The Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) industry, known for its cautious stance on technology, is swiftly undergoing a transformational modernisation journey. Areas such as digital customer experiences, automated fraud detection, and real-time risk assessment are all part of a technology-led roadmap. This shift is transforming the cybersecurity stance of BFSI organisations, which have conventionally favoured centralising everything within a data centre behind a firewall.
Ecosystm research finds that 75% of BFSI technology leaders believe that a data breach is inevitable. This requires taking a new cyber approach to detect threats early, reduce the impact of an attack, and avoid lateral movement across the network.
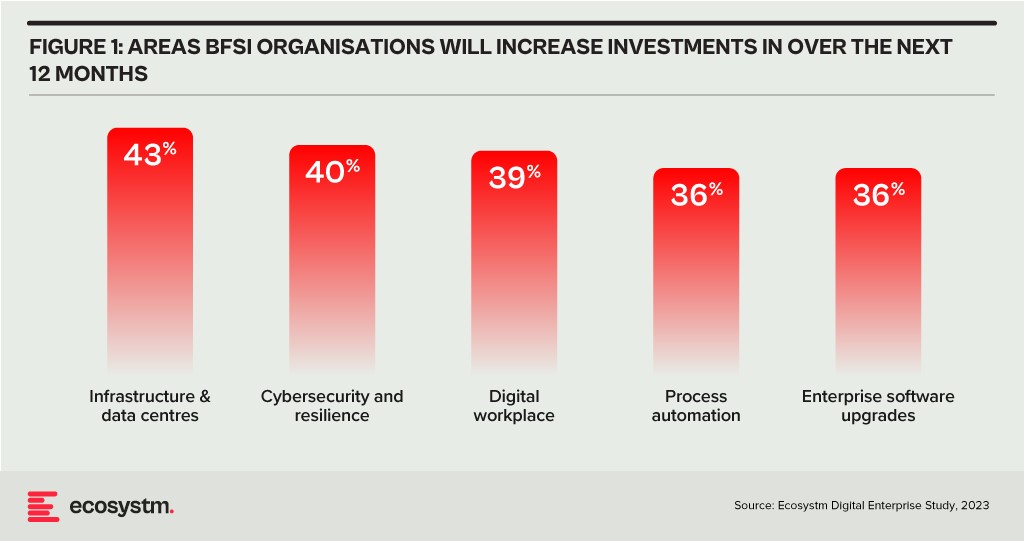
BFSI organisations will boost investments in two main areas over the next year: updating infrastructure and software, and exploring innovative domains like digital workplaces and automation. Cybersecurity investments are crucial in both of these areas.
As a regulated industry, breaches come with significant cost implications, underscoring the need to prioritise cybersecurity. BFSI cybersecurity and risk teams need to constantly reassess their strategies for safeguarding data and fulfilling compliance obligations, as they explore ways to facilitate new services for customers, partners, and employees.
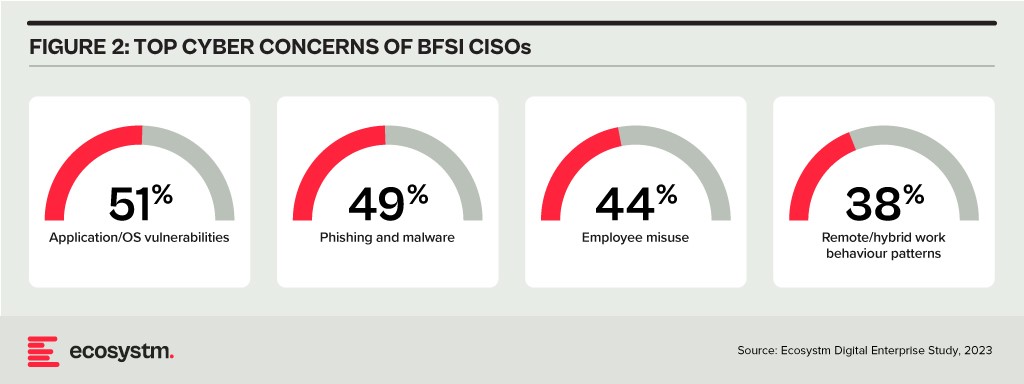
The primary concerns of BFSI CISOs can be categorised into two distinct groups:
- Expanding Technology Use. This includes the proliferation of applications and devices, as well as data access beyond the network perimeter.
- Employee-Related Vulnerabilities. This involves responses to phishing and malware attempts, as well as intentional and unintentional misuse of technology.
Vulnerabilities Arising from Employee Actions
Security vulnerabilities arising from employee actions and unawareness represent a significant and ongoing concern for businesses of all sizes and industries – the risks are just much bigger for BFSI. These vulnerabilities can lead to data breaches, financial losses, damage to reputation, and legal ramifications. A multi-pronged approach is needed that combines technology, training, policies, and a culture of security consciousness.
Training and Culture. BFSI organisations prioritise comprehensive training and awareness programs, educating employees about common threats like phishing and best practices for safeguarding sensitive data. While these programs are often ongoing and adaptable to new threats, they can sometimes become mere compliance checklists, raising questions about their true effectiveness. Conducting simulated phishing attacks and security quizzes to assess employee awareness and identify areas where further training is required, can be effective.
To truly educate employees on risks, it’s essential to move beyond compliance and build a cybersecurity culture throughout the organisation. This can involve setting organisation-wide security KPIs that cascade from the CEO down to every employee, promoting accountability and transparency. Creating an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting security concerns is critical for early threat detection and mitigation.
Policies. Clear security policies and enforcement are essential for ensuring that employees understand their roles within the broader security framework, including responsibilities on strong password use, secure data handling, and prompt incident reporting. Implementing the principle of least privilege, which restricts access based on specific roles, mitigates potential harm from insider threats and inadvertent data exposure. Policies should evolve through routine security audits, including technical assessments and evaluations of employee protocol adherence, which will help organisations with a swifter identification of vulnerabilities and to take the necessary corrective actions.
However, despite the best efforts, breaches do happen – and this is where a well-defined incident response plan, that is regularly tested and updated, is crucial to minimise the damage. This requires every employee to know their roles and responsibilities during a security incident.
Tech Expansion Leading to Cyber Complexity
Cloud. Initially hesitant to transition essential workloads to the cloud, the BFSI industry has experienced a shift in perspective due to the rise of inventive SaaS-based Fintech tools and hybrid cloud solutions, that have created new impetus for change. This new distributed architecture requires a fresh look at cyber measures. Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) providers are integrating a range of cloud-delivered safeguards, such as FWaaS, CASB, and ZTNA with SD-WAN to ensure organisations can securely access the cloud without compromising on performance.
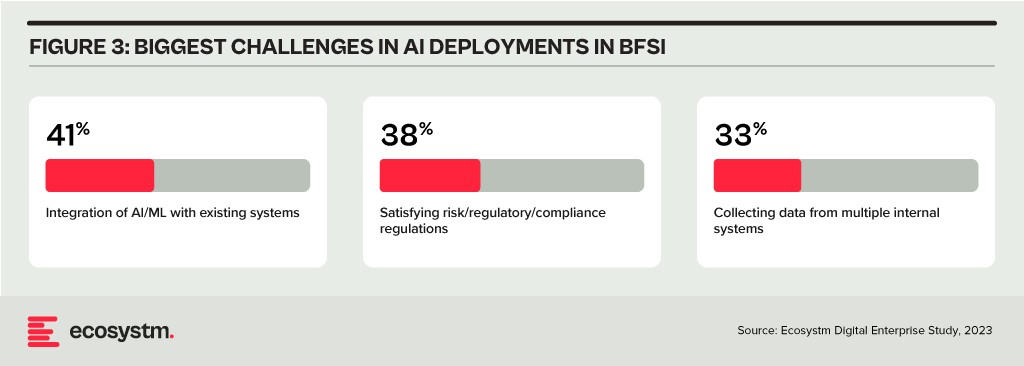
Data & AI. Data holds paramount importance in the BFSI industry for informed decision-making, personalised customer experiences, risk assessment, fraud prevention, and regulatory compliance. AI applications are being used to tailor products and services, optimise operational efficiency, and stay competitive in an evolving market. As part of their technology modernisation efforts, 47% of BFSI institutions are refining their data and AI strategies. They also acknowledge the challenges associated – and satisfying risk, regulatory, and compliance requirements is one of the biggest challenges facing BFSI organisations in the AI deployments.
The rush to experiment with Generative AI and foundation models to assist customers and employees is only heightening these concerns. There is an urgent need for policies around the use of these emerging technologies. Initiatives such as the Monetary Authority of Singapore’s Veritas that aim to enable financial institutions to evaluate their AI and data analytics solutions against the principles of fairness, ethics, accountability, and transparency (FEAT) are expected to provide the much-needed guidance to the industry.
Digital Workplace. As with other industries with a high percentage of knowledge workers, BFSI organisations are grappling with granting remote access to staff. Cloud-based collaboration and Fintech tools, BYOD policies, and sensitive data traversing home networks are all creating new challenges for cyber teams. Modern approaches, such as zero trust network access, privilege management, and network segmentation are necessary to ensure workers can seamlessly but securely perform their roles remotely.

Looking Beyond Technology: Evaluating the Adequacy of Compliance-Centric Cyber Strategies
The BFSI industry stands among the most rigorously regulated industries, with scrutiny intensifying following every collapse or notable breach. Cyber and data protection teams shoulder the responsibility of understanding the implications of and adhering to emerging data protection regulations in areas such as GDPR, PCI-DSS, SOC 2, and PSD2. Automating compliance procedures emerges as a compelling solution to streamline processes, mitigate risks, and curtail expenses. Technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA), low-code development, and continuous compliance monitoring are gaining prominence.
The adoption of AI to enhance security is still emerging but will accelerate rapidly. Ecosystm research shows that within the next two years, nearly 70% of BFSI organisations will have invested in SecOps. AI can help Security Operations Centres (SOCs) prioritise alerts and respond to threats faster than could be performed manually. Additionally, the expanding variety of network endpoints, including customer devices, ATMs, and tools used by frontline employees, can embrace AI-enhanced protection without introducing additional onboarding friction.
However, there is a need for BFSI organisations to look beyond compliance checklists to a more holistic cyber approach that can prioritise cyber measures continually based on the risk to the organisations. And this is one of the biggest challenges that BFSI CISOs face. Ecosystm research finds that 72% of cyber and technology leaders in the industry feel that there is limited understanding of cyber risk and governance in their organisations.
In fact, BFSI organisations must look at the interconnectedness of an intelligence-led and risk-based strategy. Thorough risk assessments let organisations prioritise vulnerability mitigation effectively. This targeted approach optimises security initiatives by focusing on high-risk areas, reducing security debt. To adapt to evolving threats, intelligence should inform risk assessment. Intelligence-led strategies empower cybersecurity leaders with real-time threat insights for proactive measures, actively tackling emerging threats and vulnerabilities – and definitely moving beyond compliance-focused strategies.

In my last Ecosystm Insight, I spoke about the 5 strategies that leading CX leaders follow to stay ahead of the curve. Data is at the core of these CX strategies. But a customer data breach can have an enormous financial and reputational impact on a brand.
Here are 12 essential steps to effective governance that will help you unlock the power of customer data.
- Understand data protection laws and regulations
- Create a data governance framework
- Establish data privacy and security policies
- Implement data minimisation
- Ensure data accuracy
- Obtain explicit consent
- Mask, anonymise and pseudonymise data
- Implement strong access controls
- Train employees
- Conduct risk assessments and audits
- Develop a data breach response plan
- Monitor and review
Read on to find out more.
Download ‘A 12-Step Plan for Governance of Customer Data’ as a PDF

With organisations facing an infrastructure, application, and end-point sprawl, the attack surface continues to grow; as do the number of malicious attacks. Cyber breaches are also becoming exceedingly real for consumers, as they see breaches and leaks in brands and services they interact with regularly. 2023 will see CISOs take charge of their cyber environment – going beyond a checklist.
Here are the top 5 trends for Cybersecurity & Compliance for 2023 according to Ecosystm analysts Alan Hesketh, Alea Fairchild, Andrew Milroy, and Sash Mukherjee.
- An Escalating Cybercrime Flood Will Drive Proactive Protection
- Incident Detection and Response Will Be the Main Focus
- Organisations Will Choose Visibility Over More Cyber Tools
- Regulations Will Increase the Risk of Collecting and Storing Data
- Cyber Risk Will Include a Focus on Enterprise Operational Resilience
Read on for more details.
Download Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Trends for Cybersecurity & Compliance in 2023 as a PDF

Last week, the Australia government joined other countries in the Asia Pacific region in highlighting the growth of attack surface in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In our recently launched study Digital Priorities in the New Normal, we find that 87% of organisations in the Asia Pacific have increased investments in one or more cybersecurity solutions. However, this has to be backed by a reassessment of organisations’ risk positions and a re-evaluation of data protection and compliance policies.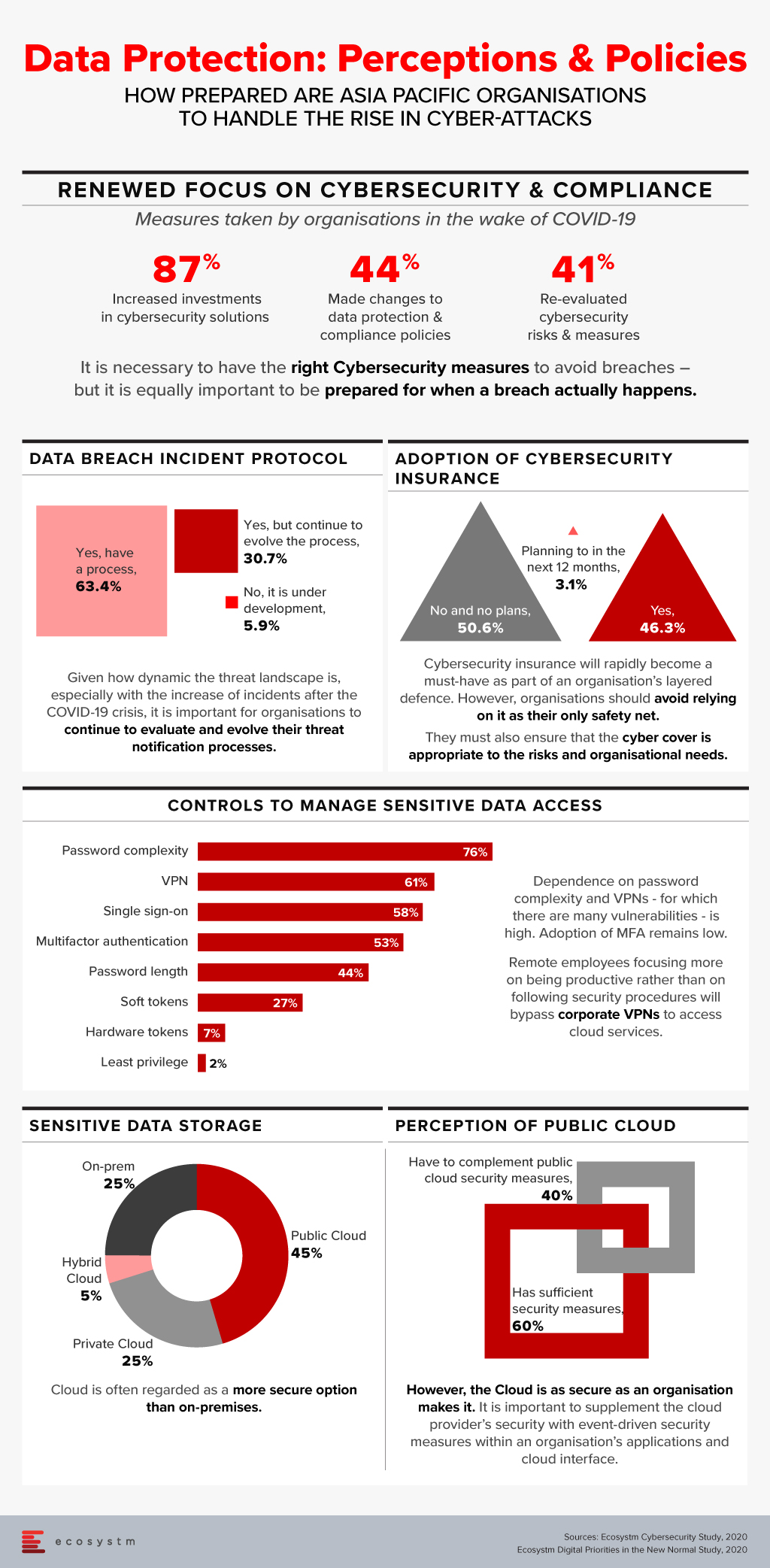

There has been a widespread adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud architectures in the recent past and this trend is only expected to go up in the near future. A hybrid cloud adoption has its challenges though; including the need for organisations to baseline their security practices across so many different environments. Organisations that are aware of the cybersecurity risks associated are increasingly looking for external specialised help in managing their cloud security measures, especially with an aim to automate the processes.
Zscaler Acquires CloudNeeti
In a recent announcement, Zscaler announced its intentions to acquire Cloudneeti, a niche Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) start-up based in Redmond, Washington. This is set to expand Zscaler’s Cloud Security Platform capabilities to include data protection. With this acquisition, Zscaler will be able to complement its own offerings to provide:
- A complete Data Protection and Exposure Prevention suite, that works across locations, users and applications and ensures better compliance with regulations
- A Unified Compliance Assurance platform that provides compliance visibility and breach mitigation across the multiple SaaS applications an organisation uses
- Risk Reduction through automated remediations following both industry compliance laws and organisations’ own risk management program guidelines
Ecosystm research finds that organisations are struggling with their cybersecurity implementations, especially as the solutions get increasingly complicated to combat the complex and evolving threat environment (Figure 1). Integration with existing cybersecurity measures, and a lack of sufficiently skilled IT staff to handle the myriad needs of the multiple systems and applications, builds a strong case for automation in cybersecurity practices.

Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Alex Woerndle says, “Automation is critical in cybersecurity, given the volume of data, alerts and incidents that are being dealt with on a daily basis, globally. Automating recurrent and high-volume tasks is a critical step in getting on top of this challenge.”
Importance of Automating Cybersecurity Processes
Woerndle sees a growing role for CSPM providers for multiple reasons. “Firstly, a lot of companies are finding that they cannot be ‘fully cloud’ and as such, end up with a complex architecture spanning on-premise, private cloud environments and multiple public cloud tenancies. Secondly, due to poorly planned cloud migrations, changing priorities, differences in service requirements, cost differences and also personal preferences across multiple teams, a lot of companies end up consuming different services across multiple public cloud providers (Azure, AWS, GCP, and so on). IT teams are struggling to be experts in all aspects of the shared responsibility model and with the capabilities to secure the various services. Finally, there is a constant stream of upgrades and addition of new services team members, given the easy accessibility public cloud environments provide. CSPM solutions provide the ability to establish baselines, enforce security controls and run regular checks to ensure compliance. Doing this manually is time consuming, expensive and always three steps behind.”
Woerndle also sees further complications because of the COVID-19 crisis. “COVID-19 has shifted the world to remote working overnight. Once workers are outside of the trusted corporate network and have access to cloud resources from their home networks, additional complexity to the corporate security posture is highlighted. Depending on how organisations have prepared for this, they either maintain control of all services and applications, and the access into each, or if not prepared, open direct access to a lot of unsecured applications from potentially very unsecured networks.” In fact Zscaler has seen its stock prices rising in the aftermath of the global crisis.
However, Woerndle warns, “While the conversation certainly supports the use of CSPMs, there is a lot more to it in terms of securing home networks, identity and access management, and so on.”
Zscaler’s acquisition of CloudNeeti certainly appears to be a timely move, in the current environment when organisations are struggling with a lack of resources with the extensive knowledge to understand all private and public cloud environments. There are controls required to secure each application, resource and system within an organisation – along with the time and effort required to implement, monitor, audit and improve cybersecurity measures over time.
The Malaysia Digital Economy Corporation (MDEC) has estimated that the country’s Digital Economy is worth USD3 trillion. Several initiatives have been introduced to promote the vision of a Digital Economy including: creating the Malaysia Tech Entrepreneur Programme (MTEP) aimed at tech founders who want to make Malaysia their base; the Malaysia Innovation Policy Council for industry collaboration on digital technology initiatives and streamlining policy/regulatory issues to support innovation; and the National eCommerce Roadmap aimed at small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to promote cross-border eCommerce.
Data Protection Laws for a Digital Economy
However, any country that aspires to be a Digital Economy, must have robust data protection laws that safeguards its citizens’ data. Malaysia’s Personal Data Protection Act 2010 (PDPA), was passed by the Malaysian Parliament in 2010 and came into force in late 2013. While the PDPA does provide guidelines for personal data protection to some extent, in light of technological advances, newer laws such as GDPR that are shaping the industry, and to keep up with the aspirations of creating a Digital Economy, there is a need for more comprehensive privacy laws.
“Growing the Digital Economy is a key agenda for Malaysia and a revised PDPA is a key component in ensuring trust and transparency,” says Shamir Amanullah, Principal Advisor Ecosystm. “The increasing and complex use of data and the proliferation of devices pose serious challenges which the data protection laws have to address. The recent US Federal Trade Commission’s hefty fines on Facebook and Equifax highlight the need to protect data of consumers and businesses alike.”
The PDPA is clearly a work in progress where while fast-growing areas such as electronic marketing and online privacy are mentioned in the act, there are no specific provisions to deal with breaches in these areas.
Updating the PDPA
In the last few years, Malaysia has realised that the PDPA fails to cover some areas. As an example, it does not take into consideration the proliferation of biometric data. The national ID card (MyKad) stores data using biometrics (thumbprints) and there is a clear rise in use of facial recognition technology in the country. Grab partnered with the Ministry of Transport last year, to use facial recognition technology to protect their drivers.
Malaysia is committed to their Digital Economy vision and is looking to update the PDPA, to make it more appropriate for contemporary needs and technology. The Government is consulting its citizens on possible ways to improve the PDPA. Between 14-28 February, the public can provide feedback on their thoughts and requirements on data privacy, through the Ministry of Communications and Multimedia’s web portal.
Some of the areas that have been found lacking and where feedback is being sought are expanding applications of the PDPA to data processors, making it compulsory to notify data breaches and simplifying cross-border personal data transfer.
Speaking about the areas that are likely to be addressed, Amanullah notes, “The review of the PDPA and the ongoing public consultation will deliberate extending the PDPA to non-commercial transactions. The existing PDPA does not cover non-commercial transactions involving charities, religious activities and even social media. The EU, Japan and – closer home – the Philippines have data protection acts which regulate both commercial and non-commercial transactions.”
Malaysia’s Communications & Multimedia Minister, Gobind Singh Deo, has from the start spoken about the need to update and bring the PDPA up to speed. “The goal of the Digital Economy is to take Malaysian enterprises beyond the country to Southeast Asian and global markets,” says Amanullah. “The EU GDPR is recognised as a leading global framework for data protection and is set to play a big role in the revised PDPA, to ensure that Malaysian companies adhere to the same data protection standards as global organisations.”
“The appointment of Data Protection Officers will be a major move to ensure that companies that hold sensitive private data have the necessary skills, processes and technology in place to comply with data protection laws.”