The AI landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, moving from traditional predictive AI use cases towards Generative AI (GenAI). Currently, most GenAI use cases promise an improvement in employee productivity, without focusing on how to leverage this into new or additional revenue generating streams. This raises concerns about the long-term return on investment (ROI) if this is not adequately addressed.
The Rise of Generative AI Over Predictive AI
Traditionally, predictive AI has been integral to business strategies, leveraging data to forecast future outcomes with remarkable accuracy. Industries across the board have used predictive models for a range of applications, from demand forecasting in retail to fraud detection in finance. However, the tide is changing with the emergence of GenAI technologies. GenAI, capable of creating content, designing products, and even coding, holds the promise to revolutionise how businesses operate, innovate, and compete.
The appeal of GenAI lies in its versatility and creativity, offering solutions that go beyond the capabilities of predictive models. For example, in the area of content creation, GenAI can produce written content, images, and videos at scale, potentially transforming marketing, entertainment, and education sectors. However, the current enthusiasm for GenAI’s productivity enhancements overshadows a critical aspect of technology adoption: monetisation.
The Productivity Paradox
While the emphasis on productivity improvements through GenAI applications is undoubtedly beneficial, there is a notable gap in exploring use cases that directly contribute to creating new revenue streams. This productivity paradox – prioritising operational efficiency and cost reduction – may not guarantee the sustained growth and ROI necessary from AI investments.
True innovation in AI should not only aim at making existing processes more efficient but also at uncovering opportunities for monetisation. This involves leveraging GenAI to develop new products, services, or business models to access untapped markets or enhance customer value in ways that directly impact the bottom line.
The Imperative for Strategic Reorientation
Ignoring the monetisation aspect of GenAI applications poses a significant risk to the anticipated ROI from AI investments. As businesses allocate resources to AI adoption and integration, it’s also important to consider how these technologies can generate revenue, not just save costs. Without a clear path to monetisation, the investments in AI, particularly in the cutting-edge domain of GenAI, may not prove viable in the next financial year and beyond.
To mitigate this risk, companies need to adopt a dual approach. First, they must continue to explore and exploit the productivity gains offered by GenAI, which are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and achieving operational excellence. At the same time, businesses must strategically explore and invest in GenAI-driven opportunities for monetisation. This could mean innovating in product design, personalised customer experiences, or entirely new business models that were previously unfeasible.
Conclusion
The excitement around GenAI’s potential to transform industries is well-founded, but it must be tempered with strategic planning to ensure long-term viability and ROI. Businesses that recognise and act on the opportunity to not only improve productivity but also to monetise GenAI innovations will lead the next wave of growth in their respective sectors. The challenge lies in balancing the drive for efficiency with the pursuit of new revenue streams, ensuring that investments in AI deliver sustainable returns. As the AI landscape evolves, the ability to innovate in monetisation as much as in technology will distinguish the leaders from the followers.

The Retail industry has faced significant challenges in recent times. Retailers have had to deliver digital experiences and delivery models; navigate global supply chain disruptions; accommodate the remote work needs of their employees; and keep up with rapidly changing customer expectations. To remain competitive, many retailers have made significant investments in technology.
However, despite these investments, many retailers have struggled to create market differentiation. The need for innovation and constant evolution remains.
As retailers cope with hypersonalisation trends, supply chain vulnerabilities, and the rise of ESG consciousness, the industry is seeing several instances on innovation.
Read on to find out how brands such as Clinique, Gucci, Tommy Hilfiger, Nike, Woolworths, Prada, Levi Strauss, Mahsenei Hashuk and Instacart are using emerging technologies such as the Metaverse and Generative AI to create the much-needed market edge.
Download “The Future of Retail” as a PDF

Customer Experience teams are focused on creating a great omnichannel experience for their customers – allowing customers to choose their preferred channel or touchpoint. And many of these teams are aware of the challenges of omnichannel – often trying to prise the experience from one channel into another. Too often we create sub-optimal experiences, forcing customers to work harder for the outcome than if they were using other channels.
I know there have been times when I have found it easier to jump in the car and drive to a store or service centre, rather than filling in a convoluted online form or navigating a complex online buying process. I constantly crave larger screens as full web experiences are often better than mobile web experiences (although perhaps that is my ageing eyes!).
One of the factors that came out in a study conducted by Ecosystm and Sitecore is that customers don’t just want personalised experiences – they want optimised experiences. They want to have the right experience on the right device or touchpoint. It is not about the same experience everywhere – the focus should be on optimising experiences for each channel.
We call this “opti-channel”.
Use an Opti-Channel Strategy to Guide Investment and Effort
This is what you are probably doing already – but by accident. I suggest you formalise that strategy. Design customer experiences that are optimised for the right channel or touchpoint – and personalised for each customer. Stop forcing customers into sub-optimal experiences because you were told to make every customer experience an omnichannel one.
The move towards opti-channel accelerates your ability to provide the best experience for each customer, as you ask the important question “Does this channel suit this experience for this customer?” before the fact – not after the experience has been designed. It also eliminates the rework of existing experiences for new channels and provides clear guidance on the next-best action for each employee.

There Will be Conflict Between Opti-Channel and Personalisation
The challenge for opti-channel strategies will be to align them to your personalisation strategy. How will it work when you have analytics driving your personalisation strategy that say customer X wants a fully digital experience but your opti-channel strategy says part of the digital experience is sub-standard? And the answer to this lies in understanding the scope of your experience creation – are you trying to improve the existing experience or are you looking to create a new improved experience?
- If you are improving the existing experience, then you have less license to shift transactions and customer between channels – even if it is a better experience.
- If you are creating a new experience, you have the opportunity to start again with the overall experience and prove to customers that the new experience is actually a better one.
For example, when airlines moved away from in-person check-in to self-check-in kiosks, there was an initial uproar from customers who had not yet experienced it – claiming that it was less personal and less human. But the reality is that the airlines took the check-in screen that the agents were using and made it customer-facing. Travellers can now see the seats and configuration and select what is best for them.
This experience was reinvented again when the check-in moved to web and mobile. By turning the screen around to the customer, the experience actually felt more human and personal – not less. And by scattering agents around the screens and including a human check-in desk for the “exceptions”, the airlines could continue to optimise AND personalise the experience as required.
Opti-Channel Opens Many New Business Opportunities
Your end-state experience should consider what is the best channel or touchpoint for each step in a journey – then determine the logic or ability to shift channels. Pushing customers from a chatbot to web chat is easy. Moving from in-store to online might be harder, but there are currently some retailers looking to merge the in-store and digital experience – from endless aisle solutions to nearly 100% digital in-store. Some shoe and clothing stores offer digital foot and body scans in-store that help customers choose the right size when they shop online. And we are beginning to see the rollout of “magic mirrors” – such as one retailer who has installed them in fitting rooms and you can virtually try different colours of the same item without actually getting them off the shelf.
Businesses are trying to change customer behaviour – whether it is getting them into stores or mainly shopping online or encouraging them to call the contact centre or to even visit a service centre. Creating reasons for why that might be a better option, while also providing scaled-back omnichannel options is a great way to meet the needs of existing customers, create brand loyalty and attract new customers to your company or brand.

As economies around the world are beginning to recover from the recessions and slowdowns caused by the pandemic, we are beginning to witness, what I like to call, the “Great Bounce Forward”.
Why the Great Bounce Forward? Because too many businesses, journalists and economists are talking about businesses “bouncing back”. But there is no bounce back. We are bouncing into the “economic unknown”. The trading conditions we see today are nothing like what they were at the beginning of 2020. While many people refer to the “new normal” I have heard few talks about how they are or will benefit from these new market conditions.
Bouncing back may not be relevant as we negotiate the economic unknown – it is time to evaluate how we can bounce forward!
Leaping Ahead Through Digital First
Customer interactions have changed – digital-first is now a requirement – and many customers expect a personalised and optimised experience. Many companies are starting to personalise experiences today – thinking they are “delighting customers” through personalised transactions and journeys. But you don’t delight customers by giving them what they want – you disappoint them if you don’t offer a true personalised experience.
Digital changes are coming thick and fast. For example, Australia Post has announced that online sales are currently 20% higher than what they were at the previous highest peak in December 2020. Yes – much of Australia is in a lockdown, but online sales are dwarfing what they were during lockdowns in 2020.
But it is not just about offering online sales. In the digital world, customers now expect to be able to track packages, get alerts when they are delivered, and have access to easy and free returns. Again – if you don’t do this today, you are creating poor customer experiences and are most likely losing business to those that offer great experiences.
Here is what organisations are witnessing:
The need to evolve their CRM solution. Salespeople expect the CRM to give them insights on who to sell to, why to sell to them and what approach will work best. CRM systems that don’t provide this analysis are letting businesses and salespeople down.
Analytics has to be turned into actions. More businesses are telling their analytics partners to stop telling them what to do, and just do it! Automating the outcomes of BI and analytics is beginning to be expected.
Ease of use has become essential. Interactions and processes need to be intelligent and easy to automate. We no longer throw teams of people at challenges – we automate the outcomes and use technology to deliver entirely new experiences without teams of employees pulling strings behind the scenes.
Process and technology changes happen quickly and seamlessly. We have been taught this by Zoom, Microsoft, AWS and Google. If you aren’t doing this today, you are behind the market and behind the expectations of your employees and customers.
Ecosystems are emerging to enable this agility and innovation. We can now innovate with a growing range of partners. Companies can partner for a single sale and move on. Start-ups are being embraced by dinosaurs, and competitors are becoming partners. More companies than ever are involving their own customers in their innovation processes. Ecosystems are changing the ability of technology and business teams to offer new and improved services to customers and employees.

Time for a Shift in Organisational Culture
Seemingly, the world changed overnight. But many of these changes have been in the works for years. It just took a global crisis to highlight how important they are and how much organisations need to change to embrace these opportunities. The only thing holding businesses back from thriving in the Great Bounce Forward are their people and culture. If you can embrace these changes, your businesses will move forward and emerge as different companies to the ones that entered the pandemic in early 2020. You’ll be more open, agile, innovative and digitally aware. You’ll be able to move in new, unheralded directions, driving improved customer, shareholder, or citizen value.
So stop thinking about how your business will bounce back. Make plans for it to bounce forward into the unknown.

Back in 2019 – when life was simpler and customers only expected minor miracles from the brands they interacted with – personalisation of the customer experience (CX) was a “good idea but the time has not yet come” for the majority of marketing and CX professionals.
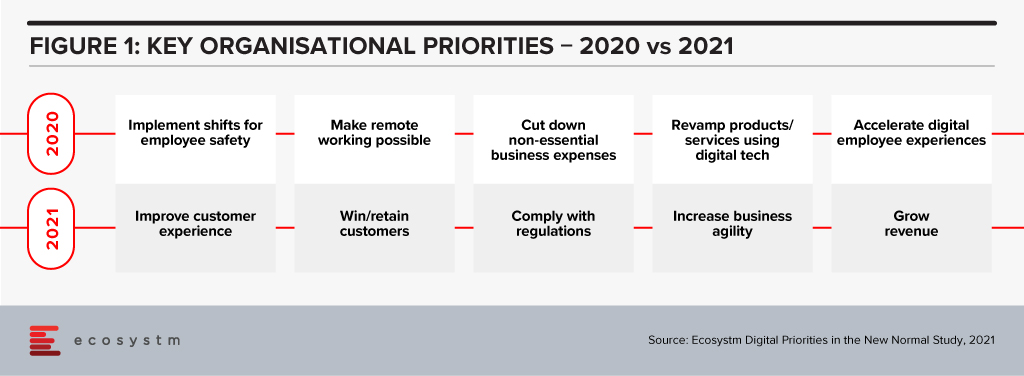
Fast forward 24 months and the world has changed – in more ways than we could have imagined! For a start, CX dropped off the top business priority during 2020 as businesses adapted to the changing market and employee experiences. But as some economies start to create a new sense of normal, CX has returned to the top of the list of business priorities (Figure 1) – renewing pressure on CX teams to create great experiences for customers.
In 2020 many marketing teams went back to the drawing board to create truly meaningful customer experiences. Suddenly “trust” was a core expectation of a brand, and that lens allowed marketers and CX teams to rethink what a personalised experience looks like. It is no longer about selling more products and creating more chances for commerce – it is now about creating an experience that makes brands easy to deal with. It is about understanding the customer and creating an optimised experience when they want or need to interact with the brand. A great personalised experience feels normal today – it has lost the “creepy” edge and is now about the brand giving customers the service, products, or levers that they need when and where they need them.
For some brands and customers, a personalised experience is about getting out of the way of customers and just giving them the outcome they desire. For others it is about creating a memorable journey. Some customers require that extra hand holding along the way and need to be nudged in the right direction, and just need to be left alone to make their decisions – not requiring that extra EDM, alert or message.
In some sectors – such as Banking and eCommerce – if you are not personalising your CX you are a long way behind, but in others, such as Government and Insurance, personalisation is only beginning to gain traction today, and will see slow and steady growth over the next few years.
Good Data is Key to a Great Personalisation Strategy
Lack of data is the primary reason personalisation fails and why some marketing teams have abandoned their personalisation efforts. The right data may not exist completely within your business – you may need to partner or work with ecosystem providers to create a complete view of your customers – and new restrictions around the use of cookies is making this harder to achieve. Forward thinking businesses have already forged partnerships with third parties and partners to share relevant data to help them create the personalised experience their customers demand.
Personalisation Should Apply Across the Customer Journey
A clear understanding of brand values, customer desires and ideal customer journeys is also important to ensure personalised experiences meet the needs of customers. Creating a personalised experience that deviates from brand values means that either brands don’t understand their customers, or customer experience professionals don’t understand their brands (or both!).
Personalisation needs to focus on the entire customer journey – from prospect through to customer and even through to churn. While you have significantly more data about your customers than your prospects, a personalised experience for non-customers is still possible and sets the scene for better and easier CX once your prospects take the longer journey with your brand. Creating a personalised churn experience – making the departure from your brand memorable, friendly and easy – provides the perfect springboard for return and tells your customers that you care about them through the entire journey.

Build a Proof of Concept for Personalisation
If you have not yet started personalising your customer’s experience, now is the perfect time to build a Proof of Concept (POC) demonstrating the business and customer outcomes you can achieve. This will help the CX and/or marketing teams to understand what data you need to collect from existing systems and processes – or source externally to create the desired experience. Initially your personalisation experience may target a limited number of key personas – but it should have the capability to roll out to all customers and/or prospects, eventually considering many scenarios and requirements. It should continue to learn and adapt. Too many businesses discovered during the pandemic that static personalisation programs will fail when market conditions change.
The POC can provide the data that your senior leadership will need to deepen their investments in and think of personalisation as a business capability – not a single project. They can demonstrate the ROI (or lack of return) and will help to guide the larger spend should the POC be a success.
Invest in Behavioural Science Skills
Building a successful personalisation strategy often goes beyond simply listening to the experts within the business and even listening to your customers. Often your customers don’t know what affects their behaviour – and will mis-report motivations or mis-attribute actions. It is important to understand the science behind behaviour – what is possible, what can work, what is guidance and what is coercion. These experts, along with your legal or privacy teams, can help to set up the guide rails for the personalisation program to operate within, and help you create customer journeys where customers can achieve their desired outcomes.
Target Consent as a Key Customer KPI
Consent is a key enabler of deep personalisation capabilities. While some level of personalisation without formal consent can be created, the real benefits of personalised journeys come with consent to use customer data to offer better services. Many businesses ask for consent in the sign-up process, but often it feels like wishful thinking – not a serious attempt to offer a better customer experience. Businesses that make “Consent to Use Data” a CX KPI think more broadly of the customer journey, the brand promise and what that means to levels of consent. It isn’t a “tick-a-box” activity at sign-up – it considers what the customer wants to get out of the engagement or a longer relationship. It focuses on helping customers achieve their instant goals more effectively and the benefits the data can bring to nurture a longer-term relationship.
Businesses that seek a higher level of consent use more tangible outcomes, simpler language and no “sweeping statements” in their consent request. They are explicit how they will use data and what data they will use. Sometimes they don’t even ask for consent to use data at sign-up – they ask after they have formed a relationship and the customer has developed a level of trust in the brand or company.
Start Your Personalisation Journey Today
Your competitors are already thinking about personalisation – some have even implemented personalised elements within their existing or new customer journeys. Personalisation – while easier than ever – is still a significant capability to build within your business. You are likely to need new technology tools and/or platforms, new skills, and new budgets. The impact for your customers – and therefore for your business – can be significant. And the impact of no action can potentially be damaging. Start your personalisation journey today to help your business take the next step towards becoming a customer-obsessed, agile, and digital business.

The past twelve months have been tough. Most businesses in Singapore (68%) still haven’t seen revenue recover to pre-pandemic levels. Many budgets are down and you are likely to have a long list of spending options that might help you grow revenue and pull your business out of the pandemic-induced slump. Even if your business is doing well, the pressure on budgets is real.
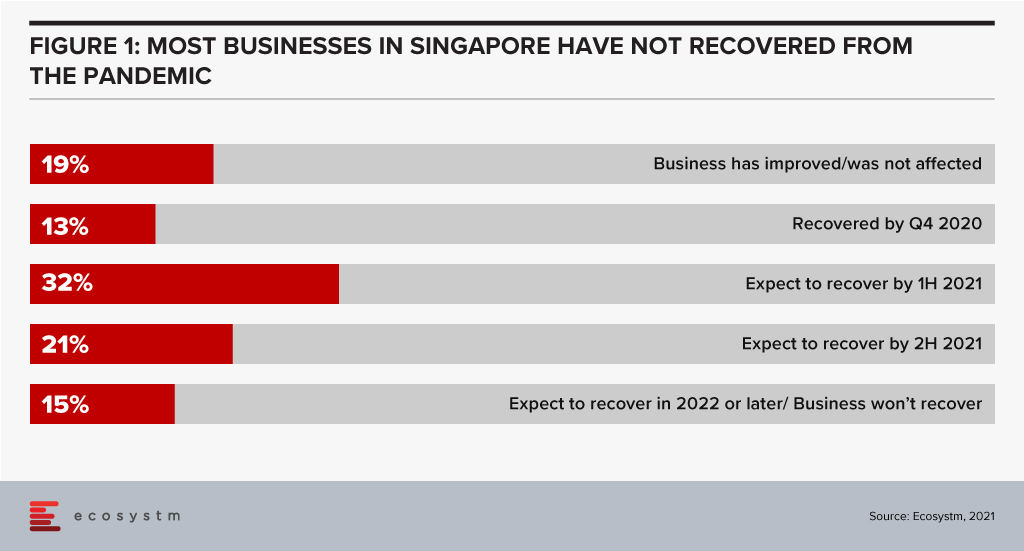
Increasing your CX Spend
Despite the pressure on budgets Ecosystm data makes a strong case to not cut your customer experience (CX) spend! Businesses in Singapore that are cutting their CX spend are less likely to return to growth, more likely to be competing on price (hence cutting margins), not focused on their digital and omnichannel customers, and have lower levels of innovation. Funnily enough, these are also the businesses with complex, legacy systems which need more focus to provide an improved CX! To be quite frank, businesses in Singapore who are cutting CX spend are setting themselves up for failure. With other businesses increasing CX spend, the gap between the customer experiences will grow to a point where customers will leave and it will be hard to catch up.
Prioritising your CX Spend
So now that you have secured your CX spend, where will you get the biggest bang for your buck? Let’s look at where businesses in Singapore are focusing their CX initiatives in 2021.
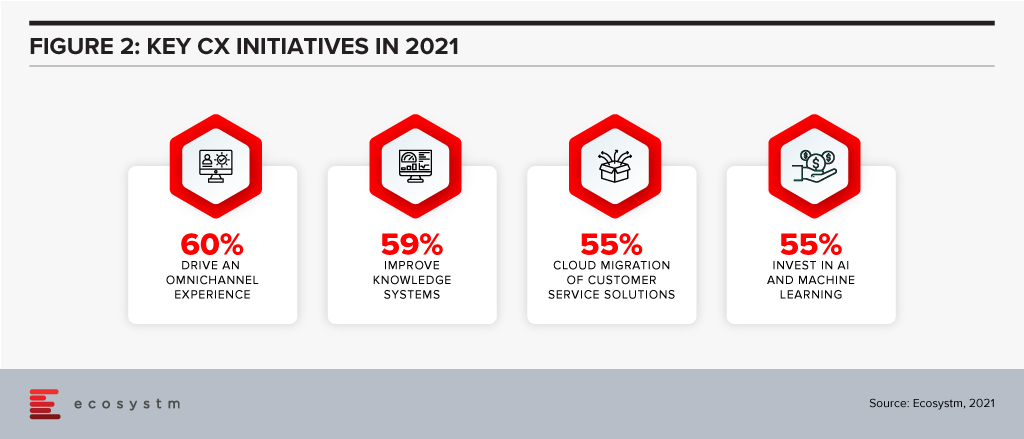
Offering an omnichannel experience. Your customers expect more than just a great digital experience – they want the right experience at the right touchpoint. The CX leaders in Singapore (who, unsurprisingly are often the market leaders) are already offering great omnichannel experiences, so this is quickly becoming about catching up – and not about getting ahead. Providing a consistent, personalised, and optimised experience across your digital touchpoints needs to be a top priority for your business today. If you are not offering conversational commerce solutions, start that strategy as soon as possible – you need to be where your customers are today. Extending this to physical channels and broader ecosystem partners should also be on your agenda.
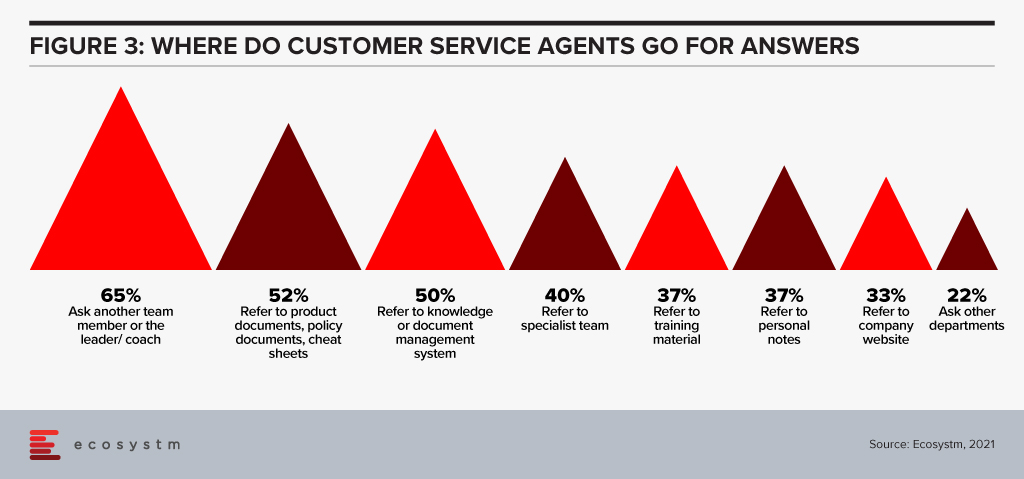
Improving knowledge systems. Your knowledge systems don’t do what they say on the box. They don’t provide answers to questions – for employees or customers. In fact, if your customer service agents get asked a question they don’t know the answer to, their number one source for answers is actually their colleagues or team leaders – NOT the knowledge management system! Start investing in systems – or ideally a single system – that help your employees get better, faster answers to questions. Make sure that the system is providing the same answers to both your employees and your customers across all touchpoints – physical and digital.
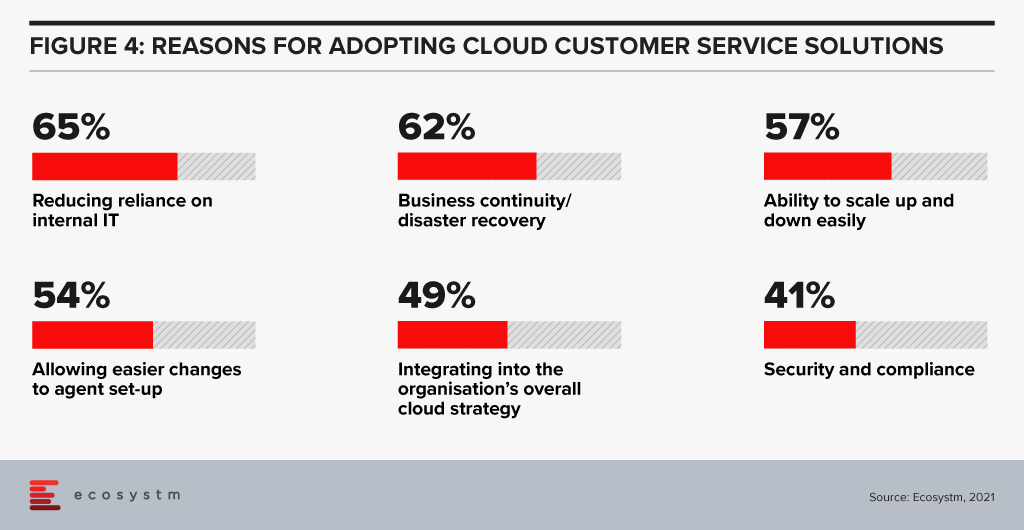
Migrating customer service platforms to the cloud. Over half the businesses in Singapore that we assessed have this as a top CX priority. Cloud solutions offer faster time to value, lower management costs, give access to more regular improvements and often provide the ability to easily integrate with partners who offer product extensions and customisations. This trend will continue in 2021 and 2022 as more businesses realise that their legacy customer service or contact centre platform is inhibiting their ability to innovate their customer experience. These systems also help businesses to stay compliant and reduce the reliance on internal IT – which has traditionally struggled to keep up with the fast-changing nature of the contact centre and customer service teams.
Investing in AI and machine learning. Many businesses are using AI to provide the personalised and optimised customer experiences they aspire to. AI and machine learning are allowing businesses to create personalised offers, offer a next-best action and automate services. Advanced banks in Singapore can create interest rate offers for each individual customer based on their credit profile and history. 46% of businesses in Singapore are already using AI to offer recommendations for customer service agents, 44% to optimise or test messaging and campaigns and 43% to provide faster, more accurate access to information and knowledge. 18 months ago, AI was a business differentiator – allowing your business to create a stand-out CX. Today AI is quickly becoming a standard practice – the battle now is around using AI to create personalised and optimised experiences.
A great customer experience will be the most important factor in lifting your business to pre-pandemic growth levels and helping your business remain competitive in today’s tough business conditions. When it comes to CX, there is no such thing as “saving your way to growth”.
Your opportunity to drive greater business success lies in your ability to better win, serve and retain your customers. Refresh your customer strategy and capability today to make 2021 an exceptional year for your business.

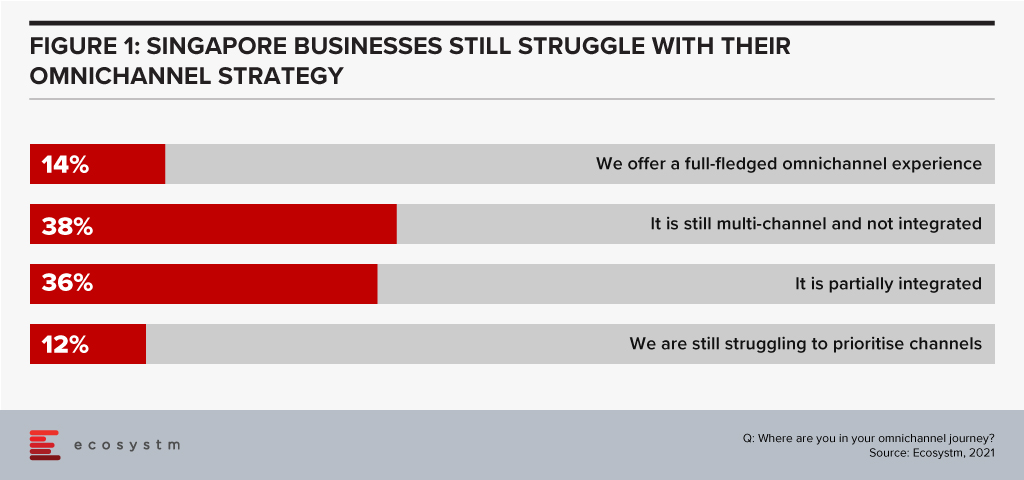
Customer needs are changing. Quickly. In 2020 having a great digital strategy went from being a nice-to-have to an absolute necessity. And in 2021, businesses that have great omnichannel experiences will go from a small minority to a majority as customers demand that they are served on their terms in their chosen platform. Only 14% of businesses in Singapore offer a complete omnichannel experience today – serving customers on their terms regardless of the location or platform (Figure 1). These businesses are setting the benchmark that the rest of the market needs to meet soon.
The Growing Importance of Social Media in Delivering Customer Experience
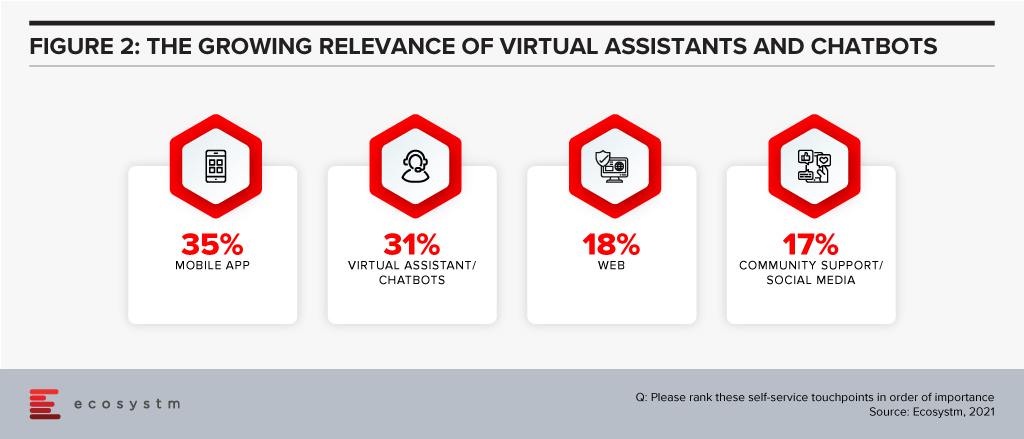
Chat and messaging are quickly becoming the normal way to interact with businesses – the view of a few years ago that “no one wants to chat with a bot” has quickly turned around. Now virtual assistants and chatbots are the second most important self-service channel for businesses in Singapore (Figure 2).
In fact, Zendesk’s global study shows that most customers (45%) use embedded messaging over social messaging apps (31%) and text/SMS (20%). That might be great for self-service, but for commerce, boundless opportunities exist to move to where the customer lives, communicates, and socialises today.
Smart businesses understand that customers spend their lives in other chat and social media platforms – such as Facebook Messenger, TikTok, Instagram, WeChat, Discord and WhatsApp. More customers expect to be served in these channels; they expect to be able to transact with their brands of choice. Why should they go to a mobile banking app to find their balance? Why can’t they get it in WhatsApp? They are often learning about the next Jordan or Yeezy shoe drop from their social network in Messenger – so why not transact with them there? Consider all your own personal WhatsApp, Messenger and other messaging platform groups discussing social activities, sporting teams, school activities or the latest fashion – these are ALL opportunities for commerce (Figure 3).

And there are use cases now. Airlines – such as KLM and Etihad Airways – are engaging customers on WeChat, Kakao Talk, and WhatsApp, helping them reschedule flights and answering customer service queries. Telecommunications providers are allowing customers to raise issues on messaging platforms – and are also using them to upsell and cross-sell new services. Transportation providers are making it easier to find a car or the the next scheduled bus right there in the messaging platforms. Retailers – such as 1-800 Flowers and Culture Kings – are not only serving customers but finding new customers on these messaging platforms.
Going beyond the messaging platforms, businesses are also looking to serve customers on their smart devices – such as Amazon Alexa/Echo and Google Nest/Home devices. Alerting customers to order updates, shipping details and product promotions is becoming standard practice for leading businesses. Digitally-savvy banks are allowing customers to not only track their balance but also make transfers and payments using these smart platforms.
Customers are more comfortable with these conversational commerce options – and they actually expect you to offer such services on your site, in your app, on their smart devices, and on their messaging platforms of choice. Your ability to provide outstanding customer experiences will not only be your ticket back to revenue growth but the recipe for long term business success. Meeting customer needs on their terms is a good place to start.
Delivering a Personalised Conversational Customer Experience
Customer experience (CX) decision-makers will have to rethink how they approach building richer CX capabilities to deliver personalised conversational interactions with customers.
Messaging should become part of a wider AI, Data, and Mobile strategy. Contact centre teams might feel that this is too ambitious a project and would prefer to continue to serve customers through the more traditional channels only. So, it is important to identify the key stakeholder/s who will drive the initiative. And the contact centre team should work with the Digital, Innovation and Marketing teams.
Designing the mobile experience and in app messaging for CX should have some of the following features:
- Ability to click a button to request for a service or escalate an issue that will, in turn, result in the company contacting the customer either by messaging or calling.
- Giving customers the option to contact through popular messaging platforms such as Facebook Messenger, WhatsApp, LINE, WeChat, and others. Unifying these systems in a single interface that integrates with your customer service application is best practice.
- Having one single interface to manage and make payments – within the app itself or on the social messaging platform. Conversational commerce is about creating an ongoing relationship with customers throughout the entire customer journey. Don’t just focus on the sale or the post-sales experience – customers expect to be able to interact with your business from their platform of choice regardless of their need or stage in the customer journey.
- Embed deep analytics into the communication services to help the organisation better deliver a personalised CX.
- Ensure you have a solid, unified knowledge management interface at the backend so that all questions lead to the same answers regardless of channel, platform or touchpoint.
Your opportunity to drive greater business success lies in your ability to better win, serve and retain your customers. Refresh your customer strategy and capability today to make 2021 an exceptional year for your business.




















