2023 has started amidst concerns. Economists are talking about slowdowns, recessions, and downsizing. In the past, every time the economy has been uncertain, we have seen a downtrend in tech spend by companies.
2023 will be different!
Today, all organisations know of the power of digital transformation and will continue to invest in technology to counter the market uncertainties. They will respond to the emerging forces of innovation, deploy automation to counter skills gaps, and focus on being nimble and agile businesses – all with the help of technology.
Here are the 5 trends that will impact tech spending in 2023.
- Organisations will aim for “Big Ticket Innovations”. This will see innovation becoming integral to strategic discussions on culture, people, process, and technology; and the resurgence of emerging technologies.
- AI will replace Cloud as organisations’ transformation goal. Organisations will evolve their AI roadmaps and strategies – focusing on both short-term wins and long-term success factors. They will also make an effort to identify digital debt and weed out applications and services that are sub-optimal for AI
- Building the right data platform architecture will gain importance. Data platforms will become free from the constraints of operational technologies. This will see a reduction of dependence on centralised data repositories; and an uptick in adoption of data fabric architecture to manage distributed data
- Organisations will invest in proactive cyber protection amidst escalating threats. Organisations will focus on immutable backups, data masking techniques and on building a single pane of glass view of all cyber tools and applications
- Sustainability will drive tech investments. This will see an evaluation of all infrastructure (whether cloud or on-premises) with a focus on cost and sustainability and a growing need to integrate all organisational data – across digital, IT, and OT systems
To find out more, read below.
Download 5 Trends Impacting Tech Investments in 2023 as a PDF.

Ecosystm supported by their partner EY, conducted an invitation-only Executive ThinkTank at the Point Zero Forum in Zurich. A select group of regulators, investors, technology providers, and senior leaders from financial institutions from across the globe came together to share their insights and experiences on the practicability, regulatory support, and implications of sustainable finance portfolios.
Here are some of the key takeaways from the ThinkTank.
- The Barriers to a Sustainable Future. The first step towards a sustainable future is recognising the challenges organisations face when pursuing Net Zero targets. Often, Net Zero targets are looked upon as additional costs.
- Overcoming the Challenges. It is important to connect Net Zero back to business goals, given that there might be sudden shifts in regulations and because of the emergence of environment-conscious consumers.
- A Sustainable Future Requires a Collaborative Approach. Global governments, regulators, Financial Services institutions, other enterprises, and technology providers need to collaborate on building a sustainable future.
- A Time for Simplification. Clear mandates on reporting climate aspects similar to how financial aspects are reported, will result in greater adoption of sustainability and ESG measures.
- The Role of Digital Architecture. The path to a Net Zero, decarbonised world will be technology-led.
Read below to find out more.
Download Risks and Opportunities of Net Zero Commitments and Decarbonisation Pathways as a PDF

Southeast Asia has evolved into an innovation hub with Singapore at the centre. The entrepreneurial and startup ecosystem has grown significantly across the region – for example, Indonesia now has the 5th largest number of startups in the world.
Organisations in the region are demonstrating a strong desire for tech-led innovation, innovation in experience delivery, and in evolving their business models to bring innovative products and services to market.
Here are 5 insights on the patterns of technology adoption in Southeast Asia, based on the findings of the Ecosystm Digital Enterprise Study, 2022.
- Data and AI investments are closely linked to business outcomes. There is a clear alignment between technology and business.
- Technology teams want better control of their infrastructure. Technology modernisation also focuses on data centre consolidation and cloud strategy
- Organisations are opting for a hybrid multicloud approach. They are not necessarily doing away with a ‘cloud first’ approach – but they have become more agnostic to where data is hosted.
- Cybersecurity underpins tech investments. Many organisations in the region do not have the maturity to handle the evolving threat landscape – and they are aware of it.
- Sustainability is an emerging focus area. While more effort needs to go in to formalise these initiatives, organisations are responding to market drivers.
More insights into the Southeast Asia tech market below.
Click here to download The Future of the Digital Enterprise – Southeast Asia as a PDF

Organisations are being driven to develop and demonstrate an ESG consciousness and a sustainability commitment in their actions and investments – by their customers, investors and by governments’ sustainability mandates. Early adopter organisations often realise several benefits – from achieving better financial outcomes to creating competitive differentiation. However, more organisations need to get serious about their sustainability journeys – and as regulations firm up, organisations will be forced to report on their sustainability initiatives.
The Ecosystm Kyndryl ASEAN Digital Transformation Study 2022 was launched earlier this year to understand the pulse of C-level leaders and the business and technology transformation goals of organisations in the ASEAN region. This included a closer look on where organisations stand when it comes to setting sustainability goals and strategies, and their key challenges.
Here are 5 insights on the state of the Sustainable Organisation in ASEAN.
Download 5 Insights on the State of the Sustainable Organisation – An ASEAN View as a PDF

Innovation is at the core of Singapore’s ethos. The country has perfected the art of ‘structured innovation’ where pilots and proof of concepts are introduced and the successful ones scaled up by recalibrating technology, delivery systems, legislation, and business models. The country has adopted a similar approach to achieving its sustainability goals.
The Singapore Green Plan 2030 outlines the strategies to become a sustainable nation. It is driven by five ministries: Education, National Development, Sustainability and the Environment, Trade and Industry, and Transport, and includes five key pillars: City in Nature, Sustainable Living, Energy Reset, Green Economy, and Resilient Future. We will see a slew of new programs and initiatives in green finance, sustainability, solar energy, electric vehicles (EVs), and innovation, in the next couple of years.
Singapore’s Intentions of Becoming a Green Finance Leader
Singapore is serious about becoming a world leader in green finance. The Green Bonds Programme Office was set up last year, to work with statutory boards to develop a framework along with industry and investor stakeholders. We have seen a number of sustainable finance initiatives last year, such as the National Environment Agency (NEA) collaborating with DBS to raise USD 1.23 billion from its first green bond issuance. The proceeds will fund new and ongoing sustainable waste management initiatives. Temasek collaborated with HSBC for a USD 110 million debt financing platform for sustainable projects and Sembcorp issued sustainability bonds worth USD 490 million.
Building an Ecosystm of Sustainable Organisations
Sustainability has to be a collective goal that will require governments to work with enterprises, investors and consumers. To ensure that enterprises are focusing on Sustainability, governments have to keep in mind what drives these initiatives and the challenges organisations face in achieving their goals.
There are several reasons driving organisations in Singapore to adopt sustainability goals and ESG responsibilities (Figure 1)
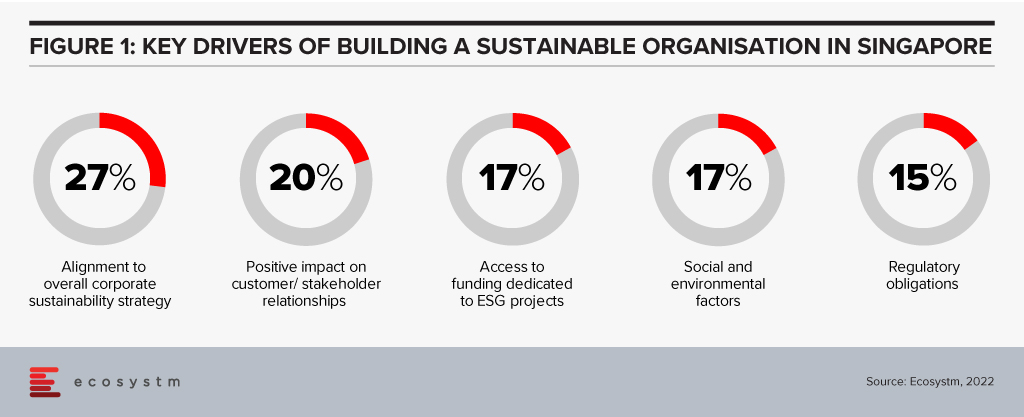
It is equally important to address organisations’ challenges in building sustainability in their business processes. Last week, the Institute of Banking and Finance (IBF) and the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) set out 12 Sustainable Finance Technical Skills and Competencies (SF TSCs) required by people in various roles in sustainable finance. This addresses the growing demand for sustainable finance talent in Singapore; and covers knowledge areas such as climate change policy developments, natural capital, green taxonomies, carbon markets and decarbonisation strategies. There are Financial Services related competencies as well, such as sustainability risk management, sustainability reporting, sustainable investment management, and sustainable insurance and reinsurance solutions. The SF TSCs are part of the IBF Skills Framework for Financial Services.
Sustainable Resources Initiatives
Singapore is not only focused on Sustainable Finance. If we look at NEA’s Green Bonds, there are specific criteria that projects must satisfy in order to qualify, including a focus on sustainable waste management.
Last week the Government announced that the National Research Fund (NRF) will allocate around USD 160 million to drive new initiatives in water, reuse and recycling technologies, as part of the Research, Innovation and Enterprise 2025 plan (RIE2025). Part of the fund will be allocated to the Closing the Resource Loop (CTRL) initiative, administered by the NEA that will fund sustainable resource recovery solutions.
Singapore faces severe resource constraints, and water security is not a new challenge for the country. The NRF funding will also be used partially for R&D in 3 water technology focus areas: desalination and water reuse; used water treatment; and waste reduction and resource recovery.
The Government is Leading the Way
The Government’s concerted efforts to make the Singapore Green Plan 2030 a success is seeing corporate participation in the vision. In February, Shell started supplying sustainable aviation fuel (SAF) to customers such as SIA Engineering Company and the Singapore Air Force in Singapore. Shell has also upgraded their Singapore facility to blend SAF at multiple, key locations. Last week, Atlas announced their commitment to Web 3.0 technologies and “tech for good”. They aim to increase their green energy use to 75% by 2022; 90% by 2023; and 100% by 2024. ESG consciousness is percolating down from the Government.
The success of Singapore’s Sustainability strategies will depend on innovation, the Government’s ongoing commitment, and the support provided to enterprises, investors, and consumers. The Singapore Government is poised to lead from the front in building a Sustainable Ecosystem.

COP26 has firmly put environmental consciousness as a leading global priority. While we have made progress in the last 30 odd years since climate change began to be considered as a reality, a lot needs to be done.
No longer is it enough for only governments to lead on green initiatives. Now is the time for non-profit organisations, investors, businesses – corporate and SMEs – and consumers to come together to ensure we leave a safer planet for our children.
February saw examples of how technology providers and large corporates are delivering on their environmental consciousness and implementing meaningful change.
Here are some announcements that show how tech providers and corporates are strengthening the Sustainability cause:
- IBM launches Sustainability Accelerator Program
- Microsoft boosts their Sustainability offerings by extending extend their EID tool for Microsoft 365
- Salesforce officially announce sustainability as a core company value
- Google enables Sustainable AIOps
- The Aviation industry (Southwest Airlines, ANA, Norwegian Air and Singapore Airlines) appears to be making a concerted effort to reduce carbon footprint.
Read on to find more.
Click here to download a copy of The Future of Sustainability as a PDF.

There have been some long-term shifts in market dynamics in the telecom industry. Network traffic growth rates have accelerated; new business models emerged; and cloud services matured and spread to new verticals, applications and customer sizes. Networks are more important than ever. Revenue growth rates and profitability in the three segments – telecom, webscale, and carrier-neutral – have been stronger in recent quarters than anticipated.
Looking ahead, networks will increasingly revolve around data centres, which will continue to proliferate both at the core and edge.
Data centre innovation will be rapid, as webscalers push the envelope on network design and function, and telecom operators seek cheaper ways of running their networks. The telecom operator’s need for cost efficiency will increase as overhyped 5G-based opportunities fail to materialise in any big way. Carrier-neutral operators (CNNOs) will benefit from an ongoing wave of new capital which will help them transform to more integrated providers of “digital infrastructure” assets.
Read on to find out about
- The interdependence of network operators
- The growth potential of the telecom, webscale, and CNNO markets
- How webscalers such as Facebook and Alibaba are leveraging scale
- Acquisition and deals in the CNNO market such as the American Tower-CoreSite acquisition and the Digital Realty deal with Ciena.
- The growth of environmental consciousness in the telecom industry
Click here to download The Future of Telecom: Industry Outlook for 2022 and Beyond slides as a PDF.

Telecom companies’ spending on utilities (electricity, fuel, and water) amounted to an estimated 5.2% of OpEx (excluding depreciation and amortisation) in 2020, a bit up from the previous three years. There is modest evidence that 5G adoption is driving costs higher. Early adopters, such as China Mobile, Ooredoo, Swisscom, Telecom Italia, and all three of Korea’s big telecom providers (SKT, KT, and LG Uplus) saw increases in utilities spend in 2020. Increases generally weren’t big but serve as a good reminder that telecom providers will need to seek out energy efficient equipment, software, and network architectures as 5G penetration grows.
Telecom providers also need to rise to the challenge of truly serving as enablers of sustainability. Rather than just viewing energy as a cost centre, they should work with customers and partners to move rapidly towards green energy and reductions in usage.
Some providers are already on this path, but not nearly enough.
At the COP26 there was a strong focus on collective action aimed at curtailing climate change trends. It is all the more important for private companies to take voluntary action. Unfortunately, they’ll only do that if they get public credit for such actions, or if the changes turn out to save money.
Telecom providers have a role to play here. They have an intimate relationship with millions of customers, and an understanding of how their behavior impacts energy usage. It’s time for them to start monetising the insights, help their customers decrease consumption, save cash and position themselves as climate friendly. Recent offerings from European telecoms such as KPN, Swisscom and Vodafone point in the right direction.
Click here to download Sustainability in the Telecom Industry as a PDF

2020 was a watershed year for the industry as they proved to be the backbone for the rapid changes in work practices, communication and entertainment. This has led telecom providers to embark on their won digital transformation journeys.
The challenges continue for the industry, especially as 5G has not yet delivered on the early promises. Telecom operators today are having to provide cutting-edge services and top-notch customer experience as they continue to be challenged by new market entrants and strong regulatory pressures.
In 2022, telecom providers will be driven by the need to innovate and improve their product and service lines; improve customer experience; comply with changing regulations; and to optimise costs.
Read on to find out what Ecosystm Analysts Darian Bird and Matt Walker think will be the key trends in the telecom industry in 2022.


















































































