Banks, insurers, and other financial services organisations in Asia Pacific have plenty of tech challenges and opportunities including cybersecurity and data privacy management; adapting to tech and customer demands, AI and ML integration; use of big data for personalisation; and regulatory compliance across business functions and transformation journeys.
Modernisation Projects are Back on the Table
An emerging tech challenge lies in modernising, replacing, or retiring legacy platforms and systems. Many banks still rely on outdated core systems, hindering agility, innovation, and personalised customer experiences. Migrating to modern, cloud-based systems presents challenges due to complexity, cost, and potential disruptions. Insurers are evaluating key platforms amid evolving customer needs and business models; ERP and HCM systems are up for renewal; data warehouses are transforming for the AI era; even CRM and other CX platforms are being modernised as older customer data stores and models become obsolete.
For the past five years, many financial services organisations in the region have sidelined large legacy modernisation projects, opting instead to make incremental transformations around their core systems. However, it is becoming critical for them to take action to secure their long-term survival and success.
Benefits of legacy modernisation include:
- Improved operational efficiency and agility
- Enhanced customer experience and satisfaction
- Increased innovation and competitive advantage
- Reduced security risks and compliance costs
- Preparation for future technologies
However, legacy modernisation and migration initiatives carry significant risks. For instance, TSB faced a USD 62M fine due to a failed mainframe migration, resulting in severe disruptions to branch operations and core banking functions like telephone, online, and mobile banking. The migration failure led to 225,492 complaints between 2018 and 2019, affecting all 550 branches and required TSB to pay more than USD 25M to customers through a redress program.
Modernisation Options
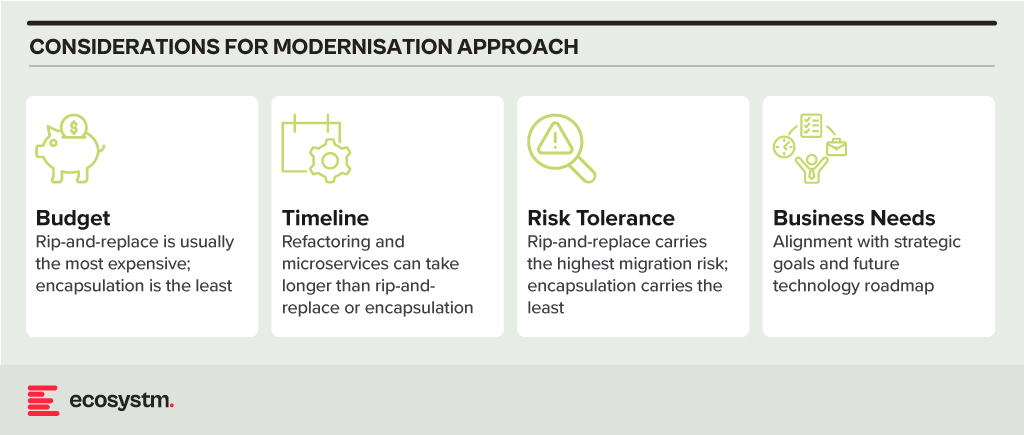
- Rip and Replace. Replacing the entire legacy system with a modern, cloud-based solution. While offering a clean slate and faster time to value, it’s expensive, disruptive, and carries migration risks.
- Refactoring. Rewriting key components of the legacy system with modern languages and architectures. It’s less disruptive than rip-and-replace but requires skilled developers and can still be time-consuming.
- Encapsulation. Wrapping the legacy system with a modern API layer, allowing integration with newer applications and tools. It’s quicker and cheaper than other options but doesn’t fully address underlying limitations.
- Microservices-based Modernisation. Breaking down the legacy system into smaller, independent services that can be individually modernised over time. It offers flexibility and agility but requires careful planning and execution.
Financial Systems on the Block for Legacy Modernisation
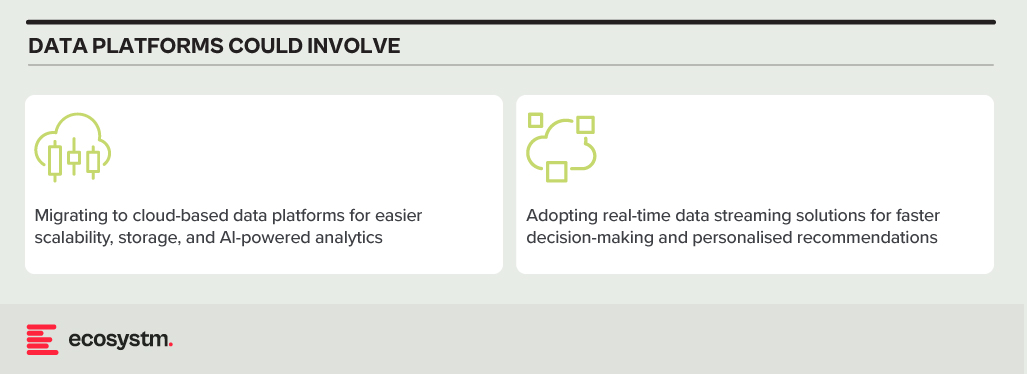
Data Analytics Platforms. Harnessing customer data for insights and targeted offerings is vital. Legacy data warehouses often struggle with real-time data processing and advanced analytics.
CRM Systems. Effective customer interactions require integrated CRM platforms. Outdated systems might hinder communication, personalisation, and cross-selling opportunities.

Payment Processing Systems. Legacy systems might lack support for real-time secure transactions, mobile payments, and cross-border transactions.

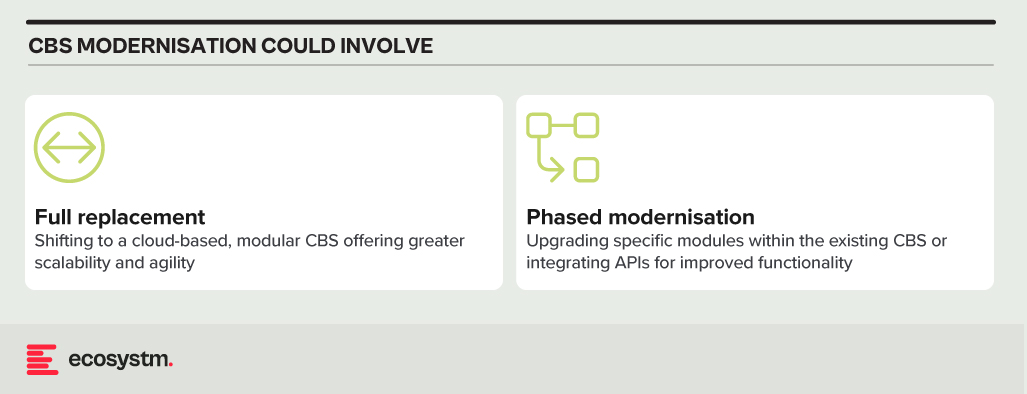
Core Banking Systems (CBS). The central nervous system of any bank, handling account management, transactions, and loan processing. Many Asia Pacific banks rely on aging, monolithic CBS with limited digital capabilities.
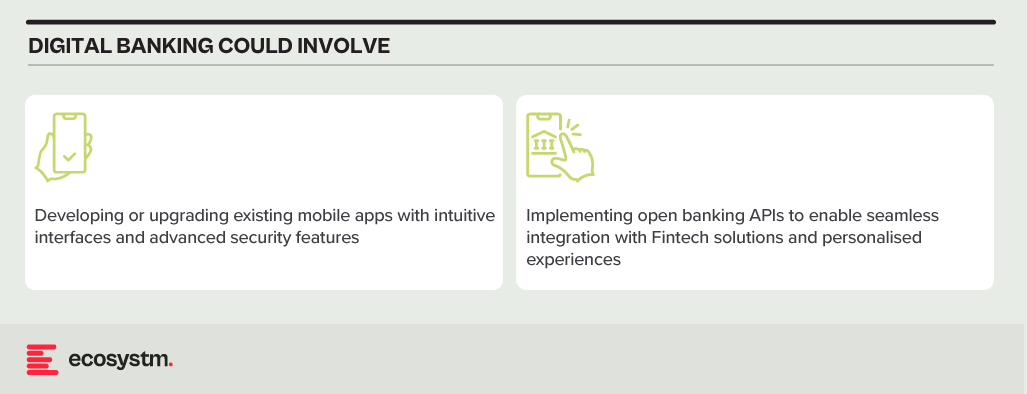
Digital Banking Platforms. While several Asia Pacific banks provide basic online banking, genuine digital transformation requires mobile-first apps with features such as instant payments, personalised financial management tools, and seamless third-party service integration.
Modernising Technical Approaches and Architectures
Numerous technical factors need to be addressed during modernisation, with decisions needing to be made upfront. Questions around data migration, testing and QA, change management, data security and development methodology (agile, waterfall or hybrid) need consideration.
Best practices in legacy migration have taught some lessons.
Adopt a data fabric platform. Many organisations find that centralising all data into a single warehouse or platform rarely justifies the time and effort invested. Businesses continually generate new data, adding sources, and updating systems. Managing data where it resides might seem complex initially. However, in the mid to longer term, this approach offers clearer benefits as it reduces the likelihood of data discrepancies, obsolescence, and governance challenges.
Focus modernisation on the customer metrics and journeys that matter. Legacy modernisation need not be an all-or-nothing initiative. While systems like mainframes may require complete replacement, even some mainframe-based software can be partially modernised to enable services for external applications and processes. Assess the potential of modernising components of existing systems rather than opting for a complete overhaul of legacy applications.
Embrace the cloud and SaaS. With the growing network of hyperscaler cloud locations and data centres, there’s likely to be a solution that enables organisations to operate in the cloud while meeting data residency requirements. Even if not available now, it could align with the timeline of a multi-year legacy modernisation project. Whenever feasible, prioritise SaaS over cloud-hosted applications to streamline management, reduce overhead, and mitigate risk.
Build for customisation for local and regional needs. Many legacy applications are highly customised, leading to inflexibility, high management costs, and complexity in integration. Today, software providers advocate minimising configuration and customisation, opting for “out-of-the-box” solutions with room for localisation. The operations in different countries may require reconfiguration due to varying regulations and competitive pressures. Architecting applications to isolate these configurations simplifies system management, facilitating continuous improvement as new services are introduced by platform providers or ISV partners.
Explore the opportunity for emerging technologies. Emerging technologies, notably AI, can significantly enhance the speed and value of new systems. In the near future, AI will automate much of the work in data migration and systems integration, reducing the need for human involvement. When humans are required, low-code or no-code tools can expedite development. Private 5G services may eliminate the need for new network builds in branches or offices. AIOps and Observability can improve system uptime at lower costs. Considering these capabilities in platform decisions and understanding the ecosystem of partners and providers can accelerate modernisation journeys and deliver value faster.
Don’t Let Analysis Paralysis Slow Down Your Journey!
Yes, there are a lot of decisions that need to be made; and yes, there is much at stake if things go wrong! However, there’s a greater risk in not taking action. Maintaining a laser-focus on the customer and business outcomes that need to be achieved will help align many decisions. Keeping the customer experience as the guiding light ensures organisations are always moving in the right direction.

2024 and 2025 are looking good for IT services providers – particularly in Asia Pacific. All types of providers – from IT consultants to managed services VARs and systems integrators – will benefit from a few converging events.
However, amidst increasing demand, service providers are also challenged with cost control measures imposed in organisations – and this is heightened by the challenge of finding and retaining their best people as competition for skills intensifies. Providers that service mid-market clients might find it hard to compete and grow without significant process automation to compensate for the higher employee costs.
Why Organisations are Opting for IT Service
- Organisations are seeking further cost reductions. Managed services providers will see more opportunities to take cost and complexity out of organisation’s IT functions. The focus in 2024 will be less on “managing” services and more on “transforming” them using ML, AI, and automation to reduce cost and improve value.
- Big app upgrades are back on the agenda. SAP is going above and beyond to incentivise their customers and partners to migrate their on-premises and hyperscale hosted instances to true cloud ERP. Initiatives such as Rise with SAP have been further expanded and improved to accelerate the transition. Salesforce customers are also looking to streamline their deployments while also taking advantage of the new AI and data capabilities. But many of these projects will still be complex and time-consuming.
- Cloud deployments are getting more complex. For many organisations, the simple cloud migrations are done. This is the stage of replatforming, retiring, and refactoring applications to take advantage of public and hybrid cloud capabilities. These are not simple lift and shift – or switch to SaaS – engagements.
- AI will drive a greater need for process improvement and transformation. This will happen along with associated change management and training programs. While it is still early days for GenAI, before the end of 2024, many organisations will move beyond experimentation to department or enterprise wide GenAI initiatives.
- Increasing cybersecurity and data governance demands will prolong the security skill shortage. More organisations will turn to managed security services providers and cybersecurity consultants to help them develop their strategy and response to the rising threat levels.
Choosing the Right Cost Model for IT Services
Buyers of IT services must implement strict cost-control measures and consider various approaches to align costs with business and customer outcomes, including different cost models:
Fixed-Price Contracts. These contracts set a firm price for the entire project or specific deliverables. Ideal when project scope is clear, they offer budget certainty upfront but demand detailed specifications, potentially leading to higher initial quotes due to the provider assuming more risk.
Time and Materials (T&M) Contracts with Caps. Payment is based on actual time and materials used, with negotiated caps to prevent budget overruns. Combining flexibility with cost predictability, this model offers some control over total expenses.
Performance-Based Pricing. Fees are tied to service provider performance, incentivising achievement of specific KPIs or milestones. This aligns provider interests with client goals, potentially resulting in cost savings and improved service quality.
Retainer Agreements with Scope Limits. Recurring fees are paid for ongoing services, with defined limits on work scope or hours within a given period. This arrangement ensures resource availability while containing expenses, particularly suitable for ongoing support services.
Other Strategies for Cost Efficiency and Effective Management
Technology leaders should also consider implementing some of the following strategies:
Phased Payments. Structuring payments in phases, tied to the completion of project milestones, helps manage cash flow and provides a financial incentive for the service provider to meet deadlines and deliverables. It also allows for regular financial reviews and adjustments if the project scope changes.
Cost Transparency and Itemisation. Detailed billing that itemises the costs of labour, materials, and other expenses provides transparency to verify charges, track spending against the budget, and identify areas for potential savings.
Volume Discounts and Negotiated Rates. Negotiating volume discounts or preferential rates for long-term or large-scale engagements, makes providers to offer reduced rates for a commitment to a certain volume of work or an extended contract duration.
Utilisation of Shared Services or Cloud Solutions. Opting for shared or cloud-based solutions where feasible, offers economies of scale and reduces the need for expensive, dedicated infrastructure and resources.
Regular Review and Adjustment. Conducting regular reviews of the services and expenses with the provider to ensure alignment with the budget and objectives, prepares organisations to adjust the scope, renegotiate terms, or implement cost-saving measures as needed.
Exit Strategy. Planning an exit strategy that include provisions for contract termination, transition services, protects an organisation in case the partnership needs to be dissolved.
Conclusion
Many businesses swing between insourcing and outsourcing technology capabilities – with the recent trend moving towards insourcing development and outsourcing infrastructure to the public cloud. But 2024 will see demand for all types of IT services across nearly every geography and industry. Tech services providers can bring significant value to your business – but improved management, monitoring, and governance will ensure that this value is delivered at a fair cost.

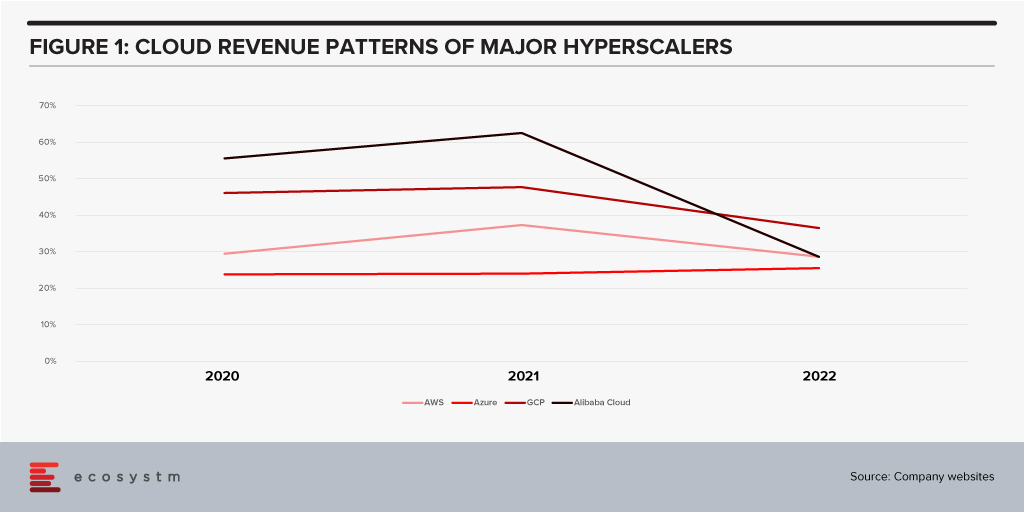
All growth must end eventually. But it is a brave person who will predict the end of growth for the public cloud hyperscalers. The hyperscaler cloud revenues have been growing at between 25-60% the past few years (off very different bases – and often including and counting different revenue streams). Even the current softening of economic spend we are seeing across many economies is only causing a slight slowdown.
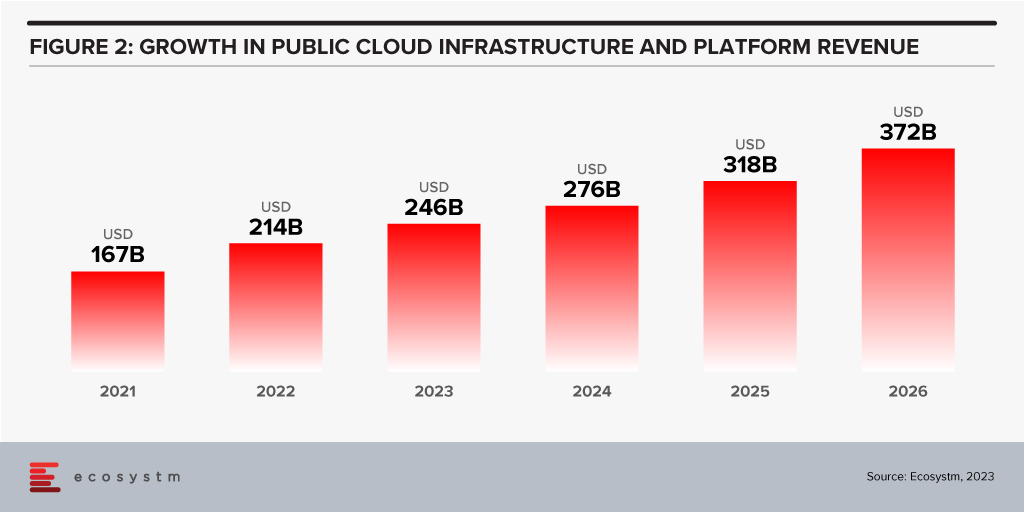
Looking forward, we expect growth in public cloud infrastructure and platform spend to continue to decline in 2024, but to accelerate in 2025 and 2026 as businesses take advantage of new cloud services and capabilities. However, the sheer size of the market means that we will see slower growth going forward – but we forecast 2026 to see the highest revenue growth of any year since public cloud services were founded.
The factors driving this growth include:
- Acceleration of digital intensity. As countries come out of their economic slowdowns and economic activity increases, so too will digital activity. And greater volumes of digital activity will require an increase in the capacity of cloud environments on which the applications and processes are hosted.
- Increased use of AI services. Businesses and AI service providers will need access to GPUs – and eventually, specialised AI chipsets – which will see cloud bills increase significantly. The extra data storage to drive the algorithms – and the increase in CPU required to deliver customised or personalised experiences that these algorithms will direct will also drive increased cloud usage.
- Further movement of applications from on-premises to cloud. Many organisations – particularly those in the Asia Pacific region – still have the majority of their applications and tech systems sitting in data centre environments. Over the next few years, more of these applications will move to hyperscalers.
- Edge applications moving to the cloud. As the public cloud giants improve their edge computing capabilities – in partnership with hardware providers, telcos, and a broader expansion of their own networks – there will be greater opportunity to move edge applications to public cloud environments.
- Increasing number of ISVs hosting on these platforms. The move from on-premise to cloud will drive some growth in hyperscaler revenues and activities – but the ISVs born in the cloud will also drive significant growth. SaaS and PaaS are typically seeing growth above the rates of IaaS – but are also drivers of the growth of cloud infrastructure services.
- Improving cloud marketplaces. Continuing on the topic of ISV partners, as the cloud hyperscalers make it easier and faster to find, buy, and integrate new services from their cloud marketplace, the adoption of cloud infrastructure services will continue to grow.
- New cloud services. No one has a crystal ball, and few people know what is being developed by Microsoft, AWS, Google, and the other cloud providers. New services will exist in the next few years that aren’t even being considered today. Perhaps Quantum Computing will start to see real business adoption? But these new services will help to drive growth – even if “legacy” cloud service adoption slows down or services are retired.
Hybrid Cloud Will Play an Important Role for Many Businesses
Growth in hyperscalers doesn’t mean that the hybrid cloud will disappear. Many organisations will hit a natural “ceiling” for their public cloud services. Regulations, proximity, cost, volumes of data, and “gravity” will see some applications remain in data centres. However, businesses will want to manage, secure, transform, and modernise these applications at the same rate and use the same tools as their public cloud environments. Therefore, hybrid and private cloud will remain important elements of the overall cloud market. Their success will be the ability to integrate with and support public cloud environments.
The future of cloud is big – but like all infrastructure and platforms, they are not a goal in themselves. It is what cloud is and will further enable businesses and customers which is exciting. As the rates of digitisation and digital intensity increase, the opportunities for the cloud infrastructure and platform providers will blossom. Sometimes they will be the driver of the growth, and other times they will just be supporting actors. But either way, in 2026 – 20 years after the birth of AWS – the growth in cloud services will be bigger than ever.

There is no doubt that 2023 is off to an uncertain start. However, despite the economic headwinds we expect that some areas of technology will see continued growth. In fact, from our conversations with business and technology leaders, it appears that many organisations will take the opportunity to right-size their businesses, remove excess fat and waste, and accelerate their transformation efforts. The plan is to emerge from a global slowdown – leaner, smarter and better.
Where there is an opportunity to automate organisations will take it – and technology spend will trump people spend in 2023.
But it won’t all be smooth sailing as technology buyers become more discerning than ever and manage costs closely.
Here is what tech providers should focus on to remain resilient in these uncertain times.
- Be prepared to work harder – especially cloud and SaaS providers
- Help customers optimise costs
- Accelerate innovation to stay ahead of M&A activity
- Employ security to manage risk
- Prepare for product-led growth
Read on to find out why.
Download Be Alert – Not Alarmed: Analyst Guidance for Tech Providers as a PDF

Life never gets any easier for the digital and information technology teams in organisations. The range and reach of the different technologies continue to open new opportunities for organisations that have the foresight and strategy to chase them. Improving offers for existing customers and reaching new segments depend on the organisation’s ability to innovate.
But the complexity of the digital ecosystem means this ability to innovate will be heavily constrained, causing improvements to take longer and cost more in many cases. Addressing the top business priorities expressed in the Ecosystm Digital Enterprise Study, 2022, will need tech teams to look to simplify as well as add features.
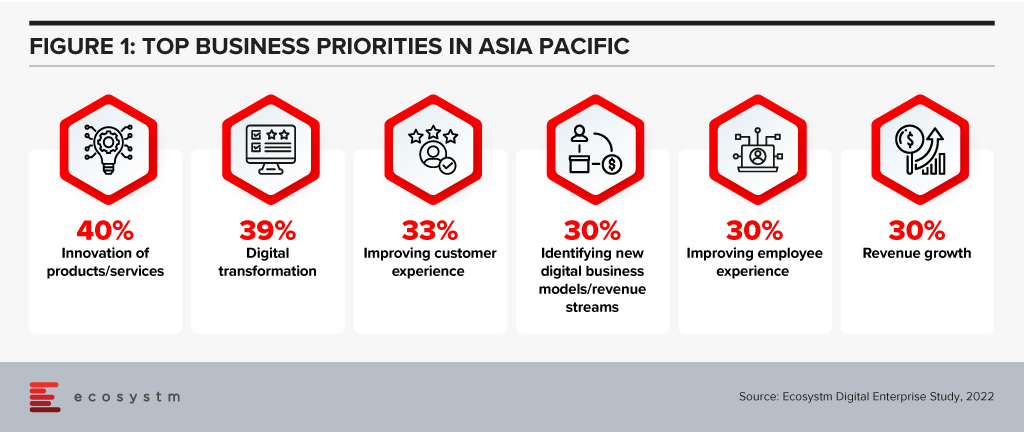
Complexity is Not Just an IT Issue
Many parts of an organisation have been making decisions on implementing new digital capabilities, particularly those involved in remote working. Frequently, the IT organisation has not been involved in the selection, implementation and use of these new facilities.
The number of start-up organisations delivering SaaS has continued to explode. A particular area has been the expansion of co-creation tools used by teams to deliver outcomes. In many cases, these have been introduced by enthusiastic users looking to improve their immediate working environment without the understanding of single-sign-on requirements, security and privacy of information or the importance of backup and business continuity planning.
SaaS tools such as Notion, monday.com and ClickUp (amongst many, many others), are being used to coordinate and manage teams across organisations of all sizes. While these are all cloud services, the support and maintenance of them ultimately will fall to the IT organisation. And they won’t be integrated at all with the tools the IT organisation uses to manage and improve user experience.
Every new component adds to the complexity of the tech environment – but with that complexity comes increased dependencies between components, which slows an organisation’s ability to adapt and evolve. This means each change needs more work to deliver, costs increase, and it takes longer to deliver value.
And this increasing complexity causes further problems with cybersecurity. Without regular attention, legacy systems will increase the attack surface of organisations, making it easier to compromise an organisation’s environment. At a recent executive forum with CISOs, attendees rated the risks caused by their legacy systems as their most significant concern.
An organisation’s leadership needs to both simplify and advance their organisation’s digital capabilities to remain competitive. This balance should not be left to the IT organisation to achieve as they will not be able to deliver both without wider support and recognition of the problems.
Discriminate on Differentiating Skills
One thing we can be sure of is that we won’t be able to employ all the skills we need for our future capabilities. We are not training enough people in the skills that we need now and for the future, and the range of technologies continues to expand, increasing the number of skills that we will need to keep an organisation running.
Most organisations are not removing or replacing ageing systems, preferring to keep them running at an apparently low cost. Often these legacy systems are fully depreciated, have low maintenance costs and have few changes made to them, as other areas of the organisation offer better investment options. But this also means that the old skills remain necessary.
So organisational leaders are adding new skills requirements on top of old, with the older skills being less attractive with so many new languages, frameworks and databases becoming available. Wikipedia has a very long list of languages that have been developed over the years. Some from the 1950s, like FORTRAN and LISP, continue to be used today.
Organisations will not be in a position to employ all the skills it needs to implement, develop and maintain for its digital infrastructure and applications. The choice is going to be which skills are most important to an organisation. This selection needs to be very discriminating and focus on differentiating skills – those that really make a difference within your ecosystem, particularly for your customers and employees.
Organisations will need a great partner who can deliver generic skills and more services. They will have better economies of scale and skill and will free management to attend to those things most important to customers and employees.
Hybrid Cloud has an Edge
Almost every organisation has a hybrid cloud environment. This is not a projection – it has already happened. And most organisations are not well equipped to deal with this situation.
Organisations may not be aware that they are using multiple public clouds. Many of the niche SaaS applications used by an organisation will use Microsoft Azure, AWS or GCP, so it is highly likely organisations are already using multiple public clouds. Not to mention the offerings from vendors such as Oracle, Salesforce, SAP and IBM. IT teams need to be able to monitor, manage and maintain this complex set of environments. But we are only in the early stages of integrating these different services and systems.
But there is a third leg to this digital infrastructure stool that is becoming increasingly important – what we call “the Edge” – where applications are deployed as part of the sensors that collect data in different environments. This includes applications such as pattern recognition systems embedded in cameras so that network and server delays cannot affect the performance of the edge systems. We can see this happening even in our homes. Google supports their Nest domestic products, while Alexa uses AWS. Not to mention Amazon’s Ring home security products.
With the sheer number of these edge devices that already exist, the complexity it adds to the hybrid environment is huge. And we expect IT organisations to be able to support and manage these.
Simplify, Specialise, Scale
The lessons for IT organisations are threefold:
- Simplify as much as possible while you are implementing new features and facilities. Retiring legacy infrastructure elements should be consistently included in the IT Team objectives. This should be done as part of implementing new capabilities in areas that are related to the legacy.
- Specialise in the skills that are the differentiators for your organisation with its customers and employees. Find great partners who can provide the more generic skills and services to take this load off your team.
- Scale your hybrid management environment so that you can automate as much of the running of your infrastructure as possible. You need to make your IT Team as productive as possible, and they will need power tools.
For IT vendors, the lessons are similar.
- Simplify customer offers as much as possible so that integration with your offering is fast and frugal. Work with them to reduce and retire as much of their legacy as possible as you implement your services. Duplication of even part of your offer will complicate your delivery of high-quality services.
- Understand where your customers have chosen to specialise and look to complement their skills. And consistently demonstrate that you are the best in delivering these generic capabilities.
- Scale your integration capabilities so that your customers can operate through that mythical single pane of glass. They will be struggling with the complexities of the hybrid infrastructure that include multiple cloud vendors, on-premises equipment, and edge services.

–
What is happening to the data that you are sharing with your ecosystem of suppliers?
Just before Christmas, a friend recommended reading “Privacy is Power” by Carissa Véliz. But the long list of recommendations that the author provides on what you could and should do is quite disheartening. I feel that I have to shut off a lot of the benefits that I get from using the Internet in order to maintain my privacy.
But then over the past couple of days came a couple of reminders of our exposure – our suppliers will share our data with their suppliers, as well as be prepared to use our resources to their benefit. I am reasonably technical and still find it difficult, so how does a person who just wants to use a digital service cope?
Bunnings’ Data Breach with FlexBooker
First example. Bunnings started using a service called FlexBooker to support their click-and-collect service.
To do this, they share personal information with the company for the service to work correctly. But hackers have stolen data for over three million customers from FlexBooker in a recent data breach.
How many of Bunnings’ customers were aware that their data was being shared with FlexBooker? How many would have cared if they had known?
I have only read the comments from Bunnings included in the Stuff report but I believe the reported reaction lacks the level of concern that this breach warrants. What did Bunnings do to verify FlexBooker’s privacy and security standards before sharing their customers’ data with them? What is going to change now that the vulnerability has been identified?
Neither of these things is clear. It is not clear if Bunnings have advised their customers that they could have been affected. There is no clear message on the Bunnings New Zealand site on the details of the breach.
In “Privacy is Power”, the author makes a strong case for customers to demand protection of their privacy. Organisations that use other companies as part of their services must be as demanding of their suppliers as their own customers would be of them.
Is Crypto Mining part of antivirus?
The second example is a little different. Norton has released crypto mining software as part of their antivirus suite. This crypto mining software uses the spare capacity of your computer to join with a pool of computers that are working to create a new blockchain block. Each time a new block is added, you would earn some cryptocurrency that you could change to a fiat currency, i.e. normal cash.
But I question why a crypto miner is part of an antivirus suite. Norton makes the case that they are a trusted partner, so can deliver a safer mining experience than other options.
Norton have made the use of this software optional, but to me, it does indicate the avarice of companies where they see a potential income opportunity. If they had included the software in their internet security suite, then there may be some logic in adding the capability. But to antivirus?
The Verge did some unscientific measurements on the value to a user of running this software. They found the cost of the electricity used during the operation of Norton’s mining software was about the same as what they earned. So Norton, with their 15% fee, would be the only ones making money.
The challenge remains for most of us. Our software vendors are adding new functionality to our services regularly because it is what we as customers expect. But I rarely check to see what has been changed in a new release as normally you will only see a “bugs squashed, performance improved” messaging. We have no guarantee that they have not implemented some new way of using our information or assets without gaining explicit approval from the user for this new use.
To Norton’s credit, they have made crypto mining optional and do not activate the software without their users’ consent. Others are less likely to be as ethical.
Summary
Both of these examples show how vulnerable customers of companies are to the exposure of their private data and assets. All organisations are increasing their use of different external services as SaaS options become more attractive. Commercial terms are the critical points of negotiation, not customer privacy. What assurance do customers get that their privacy is being maintained as they would expect?
One point that is often overlooked is that many cloud service contracts define the legal jurisdiction as being either the cloud provider’s home jurisdiction or one that is more advantageous for them. So, any intended legal action could be taking place in a foreign jurisdiction with different privacy laws.
Customer service organisations (i.e. pretty much all organisations) need to look after their customers’ data much more effectively. Customers need to demand to know how their rights are being protected, and governments have to put in place appropriate consequences for organisations where breaches occur outside that government’s jurisdiction.

One of the biggest impacts of the pandemic has been the uptick in cloud adoption. Ecosystm research shows that more than half the organisations are either building cloud native applications or have a Cloud-First strategy. Cloud infrastructure, platforms and software became a key enabler of the business agility and innovation that organisations needed to survive and succeed.
However, as organisations look to become data-driven and digital, they will require seamless access to their data, irrespective of where they are generated (enterprise systems, IoT devices or AI solutions) and where they are stored (public cloud, Edge, on-premises or data centres) to unlock the full value of the data and deliver the insights needed. This will shape the Cloud and Data Centre ecosystem in 2022.
Read on to find out what Ecosystm Analysts, Claus Mortensen, Darian Bird, Peter Carr and Tim Sheedy think will be the leading Cloud & Data Centre trends in 2022.
Click here to download Ecosystm Predicts: The Top 5 Trends for Cloud & Data Centre in 2022 as PDF

It is true that the Retail industry is being forced to evolve the experiences they deliver to their customers. However, if Retail organisations are only focused on creating digital experiences, they are not creating the differentiation that will be required to leap ahead of the competition. It is time for Retail organisations to leverage data to empower multiple roles across the organisation to prepare for the different ways customers want to engage with their brands.
Another trend that is creating a shift in the industry is the rise of small and medium-sized retailers. Traditionally, larger retailers have made larger investments in technology – they simply had deeper pockets for the on-premise investments. However, with the rise of SaaS, size may no longer be such an advantage in Retail.
Here is how organisations such as Walmart, Adobe, GoDaddy and Google are empowering the SME retailer.

Digital and IT organisations are going through some dramatic changes as they adopt cloud and as-a-service capabilities. In this post, I want to write about two of these – one that is very much a consequence of the other.
Contract Numbers are Exploding
We’re seeing an explosion in the number of IT suppliers to a typical organisation.
Pre-cloud, the typical organisation probably had five to ten contracts that covered most of the external services that were in use. With suppliers increasingly providing niche functionality and the increased use of credit cards to buy external services, it is often difficult to determine exactly how many contracts are in place. Or, indeed, have a clear understanding of the terms and conditions of each of these contracts.
Where once an organisation might have had contracts for an on-premises ERP and CRM system, a typical organisation will still have those contracts as well as a supply chain forecasting service, a marketing email management tool, not to mention online spreadsheets and task management capabilities.
So with many more contracts in place, the complexity of managing these contracts and understanding the technical, legal and business risks encapsulated in these contracts has become dramatically more difficult.
I’ll return to this point in a later post, as most organisations struggle with this increasing complexity.
What Is Happening to Your People?
The existence of these contracts means that you are increasingly becoming dependent on the people employed by these external organisations. But when you sign up for these contracts, do you investigate how these suppliers develop their talent?
The New Zealand Herald recently carried an interesting article on one organisation that has developed a paid intern program. Something very rare in the industry.
The article prompted me to think through some of the implications of using cloud services. Tech buyer organisations will have less need for technical capabilities as increasingly these are delivered by the cloud suppliers.
But the growth in demand for digital and IT skills just continues to increase as more and more industries digitalise. In the past, tech buyer organisations would have invested (at least the good employers did!) in the development of their people. The cloud suppliers are increasingly doing this talent development.
Most contract negotiations are based on cost, quality and customer service. A significant proportion of cloud contracts are now boilerplate – you pay with a credit card for a monthly service and have little or no ability to negotiate terms and conditions.
The trade-off is required to get a short commitment term and a variable cost profile. No tech vendor can afford to negotiate bespoke contracts for this type of commercial arrangement.
This situation leaves the question of how tech buyers can influence tech vendors to develop their people’s talent appropriately. Some would say that the tech vendors will do this as a matter of course, but the statistics, as highlighted in the Ecosystm research data in Figure 1, show that we are not bringing people in at the rate the industry requires.
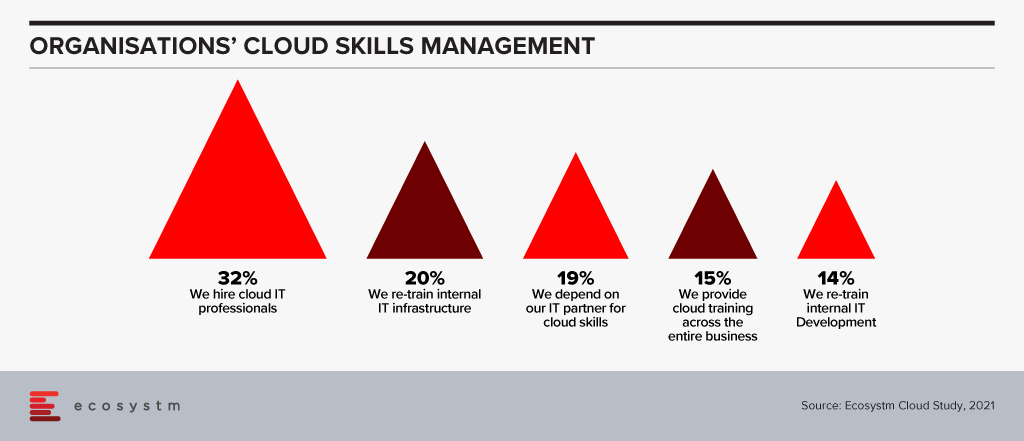
Advice for Tech Buyers
I recommend you look closely at using two tactics with the tech vendors that you are working with:
- First, look to consolidate as much workload as practical under a single contract with the supplier. This is not a new recommendation for contracts – but with the increasing use of boilerplate contracts, it is one of the few ways an organisation can increase its value and importance to a tech vendor.
- Second, start finding those tech vendors that are developing new and existing talent in practical ways and favour these organisations in any purchase decision.
Most organisations, individually, do not have the commercial power to dictate terms to the cloud providers. Still, if enough tech buyers adopt this critical criterion, the cloud providers may see the value in investing in the industry’s talent development in meaningful ways.
The downside? Talent development does not come free. Tech buyers may need to pay a higher fee to encourage the suppliers but paying a low-cost provider who does not develop their talent sounds like a recipe for poor quality service.
If you would like to discuss any of these thoughts or issues further, please feel free to reach out and contact me. This is an industry issue and one for our broader society, so I would be interested in hearing how your organisations are addressing this challenge.






































