For many organisations migrating to cloud, the opportunity to run workloads from energy-efficient cloud data centres is a significant advantage. However, carbon emissions can vary from one country to another and if left unmonitored, will gradually increase over time as cloud use grows. This issue will become increasingly important as we move into the era of compute-intensive AI and the burden of cloud on natural resources will shift further into the spotlight.
The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates that data centres are responsible for up to 1.5% of global electricity use and 1% of GHG emissions. Cloud providers have recognised this and are committed to change. Between 2025 and 2030, all hyperscalers – AWS, Azure, Google, and Oracle included – expect to power their global cloud operations entirely with renewable sources.
Chasing the Sun
Cloud providers are shifting their sights from simply matching electricity use with renewable power purchase agreements (PPA) to the more ambitious goal of operating 24/7 on carbon-free sources. A defining characteristic of renewables though is intermittency, with production levels fluctuating based on the availability of sunlight and wind. Leading cloud providers are using AI to dynamically distribute compute workloads throughout the day to regions with lower carbon intensity. Workloads that are processed with solar power during daylight can be shifted to nearby regions with abundant wind energy at night.
Addressing Water Scarcity
Many of the largest cloud data centres are situated in sunny locations to take advantage of solar power and proximity to population centres. Unfortunately, this often means that they are also in areas where water is scarce. While liquid-cooled facilities are energy efficient, local communities are concerned on the strain on water sources. Data centre operators are now committing to reduce consumption and restore water supplies. Simple measures, such as expanding humidity (below 20% RH) and temperature tolerances (above 30°C) in server rooms have helped companies like Meta to cut wastage. Similarly, Google has increased their reliance on non-potable sources, such as grey water and sea water.
From Waste to Worth
Data centre operators have identified innovative ways to reuse the excess heat generated by their computing equipment. Some have used it to heat adjacent swimming pools while others have warmed rooms that house vertical farms. Although these initiatives currently have little impact on the environmental impact of cloud, they suggest a future where waste is significantly reduced.
Greening the Grid
The giant facilities that cloud providers use to house their computing infrastructure are also set to change. Building materials and construction account for an astonishing 11% of global carbon emissions. The use of recycled materials in concrete and investing in greener methods of manufacturing steel are approaches the construction industry are attempting to lessen their impact. Smaller data centres have been 3D printed to accelerate construction and use recyclable printing concrete. While this approach may not be suitable for hyperscale facilities, it holds potential for smaller edge locations.
Rethinking Hardware Management
Cloud providers rely on their scale to provide fast, resilient, and cost-effective computing. In many cases, simply replacing malfunctioning or obsolete equipment would achieve these goals better than performing maintenance. However, the relentless growth of e-waste is putting pressure on cloud providers to participate in the circular economy. Microsoft, for example, has launched three Circular Centres to repurpose cloud equipment. During the pilot of their Amsterdam centre, it achieved 83% reuse and 17% recycling of critical parts. The lifecycle of equipment in the cloud is largely hidden but environmentally conscious users will start demanding greater transparency.
Recommendations
Organisations should be aware of their cloud-derived scope 3 emissions and consider broader environmental issues around water use and recycling. Here are the steps that can be taken immediately:
- Monitor GreenOps. Cloud providers are adding GreenOps tools, such as the AWS Customer Carbon Footprint Tool, to help organisations measure the environmental impact of their cloud operations. Understanding the relationship between cloud use and emissions is the first step towards sustainable cloud operations.
- Adopt Cloud FinOps for Quick ROI. Eliminating wasted cloud resources not only cuts costs but also reduces electricity-related emissions. Tools such as CloudVerse provide visibility into cloud spend, identifies unused instances, and helps to optimise cloud operations.
- Take a Holistic View. Cloud providers are being forced to improve transparency and reduce their environmental impact by their biggest customers. Getting educated on the actions that cloud partners are taking to minimise emissions, water use, and waste to landfill is crucial. In most cases, dedicated cloud providers should reduce waste rather than offset it.
- Enable Remote Workforce. Cloud-enabled security and networking solutions, such as SASE, allow employees to work securely from remote locations and reduce their transportation emissions. With a SASE deployed in the cloud, routine management tasks can be performed by IT remotely rather than at the branch, further reducing transportation emissions.

Ecosystm research reveals a stark reality: 75% of technology leaders in Financial Services anticipate data breaches.
Given the sector’s regulatory environment, data breaches carry substantial financial implications, emphasising the critical importance of giving precedence to cybersecurity. This is compelling a fresh cyber strategy focused on early threat detection and reduction of attack impact.
Read on to find out how tech leaders are building a culture of cyber-resilience, re-evaluating their cyber policies, and adopting technologies that keep them one step ahead of their adversaries.
Download ‘Cyber-Resilience in Finance: People, Policy & Technology’ as a PDF

It seems for many employees, the benefits of working from home or even adopting a hybrid model are a thing of the past. Employees are returning to the grind of long commutes and losing hours in transit. What is driving this shift in sentiment? CEOs, who once rooted for remote work, have undergone a change of heart – many say that remote work hampers their ability to innovate.
That may not be the real reason, however. There is a good chance that the CEO and/or other managers feel they have lost control or visibility over their employees. Returning to a more traditional management approach, where everyone is within direct sight, might seem like a simpler solution.
The Myths of Workplace Innovation
I find it ironic that organisations say they want employees to come into the office because they cannot innovate at the same rate. What the last few years have demonstrated – and quite conclusively – is that employees can innovate wherever they are, if they are driven to it and have the right tools. So, organisations need to evaluate whether they have innovated on and evolved their hybrid and remote work solutions effectively, to continue to support hybrid work – and innovation.
What is confusing about this stance that many organisations are taking, is that when an organisation has multiple offices, they are effectively a hybrid business – they have had people working from different locations, but have never felt the need to get all their staff together for 3-5 days every week for organisation-wide innovation that is suddenly so important today.
The CEO of a tech research firm once said – the office used to be considered the place to get together to use the tools we need to innovate; but the reality is that the office is just one of the tools that businesses have, to drive their organisation forward. Ironically, this same CEO has recently called everyone back into the office 3 days a week!
Is Remote Work the Next Step in Employee Rights?
It has become clear that remote and hybrid work is the next step in employees getting greater rights. Many organisations fought against the five-day work weeks, claiming they wouldn’t make as much money as they did when employees worked whenever they were told. They fought against the 40-hour work week (in France some fought against the 35-hour work week!) They fight against the introduction of new public holidays, against increases to the minimum wages, against paid parental leave.
Some industries, companies, unions, and countries are looking to (or already have) formalised hybrid and remote work in their policies and regulations. More unions and businesses will do this – and employees will have choice.
People will have the option to work for an employer who wants their employees to come into the office – or work for someone else. And this will depend on preferences and working styles – some employees enjoy the time spent away from home and like the social nature of office environments. But many also like the extra time, money, and flexibility that remote work allows.
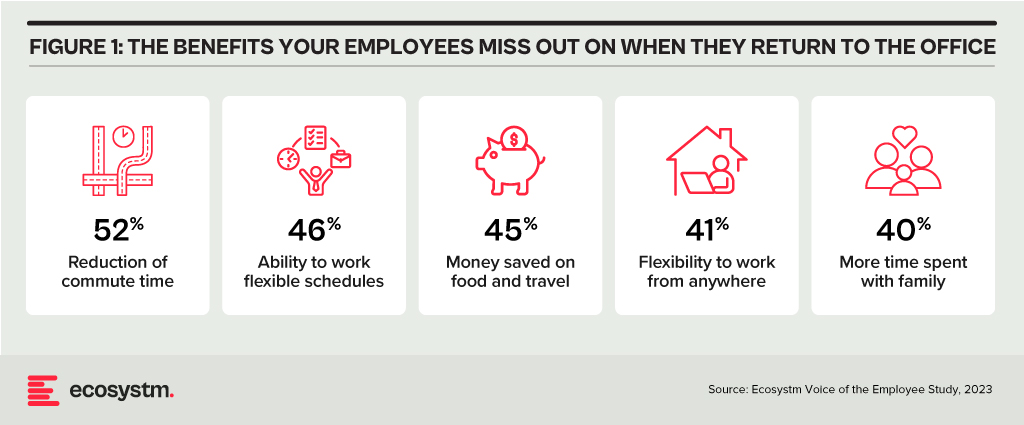
There might be many reasons why leadership teams would want employees to come into the office – and establishing and maintaining a common corporate culture would be a leading reason. But what they need to do is stop pretending it is about “innovation”. Innovation is possible while working remotely, as it is when working from separate offices or even different floors within the same building.
Evolving Employee Experience & Collaboration Needs
Organisations today face a challenge – and it is not the inability to innovate in a hybrid work environment! It is in their ability to deliver the employee experience that their employees want. This is more challenging now because there are more preferences, options, and technologies available. But it is established that organisations need to continue to evolve their employee experience.
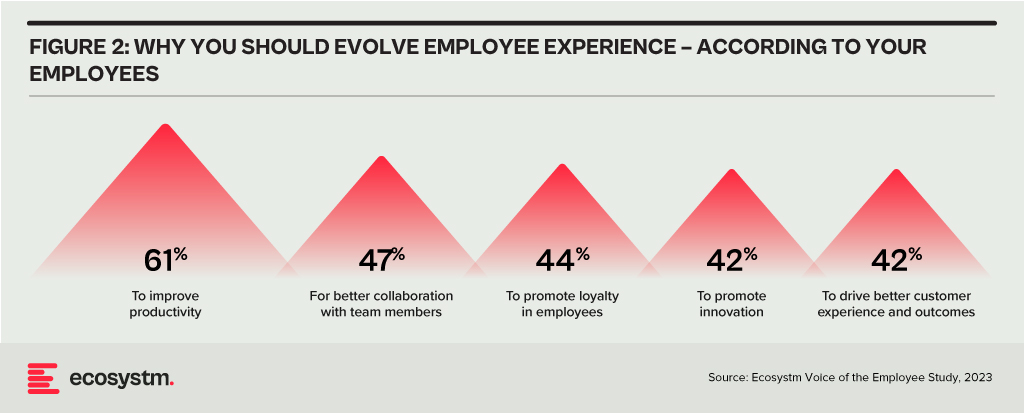
Technology does and will continue to play an important role in keeping our employees connected and productive. AI – such as Microsoft Copilot – will continue to improve our productivity. But the management needs to evolve with the technology. If the senior management feels that connecting people will help to solve the current growth challenges in the business, then it becomes the role of managers to better connect people – not just teams in offices, but virtual teams across the entire organisation.
Organisations that have focused their energies on connecting their employees better, regardless of their location (such as REA in Australia), find that productivity and innovation rates are better than when people are physically together. What do they do differently?
- Managers find their roles have moved from supporting individual employees to connecting employees
- Documentation of progress and challenges means that everyone knows where to focus their energies
- Managed virtual (and in-person) meetings mean that everyone has a voice and gets to contribute (not the loudest, most talkative or most senior person)
Remote and hybrid workers are often well-positioned to come up with new and innovative ideas. Senior management can encourage innovation and risk-taking by creating a safe environment for employees to share their ideas and by providing them with the resources they need to develop and implement their ideas. Sometimes these resources are in an office – but they don’t have to be. Manufacturers are quickly moving to complete digital development, prototyping, and testing of their new and improved products and services. Digital is often faster, better, and more innovative than physical – but employees need to be allowed to embrace these new platforms and tools to drive better organisational and customer outcomes.
What the pandemic has taught us is that people are good at solving problems; they are good at innovating irrespective of whether their managers are watching or not.

The way we work in Australia and New Zealand (ANZ) is changing. In 2020 “work” went from a place you go to something you do.
Through the many restrictions in 2020 and 2021, knowledge workers in ANZ changed their work behaviours and employers changed their expectations of their employees. Tighter border controls and fast economic recoveries have swung the pendulum in the favour of employees, and “The Great Resignation” has started to play out across the region.
The Ecosystm Voice of the Employee Study aims to explore the emerging global Future of Work trends from an employee’s point-of-view. In an environment of uncertainty, this study is designed to be an ongoing, dynamic study that will be able to track the major shifts in preferences, perceptions, and practices through 2022.
Here are some insights from the study that can help businesses in ANZ develop strategies and capabilities to better serve their remote and office-based employees.
- The Great Resignation has begun in ANZ
- Women are more likely to work entirely from home
- Those working entirely from home are more likely to change jobs/careers in 2022
- Knowledge workers in ANZ are enjoying the Work from Home model
- Employees are looking for more flexibility and choice
Read on to find out more.

The first impact of the pandemic and the disruption it caused, was organisations scrambling to empower their remote employees. Over the last 2 years, significant investments have been made on collaboration platforms and tools. Now organisations are having to work towards making these workplaces truly hybrid where organisations have to ensure that all employees get the same experience, irrespective of where they choose to work from.
In 2022, organisations will continue to invest in building the Digital Workplace and address the associated technology, people, and process challenges.
Read on to find out what Ecosystm Analysts, Audrey William, Tim Sheedy and Venu Reddy think will be the key trends for the Digital Workplace in 2022.
Click here to download Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Trends for the Digital Workplace in 2022 as PDF

Cisco has recently announced their intention to acquire Socio Labs, a US-based event technology platform – the latest in a series of acquisitions. Cisco’s Webex Events provides meeting, webinar and webcast capabilities, including polling, Q&A, chat and real-time translation. This acquisition will allow Webex Events to cater to large-scale, hybrid events and conferences. Solution capabilities will include live streaming, sponsorship, networking, and advanced analytics – including for pre-event and post-event activities.
Collaboration Platforms are Here to Stay
2020 was the year video conferencing and collaboration finally became mainstream. With the exponential rise of remote and hybrid working, the investments in collaboration technologies has increased – and Ecosystm research shows that the trend is continuing well into 2021.
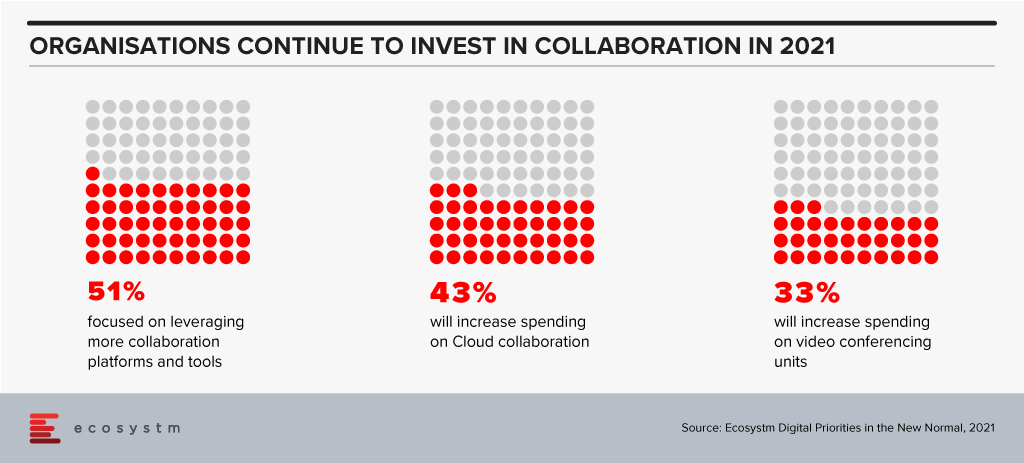

The other aspect that has been impacted by the pandemic is the Events business. With social distancing regulations, Events and Marketing teams are being challenged in their outreach and go-to-market initiatives. Even when countries allow in-person events, it is becoming increasingly difficult to get people to attend events. With most organisations allowing remote working many attendees are away from the CBD/ commercial areas and are reluctant to commute to attend events. This has seen the rise of a hybrid event model that caters to both in-person and virtual attendees.
While some countries are beginning to bring back in-person events, they will remain largely virtual. Event organisers will have to cater for those who are happy to attend in-person and those who want to access the event virtually. Providing a better experience for hybrid events, will require richer features using video and collaboration platforms to allow live streaming, chat, feedback, analytics – to gauge audience engagement – polling and other interesting ways to retain audience attention. Additionally, it will be important for these platforms to facilitate sponsorship, registrations and even ticketing capabilities directly from within the platform. These new dimensions to step up engagements for both virtual and in-person events have become necessary for the world we are living in.
Cisco Strengthening Collaboration Capabilities
Cisco is enhancing the virtual/hybrid meeting and events experience they provide and this has been evident from their recent acquisitions. They clearly see the need to enhance audience participation and engagement from pure static video and collaboration environments. Socio Labs’ business accelerated during the pandemic and they built a platform that offers a deeper engagement with the audience. Their customers include Google, Microsoft, PepsiCo and Hyundai.
Last year Cisco acquired BabbleLabs, a noise removal technology provider and the product has been integrated into their Webex platform, to improve the audio experience. Earlier this month Cisco also completed their acquisition of Slido. This means that Webex users can now leverage Slido’s capability of gathering real-time audience feedback, rather than just asking questions via text or chat. The solution can also enhance the learning experience during team training sessions and offers built-in analytics to gauge audience participation and where the gaps are. These acquisitions are an indication that Cisco is serious about their market presence in the video and collaboration space – and is keen on making a mark in the Events market.

Last week AT&T announced a partnership with Fortinet to expand their managed security services portfolio. This partnership provides global managed Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) solutions at scale. The solution uses Fortinet’s SASE stack which unifies software-defined wide-area network (SD-WAN) and network security capabilities into AT&T managed cybersecurity framework. Additionally, AT&T SASE and Fortinet will integrate with AT&T Alien Labs Threat Intelligence platform, a threat intelligence unit to enhance detection and response. AT&T has plans to update its managed SASE service during the year and will continue to bring more options.
Talking about the AT&T-Fortinet partnership, Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Ashok Kumar says, “This move continues the trend of the convergence of networking and security solutions. AT&T is positioning themselves well with their integrated offer of network and security services to address the needs of global enterprises.”
Convergence of Network & Security
AT&T’s improved global managed security service includes features such as secure web gateway, firewall-as-a service, cloud access security broker (CASB) and zero-trust access, which provides security teams and analysts with unified capabilities across the cloud, networks and endpoints. The solution aims to enable enterprises to create a more resilient network bringing the core capabilities of the two companies that will reduce operational costs and deliver a unified offering.
Last year AT&T also partnered with Cisco to expand its SD-WAN solution and to support AT&T Managed Services using Cisco’s vManage controller through a single management interface. Over the past years multiple vendors including Fortinet have developed comprehensive SASE solution capabilities through partnerships or acquisitions to provide a unified offering. Last year Fortinet acquired Opaq, a SASE cloud provider to bolster their security capabilities through OPAQ’s patented Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) cloud solution and to strengthen SD-WAN, security and edge package.
The Push Towards Flexible Networking
Kumar says, “The pandemic has created a higher demand and value for secure networking services. Enterprises experienced greater number of phishing and malware attacks last year with the sudden increase in work-from-home users. The big question enterprises need to ask themselves is whether legacy networks can support their evolving business priorities.”
“As global economies look to recover, securing remote users working from anywhere, with full mobility, will be a high priority for all enterprises. Enterprises need to evaluate mobile SASE services that provide frictionless identity management with seamless user experiences, and be compatible with the growing adoption of 5G services in 2021 and beyond.”
The Top 5 Telecommunications & Mobility Trends that will dominate the telecom industry to watch out for in 2021. Signup for Free to download the report.

BetterUp, a mobile-based professional learning and wellness platform that connects employees with career experts recently raised USD 125 million Series D funding backed by Salesforce Ventures, in partnership with ICONIQ Capital, Lightspeed Venture Partners, Threshold Ventures, and Sapphire Ventures among others, bringing the company’s valuation to USD 1.73 billion. Previously in 2012, the company had raised USD 43 million in venture capital funding with an additional Series B funding of USD 30 million in March 2018. The BetterUp platform combines behavioural science, AI, and human interaction to enhance employees’ personal and professional well-being. Recently, the company also revealed two new products – Identify AI, to help organisations determine the right people to invest in and the appropriate coaching needed through the use of AI; and Coaching Cloud for customised training for frontline, professional, and executive employees.
This announcement comes on the back of several wins for BetterUp. To boost employee performance and organisational growth NASA and the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) partnered with BetterUp to support new ways of coaching and preparing a workforce for change. The world’s largest brewer, AB InBev has partnered with BetterUp to strengthen diversity and inclusion through BetterUp’s coaching platform.
The Need to Improve Employee Experience
The pandemic changed the working arrangement of millions of employees and industries across the globe who are now working remotely or in a hybrid environment.
Ecosystm Principal Advisor, Audrey William says, “Driving better employee experience (EX) should take centre stage this year with enterprises putting employees at the centre of all initiatives. We will see EX platforms get integrated further and deeper into workplace collaboration and HR applications. In the last 12 months, we have seen apps monitoring wellness and sleep, training and coaching, meditation, employee motivation, and so on sit within larger collaboration platforms such as Slack, Zoom, Microsoft, Cisco and others.”
While the primary focus has been on optimising the work environment, it is time for organisations to start focusing on employee well-being. Ecosystm research shows that organisations implemented several measures to empower a remote workforce last year when the pandemic hit. But there was not enough focus on employee well-being (Figure 1).
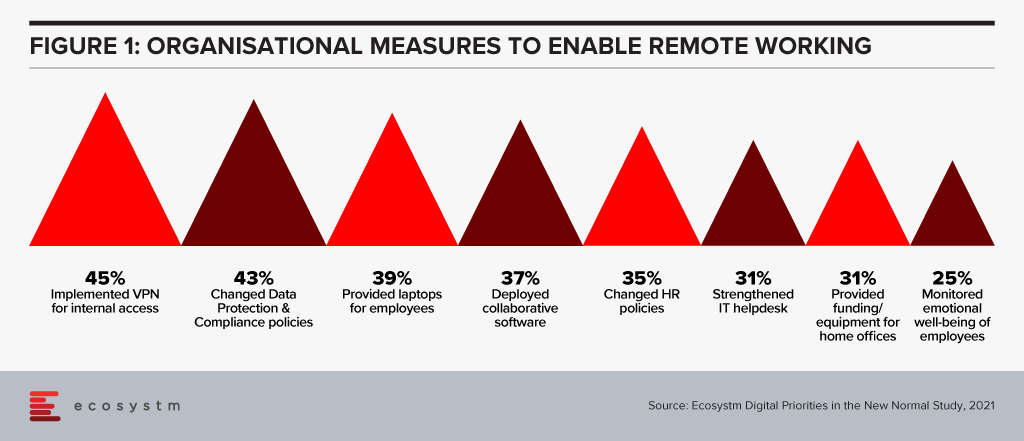
William says, “A hybrid work environment may have negative impact on your employees. You may face issues such as longer working hours, employee burnout, lesser social engagements and connection, loneliness – and mental and emotional issues and depression”.
“Organisations that place an emphasis on the employees will see their revenues grow and also see less attrition. The more you invest in your people, the more you will get back in return. It is as simple as that! You can see that now in some organisations where employees are being given more flexibility, employers are not dictating how they should work, diversity and inclusion efforts have become mainstream, and efforts are being made to make employees feel like they belong.”
William adds, “However, Ecosystm research finds that organisations have gone back to putting customers and business growth first – losing focus on their employees. Only 27% of organisations globally say that they have improving employee experience as a key business priority in 2021. It is time for this culture and mindset to change. And solutions such as BetterUp can make a difference.”
Transform and be better prepared for future disruption, and the ever-changing competitive environment and customer, employee or partner demands in 2021. Download Ecosystm Predicts: The top 5 Future of Work Trends For 2021.

In 2009 one of the foremost Financial Services industry experts was giving my team a deep dive into the Global Financial Crisis (GFS) and its ramifications. According to him, one of the key reasons why it happened was that most people in key positions in both industry and government had probably never seen a full downturn in their careers. There was a bit of a hiccup during the dot com bust but nothing that seriously interrupted the long boom that began somewhere in 1988. They had never experienced anything quite like 2008; so they never imagined that such a crisis could actually happen.
Similarly, 2020 was an unprecedented year – in our lives and certainly for the tech industry. The GFC (as the name suggests) was a financial crisis. A lot of people lost their jobs, but after the bailouts things went largely back to normal. COVID-19 is something different altogether – the impact will be felt for years and we don’t yet know the full implications of the crisis.
While we would like to start 2021 with a clean slate and never talk about the pandemic again, the reality is that COVID-19 will shape what we will see this year. In the first place it looks like the disease will still be around for a substantial part of the year. Secondly, all the changes it has brought in 2020 with entire workforces suddenly moving to operating from home will have profound implications for technology and customer experience this year.
As we ease into 2021, I look at some of the organisational and technology trends that are likely to impact customer experience (CX) in 2021.
#1 All Business is Now eBusiness
COVID-19 has ensured that the few businesses which did not have an online presence became acutely aware that they needed one. It created a need for many businesses to quickly initiate eCommerce. Forbes reported a 77% increase in eCommerce infrastructure spending YoY. This represents about 4 years of growth squeezed into the first 6 months of 2020!
From a CX point of view there is going to be far more interaction with brands and products through online channels. This is not just about eCommerce and buying from a portal. It is also about using tools like Instagram, Facebook and other social media platforms more widely. It is about learning to interact with the customer in multiple ways and touching their journeys at multiple points, all virtually using the web – mostly the mobile web.
Ecosystm research shows that almost three out of four companies have decided on accelerating or modifying the digitalisation they were undergoing (Figure 1). It is fair to expect that this gives a further boost to moving to the cloud. For the customer it will mean being able to access information in many new ways and connect with products, services, brands at multiple points on the web.
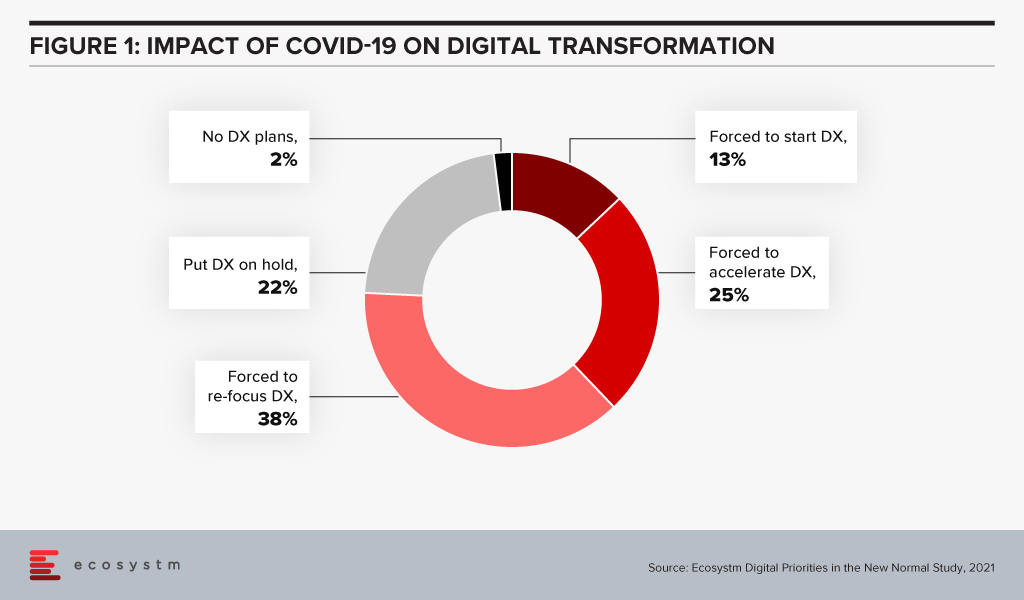
Since interacting with the customer at multiple points is new for most services, I foresee a lot of missed opportunities as companies learn to navigate a completely different landscape. Customers pampered by digitally native organisations often react harshly to even a small mistake. It will become critical for companies to not just become a bigger presence online but also to manage their customers well.
New solutions such as Customer Data Platforms (CDP), as opposed to CRM will become common. Players who are into Customer Experience management are likely to see huge business growth and new players will rapidly enter this space. They will promise to affordably manage CX across the globe, leveraging the cloud.
#2 Virtual Merges with Real
Virtual and Augmented Reality are not new. They have been around for a while. This will now cross the early adoption stage and is likely to proliferate in terms of use cases and importance.
AR/VR has so far been seen mainly in games where one wears an unwieldy – though ever-improving – headset to transport oneself into a 3D virtual world. Or in certain industrial applications e.g., using a mobile device to look at some machinery; the device captures what the eye can see while providing graphical overlays with information. In 2021 I expect to see almost all industrial applications adopting some form of this technology. This will have an impact on how products are serviced and repaired.
For the mainstream, 2020 was the year of videoconferencing – as iconic as the shift to virtual meetings has been, there is much more to come. Meetings, conferences, events, classrooms have all gone virtual. Video interaction with multiple people and sharing information via shared applications is commonplace. Virtual backgrounds which hide where you are actually speaking from are also widely used and getting more creative by the day.
Imagine then a future where you get on one of these calls wearing a headset and are transported into a room where your colleagues who are joining the call also are. You see them as full 3D people, you see the furniture, and the room decor. You speak and everyone sees your 3D avatar speak, gesture (as you gesture from the comfort of your home office) and move around. It will seem like you are really in the conference room together! If this feels futuristic or unreal try this or look at how the virtual office can look in the very near future.
While the solutions may not look very sophisticated, they will rapidly improve. AR/VR will start to really make its presence felt in the lives of consumers. From being able to virtually “try” on clothes from a boutique to product launches going virtual, these technologies will deeply impact customer experience in 2021 and beyond
In the immortal words of Captain Kirk, we will be going where no man has gone before – enabled by AR / VR.
#3 Digital CX will involve Multiple Technologies
AI, IoT and 5G will continue to support wider CX initiatives.
The advances that I have mentioned will gain impetus from 5G networking, which will enable unprecedented bandwidth availability. To deliver an AR experience over the cloud, riding on a 5G network, will literally be a game changer compared to the capabilities of older networks.
Similarly, IoT will lead to massive changes in terms of product availability, customisation and so on. 5G-enabled IoT will allow a lot more data to be carried a lot faster; and more processing at the edge. IoT will have some initial use cases in Retail, Services and other non-manufacturing sectors – but perhaps not as strongly as some commentators seem to indicate.
AI continues to drive change. While AI may not transform CX in 2021, this is a technology which will be a component of most other CX offerings, and so will impact customer experience in the next few years. In fact, thinking of businesses in 2025 I cannot believe that there will be a single business to customer (B2C) interaction which will not feature some form of AI technology.
I’d be interested to hear your thoughts on the technologies which will impact CX in 2021 – Connect with me on the Ecosystm platform.






































