The last week or so has seen a numbers of central banks (such as the US and Australia) ease their monetary policies – lowering interest rates in order to stimulate investment and economic activity. But this alone won’t be enough to slow down economic growth – the generally accepted wisdom is that governments will need to quickly roll out stimulus packages to get money into the economy faster. Some countries, like Hong Kong, have already kicked off this process – others are likely be announce packages over the next few weeks.
Typically, these stimulus packages are designed to get the economy moving again – bringing forward existing spending plans or creating new spend. Good stimulus packages will have a broad impact but also drive improved business and employment outcomes. Some are targeted towards the sectors most impacted (e.g. in Australia the seafood export market has been impacted heavily by China’s decision to stop importing any seafood; in Thailand the tourism sector is hit hard by the slowdown in arrivals from China – that makes up a large percentage of the tourists in an economy where tourism is a significant sector).
But often they are not targeted. Some governments might just let businesses write off any investment faster than usual (such as within a single financial year instead of depreciating the spend over a number of years) or will just send a cheque to every income earner. The issue with these stimulus packages is that they don’t drive a specific outcome apart from getting spend into the economy faster. Stimulus packages have an opportunity to drive change – and the COVID-19 virus has shown that some businesses are not well equipped for the digital era. They are finding it hard managing the distributed workforce when they ask their staff to work at home. There are also many challenges that governments and businesses are facing in serving customers across digital channels.
This is the opportunity for governments to stimulate the economy and help businesses improve the digital experiences of customers and employees. The world is going digital – we all know what good digital experiences look like as we have them on our smartphones in our pockets. But we also know that most companies and government agencies we deal with are not offering great digital experiences… And while we all hope that virus outbreaks such as COVID-19 don’t happen that often, we know that something like this will happen again – so it would be great if businesses were prepared for such an outcome.
Therefore now is the chance to target the stimulus packages towards both the impacted sectors of the economy as well as the areas of spend that will drive better digital experiences for customers and employees. There could be incentives to spend more on software and cloud services, spend more with consultancies or spend more with digital marketing agencies. It will also help small businesses compete with larger businesses on an equal playing field (for example, the large takeaway food outlets have an app that lets you pre-order food, but many small ones do not).
In 2009, the Australian government rolled out a stimulus package – one that was ultimately one of the major reasons the economy came through the global financial crisis without falling into recession. They gave an immediate cash stimulus to taxpayers which helped get an immediate spend in the economy. They also had a housing insulation spend which promised roof insulation for 2.7 million homes – this provided stimulus to the economy in the mid-term. They then provided new school halls, social housing and roads – which provided the stimulus in the longer term. While it can be argued that the programs were not effectively administered, the stimulus got the economy moving and also helped the government hit some longer term goals – such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions (through better housing insulation therefore less use of electricity to heat and cool homes) and also upgrading aging infrastructure in schools across the country. For many businesses, the focus today is on providing great customer experiences – and many of those experiences will be digital. Governments have the chance to use their stimulus p to accelerate that outcome.

Governments across the globe are realising the true potential of emerging technologies to provide better citizen services and to ensure transparency and accountability. Blockchain is one of the emerging technologies that is helping and will continue to help governments to achieve transformation. Government departments and agencies are being increasingly pushed to be collaborative and share data across agencies, while at the same time maintain the security of the data in their care. A distributed ledger that can share information based on agreed-upon protocols helps governments immensely in collaborating without losing accountability.
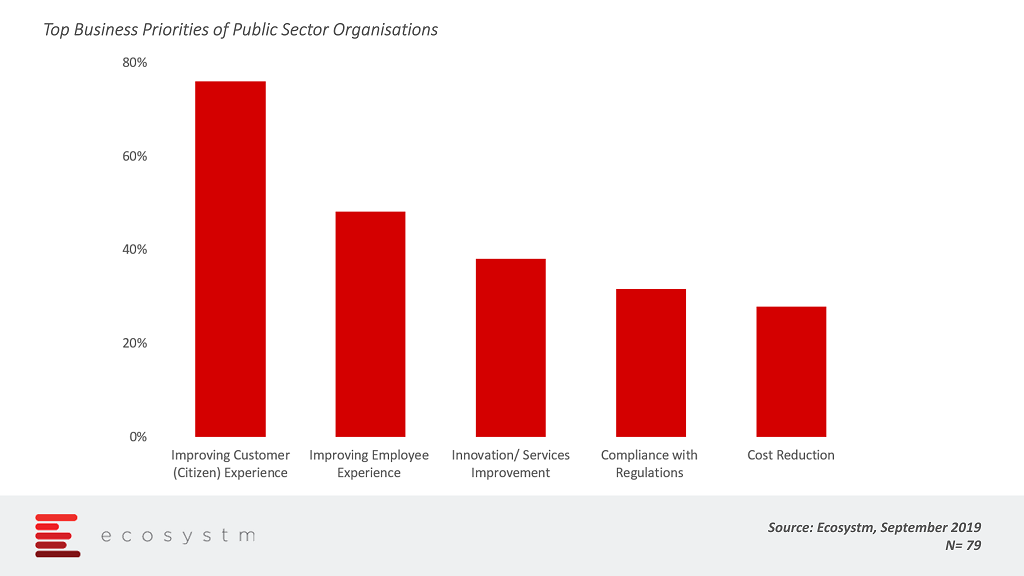
What are the key priorities of public sector organisations? The global Ecosystm CX study finds that citizens and employees are the top priorities for government agencies and departments.
Blockchain can help the public sector achieve many of its goals –
Improving Citizen Services
As more countries aim to be eGovernments, there is a need for real-time data access, information management, and fraud prevention. Blockchain is enabling governments to provide innovative services to citizens. It is possible now to decentralise the citizen database, reducing the time and cost of fetching records. Moreover, Blockchain enhances transparency and makes the highly regulated public sector audit-ready by creating a single source of truth for all connected devices and stakeholders.
One of the earliest use cases we see is in records management. Population records are useful for several agencies from healthcare to civil services to welfare departments. In Myanmar, UNICEF has collaborated with the industry to introduce a mobile birth and death registration system based on Blockchain. This digital mobile recording system is maintained on an integrated platform controlled by several parties who maintain birth and death records of Myanmar’s citizens and is a step towards achieving universal registration.
Citizen services such as notarisation, recording and time-stamping events, transactional real-estate contracts, online storing and verification of academic degrees, identity management and so on are benefiting from Blockchain deployment.
In Georgia, the government department of Land, Property and Housing Management is using Blockchain to maintain land and property records. The blockchain-based land registry allows speedier approvals with no involvement of paperwork or multi-party signatures on physical documents. This is enhancing service quality while offering better security measures as the data is digitally stored in the National Agency of Public Registry’s land title database.
Improving Employee Experience
Maintaining massive records about individuals, organisations, assets, activities, location and national information by the government department employees is a time-consuming process. In addition to this, managing and updating the ever-growing records is made more difficult by data silos and information management protocols and of course errors creep in.
Blockchain is streamlining the workflow and information management system at an individual as well as at a departmental level. In government departments, Blockchain can redefine processes by including events and agents in a block-based system where each activity can be easily managed and accounted for. This prevents issues such as miscounts, delayed processes and slipped deadlines.
The Chilean National Energy Commission has piloted a Blockchain platform to regulate the energy sector such as installed capacity, average market price, marginal costs, hydrocarbons and more. To implement this, first the energy data was stored on an Open Energy database which was then distributed across hundreds of secure servers countrywide. Later the employees verified anomalies which minimised their workload and made it convenient to edit the central database. The information added to open ledger is readily available to employees and citizens.
Compliance with Regulations
One of the primary benefits of Blockchain technology in the public sector is compliance. The transactions recorded on distributed ledgers are documented in a central ledger providing a comprehensive, precise, irreversible, permanent and secure trail. For instance, Blockchain is used to streamline cross-border compliance adherence by matching the data with the actual trade transactions. This creates an efficient and secure system ensuring real-time compliance, significant reduction of transaction costs, elimination of customs evasion and fraud from the outset.
In June, the Chinese Customs deployed its cross-border Blockchain compliance solution. The platform aims to increase efficiency by monitoring the flow of imports and exports and helping with risk assessments and document management. As transaction information can be stored safely and transparently on a Blockchain, the platform enables easy identification of documents to be checked, making compliance easier.
Data Management and Privacy
Blockchain acts as a default record keeper for society and governments and prevents the data from being misused by criminals and hackers. Through the responsible deployment of Blockchain data structures, governments can strengthen network security by reducing risks of single points-of-failure and preventing data breaches.
Democracy Earth – a Blockchain-based community has established a decentralised online governance platform, entirely built on open source technologies. The website helps users to cast votes on various policies based on tokens assigned to the users. This also minimises expenses and creates a secure information flow in a Blockchain-based voting system.
Government agencies, such as the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS), are also getting serious about Blockchain applications in data management and privacy. DHS is funding R&D in Blockchain start-ups to explore new approaches to cybersecurity. The U.S. military is also utilising Blockchain (SIMBA Chain) to secure its military communication, messaging and applications. Blockchain is used for communication between ground troops and their headquarters. In addition to securing communications, the US Airforce is using Blockchain to track 3D printed components throughout their life cycle. With SIMBA, the top-secret printing blueprints are shared without much surveillance – this has enabled the Department of Defense to maintain a digital library of parts.
Cost Reductions
The government has clear citizen responsibilities and fulfilling them with a limited set of resources is one of the prime challenges for public departments. Reconciling expenditure with the budget is a time-consuming, and expensive procedure. Blockchain-based payment and accounting systems can help governments to reduce process costs by removing redundancies, streamlining processes, decreasing audit burden and ensuring systems integrity. By removing the requirement for third-party agencies to handle operations and maintain records, Blockchain technology is helping governments to reduce costs.
Blockchain is still an emerging concept with significant benefits. The Ecosystm IoT study finds that only 20% of public sector IT decision-makers are fully aware of the capabilities and limitations of Blockchain. Adopters and developers are still resolving the challenges. On the technology side, there are concerns on platform scalability, integration, standardisation and validation methods. On the management side, there are concerns about business models, transaction scale, maturity, and structure. However, government agencies will benefit immensely from the technology in the near future.
Authored by attending Ecosystm analysts, Sash Mukherjee (Principal Analyst, Government & Healthcare) and Sid Bhandari (Director, Consulting & Advisory Services)
The recently held AWS Public Sector Summit in Singapore showcased some of the regional AWS implementations, and how organisations are leveraging the Public Cloud differently.
In her keynote address, Teresa Carlson, Vice President, Worldwide Public Sector set the tone for the industry show cases by saying that a successful Digital Transformation (DX) starts from a radical rethinking of how an organisation uses cloud computing technology, people, and processes to fundamentally change business performance.
AWS Empowering the Public Sector
Carlson is clear on what Public Sector organisations must do and where AWS can help them:
- Define what Cloud refers to in the organisation. The first step in bringing about a Cloud First transformation is to be clear on the true definition of cloud computing.
- Create a “Cloud First” policy. To adopt a Cloud First policy, it is imperative to have leaders with a clear vision who really drive technology initiatives forward for all the right reasons like security, cost reduction, scalability, privacy and rapid acceleration of citizen services.
- Focus on Security & Compliance. AWS has global compliance certifications with 200+ services and key features focused on security, compliance and governance. New services such as the use of AI for threat detection have been implemented and are quickly evolving into a mainstream feature.
- Modify your Procurement vehicle. A formal cloud procurement model must be adopted instead of creating ad-hoc processes and a rush to adopt cloud to meet the specific needs of individual departments. AWS has the expertise to assist government IT leaders in selecting the right acquisition approach for their agency.
- Do not ignore Skills Development. Investing in cloud skills development – whether at the central IT level or in the individual business units in the Public Sector – is imperative, as roles evolve and new roles emerge. AWS has over the years offered free courses and industry certifications to Public Sector employees interested in learning the foundations of cloud computing, storage, and networking on AWS to advanced skills courses in emerging technologies such as AI.
Ecosystm Comment:
While cloud may have started off as a means of offsetting CapEx, its role has since evolved into being a major vehicle for DX. Several governments across the world have adopted Cloud First policies to spearhead innovation, increase agility, and improve citizen services. Cloud is increasingly seen as a foundation for many emerging technologies that governments are experimenting with and implementing such as AI, automation, Big Data analytics and Smart Nation initiatives.
The skepticism around Public Cloud security seems to have diminished over the years, with the perception that cloud providers use state-of-the-art technologies to protect their environment and continue to upgrade their security features in the face of new and evolving threats. However, the Ecosystm Cybersecurity study finds that nearly 53% of Public Sector and allied organisations that use Public Cloud feel that the security measures offered are sufficient. Leading cloud providers such as AWS should make it clear that essentially it is a shared responsibility and impress on organisations that the responsibility to secure their own applications and the interface with the Public Cloud ultimately lies with the deploying organisations.
Industry Use Cases
There were several industry use cases presented over the 2 days and it was heartening to see so many Asia Pacific examples of transformation. Tan Kok Yam, Deputy Secretary, Smart Nation & Digital Government Office shared that the key to a successful Smart Nation initiative is to build user-centric services rather than having an agency-centric approach, in his presentation on Singapore’s “The Moments of Life” app. Edwin H. Chaidir, IT Manager at WWF Indonesia presented on how AWS’s machine learning capabilities has helped the organisation to automate identification of specific orangutans in the wild, freeing up resources (money and time) to reinvest in other wildlife protection initiatives.
One of the implementation stories that impressed the Ecosystm analysts was the one shared by Rookie Nagtalon, Consultant for Digital Transformation at the Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center (CGHMC) in the Philippines, where he spoke about how they were able to bring about transformation in their patient life-cycle management. Healthcare in Asia Pacific is a diverse and disparate market with organisations at different levels of IT and business maturity – against a backdrop of different country-level goals and healthcare policies. It was encouraging to hear about a transformation project in a not-for-profit organisation from an emerging economy.
The challenges that healthcare organisations face are unique in many ways:
- Legacy systems that still work and hence there is no business case for replacing them
- Approximately 2/3rd of the IT budget going into running the basics, leaving limited resources for emerging technology adoption and transformation projects
- The shift to value-based healthcare and the need for data-driven insights to support it
- The unpredictability of the workload and the need for an agile IT infrastructure
- Security and compliance mandates that protect patient data and require storage of records over extended periods
Working with these challenges, how does a healthcare organisation bring about Digital Transformation?
Nagtalon’s team was assigned the task to bring about this transformation within a 10-month timeframe.
- The key challenge. An awareness that no one vendor can provide the entire gamut of functionalities required for patient lifecycle management. In spite of recent trends of multi-capability vendors, hospitals need multiple vendors for the hospital information system (HIS), ERP, HR system, document management systems, auxiliary department systems and so on. Each of these vendors have their own development team and infrastructure requirement, which stresses the internal IT resources. DX involving multiple legacy systems requires a step-by-step approach. The challenge is to identify the right systems to start the journey with.
- Vendor selection criteria. The need to find one solution that would enable seamless data sharing across the disparate systems. The vendor selection criteria that were used focused on ease of use and speed especially when working with multiple data sources. In keeping with the industry, the ability of the vendor to support mission-critical applications was put through the filter of what was referred to as ‘Code Blue’.
- The solution choice. A cloud solution that can empower teams and remove worries about the infrastructure. The hospital chose AWS as their transformation partner, who used a system interface blueprint to integrate data from their SAP ERP system, Medcurial’s MeRx HIS, 128 HR system, Canon’s documentation system and multiple diagnostics systems.
- The future roadmap. Enabling the organisation to be a Digital Hospital. The solution was implemented in 7 months and hit the right ROI requirements, reducing billing time and impacting the bottom line in terms of both recovery and revenue. It has created the base foundation for future plans such as device integration and the provider is well set on its journey of Cloud, IoT and Robotics.
Ecosystm Comment:
Nagtalon raised an important point when he was asked the key reason for the success of the project – executive buy-in. Transformation projects work best when it is enterprise-wide and senior management sponsorship is a must to enable that. However, he also mentioned humorously that he had become extremely unpopular during the implementation. This is where a centre-of-excellence with ‘champions to the cause’ from each key department helps. Organisations should look to engaging with the stakeholders early and to get their buy-in as well as the executive’s.
AWS’s marketing message to healthcare providers includes allowing them to focus on their mission and create their differentiation, and enabling them to incorporate new and emerging technologies. This implementation certainly ticked those boxes. What was particularly positive was the big thumbs up the AWS implementation team received. Organisations will increasingly partner with platform providers in their transformation journeys and implementation capabilities and best practice guidance will be the key differentiators for vendors.




