom introduced an SDK designed to help programmers embed Zoom functionality inside their applications. Zoom SDK is a component of Zoom Developer platform which includes SDKs, APIs, webhooks, chatbots, and distribution for applications and integration. Last year Zoom launched Zoom Apps and Zoom Marketplace at its Zoomtopia virtual conference to bring applications and productivity into the Zoom experience.
Zoom is not alone in evolving their Unified communications as a service (UCaaS) capabilities and market. Tencent rolled out their video conferencing solution for the global market, Facebook expanded their offerings in videoconferencing applications through the integration of new features, Google announced a series of upgrades and innovations to better support the flexibility needs of frontline and remote workers in Google Workspaces, and Microsoft introduced Viva that aims to bring together communications, knowledge, learning, resources, and insights together.

“Ecosystm research shows that 50% of organisations will continue to increase use of collaboration platforms and tools in 2021. However, if videoconferencing remains just a tool to log in to for meetings without purpose-built workflows and functionality that suit worker profiles, then it will start losing its attractiveness. Vendors need to work on user interface, UX, the lighting, security, audio quality and many other aspects that draws users to the platform.
The big question is what next for videoconferencing vendors? How can engineering teams innovate to build the capabilities organisations want when they use drawing tools, share images, have chats and discussions within collaboration platforms? How do you make the experience real so employees can “live and breathe” in the environment?
Zoom investing in understanding what apps and workflows are suited for a particular vertical or business is fundamental to the future of video and collaboration and will be a big game changer.”

“Zoom is continuing to expand the markets in which they operate and investing in start-ups increases their opportunities to grow as a platform. Their App Marketplace already offers a rich source of innovations, with Zoom themselves appearing to develop integration with market leaders such as Salesforce and HubSpot in the CRM category. This has led to Zoom integrations in close to 80 CRM products – including integrations developed in-house by Salesforce and HubSpot to supplement Zoom capabilities.
They are promoting an open web and audio-conferencing platform that does not limit users to the walled-garden approach of competitors such as Microsoft Teams.
Zoom’s strategy creates the opportunity for CIOs to access a widely used, rich functionality, digital collaboration channel – one they can integrate seamlessly into their existing digital channels knowing that their customers are likely to be highly familiar with the user experience.”
Get more insights on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and technology areas that will see innovations, as organisations get into the recovery phase.































