Over the past year we have seen global systems integrators (SIs) – Accenture, IBM, Deloitte, Fujitsu, Capgemini and others – make many acquisitions, particularly in the public cloud, AI, cybersecurity and data space. Much of the growth in spending over the past few years have been driven by these categories: in 2020 if a software company was purely or mainly SaaS, they are likely to have witnessed strong growth. If they were on-premises software, they were lucky not to see declining revenues. While it is normal for the larger SIs and consultants to play catch up through acquisition, it is becoming harder for them to gain traction in these new areas.
Technology Shifts Drive Market Fragmentation
With every technology-driven business change new SIs, consultants, and managed services providers emerge. It happened with the move to big ERP systems, the move towards Business Intelligence, the emergence of SaaS etc. But I think we are now seeing something different. More than just the smaller players going after opportunities earlier, I believe we are seeing a changing buying behaviour from tech and business buyers – a greater willingness for larger enterprises to give their most important, business-critical strategies and implementations to smaller, less established players.
And I am not suggesting that the larger SIs are not performing well. Many are growing at 10-25% YoY – but at the same time, many are also growing at a slower rate than the markets they play in. The Ecosystm RNx for global IT services and consulting providers shows that the global providers continue to power ahead. But they need to adapt to changing market conditions.

New Cloud/AI Partners Winning Consulting and Implementation Deals
We have seen a new community of partners emerge with tech changes, such as the hyperscale cloud platforms and AI/machine learning tools. Traditionally, these companies would be good at one thing – and would learn slowly. For example, in the SAP ERP growth period, the projects were large and long. A single, mid-sized SI might only be working with 2-3 clients at a time. Therefore, the IP that they collected was limited – and they would find themselves with focused or niche skills. The large SIs had done many large, long projects across the globe and had much best-practice IP to call upon, giving them a broader and deeper knowledge of the technology and industries. Smaller providers had limited IP and industry experience.
But in this cloud and AI era, specialist providers work on hundreds of smaller projects with dozens or hundreds of clients. With the technology constantly evolving, the skills are constantly improving. While the global SIs are working on many cloud and AI engagements, they are often part of longer engagements – giving the consultants and tech teams less exposure to the new and evolving cloud platforms.
In a world where technology is changing at pace, the traditional global SI practice of “learning from peers across the globe” doesn’t happen at the pace the market requires. By the time your peers in the business have completed a project, documented it, and shared learnings, the market has moved on and technology has changed. Today it is easier and faster to learn directly from the tech vendors and cloud platform providers and their training partners. The network effect of knowledge in a team on the opposite side of the globe for a global SI is less valuable to clients. Often the smaller and mid-sized SIs have a deeper, broader knowledge of the technology platforms and toolsets than the larger providers – giving them a competitive advantage. For example, if you want the actual experience of moving SAP to Azure, or Oracle to AWS – you’ll often find the smaller providers have more experience. And this continues to play out. In many markets in the world, the top 5-10 SIs for cloud, AI and cybersecurity has a high proportion of local specialist providers.
Tech Buyers No Longer Look for Culturally Aligned Partners
Tech buyers themselves are changing too. In years gone by, the smaller tech partners would tell us that they felt they were included in bids to drive down the price from the global SIs. But today the story is different. Smaller partners are admired for their agility and innovation. Large enterprise customers will choose small providers because the small SI is NOT like them. In the past, they chose the global SI because they were just like them!
Because of this, the large SIs are mopping up their smaller competitors across the globe. Accenture has acquired 40 companies in the past 10-11 months, IBM has acquired over 10, Atos and Cognizant have also acquired many companies in the past 12 months. They are doing this for the skills as much as for the clients, along with getting a foothold in a new market or strengthening their position in geography. The challenge will be to hang on to the clients, culture, and the IP of the acquired business. Often these smaller competitors are growing at a significant pace – and the biggest risk is that the acquiring company takes their eyes off the prize.
Global SIs Still Own the Industry Play
Despite these challenges, one of the areas that the global SIs will continue to dominate is the industry play. I have discussed how as technologies mature, industry plays become more relevant.
Smaller and mid-sized SIs and consultants find it hard to create deep pools of expertise across multiple industries. While some may have a deep focus on a single or two industries, only the large players have broad and deep geography and industry experience. This puts many of the acquisitions into context – the global SIs will take these acquisitions and use that deep and broad technical and business knowledge and add it to their industry knowledge to create a more compelling offering.
Their challenge will still be one of cultural alignment. As discussed, many companies seek out tech partners who represent what they want to be, not what they are. The ability for the Global SIs to retain the culture, agility and innovation of the acquired business will determine their ability to continue to see similar or improved levels of growth from the acquired business. Using their IP in the context of industries will be the key to their ongoing success.

Identifying and selecting a vendor for your tech project can be a daunting task – especially when it comes to emerging technologies or when implementing a tech solution for the first time. Organisations look for a certain degree of alignment with their tech vendors – in terms of products and pricing, sure, but also in terms of demonstrable areas of expertise and culture. Several factors are involved in the selection process – vendors’ ability to deliver, to match expected quality standards, to offer the best pricing, to follow the terms of the contract and so on. They are also evaluated based on favourable reviews from the tech buyer community.
Often businesses in a particular industry tend to have their unique challenges; for example, the Financial Services industries have their specific set of compliance laws which might need to be built into their CRM systems. Over the years, vendors have built on their industry expertise and have industry teams that can advise organisations on how their business requirements can be met through technology adoption. These experts speak in the language of the industry and understand their business and technology pain points. They are able to customise their product and service offerings to the needs of the industry for a single client – which can then be repeated for other businesses in that industry. Vendors arm themselves with a portfolio of industry use cases, especially when they are entering a new market – and this often gives them an upper hand at the evaluation stage. In the end, organisations want less customisations to keep the complexity and costs down.
Do organisations evaluate vendors on industry experience?
Ecosystm research finds that industry experience can be a significant vendor selection criterion for some tech areas (Figure 1), especially in emerging technologies such as AI. AI and automation applications and algorithms are considered to be distinctive to each industry. While a vendor may have the right certifications and a team of skilled professionals, there is no substitute for experience. With that in mind, a vendor with experience in building machine learning models for the Telecommunications industry might not be perceived as the right fit for a Utilities industry implementation.
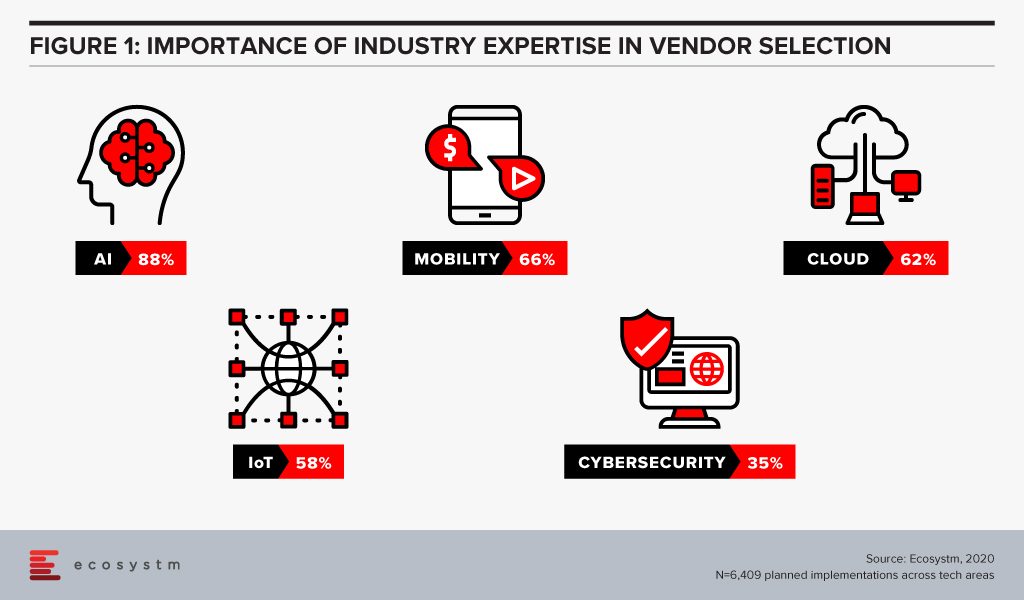
Whereas, we find that cybersecurity is at the other end of the spectrum, and organisations perceive that industry expertise is not required as network, applications and data protection requirements are not considered unique to any industry.
Is that necessarily the right approach?
Yes and no. If we look at the history of the ERP solution, as an example, we find that it was initially meant for and deeply entrenched in Manufacturing organisations. In fact, the precursor to modern-day ERP is the Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) software of the 1980s. Now, we primarily look at ERP as a cross-industry solution. Every business has taken lessons on inventory and supply chain management from the Manufacturing industry and has an enterprise-wide system. However, there are industries such as Hospitality and Healthcare that have their niche vendors who bundle in ERP features with their industry-specific solutions. This will be the general pattern that all tech solutions will follow: a) an industry use case will become popular; b) other industries will try to incorporate that solution, and in the process; c) create their own industry-specific customisations. It is important, therefore, for those who are evaluating emerging technologies to cast their net wide to identify use cases from other industries.
AI and automation is one such tech area where organisations should look to leverage cross-industry expertise. They should ask their vendors about their implementations in other allied industries and, in some cases, in industries that are not allied.
For cybersecurity, their approach should be entirely different. As companies move on from network security to more specific areas such as data security and emerging areas such as GRC communication, it will be important to evaluate industry experience. Data protection and compliance laws are often specific to industries – for example, while customer-focused industries are mandated on how to handle customer data, the Banking, Insurance, Healthcare and Public Sector industries have the need to store more sensitive data than other industries. They should look at solutions that have in-built checks and balances in place, incorporating their GRC requirements.
So, the answer to whether organisations should look for industry expertise in their vendors is that they should for more mature tech areas. An eCommerce company should look for industry experience when choosing a web hosting partner, but should look for experience in other industries such as Banking, when they are looking to invest in virtual assistants.
Are some industries more focused on industry experience than others?
Ecosystm research also sought to find out which industries look for industry expertise more than others (Figure 2). Surprisingly, there are no clear differences across industries. The Services, Healthcare and Public Sector industries emphasise marginally more on industry expertise – but the differences are almost negligible.
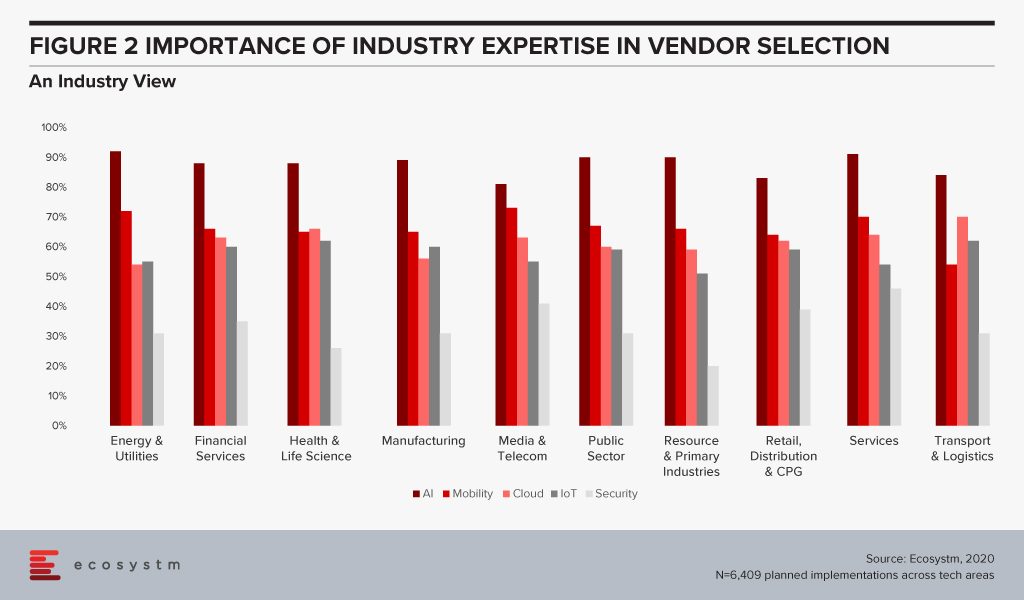
There are some differences when we look at specific tech areas, however. For example, industries that may be considered early adopters of IoT – Transportation, Manufacturing and Healthcare – tend to give more credit to industry experience because there are previous use cases that they can leverage. There are industries that are still formulating standards when it comes to IoT and they will be more open to evaluating vendors that have a successful solution for their requirement – irrespective of the industry.
The Healthcare Industry Example
Ecosystm Principal Analyst, Sash Mukherjee says, “In today’s fast-evolving technology market, it is important to go beyond use cases in only your industries and look for vendors that have a demonstrated history of innovation and experience in delivering measurable results, irrespective of the industry.” Mukherjee takes the example of the Healthcare industry. “No one vendor can provide the entire gamut of functionalities required for patient lifecycle management. In spite of recent trends of multi-capability vendors, hospitals need multiple vendors for the hospital information systems (HIS), ERP, HR systems, document management systems, auxiliary department systems and so on. For some areas such as electronic health records (EHR) systems, obviously industry expertise is paramount. However, if healthcare organisations continue to look for industry expertise and partner with the same vendors, they miss out on important learnings from other industries.”
Talking about industries that have influenced and will influence the Healthcare industry in the very near future, Mukherjee says, “Healthcare providers have learnt a lot from the Manufacturing industry – and several organisations have evaluated and implemented Lean Healthcare and Six Sigma to improve clinical outcomes. The industry has also learnt from the Retail and Hospitality industries on how to be customer focused. In the Top 5 Healthtech trends for 2020, I had pointed out the similarities between the Financial and Healthcare industries (stringent regulations, process-based legacy systems and so on). As the Healthcare industry focuses on value-based outcomes, governments introduce more regulations around accountability and transparency, and people expect the experience that they get out of their retail interactions, Healthtech start-ups will become as mainstream as Fintech start-ups.”
It is time for tech buyers to re-evaluate whether they are restricting themselves by looking at industry use cases, especially for emerging technologies. While less industry customisations mean easier deployments, it may also hamper innovation.



