Despite financial institutions’ unwavering efforts to safeguard their customers, scammers continually evolve to exploit advancements in technology. For example, the number of scams and cybercrimes reported to the police in Singapore increased by a staggering 49.6% to 50,376 at an estimated cost of USD 482M in 2023. GenAI represents the latest challenge to the industry, providing fraudsters with new avenues for deception.
Ecosystm research shows that BFSI organisations in Asia Pacific are spending more on technologies to authenticate customer identity and prevent fraud, than they are in their Know Your Customer (KYC) processes.
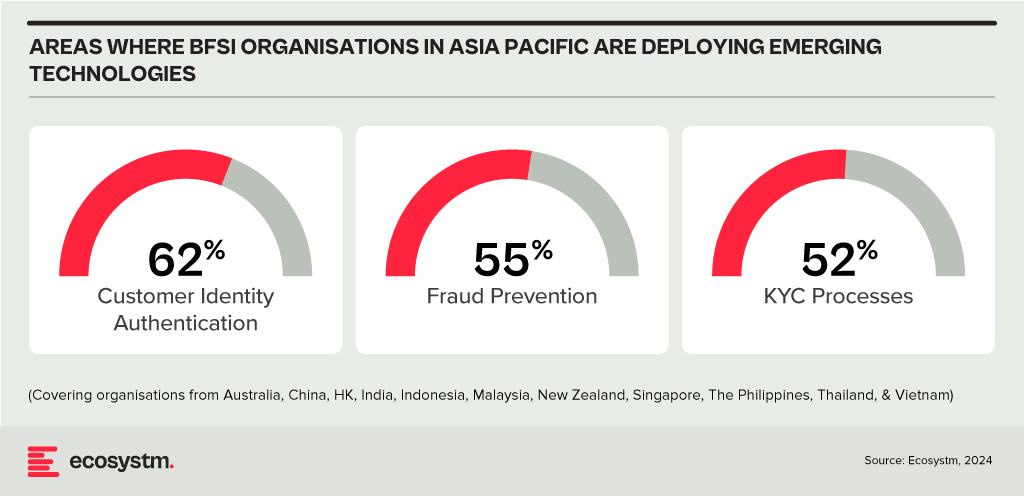
The Evolution of the Threat Landscape in BFSI
Synthetic Identity Fraud. This involves the creation of fictitious identities by combining real and fake information, distinct from traditional identity theft where personal data is stolen. These synthetic identities are then exploited to open fraudulent accounts, obtain credit, or engage in financial crimes, often evading detection due to their lack of association with real individuals. The Deloitte Centre for Financial Services predicts that synthetic identity fraud will result in USD 23B in losses by 2030. Synthetic fraud is posing significant challenges for financial institutions and law enforcement agencies, especially with the emergence of advanced technologies like GenAI being used to produce realistic documents blending genuine and false information, undermining Know Your Customer (KYC) protocols.
AI-Enhanced Phishing. Ecosystm research reveals that in Asia Pacific, 71% of customer interactions in BFSI occur across multiple digital channels, including mobile apps, emails, messaging, web chats, and conversational AI. In fact, 57% of organisations plan to further improve customer self-service capabilities to meet the demand for flexible and convenient service delivery. The proliferation of digital channels brings with it an increased risk of phishing attacks.
While these organisations continue to educate their customers on how to secure their accounts in a digital world, GenAI poses an escalating threat here as well. Phishing schemes will employ widely available LLMs to generate convincing text and even images. For many potential victims, misspellings and strangely worded appeals are the only hint that an email from their bank is not what it seems. The maturing of deepfake technology will also make it possible for malicious agents to create personalised voice and video attacks.
Identity Fraud Detection and Prevention
Although fraudsters are exploiting every new vulnerability, financial organisations also have new tools to protect their customers. Organisations should build a layered defence to prevent increasingly sophisticated attempts at fraud.
- Behavioural analytics. Using machine learning, financial organisations can differentiate between standard activities and suspicious behaviour at the account level. Data that can be analysed includes purchase patterns, unusual transaction values, VPN use, browser choice, log-in times, and impossible travel. Anomalies can be flagged, and additional security measures initiated to stem the attack.
- Passive authentication. Accounts can be protected even before password or biometric authentication by analysing additional data, such as phone number and IP address. This approach can be enhanced by comparing databases populated with the details of suspicious actors.
- SIM swap detection. SMS-based MFA is vulnerable to SIM swap attacks where a customer’s phone number is transferred to the fraudster’s own device. This can be prevented by using an authenticator app rather than SMS. Alternatively, SIM swap history can be detected before sending one-time passwords (OTPs).
- Breached password detection. Although customers are strongly discouraged to reuse passwords across sites, some inevitably will. By employing a service that maintains a database of credentials leaked during third-party breaches, it is possible to compare with active customer passwords and initiate a reset.
- Stronger biometrics. Phone-based fingerprint recognition has helped financial organisations safeguard against fraud and simplify the authentication experience. Advances in biometrics continue with recognition for faces, retina, iris, palm print, and voice making multimodal biometric protection possible. Liveness detection will grow in importance to combat against AI-generated content.
- Step-up validation. Authentication requirements can be differentiated according to risk level. Lower risk activities, such as balance check or internal transfer, may only require minimal authentication while higher risk ones, like international or cryptocurrency transactions may require a step up in validation. When anomalous behaviour is detected, even greater levels of security can be initiated.
Recommendations
- Reduce friction. While it may be tempting to implement heavy handed approaches to prevent fraud, it is also important to minimise friction in the authentication system. Frustrated users may abandon services or find risky ways to circumvent security. An effective layered defence should act in the background to prevent attackers getting close.
- AI Phishing Awareness. Even the savviest of customers could fall prey to advanced phishing attacks that are using GenAI. Social engineering at scale becomes increasingly more possible with each advance in AI. Monitor emerging global phishing activities and remind customers to be ever vigilant of more polished and personalised phishing attempts.
- Deploy an authenticator app. Consider shifting away from OTP SMS as an MFA method and implement either an authenticator app or one embedded in the financial app instead.
- Integrate authentication with fraud analytics. Select an authentication provider that can integrate its offering with analytics to identify fraud or unusual behaviour during account creation, log in, and transactions. The two systems should work in tandem.
- Take a zero-trust approach. Protecting both customers and employees is critical, particularly in the hybrid work era. Implement zero trust tools to prevent employees from falling victim to malicious attacks and minimising damage if they do.

While the discussions have centred around AI, particularly Generative AI in 2023, the influence of AI innovations is extensive. Organisations will urgently need to re-examine their risk strategies, particularly in cyber and resilience practices. They will also reassess their infrastructure needs, optimise applications for AI, and re-evaluate their skills requirements.
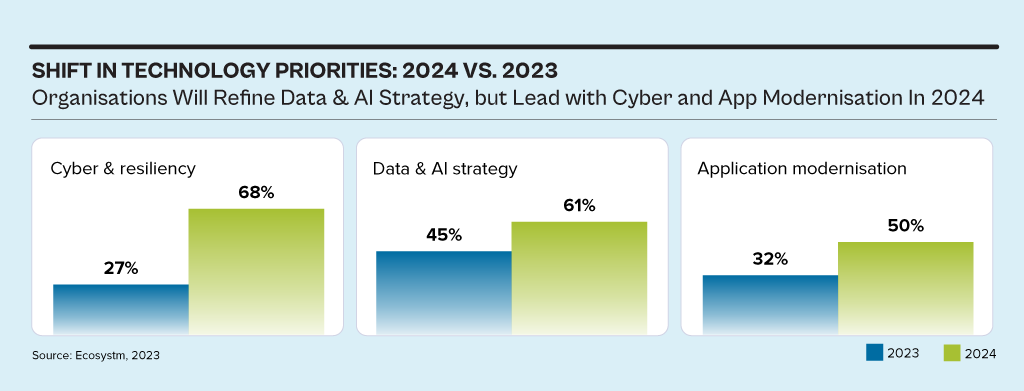
This impacts the entire tech market, including tech skills, market opportunities, and innovations.
Ecosystm analysts Alea Fairchild, Darian Bird, Richard Wilkins, and Tim Sheedy present the top 5 trends in building an Agile & Resilient Organisation in 2024.
Click here to download ‘Ecosystm Predicts: Top 5 Resilience Trends in 2024’ as a PDF.
#1 Gen AI Will See Spike in Infrastructure Innovation
Enterprises considering the adoption of Generative AI are evaluating cloud-based solutions versus on-premises solutions. Cloud-based options present an advantage in terms of simplified integration, but raise concerns over the management of training data, potentially resulting in AI-generated hallucinations. On-premises alternatives offer enhanced control and data security but encounter obstacles due to the unexpectedly high demands of GPU computing needed for inferencing, impeding widespread implementation. To overcome this, there’s a need for hardware innovation to meet Generative AI demands, ensuring scalable on-premises deployments.
The collaboration between hardware development and AI innovation is crucial to unleash the full potential of Generative AI and drive enterprise adoption in the AI ecosystem.
Striking the right balance between cloud-based flexibility and on-premises control is pivotal, with considerations like data control, privacy, scalability, compliance, and operational requirements.

#2 Cloud Migrations Will Make Way for Cloud Transformations
The steady move to the public cloud has slowed down. Organisations – particularly those in mature economies – now prioritise cloud efficiencies, having largely completed most of their application migration. The “easy” workloads have moved to the cloud – either through lift-and-shift, SaaS, or simple replatforming.
New skills will be needed as organisations adopt public and hybrid cloud for their entire application and workload portfolio.
- Cloud-native development frameworks like Spring Boot and ASP.NET Core make it easier to develop cloud-native applications
- Cloud-native databases like MongoDB and Cassandra are designed for the cloud and offer scalability, performance, and reliability
- Cloud-native storage like Snowflake, Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage provides secure and scalable storage
- Cloud-native messaging like Amazon SNS and Google Cloud Pub/Sub provide reliable and scalable communication between different parts of the cloud-native application

#3 2024 Will be a Good Year for Technology Services Providers
Several changes are set to fuel the growth of tech services providers (systems integrators, consultants, and managed services providers).
There will be a return of “big apps” projects in 2024.
Companies are embarking on significant updates for their SAP, Oracle, and other large ERP, CRM, SCM, and HRM platforms. Whether moving to the cloud or staying on-premises, these upgrades will generate substantial activity for tech services providers.
The migration of complex apps to the cloud involves significant refactoring and rearchitecting, presenting substantial opportunities for managed services providers to transform and modernise these applications beyond traditional “lift-and-shift” activities.
The dynamic tech landscape, marked by AI growth, evolving security threats, and constant releases of new cloud services, has led to a shortage of modern tech skills. Despite a more relaxed job market, organisations will increasingly turn to their tech services partners, whether onshore or offshore, to fill crucial skill gaps.

#4 Gen AI and Maturing Deepfakes Will Democratise Phishing
As with any emerging technology, malicious actors will be among the fastest to exploit Generative AI for their own purposes. The most immediate application will be employing widely available LLMs to generate convincing text and images for their phishing schemes. For many potential victims, misspellings and strangely worded appeals are the only hints that an email from their bank, courier, or colleague is not what it seems. The ability to create professional-sounding prose in any language and a variety of tones will unfortunately democratise phishing.
The emergence of Generative AI combined with the maturing of deepfake technology will make it possible for malicious agents to create personalised voice and video attacks. Digital channels for communication and entertainment will be stretched to differentiate between real and fake.
Security training that underscores the threat of more polished and personalised phishing is a must.

#5 A Holistic Approach to Risk and Operational Resilience Will Drive Adoption of VMaaS
Vulnerability management is a continuous, proactive approach to managing system security. It not only involves vulnerability assessments but also includes developing and implementing strategies to address these vulnerabilities. This is where Vulnerability Management Platforms (VMPs) become table stakes for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) as they are often perceived as “easier targets” by cybercriminals due to potentially lesser investments in security measures.
Vulnerability Management as a Service (VMaaS) – a third-party service that manages and controls threats to automate vulnerability response to remediate faster – can improve the asset cybersecurity management and let SMEs focus on their core activities.
In-house security teams will particularly value the flexibility and customisation of dashboards and reports that give them enhanced visibility over all assets and vulnerabilities.


In recent times, there appears to be a shift in motive for cyber-attacks – along with common data theft, there is a proliferation of attacks aimed at the business interruption and physical incapacitation of business operations. We have witnessed an alarming increase in high-profile attacks on manufacturing businesses and critical infrastructure providers, globally.
This appears to be a global phenomenon. Honda manufacturing plants went offline in June after a cyber-attack compromised some of the Japanese automaker’s facilities. The same pattern emerged in a separate attack at the same time targeting Edesur S.A., a company belonging to the Enel Group that confirmed its internal IT network was disrupted due to a ransomware attack, which was caught by antivirus software before the malware could infect. Both companies had machines with Internet-accessible remote desktop servers, which is a favorite infection method among attackers nowadays. One of Australia’s largest brewers, Lion also faced a ransomware outbreak, last month. In Israel, it was reported that a cyber-attack very nearly poisoned the water supply with the attackers attempting to overload the water system with chlorine, and in recent days, a fire and explosion at an Iranian nuclear plant is suspected of being caused by cyber-attack.
These attacks highlight the need for appropriate investments in cybersecurity by companies and municipalities that own or operate critical infrastructure, properties (including places of public congregation, retailers and others) that are rapidly deploying a suite of operational technologies, and businesses in the manufacturing sector.
Operational Technology (OT) is the backbone of modern industrial operations and is a network of multiple computing systems that perform operations including production line management, operations control and industrial monitoring. OT can further include specific computing systems like industrial control systems (ICS) which is a collection of control systems used to operate and/or automate industrial processes. There are several types of ICSs, the most common of which are Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems, and Distributed Control Systems (DCS). With such industrial systems and smart end-user products connected by a common network, several vulnerabilities may appear.
In OT security, the focus is much less on information, but more on the industrial process that technology controls. Hence, availability and integrity are often more important than confidentiality. Any organisation employing OT should employ continual risk-based assessments of their cybersecurity posture to prioritise and tailor recommended guidelines and solutions to fit specific security, business, and operational requirements.
Why is OT More Vulnerable?
OT systems are versatile and can be found in all kinds of industrial settings and infrastructures like smart buildings, oil and gas, energy generation/distribution, mining, wastewater treatment/distribution, manufacturing, food production, consumer devices and transport. In fact, almost every business in 2020 has an element of IoT within their operations.
A big issue with OT is that a lot of the technology in place is over 20 years old and therefore was not designed to provide the security capabilities required to face cyber threats in 2020. Legacy technology often requires legacy hardware and software to support it – much of which is the end of life and unsupported by the vendors (for example, consider SCADA systems still reliant on Windows NT or older Unix based systems, which have not been supported by their vendors for many years).
OT systems have also been damaged as unintended side effects of problems starting in corporate networks that took advantage of increasing connectivity, proving clearly that the standard PCs that now form part of a typical organisation’s IT environment are in turn used to manage OT systems and become a major vector for such cyber-attacks.
When it comes to OT, safety and reliability are the primary concerns as attackers aim to disrupt the critical services industry and their customers rely upon them. Given the increasing propensity of connecting OT systems with corporate networks for ease of management and the growing use of IoT systems, the likelihood of such systems being affected by vulnerabilities exploitable over the network is increasing exponentially.
For almost every business – not just critical infrastructure providers – most technologies we deploy include connectivity to the internet. Not knowing what systems and external access to these systems that your business is introducing in its everyday technology investment create significant risks to the broader business operations.
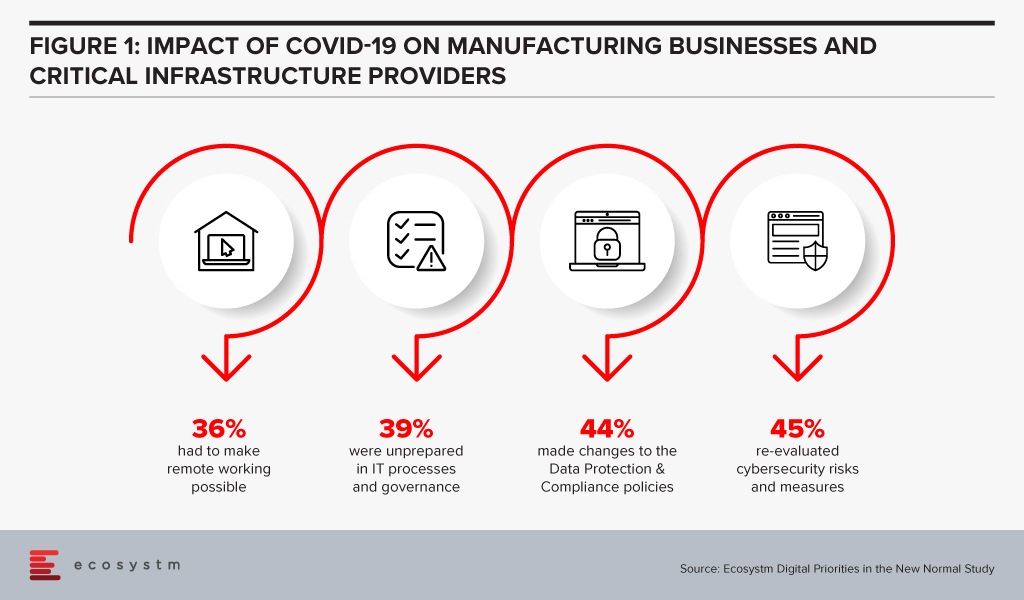
Manufacturing businesses and critical infrastructure providers realise that there is need to re-evaluate their cybersecurity measures, in the wake of the COVID-19 crisis, according to the findings of the Ecosystm’s ongoing “Digital Priorities in the New Normal” study (Figure 1).
But these measures may not be sufficient, as indicated by the slew of cyber-attacks on these organisations.
Why are these attacks successful?
There are several reasons why OT attacks are successful:
- Unauthorised access to internet-facing systems (e.g. deploying an IoT with the default username and password)
- Introduction of a compromised device (e.g. USB stick) to the environment that infects the network (often employee action)
- Exploitation of zero-day vulnerabilities in control devices and software
- Propagated malware infections within isolated computer networks (i.e. The attacker can place a receiving device to make contact over a channel that can propagate across the isolated network)
- SQL injection via exploitation of web application vulnerabilities
- Network scanning and probing
- Lateral movement (i.e. inadequate segmentation which results in attackers being able to move between systems, groups of systems, network zones and even geographical locations.)
How can they be prevented?
The mitigation cannot rely solely on the organisation building security around the deployment nor can it be a reactive approach to fixing vulnerabilities in production, as they are identified. It begins with the OT vendors building security within; however, as with most IT systems and applications, this will evolve over time. For example, there is an initiative in Australia – driven by the IoT Alliance Australia (IOTAA) – to introduce a ‘Trust Mark’ for IoT devices that pass a certification process for security and privacy in product development. This is targeted to launch in September 2020 but could take many years to gain real traction. Thus, for the foreseeable future, the best operational outcomes must be planned and managed by the consumers of the technologies.
Here are the best practices to reduce exploitable IoT weaknesses and attacks occurring in your business:
- Maintain an accurate inventory of Operational Systems and eliminate any exposure of these systems to external networks
- Establish clear roles and responsibilities for your organisation and your vendors, to ensure cybersecurity risk is being addressed and managed throughout the OT lifecycle
- Implement network segmentation and apply firewalls between critical networks and systems.
- Use secure remote access methods
- Establish Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) and implement system logging
- Use only strong passwords, change default passwords, and consider other access controls (especially for any elevated privileges) such as multi-factor authentication, privileged access management solutions, etc.
- Establish threat intelligence feeds from your OT vendors and security vendors to ensure you remain abreast of new vulnerabilities, software/firmware patches and threats targeting systems you employ
- Develop and enforce policies on mobile devices, including strict device controls for any device connecting to OT systems or network zones
- Implement an employee cybersecurity training program
- Establish and maintain rigorous testing and patching program including vulnerability assessment and penetration testing
- Implement measures for detecting compromises and develop a cybersecurity incident response plan with a specific focus on responding to a disruptive attack on your OT environment
- Maintain an up-to-date Business Continuity Plan that can be deployed rapidly in response to a significant disruption

Last week, the Australia government joined other countries in the Asia Pacific region in highlighting the growth of attack surface in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In our recently launched study Digital Priorities in the New Normal, we find that 87% of organisations in the Asia Pacific have increased investments in one or more cybersecurity solutions. However, this has to be backed by a reassessment of organisations’ risk positions and a re-evaluation of data protection and compliance policies.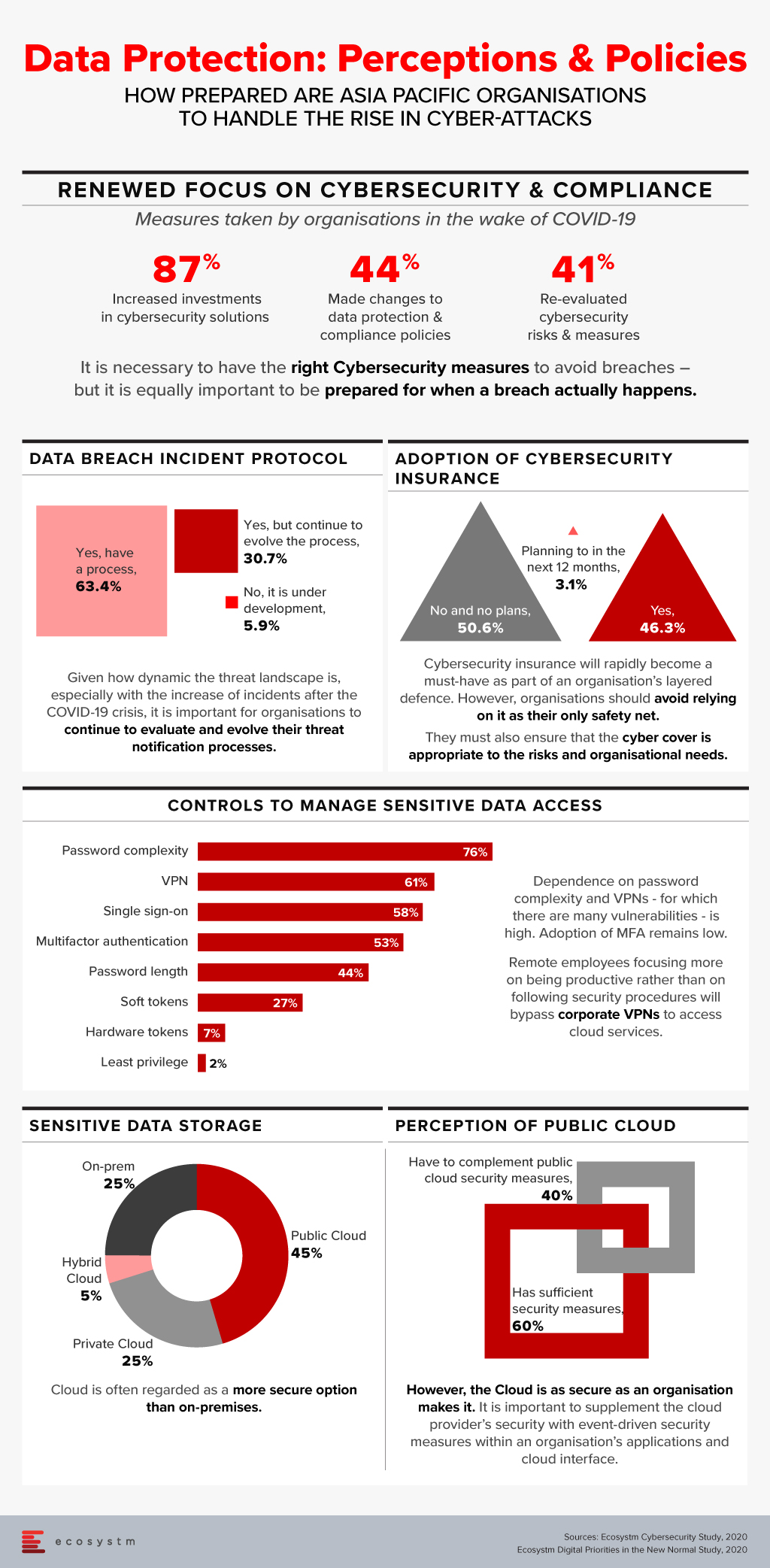

Organisations across the globe, are facing disruption on a scale never seen before, and are urgently seeking ways of remaining viable. Predictably, cybersecurity is a secondary concern and is often handled reactively. To make matters worse, a chronic cybersecurity skills shortage is being made much more severe by the crisis.
Remote working has reached unprecedented levels as organisations try hard to keep going. This is massively expanding the attack surface for cyber criminals, weakening security and leading to a cybercrime pandemic. Hacking activity and phishing, inspired by the COVID-19 crisis, are growing rapidly. Containing and suppressing this cybercrime pandemic is proving to be almost impossible.
Remote working intensifies known threats posed by phishing and ransomware. More alarming are the distinctive cybersecurity vulnerabilities associated with home working including reliance on home Wi-Fi, increased use of unpatched VPNs and devices, and the exponential growth of network access points. These vulnerabilities increase the likelihood of a breach enormously.
Corporate IT is in a very challenging position. It needs to ensure that organisations can operate in a way that they have never operated before, while ensuring that their assets are secure – a very difficult, if not an impossible task for which there is no precedent.
Some important cybersecurity considerations, during and after the COVID-19 pandemic include:
Re-enforce Basic Cyber Hygiene
As massive numbers of people work from home, basic cyber hygiene becomes more critical than ever before. Organisations must maintain awareness of security threats among employees, ensure security policies are being followed and be certain that corporate software is being updated and patched on time. With a dispersed workforce, these basic practices are more challenging, and training becomes more critical. Phishing attacks are often the primary attack vector for malicious actors, so employees must be able to identify these attacks. They increasingly exploit shortages of goods such as protective equipment and sometimes claim to offer official information relating to COVID-19.
Remote employees often access sensitive business data through home Wi-Fi networks that will not have the same security controls – such as firewalls – that are used in offices. There is more connectivity from remote locations, which requires greater focus on data privacy, and hunting for intrusions from a much larger number of entry points.
Place More Focus on Endpoint Security
The unprecedented switch to remote working is radically increasing the number of vulnerable endpoints. Given that endpoints are located at a distance from corporate premises, it is frequently difficult for IT departments to configure endpoint systems and install necessary security software.
It is vital to assess the security posture of all endpoints connecting to the corporate network. This practice enables an organisation to determine whether or not an endpoint requesting to access internal resources meets security policy requirements. It requires the ability to monitor and enforce policy across all devices, while making onboarding and offboarding seamless.
It is essential that endpoint solutions can be rapidly deployed for remote workers, as needed on both personal and corporate devices. Devices used for remote work need much more than the basic antivirus and antispyware protection. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) and on-board endpoint detection and response (EDR) capabilities are crucial.
Be More Selective About How and When Video Conferencing and Collaboration Platforms are Used
Since lockdowns spread around the world, the use of video conferencing and collaboration tools has grown beyond the wildest expectations of suppliers of these tools. The extraordinary growth of Zoom has made it a target for attackers. Many security vulnerabilities have been discovered with Zoom such as, a vulnerability to UNC path injection in the client chat feature, which allows hackers to steal Windows credentials, keeping decryption keys in the cloud which can potentially be accessed by hackers and gives the ability for trolls to ‘Zoombomb’ open and unprotected meetings. Zoom has so far managed to augment its security features in part by its recent acquisition of Keybase, a secure messaging service.
Switching to an alternative video conferencing platform will not necessarily offer greater levels of security as privacy is typically not a strength of any collaboration platform. Collaboration platforms tend to tread a fine line between a great experience and security. Too much security can cause performance and usability to be impacted negatively. Too little security, as we have seen, allows hackers to find vulnerabilities. If data privacy is critical for a meeting, then perhaps collaboration platforms should not be used, or organisations should not share critical information on them.
Protect all Cloud Workloads
In today’s remote working paradigm, cloud computing is being used more than ever. This frequently exposes organisations to risks that are not adequately mitigated.
Organisations typically need to manage a mix of on-premises technology together with multiple clouds, which are often poorly integrated. These complexities are compounded by the increasing risk from cyberattacks associated with cloud migration and hybrid cloud implementations. In cloud environments, the leading cybersecurity risks include insecure interfaces and APIs, data breaches and data loss, unauthorised access, DDoS attacks, and a lack of a unified view of assets.
Protection requirements for securing hybrid multicloud environments are evolving rapidly. In addition to tightening up endpoint security, organisations must also place greater emphasis on cloud workload protection. Cloud security solutions need to offer a unified and consistent view across all physical machines, virtual machines, serverless workloads and containers, used by an organisation.
Amend Incident Response Plans
It is the containment of breaches that often determines the success of security policies and procedures. Basic cyber hygiene as well as changes to IT architecture, such as micro segmentation, play an essential role in breach containment. But incident response plans also need to be made relevant to the current pandemic scenario.
Employees and IT teams are now working in a completely different environment than envisaged by most incident response plans. Existing plans may now be obsolete. At the very least, they will need to be modified. Usually, incident response plans are designed to respond to threats when most employees are operating in a corporate environment. This clearly needs to change. Employees need to be trained in the updated plan and know how to reach support if they believe that a security breach has occurred in their remote location.
Critically, new alert and warning systems need to be established, which can be used by employees to warn of threats as well as to receive information on threats and best practices.
Organisations are struggling to keep the lights on. In this battle to remain operational, cybersecurity has been taking a back seat. This cannot last for long as the deluge of new vulnerabilities is creating easy pickings for attackers. Cyber hygiene, endpoint security, cloud security, security policies and incident response plans must be continually reviewed.
Click here to download the full report ?
















