For many organisations migrating to cloud, the opportunity to run workloads from energy-efficient cloud data centres is a significant advantage. However, carbon emissions can vary from one country to another and if left unmonitored, will gradually increase over time as cloud use grows. This issue will become increasingly important as we move into the era of compute-intensive AI and the burden of cloud on natural resources will shift further into the spotlight.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that data centres are responsible for up to 1.5% of global electricity use and 1% of GHG emissions. Cloud providers have recognised this and are committed to change. Between 2025 and 2030, all hyperscalers – AWS, Azure, Google, and Oracle included – expect to power their global cloud operations entirely with renewable sources.
Chasing the Sun
Cloud providers are shifting their sights from simply matching electricity use with renewable power purchase agreements (PPA) to the more ambitious goal of operating 24/7 on carbon-free sources. A defining characteristic of renewables though is intermittency, with production levels fluctuating based on the availability of sunlight and wind. Leading cloud providers are using AI to dynamically distribute compute workloads throughout the day to regions with lower carbon intensity. Workloads that are processed with solar power during daylight can be shifted to nearby regions with abundant wind energy at night.
Addressing Water Scarcity
Many of the largest cloud data centres are situated in sunny locations to take advantage of solar power and proximity to population centres. Unfortunately, this often means that they are also in areas where water is scarce. While liquid-cooled facilities are energy efficient, local communities are concerned on the strain on water sources. Data centre operators are now committing to reduce consumption and restore water supplies. Simple measures, such as expanding humidity (below 20% RH) and temperature tolerances (above 30°C) in server rooms have helped companies like Meta to cut wastage. Similarly, Google has increased their reliance on non-potable sources, such as grey water and sea water.
From Waste to Worth
Data centre operators have identified innovative ways to reuse the excess heat generated by their computing equipment. Some have used it to heat adjacent swimming pools while others have warmed rooms that house vertical farms. Although these initiatives currently have little impact on the environmental impact of cloud, they suggest a future where waste is significantly reduced.
Greening the Grid
The giant facilities that cloud providers use to house their computing infrastructure are also set to change. Building materials and construction account for an astonishing 11% of global carbon emissions. The use of recycled materials in concrete and investing in greener methods of manufacturing steel are approaches the construction industry are attempting to lessen their impact. Smaller data centres have been 3D printed to accelerate construction and use recyclable printing concrete. While this approach may not be suitable for hyperscale facilities, it holds potential for smaller edge locations.
Rethinking Hardware Management
Cloud providers rely on their scale to provide fast, resilient, and cost-effective computing. In many cases, simply replacing malfunctioning or obsolete equipment would achieve these goals better than performing maintenance. However, the relentless growth of e-waste is putting pressure on cloud providers to participate in the circular economy. Microsoft, for example, has launched three Circular Centres to repurpose cloud equipment. During the pilot of their Amsterdam centre, it achieved 83% reuse and 17% recycling of critical parts. The lifecycle of equipment in the cloud is largely hidden but environmentally conscious users will start demanding greater transparency.
Recommendations
Organisations should be aware of their cloud-derived scope 3 emissions and consider broader environmental issues around water use and recycling. Here are the steps that can be taken immediately:
- Monitor GreenOps. Cloud providers are adding GreenOps tools, such as the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool, to help organisations measure the environmental impact of their cloud operations. Understanding the relationship between cloud use and emissions is the first step towards sustainable cloud operations.
- Adopt Cloud FinOps for Quick ROI. Eliminating wasted cloud resources not only cuts costs but also reduces electricity-related emissions. Tools such as CloudVerse provide visibility into cloud spend, identifies unused instances, and helps to optimise cloud operations.
- Take a Holistic View. Cloud providers are being forced to improve transparency and reduce their environmental impact by their biggest customers. Getting educated on the actions that cloud partners are taking to minimise emissions, water use, and waste to landfill is crucial. In most cases, dedicated cloud providers should reduce waste rather than offset it.
- Enable Remote Workforce. Cloud-enabled security and networking solutions, such as SASE, allow employees to work securely from remote locations and reduce their transportation emissions. With a SASE deployed in the cloud, routine management tasks can be performed by IT remotely rather than at the branch, further reducing transportation emissions.

November has seen uncertainties in the technology market with news of layoffs and hiring freezes from big names in the industry – Meta, Amazon, Salesforce, and Apple to name a few. These have impacted thousands of people globally, leaving tech talent with one common question, ‘What next?’
While the current situation and economic trends may seem grim, it is not all bad news for tech workers. It is true that people strategies in the sector may be impacted, but there are still plenty of opportunities for tech experts in the industry.
Here is what Ecosystm Analysts say about what’s next for technology workers.

Today, we are seeing two quite conflicting signals in the market: Tech vendors are laying off staff; and IT teams in businesses are struggling to hire the people they need.
At Ecosystm, we still expect a healthy growth in tech spend in 2023 and 2024 regardless of economic conditions. Businesses will be increasing their spend on security and data governance to limit their exposure to cyber-attacks; they will spend on automation to help teams grow productivity with current or lower headcount; they will continue their cloud investments to simplify their technology architectures, increase resilience, and to drive business agility. Security, cloud, data management and analytics, automation, and digital developers will all continue to see employment opportunities.
If this is the case, then why are tech vendors laying off headcount?
The slowdown in the American economy is a big reason. Tech providers that are laying of staff are heavily exposed to the American market.
- Salesforce – 68% Americas
- Facebook – 44% North America
- Genesys – around 60% in North America
Much of the messaging that these providers are giving is it is not that business is performing poorly – it is that growth is slowing down from the fast pace that many were witnessing when digital strategies accelerated.
Some of these tech providers might also be using the opportunity to “trim the fat” from their business – using the opportunity to get rid of the 2-3% of staff or teams that are underperforming. Interestingly, many of the people that are being laid off are from in or around the sales organisation. In some cases, tech providers are trimming products or services from their business and associated product, marketing, and technical staff are also being laid off.
While the majority of the impact is being felt in North America, there are certainly some people being laid off in Asia Pacific too. Particularly in companies where the development is done in Asia (India, China, ASEAN, etc.), there will be some impact when products or services are discontinued.

While it is not all bad news for tech talent, there is undoubtedly some nervousness. So this is what you should think about:
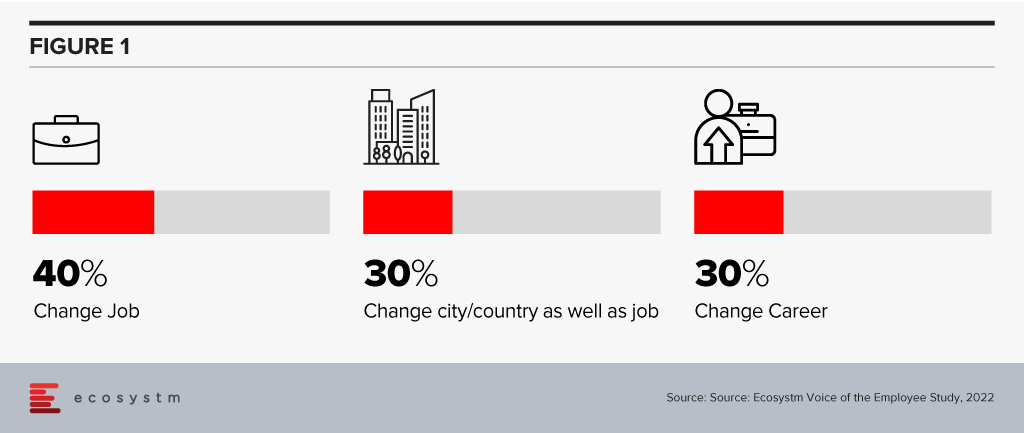
Change your immediate priorities. Ecosystm research found that 40% of digital/IT talent were looking to change employers in 2023. Nearly 60% of them were also thinking of changes in terms of where they live and their career.
This may not be the right time to voluntarily change your job. Job profiles and industry requirements should guide your decision – by February 2023, a clearer image of the job market will emerge. Till then, upskill and get those certifications to stay relevant!
Be prepared for contract roles. With a huge pool of highly skilled technologists on the hunt for new opportunities, smaller technology providers and start-ups have a cause to celebrate. They have faced the challenge of getting the right talent largely because of their inability to match the remunerations offered by large tech firms.
These companies may still not be able to match the benefits offered by the large tech firms – but they provide opportunities to expand your portfolio, industry expertise, and experience in emerging technologies. This will see a change in job profiles. It is expected that more contractual roles will open up for the technology industry. You will have more opportunities to explore the option of working on short-term assignments and consulting projects – sometimes on multiple projects and with multiple clients at the same time.
Think about switching sides. The fact remains that digital and technology upgrades continue to be organisational priorities, across all industries. As organisations continue on their digital journeys, they have an immense potential to address their skills gap now with the availability of highly skilled talent. In a recently conducted Ecosystm roundtable, CIOs reported that new graduates have been demanding salaries as high as USD 200,000 per annum! Even banks and consultancies – typically the top paying businesses – have been finding it hard to afford these skills! These industries may well benefit from the layoffs.
If you look at technology job listings, we see no signs of the demand abating!




