As the search for a COVID-19 vaccine intensifies, there is a global focus on the Life Sciences industry. The industry has been hit hard this year – having to deliver overtime through a disrupted supply chain, unexpected demand spikes, and reduction of revenues from their regular streams. Life sciences organisations are already challenged by the breadth of their focus – across R&D and clinical discovery; Manufacturing & Distribution; and Sales & Marketing. Increasingly, many pharmaceutical and medtech organisations choose to outsource some of these functions, which brings to fore the need for a robust compliance framework. In the Ecosystm Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study, two-thirds of life sciences organisations mention that they have either been forced to start, accelerate or refocus their Digital Transformation initiatives – the remaining one-third have put their Digital Transformation on hold. The industry is clearly at an inflection point.
Challenges of the Life Sciences Industry
Continued Focus on R&D. Life sciences companies operate in an extremely competitive global market where they have to work on new products against a backdrop of competition from generics and a global concern over rising healthcare expenditure. Apart from regulatory challenges, they also face immense competition from local manufacturers as they enter each new market.
Re-thinking their Distribution Strategy. Sales and distribution for many pharma and medtech organisations have been traditional – using agents, distributors, clinicians, and healthcare providers. But now they need to change their go-to-market strategies, target patients and consumers directly and package their product offerings into value-added services. This will require them to incorporate customer experience enhancers in their R&D, going beyond drug discovery and product innovation.
Tracking Global Regulations. Governments across the world are trying to manage their healthcare budgets. They are also more focused on chronic disease management. The focus has shifted to value-based medicine in general, but pharma and medtech products are being increasingly held accountable by health outcomes. Governments are increasingly implementing drug reforms around what clinicians can prescribe. Global Life Sciences organisations have to constantly monitor the regulations in the multiple countries where they operate and sell. They are also accountable for their entire supply chain, especially ensuring a high product quality and fraud prevention.
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for Life Sciences organisations, focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). They appear to be investing in emerging technology especially in their R&D and clinical discovery and Manufacturing functions.
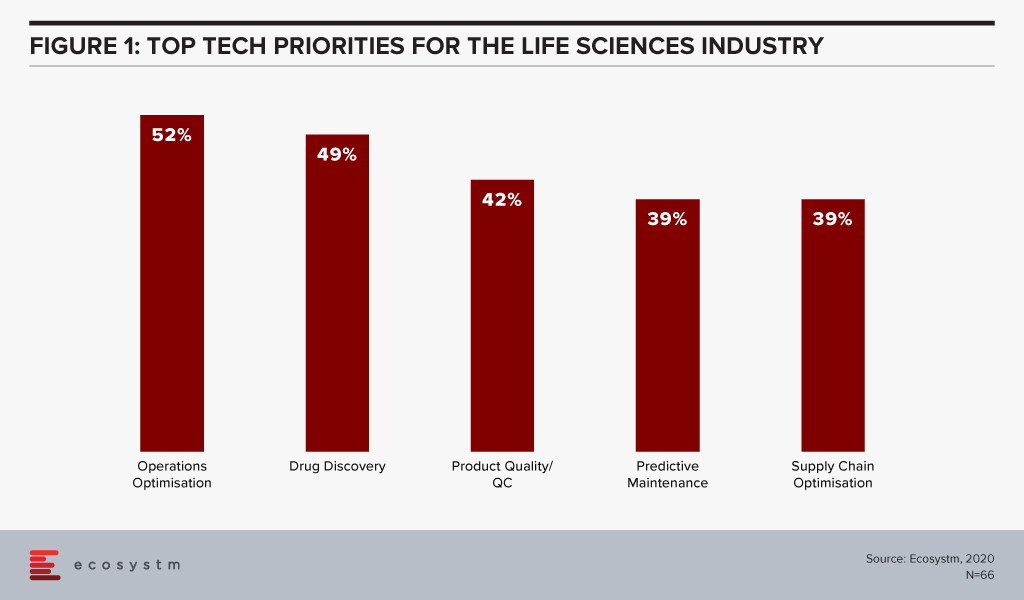
Technology as an Enabler of Life Sciences Transformation
Discovery and Development
With the evolution of technology, Life Sciences organisations are able to automate much of the mundane tasks around drug discovery and apply AI and machine learning to transform their drug discovery and development process. They are increasingly leveraging their ecosystem of smaller pharma and medtech companies, research laboratories, academic institutions, and technology providers to make the process more time and cost efficient.
Using an AI algorithm, the researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have discovered an antibiotic compound that can kill many species of antibiotic-resistant bacteria. MIT’s algorithm screens millions of chemical compounds and chooses the antibiotics which have the potential to eliminate bacteria resistant to existing drugs. Harvard’s Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering is manufacturing 3D printed organ-on-a-chip to give insights on cell, tissue, and organ biology to help the pharma sector with drug development, disease modelling and finally in the development of personalised medicine.
Life Sciences are also engaging more with technology partners – whether emerging start-ups or established players. Pfizer and Saama are working together on AI clinical data mining. The companies are developing and deploying an AI-based analytical tool where Pfizer provides clinical data and domain knowledge to train models on the Saama Life Science Analytics Cloud (LSAC). Saama was identified as a partner at a hackathon. Sanofi and Google have established a new virtual Innovation Lab to develop scientific and commercial solutions, using multiple Google capabilities from cloud computing to AI.
Tech providers also keep evolving their capabilities in the Life Sciences industry for more efficient drug discovery and better treatment protocols. Microsoft’s Project Hanover uses machine learning to develop a personalised drug protocol to manage acute myeloid leukaemia. Similarly, Apple’s ResearchKit – an open-source framework is meant to help researchers and developers create iOS-based applications in the field of medical research.
Manufacturing and Logistics
The industry also faces the challenges faced by any Manufacturing organisation and has the need to deploy manufacturing analytics, and advanced supply chain technology for better process and optimisation and agility. There is also the need for complete visibility over their supply chain and inventory for traceability, safety, and fraud prevention. Emerging technologies such as Blockchain will become increasingly relevant for real-time track and trace capability.
The MediLedger Network was established as an open network to the entire pharma supply chain. The project brings a consortium of some of the world’s largest pharmaceutical companies, and logistics providers to improve drug supply chain management.
Since the data on the distributed ledger is encrypted, it creates a secure system without any vulnerabilities. This eliminates counterfeit products and ultimately ensures the quality of the pharma products and promotes increased patient safety. To foster security and improve the supply chain, the United States Food and Drug Administration (USFDA) successfully completed a pilot with a group including IBM, KPMG, Merck and Walmart to support U.S. Drug Supply Chain Security Act (DSCSA) to trace vaccines and prescription medicines throughout the country.
Diagnostics and Personalised Healthcare
As more devices (consumer and enterprise) and applications enter the market, people will take ownership and interest in their own health outcomes. This is seeing a continued growth in online communities and comparison sites (on physicians, hospitals, and pharmaceutical products). Increasingly, insurance providers will use data from wearable devices for a more personalised approach; promoting and rewarding good health practices.
Beyond the use of wearables and health and wellness apps, we will also see an exponential increase of home-based healthcare products and services – whether for primary care and chronic disease management, or long-term and palliative care. As patients become more engaged with their care, the life sciences industry is beginning to serve them through personalised approach, medicines, right diagnosis and through advanced medical devices and products.
An online tool developed by the University of Virginia Health Systems helps identify patients that have a high risk of getting a stroke and helps them reduce that risk. This tool calculates the patient’s probability of suffering a stroke by measuring the severity of their metabolic syndrome – taking into account a number of conditions that include high blood pressure, abnormal cholesterol levels and excess body fat. Life Sciences organisations are increasingly having to invest in customer-focused solutions such as these.
Wearables with special smart software to monitor health parameters, gauge drug compatibility and monitor complications are being implemented by Life Sciences organisations. The US FDA approved a pill called Abilify MyCite fitted with a tiny ingestible sensor that communicates with a patch worn by the patient to transmit data on a smartphone. Medtech companies continue to develop FDA approved health devices that can monitor chronic conditions. Smart continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) and insulin pens send blood glucose level data to smartphone applications allowing the wearer to easily check their information and detect trends.
Technologies such as AR/VR are also enabling Life Sciences companies with their diagnostics. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals has created an AR/VR app called “In My Eyes” to better diagnose vision impairment in patients.
What is interesting about these personalised products is that not only do they improve clinical outcomes, they also give Life Sciences companies access to rich data that can be used for further product development and improvement.
The Life Sciences industry will continue to operate in an unpredictable and competitive market. This is evident by the several mergers and acquisitions that we witness in the industry. As they continue to use cutting-edge technology for their R&D practices, they will leverage technology to transform other functions as well.

We continue to receive responses from the tech buyer community on the impact of COVID-19 on Digital Transformation initiatives, and the early business and technology measures that were implemented to combat the crisis. As the months go by, it is becoming apparent that organisations have implemented the early measures and are now looking ahead to their journey to recovery.
IT Teams realised that even if they had the right technology solutions, they were unprepared for the scale or capacity to extend these technology offerings to handle the sudden and enormous changes required to manage the crisis. Their cloud business applications, cybersecurity and collaboration solutions were simply not sufficient to meet the needs of the remote workforce. As organisations become more conscious of business continuity planning (BCP) for future eventualities, they will boost their technology capabilities, over the next 12 months.
Another area the study aims to explore is how optimistic is the business outlook, when it comes to expecting a return to normalcy. Only 3% of organisations are expecting a New Normal that is very different from where things were at the beginning of the year. About a third of organisations are expecting a return to normalcy by the end of the year, while the majority expect to recover by the middle of 2021. Also, some industries are more optimistic of a recovery than others. As an example, 35% of healthcare organisations expect a return to normalcy by the end of the year. This is a positive indicator, given that the industry has been in the forefront of the crisis, for nearly 6 months now.
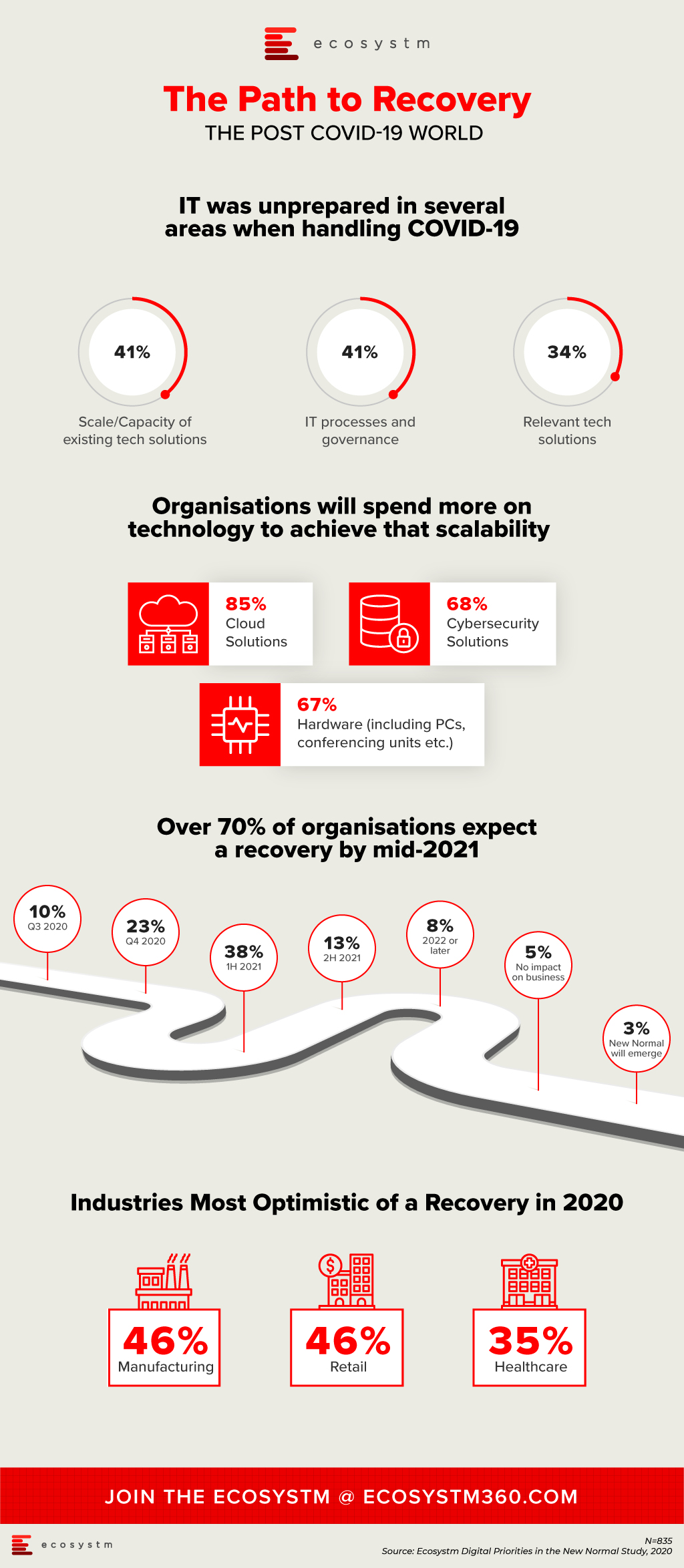
More insights on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic and technology areas that will see continued investments, as organisations get into the recovery phase, can be found in the Digital Priorities in the New Normal Study.
In recent times, there appears to be a shift in motive for cyber-attacks – along with common data theft, there is a proliferation of attacks aimed at the business interruption and physical incapacitation of business operations. We have witnessed an alarming increase in high-profile attacks on manufacturing businesses and critical infrastructure providers, globally.
This appears to be a global phenomenon. Honda manufacturing plants went offline in June after a cyber-attack compromised some of the Japanese automaker’s facilities. The same pattern emerged in a separate attack at the same time targeting Edesur S.A., a company belonging to the Enel Group that confirmed its internal IT network was disrupted due to a ransomware attack, which was caught by antivirus software before the malware could infect. Both companies had machines with Internet-accessible remote desktop servers, which is a favorite infection method among attackers nowadays. One of Australia’s largest brewers, Lion also faced a ransomware outbreak, last month. In Israel, it was reported that a cyber-attack very nearly poisoned the water supply with the attackers attempting to overload the water system with chlorine, and in recent days, a fire and explosion at an Iranian nuclear plant is suspected of being caused by cyber-attack.
These attacks highlight the need for appropriate investments in cybersecurity by companies and municipalities that own or operate critical infrastructure, properties (including places of public congregation, retailers and others) that are rapidly deploying a suite of operational technologies, and businesses in the manufacturing sector.
Operational Technology (OT) is the backbone of modern industrial operations and is a network of multiple computing systems that perform operations including production line management, operations control and industrial monitoring. OT can further include specific computing systems like industrial control systems (ICS) which is a collection of control systems used to operate and/or automate industrial processes. There are several types of ICSs, the most common of which are Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, and Distributed Control Systems (DCS). With such industrial systems and smart end-user products connected by a common network, several vulnerabilities may appear.
In OT security, the focus is much less on information, but more on the industrial process that technology controls. Hence, availability and integrity are often more important than confidentiality. Any organisation employing OT should employ continual risk-based assessments of their cybersecurity posture to prioritise and tailor recommended guidelines and solutions to fit specific security, business, and operational requirements.
Why is OT More Vulnerable?
OT systems are versatile and can be found in all kinds of industrial settings and infrastructures like smart buildings, oil and gas, energy generation/distribution, mining, wastewater treatment/distribution, manufacturing, food production, consumer devices and transport. In fact, almost every business in 2020 has an element of IoT within their operations.
A big issue with OT is that a lot of the technology in place is over 20 years old and therefore was not designed to provide the security capabilities required to face cyber threats in 2020. Legacy technology often requires legacy hardware and software to support it – much of which is the end of life and unsupported by the vendors (for example, consider SCADA systems still reliant on Windows NT or older Unix based systems, which have not been supported by their vendors for many years).
OT systems have also been damaged as unintended side effects of problems starting in corporate networks that took advantage of increasing connectivity, proving clearly that the standard PCs that now form part of a typical organisation’s IT environment are in turn used to manage OT systems and become a major vector for such cyber-attacks.
When it comes to OT, safety and reliability are the primary concerns as attackers aim to disrupt the critical services industry and their customers rely upon them. Given the increasing propensity of connecting OT systems with corporate networks for ease of management and the growing use of IoT systems, the likelihood of such systems being affected by vulnerabilities exploitable over the network is increasing exponentially.
For almost every business – not just critical infrastructure providers – most technologies we deploy include connectivity to the internet. Not knowing what systems and external access to these systems that your business is introducing in its everyday technology investment create significant risks to the broader business operations.
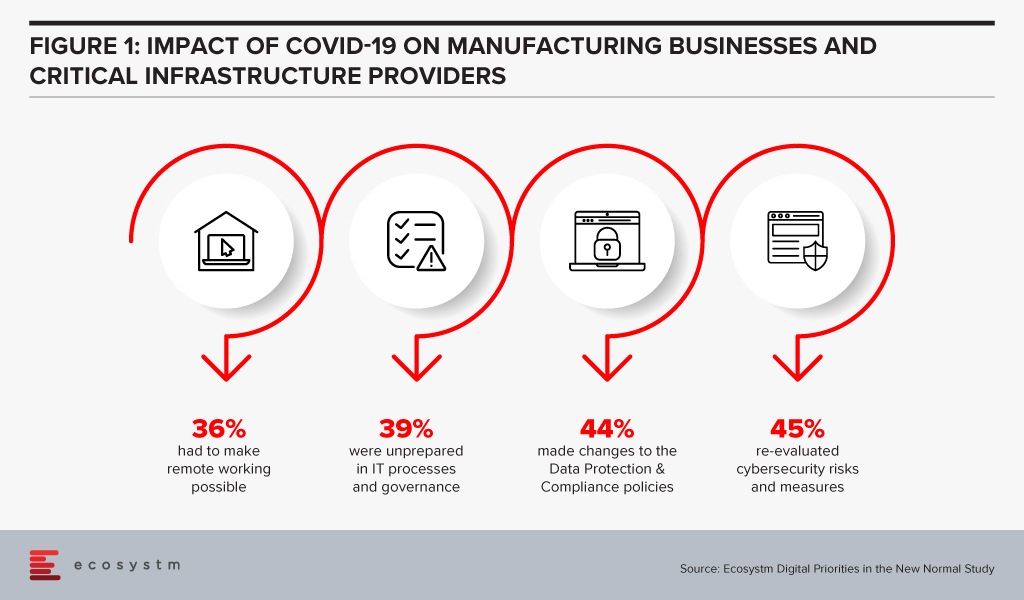
Manufacturing businesses and critical infrastructure providers realise that there is need to re-evaluate their cybersecurity measures, in the wake of the COVID-19 crisis, according to the findings of the Ecosystm’s ongoing “Digital Priorities in the New Normal” study (Figure 1).
But these measures may not be sufficient, as indicated by the slew of cyber-attacks on these organisations.
Why are these attacks successful?
There are several reasons why OT attacks are successful:
- Unauthorised access to internet-facing systems (e.g. deploying an IoT with the default username and password)
- Introduction of a compromised device (e.g. USB stick) to the environment that infects the network (often employee action)
- Exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities in control devices and software
- Propagated malware infections within isolated computer networks (i.e. The attacker can place a receiving device to make contact over a channel that can propagate across the isolated network)
- SQL injection via exploitation of web application vulnerabilities
- Network scanning and probing
- Lateral movement (i.e. inadequate segmentation which results in attackers being able to move between systems, groups of systems, network zones and even geographical locations.)
How can they be prevented?
The mitigation cannot rely solely on the organisation building security around the deployment nor can it be a reactive approach to fixing vulnerabilities in production, as they are identified. It begins with the OT vendors building security within; however, as with most IT systems and applications, this will evolve over time. For example, there is an initiative in Australia – driven by the IoT Alliance Australia (IOTAA) – to introduce a ‘Trust Mark’ for IoT devices that pass a certification process for security and privacy in product development. This is targeted to launch in September 2020 but could take many years to gain real traction. Thus, for the foreseeable future, the best operational outcomes must be planned and managed by the consumers of the technologies.
Here are the best practices to reduce exploitable IoT weaknesses and attacks occurring in your business:
- Maintain an accurate inventory of Operational Systems and eliminate any exposure of these systems to external networks
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities for your organisation and your vendors, to ensure cybersecurity risk is being addressed and managed throughout the OT lifecycle
- Implement network segmentation and apply firewalls between critical networks and systems.
- Use secure remote access methods
- Establish Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) and implement system logging
- Use only strong passwords, change default passwords, and consider other access controls (especially for any elevated privileges) such as multi-factor authentication, privileged access management solutions, etc.
- Establish threat intelligence feeds from your OT vendors and security vendors to ensure you remain abreast of new vulnerabilities, software/firmware patches and threats targeting systems you employ
- Develop and enforce policies on mobile devices, including strict device controls for any device connecting to OT systems or network zones
- Implement an employee cybersecurity training program
- Establish and maintain rigorous testing and patching program including vulnerability assessment and penetration testing
- Implement measures for detecting compromises and develop a cybersecurity incident response plan with a specific focus on responding to a disruptive attack on your OT environment
- Maintain an up-to-date Business Continuity Plan that can be deployed rapidly in response to a significant disruption

Manufacturing is estimated to account for a fifth of Singapore’s GDP and is one of its growth pillars. Singapore has been talking about re-inventing the Manufacturing industry since 2017, when the Industry 4.0 initiatives to enable digitalisation and process automation of processes and to ensure global competitiveness were first launched. As part of the long-term strategy, the Government had spoken about investment into research and development (R&D) projects, developing transformation roadmaps and strengthening the skill sets of the workforce.
Singapore’s 5G Rollout
Last month, the Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) announced that Singtel and JVCo (formed by Starhub and M1) has won the 5G Call for Proposal. They will be required to provide coverage for at least half of Singapore by end-2022, scaling up to nationwide coverage by end 2025. While Singtel and JVCo will be allocated radio frequency spectrum to deploy nationwide 5G networks, other mobile operators, including MVNOs, can access these network services through a wholesale arrangement. The networks will also be supplemented by localised mmWave deployments that will provide high capacity 5G hotspots.
In October 2019, IMDA and the National Research Foundation had set aside $40 million to support 5G trials in strategic sectors such as maritime, aviation, smart estates, consumer applications, Industry 4.0 and government applications. Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Jannat Maqbool says, “Reach, performance and robustness of connectivity and devices have long held back the ability to scale with the IoT as well as successful deployment of some solutions altogether. The integration of 5G with IoT has the potential to change that immensely. However, and possibly even more importantly, 5G will see the emergence of a true ‘Internet’, defined as ‘interconnected networks using standardised communication protocols’, made up of ‘things’ enabling never-before contemplated innovation – supporting economic development and community well-being.”
“While 5G offers enormous potential to produce economic and social benefits, to reach that potential we need to evaluate from a strategic perspective what it could mean for industries, employers and communities – then we need to invest in the infrastructure, innovation and associated development required to leverage the technology.”
Singapore’s Industry 4.0 Transformation
The Government is also focused on getting the industry ready for the transformation that 5G will bring. Last week, Singapore announced its first Industry 4.0 trial, where IMDA collaborates with IBM, M1 and Samsung to design, develop, test and benchmark 5G-enabled Industry 4.0 solutions that can be applied across various industries. The trials will begin at IBM’s facility in Singapore and involve open source infrastructure solutions from Red Hat to test Industry 4.0 use cases.
The project will test 5G-enabled use cases for Manufacturing, focusing on areas such as automated visual inspection using image recognition and video analytics, equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance, and the use of AR in increasing productivity and quality. The focus is also on leveraging 5G to reduce the cost of processing, by shifting the load from the edge device to centralised systems.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Kaushik Ghatak says, “For some time now, the Singapore Manufacturing industry has been in the quest for higher productivity in order to regain its foothold as a destination of choice for global manufacturing outsourcing. The 5G Industry 4.0 trial is a great initiative to fast-track identification and adoption of the right use cases in Manufacturing, in the areas of automation, visibility, analytics, as well as for opening new revenue streams through servitisation of smart products.”
5G will see increased collaboration in the Tech industry
With the advent of 5G, the market will see more collaboration between government agencies, telecom providers and cloud platform providers and network equipment providers. Governments globally have invested in 5G and so have the network and communications equipment providers. However, telecom providers are unsure of how to monetise 5G and cater to the shift in their customer profile from consumers to enterprises. IBM and Samsung had already announced the launch of a joint platform in late 2019. Collaborations such as these will be key to widespread 5G deployment and uptake.
Talking about the benefits of collaborative efforts such as this, Maqbool says, “Robustness and security built into 5G deployment from the outset is essential to enable the applications and innovation that many are promising the technology will deliver, including the ability to self-scale, automate fault management and support edge processing.”
It is interesting that the solutions developed will be featured at IBM’s Industry 4.0 Studio 5G Solutions Showcase, and that IBM and Samsung will evaluate successful solutions developed during the project for possible use in their operations in a broad range of markets and sectors. “Availability of proven use cases at IBM’s Solutions Showcase centre would benefit local manufactures greatly; in terms of easy access to right skills and proven technology architectures,” says Ghatak. “This initiative is a huge step towards realising the promise of the cyber physical world. The collaboration between the leaders in communications, equipment and software will ensure that the use case development is truly cutting edge.”

April saw the disruption of normal business operations due to the COVID-19 crisis. However, telecommunications companies continued initiatives to identify the best ways to serve customers and enterprises. The month saw a lot of activity in the 5G space across the globe, including partnerships, innovation in productisation and identifying 5G use cases.
Telecom providers building their 5G capabilities
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Shamir Amanullah noted in his blog that in the new normal telecom providers have fast evolved as the backbone of business and social interactions. Telecom operators are fervently working towards 5G network and services deployment in order to be an early mover in the market. In China, China Mobile has been one of the leaders in rolling out country-wide 5G. The tender to build around 250,000 fifth-generation wireless network base stations across 28 provincial regions was put out in March and in early April, Huawei emerged as the key winner with the contract to build nearly 60% of the base stations. ZTE also won nearly a third of the contract. Global network equipment providers will find entering the China market as challenge for a number of reasons, including the strength of their local players.
Huawei continues to be under scrutiny in the global market, however British telecom provider chose Ericsson to build the core of its 5G network. BT hopes to create and define a future roadmap of new services such as mobile edge computing, network slicing, enhanced mobile broadband and various enterprise services. The US market is another arena where the battle for 5G will be fought out. The T-Mobile – Sprint merger was finalised in early April. The New T-Mobile is committed to building the world’s best nationwide 5G network, which will bring lightning-fast speeds to urban areas and underserved rural communities alike. Other vendors are also vying for a larger share of the US market. Nex-Tech Wireless, a smaller rural telecom provider based in Kansas, is planning to transition from 4G to 5G by using Ericsson’s Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) to deploy 5G on existing bands. This will help Next-Tech wireless to leverage existing assets instead of building 5G capabilities from the ground-up – enabling them to seamlessly transfer from 4G to 5G.
The 5G developments are by no means limited mostly to the US and China. Korea’s telecom provider, KT and Far EasTone Taiwan (FET) signed an MOU to collaborate and jointly develop 5G services and digital content. With this deal, KT plans to boost its 5G powered content and services presence through FET.
Tech Vendors evolving their 5G offerings
Network and communications equipment providers have much to gain and more to lose as organisations look to leverage 5G for their IoT use cases. If 5G uptake does not take off, the bigger losers will be the network and communications equipment providers – the real investors in the technology. Also, as telecom providers look to monetise 5G they will find themselves dealing with a completely different customer base – they will take help from tech vendors that have more experience in the enterprise space, as well as industry expertise. Both network equipment vendors and other tech vendors are actively evolving their product offerings. There were numerous examples of this in April.
Microsoft’s decision to acquire Affirmed Networks is an example of how the major cloud providers are trying to be better embedded with 5G capabilities. This month also saw Microsoft announce Azure Edge Zones aimed at reducing latency for both public and private networks. AT&T is a good example of how public carriers will use the Azure Edge Zones. As part of the ongoing partnership with Microsoft, AT&T has already launched a Dallas Edge Zone, with another one planned for Los Angeles, later in the year. Microsoft also intends to offer the Azure Edge Zones, independent of carriers in denser areas. They also launched Azure Private Edge Zones for private enterprise networks suitable for delivering ultra-low latency performance for IoT devices.
The examples go beyond the cloud platform providers. Samsung and Xilinx, have joined forces to enable 5G deployments, with Samsung aiming to use the Xilinx Versal adaptive compute acceleration platform (ACAP) for worldwide 5G commercial deployments. Versal ACAP offers the compute density at low power consumption to perform the real-time, low-latency signal processing needed by 5G. Following the successful pilot of 450 MHz proof of concept 5G network, Nokia has partnered with PGE Systemy, a large energy sector company in Poland to deploy industrial grade 5G solutions and to support energy distribution for its next gen power grid. It is the band of choice for machine-to-machine communications in the energy sector, including smart meters. Nokia also released an AI-as-a-service offering – Nokia AVA 5G cognitive operations – to help telecom providers transform their services with AI-based solutions to support, network, business and operations.
Use cases for 5G adoption firming up
5G promises to revolutionise various industry solutions based on required data rates, low latency, reliability, and machine-type communications. Telecom providers and tech vendors alike are working on developing industry use cases to drive up adoption.
Vodafone Qatar and Dreama Orphan Care Centre and Protection Social Rehabilitation Centre (AMAN) have collaborated to support remote learning and education using 5G technology. This is aimed to enhance virtual education through e-learning, online schools, and connecting teachers and students through high-speed learning environment. In the post-COVID 19 era remote learning is expected to become a key sector and there is immense potential for uptake.
The Manufacturing industry remains a top focus area for 5G providers, with their early adoption of sensors and sensor data analytics. The Smart Internet Lab at the University of Bristol, UK has been awarded a 2 years project by UK’s Department for Digital, Culture, Media and Sport (DCMS) to enable 5G connectivity for the manufacturing sector. The project will primarily work on improving productivity and manufacturing, easy asset tracking and management with involvement of AR/VR technologies and industrial system management.
Gaming is another sector with huge potential for 5G adoption. With cloud gaming, gamers can access a library of popular high-quality games minus the need for expensive hardware which has been the case in the past. China Mobile Hong Kong and Ubitus teamed up to launch a 5G cloud gaming service – UGAME. The application is available for download from the Google Play store. While still at a beta phase, the telecom provider promises a revolutionary gaming experience, where the need for computers or consoles will be lessened by augmented smartphone capabilities.
In the midst of the uncertainties, telecom, network equipment providers and cloud platform providers appear to be gearing up for 5G in enabling a contactless and remote economy.
Identifying and selecting a vendor for your tech project can be a daunting task – especially when it comes to emerging technologies or when implementing a tech solution for the first time. Organisations look for a certain degree of alignment with their tech vendors – in terms of products and pricing, sure, but also in terms of demonstrable areas of expertise and culture. Several factors are involved in the selection process – vendors’ ability to deliver, to match expected quality standards, to offer the best pricing, to follow the terms of the contract and so on. They are also evaluated based on favourable reviews from the tech buyer community.
Often businesses in a particular industry tend to have their unique challenges; for example, the Financial Services industries have their specific set of compliance laws which might need to be built into their CRM systems. Over the years, vendors have built on their industry expertise and have industry teams that can advise organisations on how their business requirements can be met through technology adoption. These experts speak in the language of the industry and understand their business and technology pain points. They are able to customise their product and service offerings to the needs of the industry for a single client – which can then be repeated for other businesses in that industry. Vendors arm themselves with a portfolio of industry use cases, especially when they are entering a new market – and this often gives them an upper hand at the evaluation stage. In the end, organisations want less customisations to keep the complexity and costs down.
Do organisations evaluate vendors on industry experience?
Ecosystm research finds that industry experience can be a significant vendor selection criterion for some tech areas (Figure 1), especially in emerging technologies such as AI. AI and automation applications and algorithms are considered to be distinctive to each industry. While a vendor may have the right certifications and a team of skilled professionals, there is no substitute for experience. With that in mind, a vendor with experience in building machine learning models for the Telecommunications industry might not be perceived as the right fit for a Utilities industry implementation.
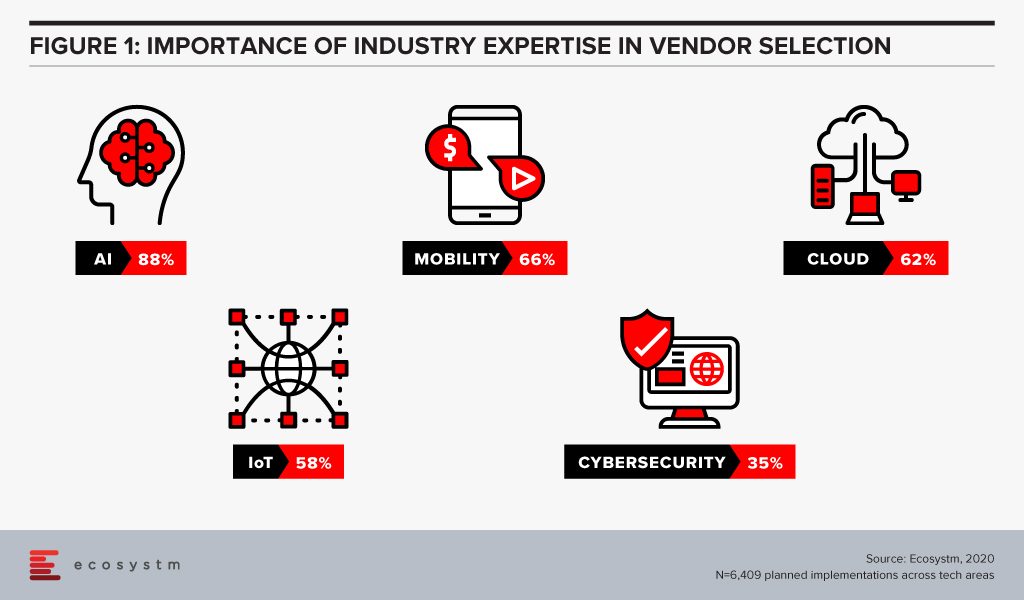
Whereas, we find that cybersecurity is at the other end of the spectrum, and organisations perceive that industry expertise is not required as network, applications and data protection requirements are not considered unique to any industry.
Is that necessarily the right approach?
Yes and no. If we look at the history of the ERP solution, as an example, we find that it was initially meant for and deeply entrenched in Manufacturing organisations. In fact, the precursor to modern-day ERP is the Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) software of the 1980s. Now, we primarily look at ERP as a cross-industry solution. Every business has taken lessons on inventory and supply chain management from the Manufacturing industry and has an enterprise-wide system. However, there are industries such as Hospitality and Healthcare that have their niche vendors who bundle in ERP features with their industry-specific solutions. This will be the general pattern that all tech solutions will follow: a) an industry use case will become popular; b) other industries will try to incorporate that solution, and in the process; c) create their own industry-specific customisations. It is important, therefore, for those who are evaluating emerging technologies to cast their net wide to identify use cases from other industries.
AI and automation is one such tech area where organisations should look to leverage cross-industry expertise. They should ask their vendors about their implementations in other allied industries and, in some cases, in industries that are not allied.
For cybersecurity, their approach should be entirely different. As companies move on from network security to more specific areas such as data security and emerging areas such as GRC communication, it will be important to evaluate industry experience. Data protection and compliance laws are often specific to industries – for example, while customer-focused industries are mandated on how to handle customer data, the Banking, Insurance, Healthcare and Public Sector industries have the need to store more sensitive data than other industries. They should look at solutions that have in-built checks and balances in place, incorporating their GRC requirements.
So, the answer to whether organisations should look for industry expertise in their vendors is that they should for more mature tech areas. An eCommerce company should look for industry experience when choosing a web hosting partner, but should look for experience in other industries such as Banking, when they are looking to invest in virtual assistants.
Are some industries more focused on industry experience than others?
Ecosystm research also sought to find out which industries look for industry expertise more than others (Figure 2). Surprisingly, there are no clear differences across industries. The Services, Healthcare and Public Sector industries emphasise marginally more on industry expertise – but the differences are almost negligible.
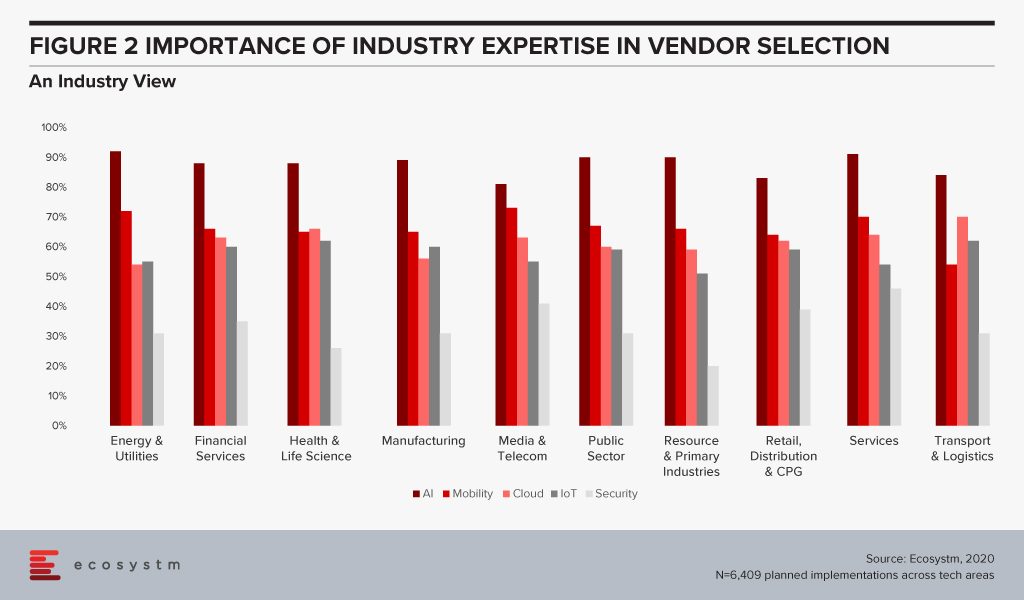
There are some differences when we look at specific tech areas, however. For example, industries that may be considered early adopters of IoT – Transportation, Manufacturing and Healthcare – tend to give more credit to industry experience because there are previous use cases that they can leverage. There are industries that are still formulating standards when it comes to IoT and they will be more open to evaluating vendors that have a successful solution for their requirement – irrespective of the industry.
The Healthcare Industry Example
Ecosystm Principal Analyst, Sash Mukherjee says, “In today’s fast-evolving technology market, it is important to go beyond use cases in only your industries and look for vendors that have a demonstrated history of innovation and experience in delivering measurable results, irrespective of the industry.” Mukherjee takes the example of the Healthcare industry. “No one vendor can provide the entire gamut of functionalities required for patient lifecycle management. In spite of recent trends of multi-capability vendors, hospitals need multiple vendors for the hospital information systems (HIS), ERP, HR systems, document management systems, auxiliary department systems and so on. For some areas such as electronic health records (EHR) systems, obviously industry expertise is paramount. However, if healthcare organisations continue to look for industry expertise and partner with the same vendors, they miss out on important learnings from other industries.”
Talking about industries that have influenced and will influence the Healthcare industry in the very near future, Mukherjee says, “Healthcare providers have learnt a lot from the Manufacturing industry – and several organisations have evaluated and implemented Lean Healthcare and Six Sigma to improve clinical outcomes. The industry has also learnt from the Retail and Hospitality industries on how to be customer focused. In the Top 5 Healthtech trends for 2020, I had pointed out the similarities between the Financial and Healthcare industries (stringent regulations, process-based legacy systems and so on). As the Healthcare industry focuses on value-based outcomes, governments introduce more regulations around accountability and transparency, and people expect the experience that they get out of their retail interactions, Healthtech start-ups will become as mainstream as Fintech start-ups.”
It is time for tech buyers to re-evaluate whether they are restricting themselves by looking at industry use cases, especially for emerging technologies. While less industry customisations mean easier deployments, it may also hamper innovation.
Traditional industry practices tend to divide industries into two distinct buckets – firms that are primarily focused on product design and improvement, and those that define their strategy based on customer services. Over the years, the lines distinguishing these organisations have all but disappeared. To be able to succeed in today’s competitive world, you need to continually improve your product offering – even for organisations in industries such as Manufacturing and Wholesale – and the best way to do so is to keep a firm eye on your customers. Likewise, unless you have a robust product, you will not be able to retain customers. As an example, online reviews are often critical of budget airlines, but the successful ones manage to hold on to their loyal customers doing what they set out to do – by not offering the best airline food service but by continuing to provide affordable airfares to places where their customers want to go. The Ecosystm CX study finds that even the most product-focused industries today, have improving customer experience (CX) as a key business priority (Figure 1). The two groups of industries tend to have similar priorities – the only major difference being customer-focused industries invest in more initiatives to promote customer loyalty.
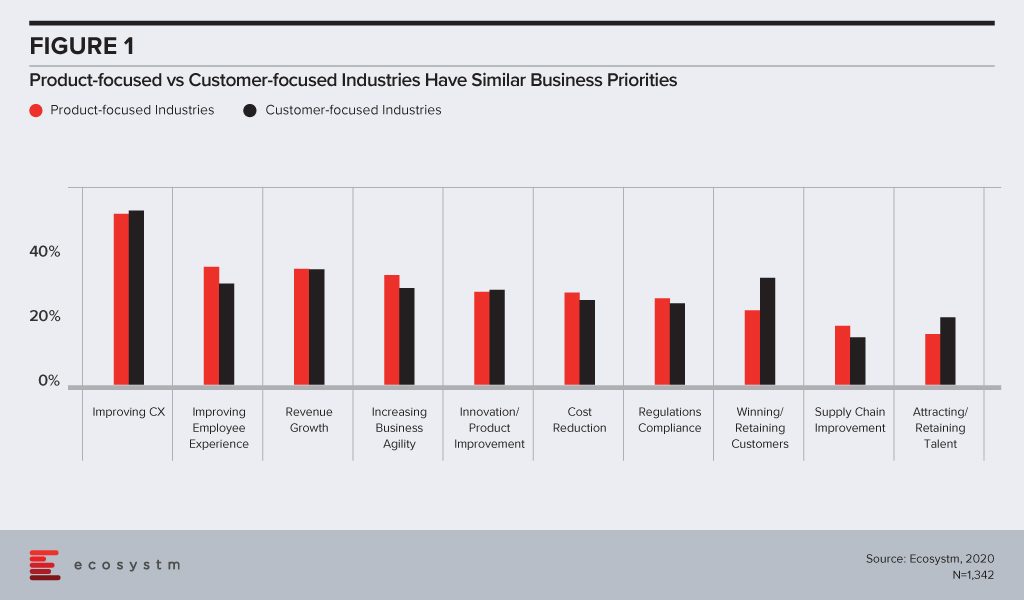
In 2016, Caterpillar showed the way forward to industries that have primarily been product-focused. They started investing in technology that is not just focused on solving, but actually predicting customer issues to improve service. Even industries such as Agriculture are increasingly becoming customer-focused, as more citizens become conscious of where and how their food has been produced. Freight Farms is a good example of customer-centricity in the industry – focusing on technology to grow food in environments not considered conducive to farming such as urban localities and places with extreme climates.
Investing in the Right Technologies
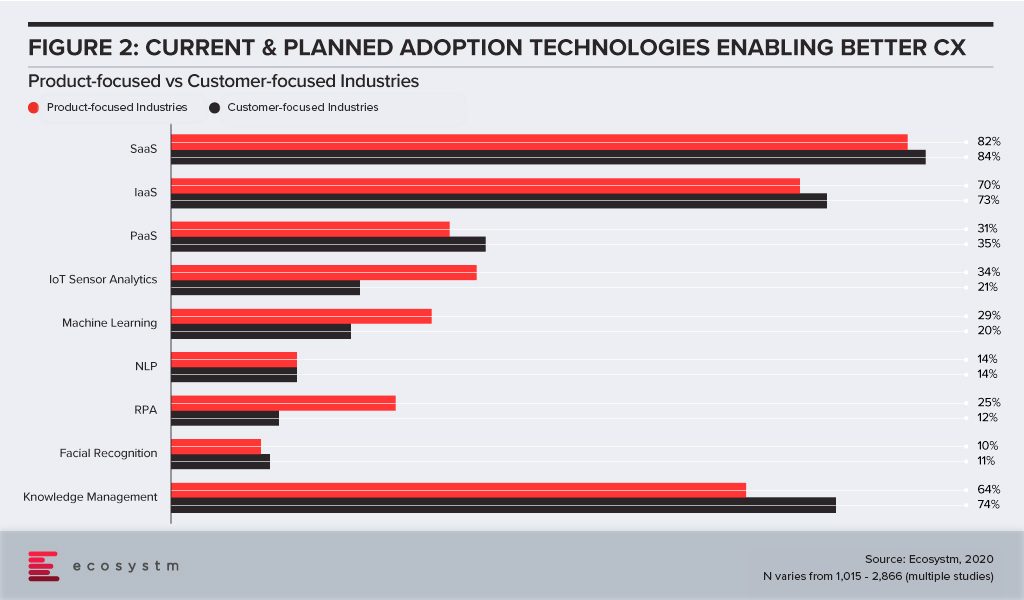
Looking at the Top 5 CX trends for 2020, we find that technologies such as Cloud and AI, and solutions such as robust knowledge management are true enablers of positive CX. So how do these two groups differ when it comes to investments in these technology areas? Customer-focused industries are slightly more enthusiastic about their Cloud investments, but only marginally (Figure 2). Obviously, they invest more in knowledge management solutions, both for CX as well as improved employee experience (EX). But surprisingly, product-focused industries also tend to invest in knowledge management, for several reasons ranging from product improvement to after-sales support.
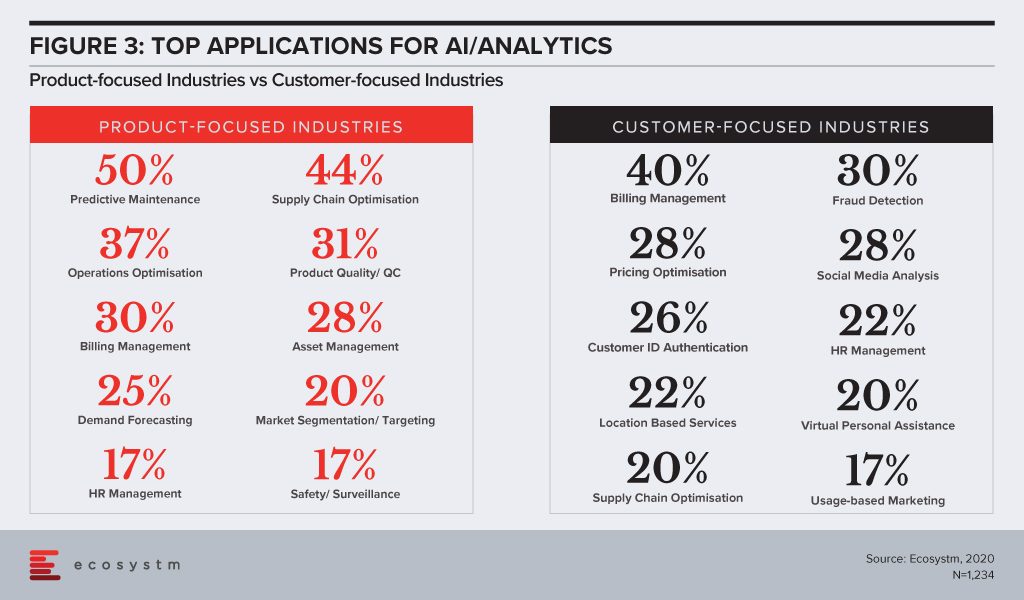
Where product-focused industries really lead is in their investments in AI/Analytics – which ties in with our observation that automation is the stepping stone for AI investments across industries. The applications of AI/Analytics are very distinct for the two groups (Figure 3). Product-based industries focus on automation and optimisation and have a clear asset focus. However, it is heartening to see some customer-centric solutions such as market segmentation. On the other hand, the top AI/Analytics application for customer-focused industries is billing management, which might significantly improve CX but falls under the purview of Finance & Operations in most organisations.
Securing Data and Building Trust
No organisation can ignore the seriousness of data breaches – whether customer data or intellectual property. Public cloud is going to be the true enabler of Digital Transformation (DX), from both cost and agility angles. Security has always been a key concern around public cloud adoption, even though organisations would mostly benefit from the robust and evolving security features of public cloud providers rather than having a go at securing their systems and data in-house and on-premises. The perception on public cloud security has changed over the years (Figure 4), but customer-focused industries appear to be savvier about the shared responsibility SLAs most public cloud providers have in place.
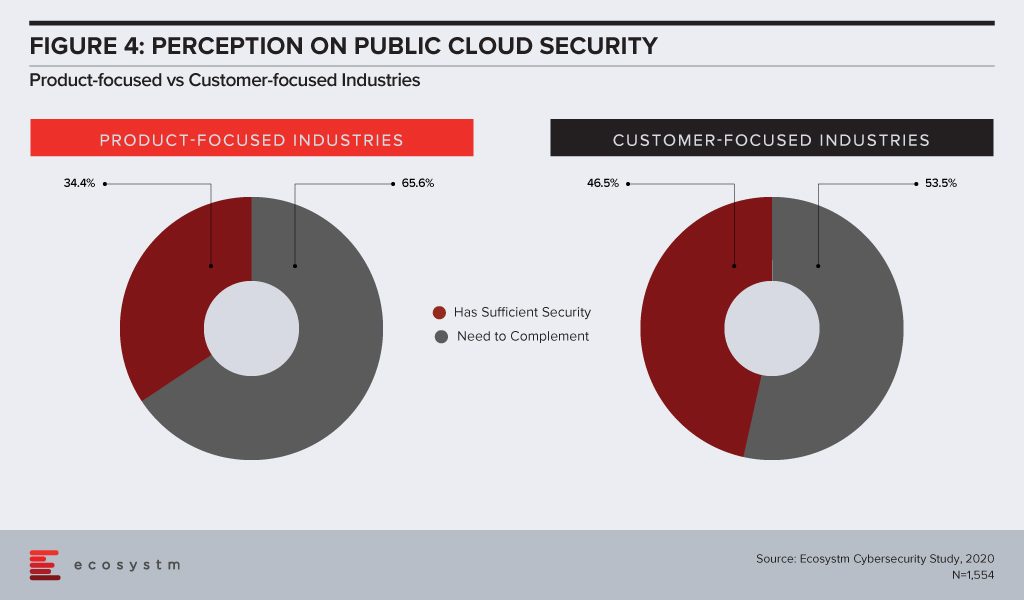
Which brings us to another important question – how much sensitive data do these organisations store on public cloud (Figure 5). Probably because they hold more customer data and must follow industry and country compliance laws that mandate how customer data should be stored and accessed, nearly a third of customer-focused organisations store sensitive data on-premises only. While their cloud adoption may be slightly higher than product-based industries, they are also more wary of storing sensitive data on the public cloud.
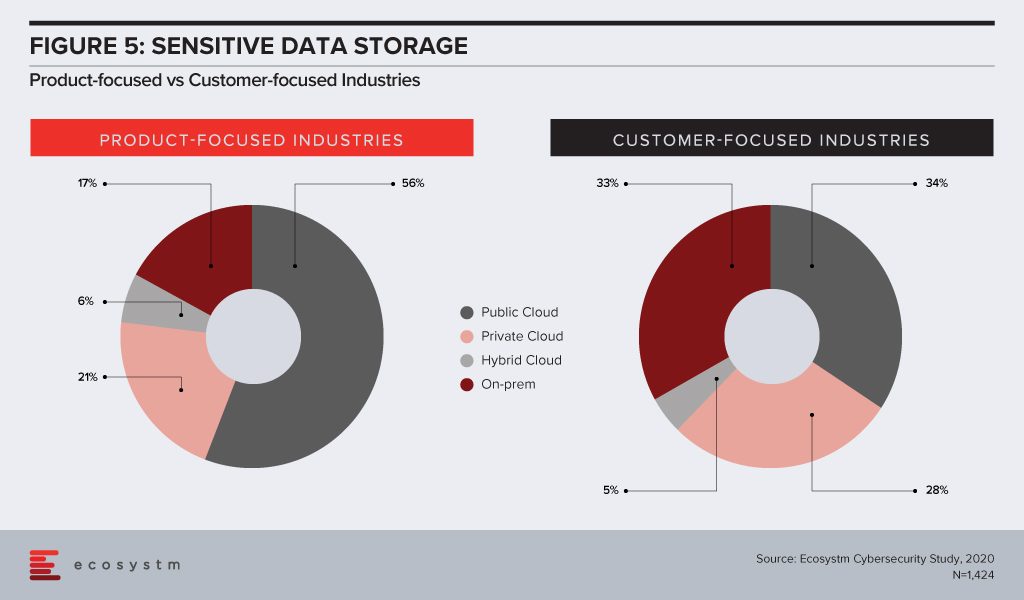
The differences in strategies between customer-focused and product-focused industries might have blurred over the past decade – both groups focusing on customer-centric products. Their technology priorities are still clearly distinct, however. It is important to bear this difference in mind – both for tech buyers who are looking at use cases across all industries when it comes to emerging technology adoption; as well as for tech vendors who now have to engage with stakeholders beyond the IT department.
NB: For the purpose of this blog, industries have been classified as follows: Product-focused Industries – Energy & Utilities, Manufacturing-based industries, Resource & Primary industries, Transport & Logistics, Wholesale and Construction; Customer-focused Industries – Banking & Financial industries, Retail & eCommerce, Healthcare, Government, Professional Services, Media & Telecommunications
Is IIoT Edge Computing solution a real Internet of Things (IoT) trend for 2019?
As large hardware manufacturers like Cisco, HPE, Dell and more are building specific, robust and secure infrastructure for the edge, it is believed that there will be a lot of money flowing in the IIoT Edge computing world.
The Development and implementation of Edge-Machine Learning solutions is a complex process and requires a combination of rich industry experience, knowledge of automation (PLCs, SCADAS, HMIs), electrical & mechanical engineering along with unique Edge Computing distributed system. This is used by Data Scientists to develop Machine Learning algorithms which can be utilised by IIoT applications in the manufacturing industry.
For organisations looking to implement these solutions, it is always a good idea to know more on adoption and ask for the continuation of a pilot project for more than a year.
Below are the top 5 things that one should follow to accelerate implementation of IIoT edge computing solutions in the Manufacturing industry –
1) Get help to find the needle in the haystack
With the fragmented ecosystem of IIoT vendors and companies talking about the Industrial Internet or Industry 4.0, the challenge that always appears in front of the customers is to ask for free pilots from the manufacturers.
It is not just finding the needle (IIoT best or cheaper solution) in the haystack (ecosystem), it is how this needle matches with your business and technology strategies.
I know, I am selling myself, but my recommendation to you is to get advice from independent IIoT experts.
2) Avoid OT Vendor Lock-In: We need machine data availability
Powerful Edge Analytics-Machine Learning applications require data exchange with the Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) of the manufacturers. By looking at the specifications we may think that it will be an easy task to extract the data from PLCs going through different ways or manufacturer’s help-guides. However, the problem is vendor lock-ins, most of the top PLC manufacturer’s do not allow “easy” data access and extraction methods neither to the customers nor to any third parties.
It is not a question of protocols, it is a question of vendor lock-in and data availability.
Customers must seek and claim for open-source solutions to avoid vendor lock-in during the long run. The open source can better lead to the path of innovation in their manufacturing plants.
3) Edge Computing and Machine Learning: The last frontier to break between IT/OT
In my article “IT and OT, Friends or Foes in the Industrial Internet of Things?” I was optimistic about the quick convergence of Information Technology (IT) and Operations Technology (OT), I was wrong. If you visit and inspect a manufacturing plant floor, you will see how much progress is still to be made.
Edge Analytics is a key component in the integration of IT & OT and requires a knowledge of both to make it work. The lack of skills & knowledge in the IT and OT fields impact the business & operations and creates a dilemma on which department should lead the Edge Analytics projects.
Manufacturing companies need a role with authority (Chief IIoT Officer or CIIoT) and resources to lead the IT/OT convergence strategy.
4) Do not stop by the dilemma of Edge: To Cloud or NOT to Cloud
When I wrote in 2016 “Do not let the fog hide the clouds in the Internet of Things”, the hype around Edge Computing and Machine Learning started. There was a confusion about fog computing and edge computing and how this layer will impact the IoT architecture, especially cloud workloads.
Today, many cloud vendors offer IoT platforms and tools that combine the Cloud and the Edge application development, machine learning and analytics at the edge, governance, and end to end security. On the OT side, companies like Siemens have launched MindSphere, an open cloud-based IoT operating system based on the SAP HANA cloud platform.
Manufacturers should continue to deploy and develop Edge Computing – Machine Learning applications to monitor the health of their machines or to improve their asset maintenance or to monitor the quality control of their plant floor processes and shouldn’t stop because of the fear of the integration of their platform with the Public or Hybrid Cloud environment.
Edge Computing solutions help manufacturers to improve their competitiveness without the Clouds but make sure your Edge IIoT solution is ready for easy integration with the Clouds.
5) Connected Machines is the only way for new Business Models
Security is another major obstacle for the adoption of IIoT in the manufacturing industry. Manufacturers have been reluctant to open their manufacturing facilities to the Internet because of the risks of cyber-attacks.
In a fast-moving era where platforms and services require products and machines connected, every manufacturing factory should be able to tap into machine data remotely and make it available for Machine vendors. This requires every Edge Computing / Machine Learning system to be built with the capability to share data remotely via open and secure protocols/standards like MTConnect and OPC-UA.
Having machines connected is the first step to make machines smarter, to build smarter factories and to flourish new business models as Remote Equipment Monitoring.
Key Takeaway
The benefits of using Edge Computing / Machine Learning solutions are very attractive to the manufacturers because it offers minimal latency, conserve network bandwidth, improve operations reliability, offers quick decision-making ability, gather data, and process the collected data to gain insights. The ROI in such IIoT solutions is very attractive.
To get these benefits and to grace IIoT journey, manufacturers have to step-up and accept to receive tangible and innovative business value.










