The UN’s global stocktake synthesis report underscores the need for significant efforts to meet the ambitious goals of the Paris Agreement to keep the global warming limit to 1.5ºC, compared to pre-industrial levels. Achieving this requires collective action from governments, organisations, and individuals.
While regulators focus on mandates, organisations today are being influenced more by individual responsibility for positive impact. Customers and employees are leading ESG actions – another fast-emerging voice driving ESG initiatives are value chain partners looking to build sustainable supply chains.
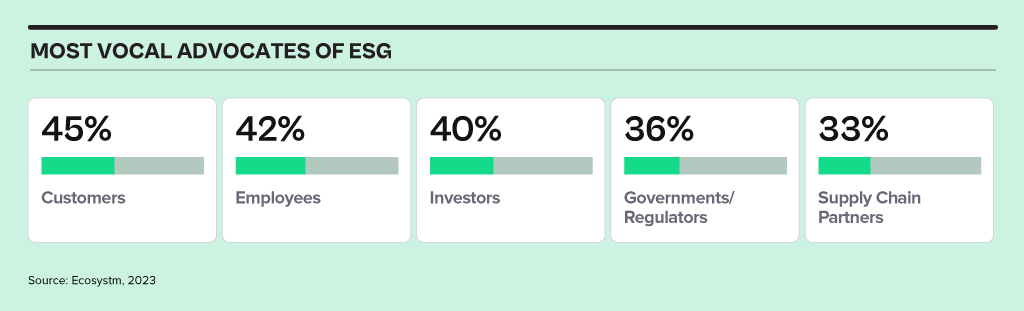
Ecosystm research reveals that only 27% of organisations worldwide currently view ESG as a strategic imperative, yet we anticipate rapid change in the landscape.
Click below to find out what Ecosystm analysts Gerald Mackenzie, Kaushik Ghatak, Peter Carr and Sash Mukherjee consider the top 5 ESG trends that will shape organisations’ sustainability roadmaps in 2024.
Click here to download ‘Ecosystm Predicts: Top 5 ESG Trends in 2024’ as a PDF.
#1 Organisations Will Evolve ESG Strategies from Compliance to Customer & Brand Value
Many of the organisations that we talk to have framed their ESG strategy and roadmaps primarily in relation to compliance and regulatory standards that they need to meet, e.g. in relation to emissions reporting and reduction, or in verifying that their supply chains are free from Modern Slavery.
However, organisations that are more mature in their journeys have realised that ESG is quickly becoming a strategic differentiator and compliance is only the start of their sustainability journey.
Customers, employees, and investors are increasingly selective about the brands they want to associate with and expect them to have a purpose and values that are aligned with their own.

#2 Sustainability Will Remain a Stepping-Stone to Full ESG
Heading into 2024, the corporate continues to navigate the nuances between Sustainability and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) initiatives. Sustainability, focused on environmental stewardship, is a common starting point for corporate responsibility, offering measurable goals for a solid foundation.
Yet, the transition to comprehensive ESG, which includes broader social and governance issues alongside environmental concerns, demands broader scope and deeper capabilities, shifting from quantitative to qualitative measures. The trend of merging sustainability with ESG risks is blurring distinct objectives, potentially complicating reporting and compliance, and causing confusion in the market. Nevertheless, this conflation ultimately paves the way for more integrated, holistic corporate strategies.
By aligning sustainability efforts with wider ESG goals, companies will develop more comprehensive solutions that address the entire spectrum of corporate responsibility.

#3 ESG Consulting Will Grow – Till Industry Templates Take Over
At the end of 2022, LinkedIn buzzed with announcements of Chief Sustainability Officer appointments. However, the Global Sustainability Barometer Study reveals that only around one-third of global organisations have a dedicated sustainability lead. What changed?
Organisations have recognised that ESG is intricate, requiring a comprehensive focus and a capable team, not just a sustainability leader.
Each organisation’s path to sustainability is unique, shaped by factors like size, industry, location, stakeholders, culture, and values. Successfully integrating ESG requires a nuanced understanding of an organisation’s barriers, opportunities, and risks, making it challenging to navigate the sustainability journey alone. This is complicated by the absence of clear government/industry mandates and guidelines that frame best practices.

#4 Sustainability Tech Will Finally Gain Traction
Many organisations initiate sustainability journeys with promises and general strategies. While the role of technology in accelerating goals is recognised, alignment has been lacking. In 2024 sustainability tech will gain traction.
Environmental Tech. Improved sensors and analytics will enhance monitoring of air and water quality, carbon footprint, biodiversity, and climate patterns.
Carbon-Neutral Transportation. Advancements in electric and hydrogen vehicles, batteries, and clean mobility infrastructure will persist.
Circular Economy. Innovations like reverse logistics and product lifecycle tracking will help reduce waste and extend product/material life.
Smart Grids and Renewable Energy. Smart grid tech and new solutions for renewable energy integration will improve energy distribution.

#5 Cleantech Innovation Will See Increased Funding
Cleantech is the innovation that is driving our adaptation to climate change. We expect that investments into, and the pace of innovation and adoption of Cleantech will accelerate into 2024.
As companies commit to their net-zero targets, the need to operationalise the technologies required to fuel this transition becomes all the more urgent. BloombergNEF reported that for Europe alone, nearly USD 220 billion was invested in Cleantech in 2022.
But to meet net-zero ambitions, annual investments in Cleantech will need to triple over the rest of this decade and quadruple in the next.


Energy providers around the world have transformed their electricity generation profiles to include solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal to reduce the carbon intensity of their economies. Many countries have surpassed expectations by approaching or exceeding 50% of production stemming from renewable sources. Concurrently, the decarbonisation of the transportation sector and the growing use of air conditioning is putting upward pressure on electricity demand.
Energy providers are keen on leveraging AI in several areas (Figure 1).
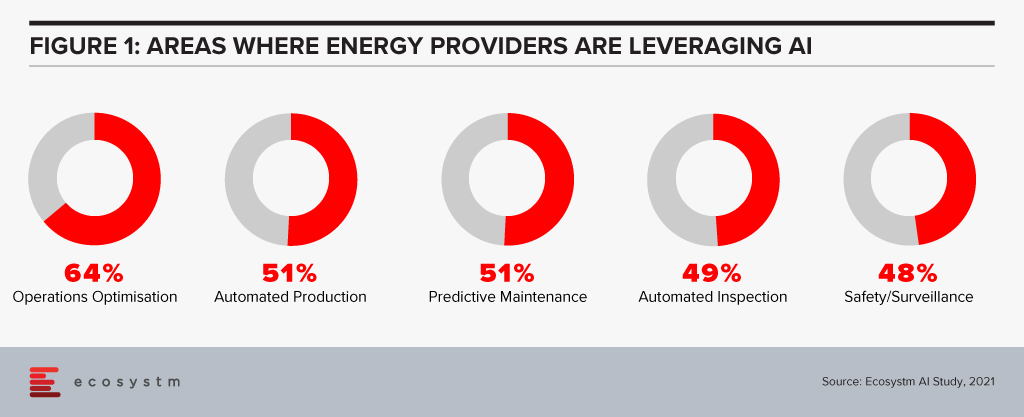
The sudden evolution of the Energy sector is creating new complexity in the grid, which human operators will be unable to monitor and manage without the assistance of AI.
Predicting Supply and Shaping Demand
Output Forecasting. The primary inhibitor to the mass adoption of renewable energy is the issue of intermittency. Solar is affected by shorter winter days and cloud cover, while wind turbines are ineffective during periods of low or even high wind speed. If electricity supply does not precisely match demand, grid operators must fire up costly and carbon-intensive peaker plants to fill the gap or resort to rolling blackouts. AI is becoming a tool for generators and grid operators to forecast renewable output more accurately, insight which can, in turn, be used to shape demand.
Competitive Pricing. Wind farm operators are beginning to use adversarial AI to judge if publicly available data for velocity, pressure, and density obey turbulent flow physics and if not, to refine their forecasts. Equipped with more accurate projections, they can bid with greater certainty on day-ahead auctions rather than relying on less profitable spot prices. This consequently makes wind power more competitive with fossil-fuel-based generators and smoothens out hourly price variability.
Predicting Usage Patterns. Improved temperature and humidity forecasts can also be used by grid operators to carry out peak shaving – encouraging consumers to reduce consumption during high-load periods. By accurately predicting intervals of increased use of home heating or cooling, programs such as Rush Hour Rewards by Nest, allow distributors to remotely adjust thermostats during seasonal extremes for cash incentives. Advanced knowledge of these weather events can also give grid operators the chance to temporarily lift regulatory hurdles or conduct emergency maintenance to ensure maximum capacity is available.
Supply Orchestration. Home battery systems and electric vehicles are growing in acceptance and their storage capacity will eventually become an important piece of infrastructure for time-shifting supply to match demand. The increasing build out of solar PV has created an oversupply in the middle of the day while the rising adoption of home air conditioning creates a spike in demand after working hours, resulting in the so-called Duck Curve (see Figure 2).
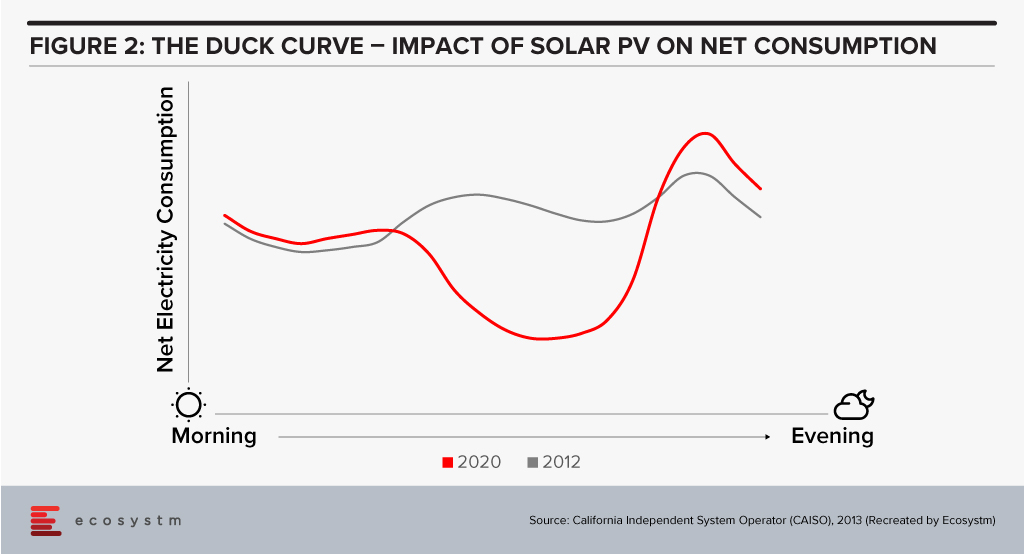
By predicting periods of potential supply shortfall, distributors can increase prices to a level attractive enough to prompt battery owners to sell excess electricity rather than store it. The complexity inherent in such a distributed system is only manageable with machine learning to constantly optimise pricing and supply orchestration to simultaneously prevent excessive degradation of battery performance. This is already available for large scale battery operators, e.g. using Tesla Autobidder, and will become accessible to networks of home and eventually vehicle owners.

The Future
Optimising Renewable Generation with AI
Renewable energy sources continue to make efficiency gains due to engineering improvements. However, advances in AI will increase generation even further. Solar PV and solar concentrators that rotate on dual-axis trackers to follow the path of the sun must each operate individually according to their own precise position and the time of day and year. This must be balanced for efficiency to reduce excessive movement, which consumes a portion of electricity output. Neural networks and fuzzy logic can be applied to optimise rotation to maximise production while reducing power consumption for operation. Input variables can include position, time, temperature, and even sky colour. Similarly, wind turbines can dynamically alter their positions to maximise wind flow across the entire fleet rather than at an individual level. The large streams of data must be processed in real-time as wind variables change to have an immediate effect on output.
Stabilising the Super Grid
To improve resiliency and lessen the effects of renewable intermittency, there is a growing push towards increasing the interconnectivity of national grids. This ensures supply even when regional generators go offline or if sudden local peaks in demand occur. Moreover, interconnected grids help even out supply from renewable sources using the philosophy that it is always windy or sunny somewhere. For example, the proposed European super grid would take advantage of higher wind generation in northern countries in winter and in North Africa in the summer. Additionally, hydroelectric plants in the north could be modified to become pumped storage facilities powered by solar thermal plants in the south to supply all of Europe.
Not only will a super grid require investment in new infrastructure, such as high voltage direct current (HVDC) for efficient long-distance transmission but also in intelligent systems to manage the new complexity. The retirement of fossil-fuel generators and greater variability of renewable sources will require rethinking grid inertia and frequency control between countries. Measurement solutions, such as GridMetrix by Reactive, have been deployed by AEMO in Australia and National Grid in the UK to better monitor how inertia fluctuates as renewable sources ebb and flow. Once real-time data becomes available for analysis, infrastructure such as synchronous condensers and quick-response batteries can be automatically utilised to regulate frequency.
A Positive Outlook
Countries such as China, India, the US, Germany, and Spain have shown that it is possible to add large amounts of solar and wind generation capacity at a pace. The next chapter in the renewable revolution will be ensuring that this can be done at scale without disrupting the grid and AI will be a key component in managing the transition.

In the midst of the current global crisis, the Utilities industry has had to continue to provide essential public services – through supply chain disruption, reduction of demand in the commercial sector, demand spikes in the consumer sector, change in peak profiles, remote staff management, cyber-attacks and so on. Robust business continuity planning and technology adoption are key to the continued success of Utilities companies. The Ecosystm Business Pulse Study which aims to find how organisations are adapting to the New Normal finds that 6 out of 10 Utilities companies are accelerating or refocusing the Digital Transformation initiatives after the COVID-19 outbreak, underpinning the industry’s need for technology adoption to remain competitive.
Drivers of Transformation in the Utilities Industry
The Evolving Energy Industry. As consumers become more energy-conscious, many are making changes in their usage pattern to stay off the grid as much as possible, potentially reducing the customer base of Utilities companies. This increases their reliance on renewable energy sources (such as solar panels and wind turbines) and batteries, forcing Power companies to diversify and leverage other energy sources such as biomass, hydropower, solar, wind, and geothermal. The challenge is further heightened by the fast depletion of fossil fuels – it is estimated that the world will have run out of fossil fuels in 60 years. The industry is also mandated by government regulations and cleaner energy pacts that focus on climate change and carbon emission – there are strict mandates around how Utilities companies produce, deliver and consume energy.
Business Continuity & Disaster Management. Perhaps no other industry is as vulnerable to natural disasters as Utilities. One of the reasons why the industry has been better prepared to handle the current crisis is because their usual business requires them to have a strong focus on business continuity through natural disasters. This includes having real-time resource management systems and processes to evaluate the requirement of resources, as well as a plan for resource-sharing. There is also the danger of cyber-attacks which has been compounded recently by employees who have access to critical systems such as production and grid networks, working from home. The industry needs to focus on a multi-layered security approach, securing connections, proactively detecting threats and anomalies, and having a clearly-defined incident response process.
The Need to Upgrade Infrastructure. This has been an ongoing challenge for the industry – deciding when to upgrade ageing infrastructure to make production more efficient and to reduce the burden of ongoing maintenance costs. The industry has been one of the early adopters of IoT in its Smart Grid and Smart Meter adoption. With the availability of technology and advanced engineering products, the industry also views upgrading the infrastructure as a means to mitigate some of its other challenges such as the need to provide better customer service and business continuity planning. For example, distributed energy generation systems using ‘micro grids’ have the potential to reduce the impact of storms and other natural disasters – they can also improve efficiency and quality of service because the distance electricity travels is reduced, reducing the loss of resources.
The Evolving Consumer Profile. As the market evolves and the number of Energy retailers increases, the industry has had to focus more on their consumers. Consumers have become more demanding in the service that they expect from their Utilities provider. They are increasingly focused on energy efficiency and reduction of energy consumption. They also expect more transparency in the service they get – be it in the bills they receive or the information they need on outages and disruptions. The industry has traditionally been focused on maintaining supply, but now there is a need to evaluate their consumer base, to evolve their offerings and even personalise them to suit consumer needs.
The global Ecosystm AI study reveals the top priorities for Utilities companies, that are focused on adopting emerging technologies (Figure 1). It is noticeably clear that the key areas of focus are cost optimisation (including automating production processes), infrastructure management and disaster management (including prevention). 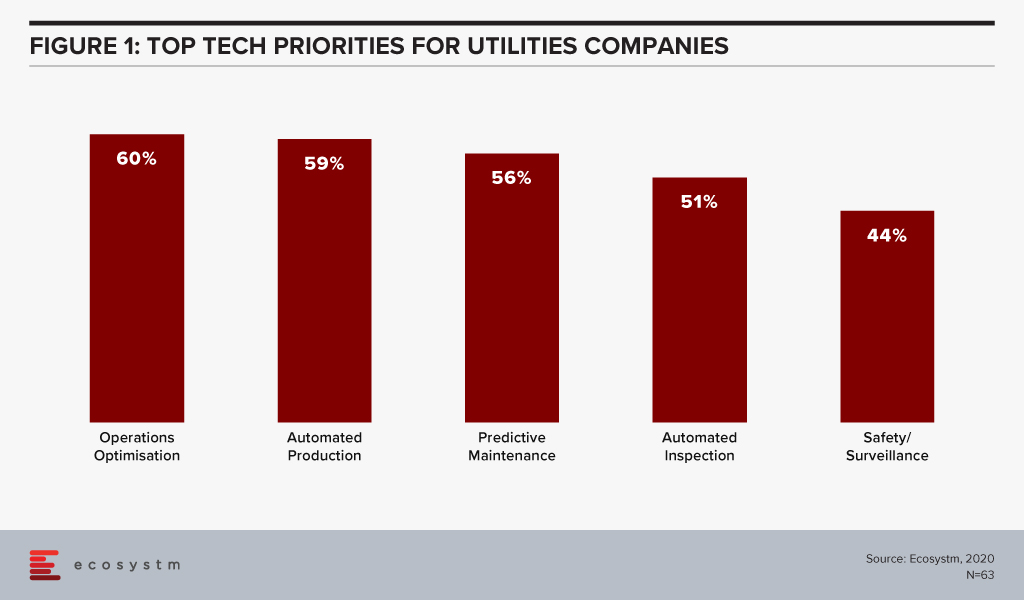
Technology as an Enabler of Utilities Sector transformation
Utilities companies have been leveraging technology and adopting new business models for cost optimisation, employee management and improved customer experience. Here are some instances of how technology is transforming the industry:
Interconnected Systems and Operations using IoT
Utilities providers have realised that an intelligent, interconnected system can deliver both efficiency and customer-centricity. As mentioned earlier, the industry has been one of the early adopters of IoT both for better distribution management (Smart Grids) and for consumer services (Smart Meters). This has also given the organisations access to enormous data on consumer and usage patterns that can be used to make resource allocation more efficient.
For instance, the US Government’s Smart Grid Investment Grant (SGIG) program aims to modernise legacy systems through the installation of advanced meters supporting two-way communication, identification of demand through smart appliances and equipment in homes and factories, and exchange of energy usage information through smart communication systems.
IoT is also being used for predictive maintenance and in enhancing employee safety. Smart sensors can monitor parameters such as vibrations, temperature and moisture, and detect abnormal behaviours in equipment – helping field workers to make maintenance decisions in real-time, enhancing their safety.
GIS is being used to get spatial data and map project distribution plans for water, sewage, and electricity. For instance, India’s Restructured Accelerated Power Development & Reforms Program (R-APDRP) government project involves mapping of project areas through GIS for identification of energy distribution assets including transformers and feeders with actual locations of high tension and low tension wires to provide data and maintain energy distribution over a geographical region. R-APDRP is also focused on reducing power loss.
Transparency and Efficiency using Blockchain
Blockchain-based systems are helping the Utilities industry in centralising consumer data, enabling information sharing across key departments and offering more transparent services to consumers.
Energy and Utilities companies are also using the technology to redistribute power from a central location and form smart contracts on Blockchain for decisions and data storage. This is opening opportunities for the industry to trade on energy, and create contracts based on their demand and supply. US-based Brooklyn Microgrid, for example, is a local energy marketplace in New York City based on Blockchain for solar panel owners to trade excess energy generated to commercial and domestic consumers. In an initiative launched by Singapore’s leading Power company, SP Group, companies can purchase Renewable Energy Certificates (RECs) through a Blockchain-powered trading platform, from renewable producers in a transparent, centralised and inexpensive way.
Blockchain is also being used to give consumers the transparency they demand. Spanish renewable energy firm Acciona Energía allows its consumers to track the origin of electricity from its wind and solar farms in real-time providing full transparency to certify renewable energy origin.
Intelligence in Products and Services using AI
Utilities companies are using AI & Automation to both transform customer experience and automate backend processes. Smart Meters, in itself, generate a lot of data which can be used for intelligence based on demographics, usage patterns, demand and supply. This is used for load forecasting and balancing supply and demand for yield optimisation. It is also being leveraged for targeted marketing including personalised messages on Smart Energy usage.
Researchers in Germany have developed a machine learning program called EWeLiNE which is helping grid operators with a program that can calculate renewable energy generation over 48 hours from the data taken from solar panels and wind turbines, through an early warning system.
Niche providers of Smart Energy products have been working with providing energy intelligence to consumers. UK start-up Verv, as an example, uses an AI-based assistant to guide consumers on energy management by tracing the energy usage data from appliances through meters and assisting in reducing costs. Increasingly, Utilities companies will partner with such niche providers to offer similar services to their customers.
Utilities companies have started using chatbots and conversational AI to improve customer experience. For instance, Exelon in the US is using a chatbot to answer common customer queries on power outages and billing.
While the predominant technology focus of Utilities companies is still on cost optimisation, infrastructure management and disaster management, the industry is fast realising the power of having an interconnected system that can transform the entire value chain.














